check oil OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 1465 of 6000
6E–348
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
oil to enter the cylinder, particularly if the deposits are
heavier on the side of the spark plug facing the intake
valve.
TS23995
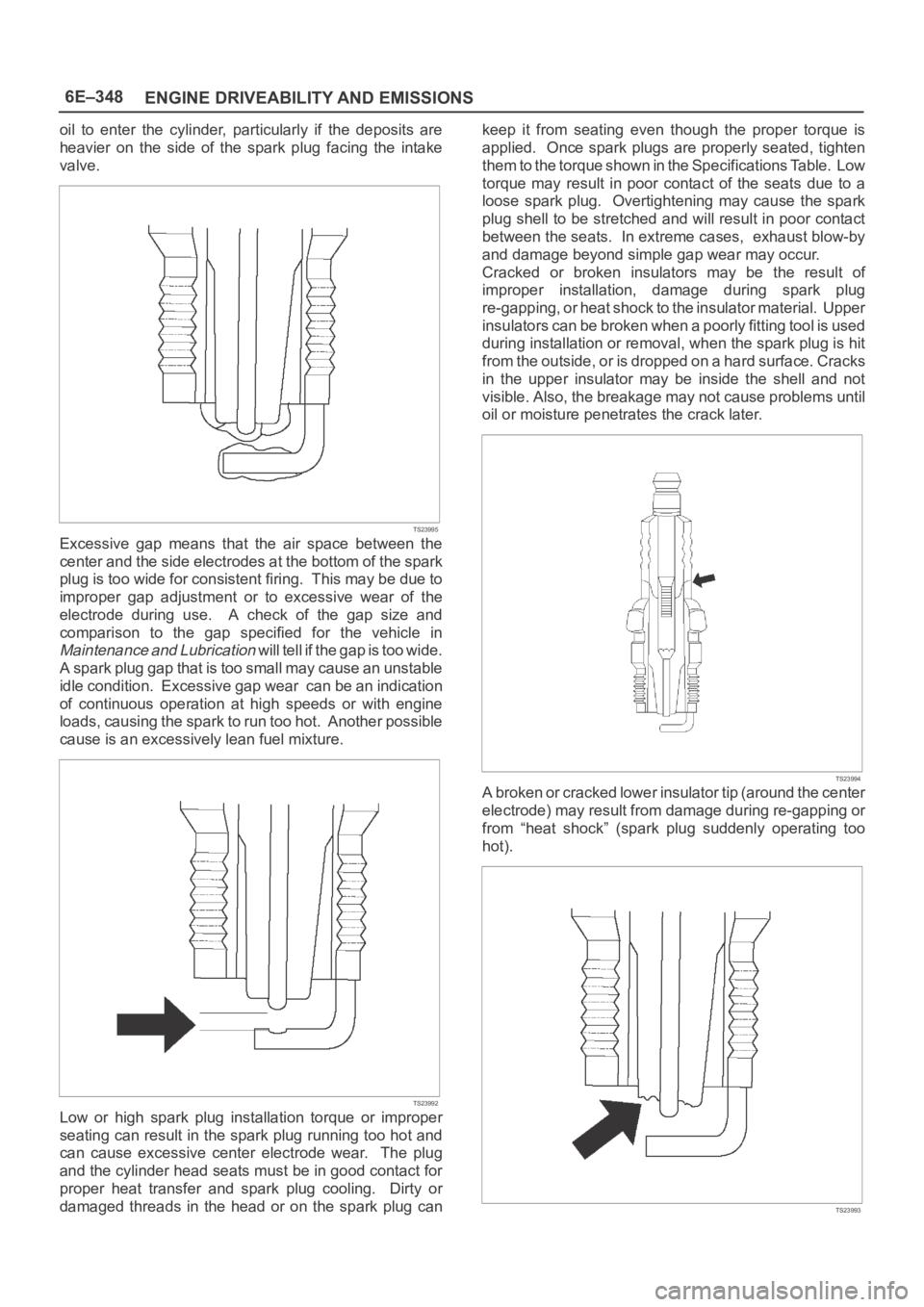
Excessive gap means that the air space between the
center and the side electrodes at the bottom of the spark
plug is too wide for consistent firing. This may be due to
improper gap adjustment or to excessive wear of the
electrode during use. A check of the gap size and
comparison to the gap specified for the vehicle in
Maintenance and Lubrication will tell if the gap is too wide.
A spark plug gap that is too small may cause an unstable
idle condition. Excessive gap wear can be an indication
of continuous operation at high speeds or with engine
loads, causing the spark to run too hot. Another possible
cause is an excessively lean fuel mixture.
TS23992
Low or high spark plug installation torque or improper
seating can result in the spark plug running too hot and
can cause excessive center electrode wear. The plug
and the cylinder head seats must be in good contact for
proper heat transfer and spark plug cooling. Dirty or
damaged threads in the head or on the spark plug cankeep it from seating even though the proper torque is
applied. Once spark plugs are properly seated, tighten
them to the torque shown in the Specifications Table. Low
torque may result in poor contact of the seats due to a
loose spark plug. Overtightening may cause the spark
plug shell to be stretched and will result in poor contact
between the seats. In extreme cases, exhaust blow-by
and damage beyond simple gap wear may occur.
Cracked or broken insulators may be the result of
improper installation, damage during spark plug
re-gapping, or heat shock to the insulator material. Upper
insulators can be broken when a poorly fitting tool is used
during installation or removal, when the spark plug is hit
from the outside, or is dropped on a hard surface. Cracks
in the upper insulator may be inside the shell and not
visible. Also, the breakage may not cause problems until
oil or moisture penetrates the crack later.
TS23994
A broken or cracked lower insulator tip (around the center
electrode) may result from damage during re-gapping or
from “heat shock” (spark plug suddenly operating too
hot).
TS23993
Page 1483 of 6000

6G–4
ENGINE LUBRICATION
11. Remove drive gear.
12. Remove oil seal.
13. Remove O-ring.
Inspection and Repair
CAUTION: Make necessary correction or parts
replacement if wear, damage or any other abnormal
conditions are found during inspection.
Relief Valve (8)
Check to see that the relief valve slides freely.
The oil pump must be replaced if the relief valve does
not slide freely.
Replace the spring and/or the oil pump assembly (5) if
the spring is damaged or badly worn.
051RS002
Body (14) and Gears (10, 11)
The pump assembly must be replaced if one or more of
the conditions below is discovered during inspection.
Badly worn or damaged driven gear (10).
Badly worn drive gear (11) driving face.
Badly scratched or scored body sliding face (14) or
driven gear (10).
Badly worn or damaged gear teeth.
Measure the clearance between the body and the driven
gear with a feeler gauge.
Standard : 0.10 mm–0.18 mm
(0.0039 in.–0.0070 in)
Limit : 0.20mm (0.0079 in)
051RS004
Measure the clearance between the drive gear and
driven gear with a feeler gauge.
Standard : 0.11 mm–0.24 mm
(0.0043 in–0.0094 in)
Limit : 0.35mm (0.0138 in)
051RS003
Measure the side clearance with a precision straight
edge and a feeler gauge.
Clearance
Standard : 0.03 mm–0.09 mm
(0.0011 in–0.0035 in)
Limit : 0.15mm (0.0059 in)
Page 1484 of 6000

6G–5 ENGINE LUBRICATION
051RS005
Oil Strainer
Check the oil strainer for cracking and scoring. If cracking
and scoring are found, the oil strainer must be replaced.
051RS006
Reassembly
1. Install drive gear (11).
2. Install driven gear (10).
3. Install oil pump cover (9) and first, loosely tighten all of
the attaching screws. Next, tighten the attaching
screws to the specified torque.
Torque : 10 Nꞏm (1.0 Kgꞏm/89 lb in)
After installation, check that the gear rotates
smoothly.
4. Install relief valve (8) and apply engine oil to the relief
valve and spring (7).
5. Install spring (7).6. Install the plug (6).
Torque : 8 Nꞏm (0.8 Kgꞏm/69 lb in)
051RS007
7. Install oil pump assembly (5).
Carefully remove any oil from the cylinder body and
the pump. Apply sealant (TB–1207B or equivalent)
to the pump fitting face as shown in illustration. Take
care that sealant is not applied to oil port surfaces.
The oil pump assembly must be installed within 5
minutes after sealant application before the sealant
hardens.
CAUTION: Do not apply an excessive amount of
sealant to the contact surface. Applying too much
sealant will overflow the contact surfaces. This
could cause serious damage to the engine.
Attach oil pump assembly to cylinder body.
Tighten the oil pump fixing bolts.
Torque : 25 Nꞏm (2.5 Kgꞏm/18 lbꞏft)
051RW002
Page 1736 of 6000

ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 3
SERVICE INFORMATION
MAIN DATA AND SPECIFICATION
Engine type Diesel, four cycle water cooled inline
Camshaft type DOHC
Number of cylinders 4
Bore x stroke (mm) 95.4 x 104.9
Total piston displacement (cc) 2999
Compression ratio (to 1) 19.0
For Europe : 18.5
Engine weight (dry) N (kg/lb) 2492 (254/560) (A/T)
For Europe : 2422 (247/545) (A/T)
2649 (270/593) (M/T)
For Europe : 2697 (275/606) (M/T)
Engine idling speed (Reference) RPM 720
Compression pressure kpa (kg/cm
2/psi)-rpm 3040 (31/441)-200
Firing order 1–3–4–2
VALVE SYSTEM
Intake valves open at: B.T.D.C. 3°
close at: A.B.D.C. 57.6°
Exhaust valves open at: B.B.D.C. 56.5°
close at: A.T.D.C. 5°
Valve clearance (at cold) mm (in)
intake: 0.15 (0.006)
exhaust: 0.25 (0.01)
Oil filter Full flow and bypass combined type
Oil capacity (Original factory fill or rebuilt engine) 9.0 liters (7.9 US quarts)
Oil capacity (Service change)
with filter change 6.0 liters (6.3 US quarts)
without filter change 5.0 liters (5.3 US quarts)
Oil cooler Water cooled type
Inter cooler Air cooled type
Turbocharger method
Control method Wastegate control
Lubrication Pressurized control
Cooling method Coolant cooled
Crankshaft
As tufftriding (Nitrizing treatment) is applied to increase
crankshaft strength, crankpins and journals should not
be reground.
Piston Cooling
An oiling jet device for piston cooling is provided in the
lubricating oil circuit from the cylinder block oil gallery
via a check valve.
Take care not to damage any oiling jet when removing
and installing piston and connecting assembly.
Fuel Injection System
The injection system is oil rail type.
Quick On Start 4 System
QOS4 preheating system which features a quick-on
glow plug with thermometer control of the glowing time
and the afterglow time function, is applied.
Page 1743 of 6000
6A – 10 ENGINE MECHANICAL
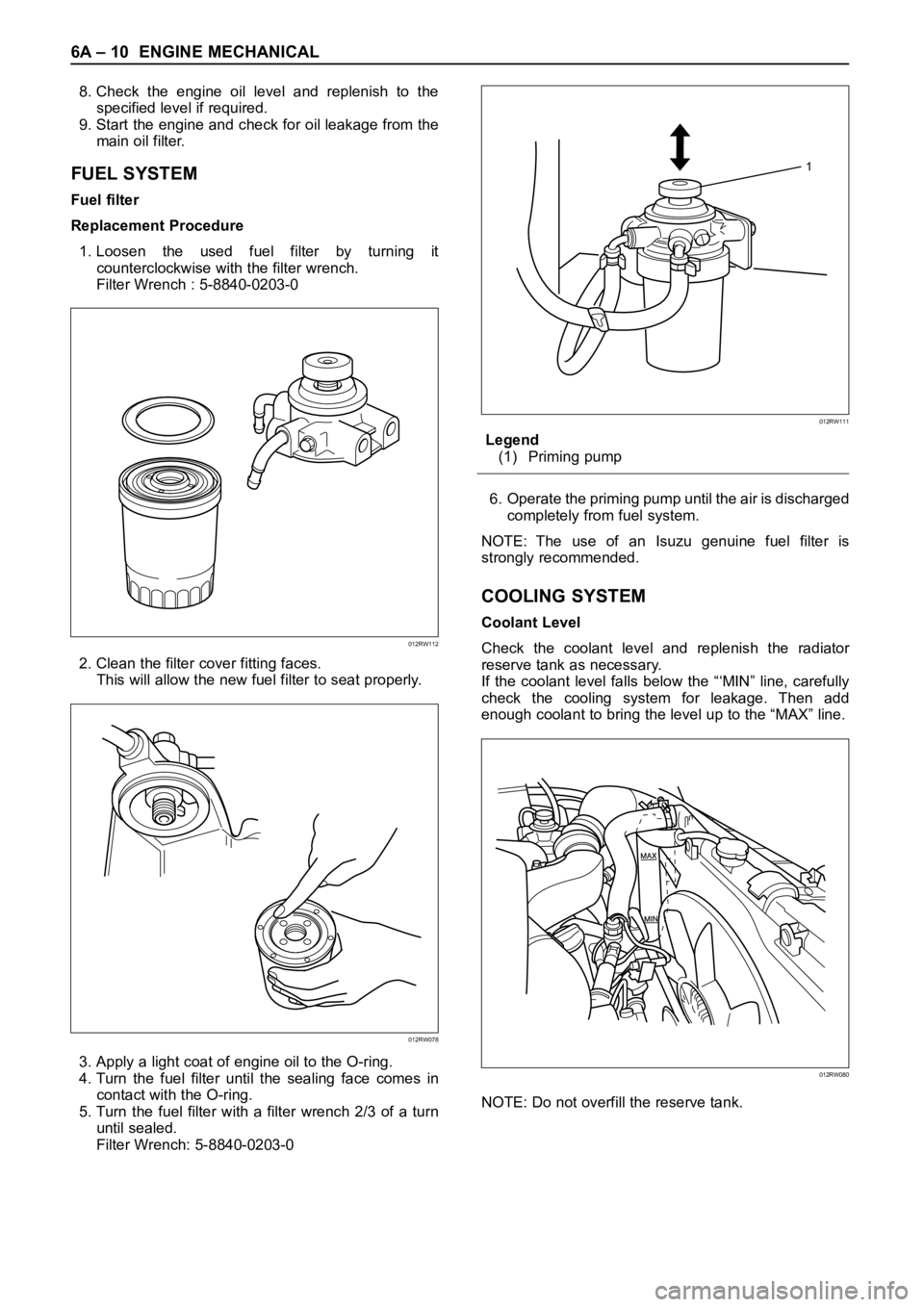
8. Check the engine oil level and replenish to the
specified level if required.
9. Start the engine and check for oil leakage from the
main oil filter.
FUEL SYSTEM
Fuel filter
Replacement Procedure
1. Loosen the used fuel filter by turning it
counterclockwise with the filter wrench.
Filter Wrench : 5-8840-0203-0
2. Clean the filter cover fitting faces.
This will allow the new fuel filter to seat properly.
3. Apply a light coat of engine oil to the O-ring.
4. Turn the fuel filter until the sealing face comes in
contact with the O-ring.
5. Turn the fuel filter with a filter wrench 2/3 of a turn
until sealed.
Filter Wrench: 5-8840-0203-0Legend
(1) Priming pump
6. Operate the priming pump until the air is discharged
completely from fuel system.
NOTE: The use of an Isuzu genuine fuel filter is
strongly recommended.
COOLING SYSTEM
Coolant Level
Check the coolant level and replenish the radiator
reserve tank as necessary.
If the coolant level falls below the “‘MIN” line, carefully
check the cooling system for leakage. Then add
enough coolant to bring the level up to the “MAX” line.
NOTE: Do not overfill the reserve tank.
012RW112
012RW078
1
012RW111
012RW080
Page 1752 of 6000
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 19
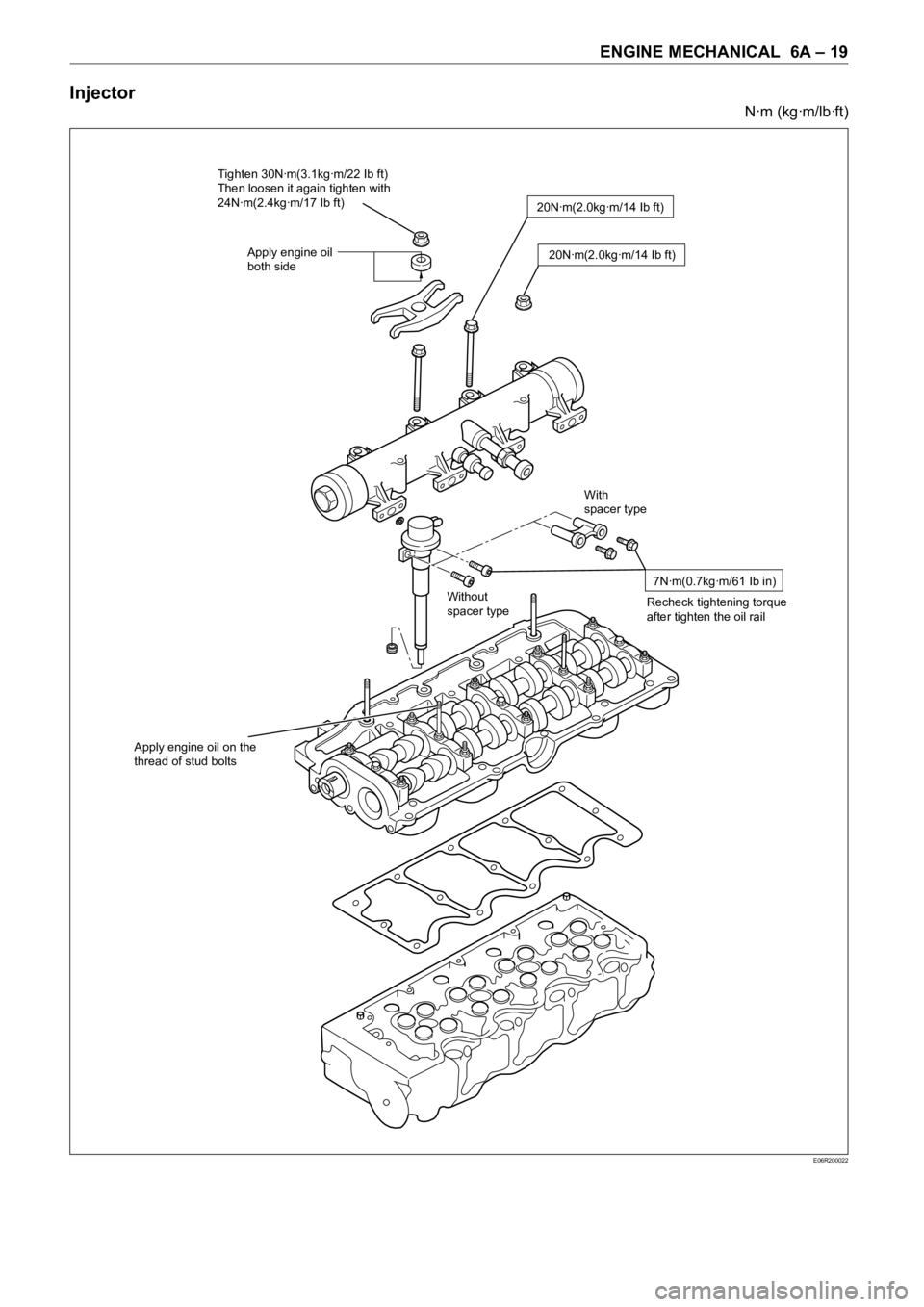
Injector
Nꞏm (kgꞏm/lbꞏft)
E06R200022
With
spacer type
Without
spacer type
20Nꞏm(2.0kgꞏm/14 Ib ft)
7Nꞏm(0.7kgꞏm/61 Ib in)
Recheck tightening torque
after tighten the oil rail
Apply engine oil on the
thread of stud bolts
20Nꞏm(2.0kgꞏm/14 Ib ft)
Tighten 30Nꞏm(3.1kgꞏm/22 Ib ft)
Then loosen it again tighten with
24Nꞏm(2.4kgꞏm/17 Ib ft)
Apply engine oil
both side
Page 1796 of 6000
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 63
Valve Guide Replacement
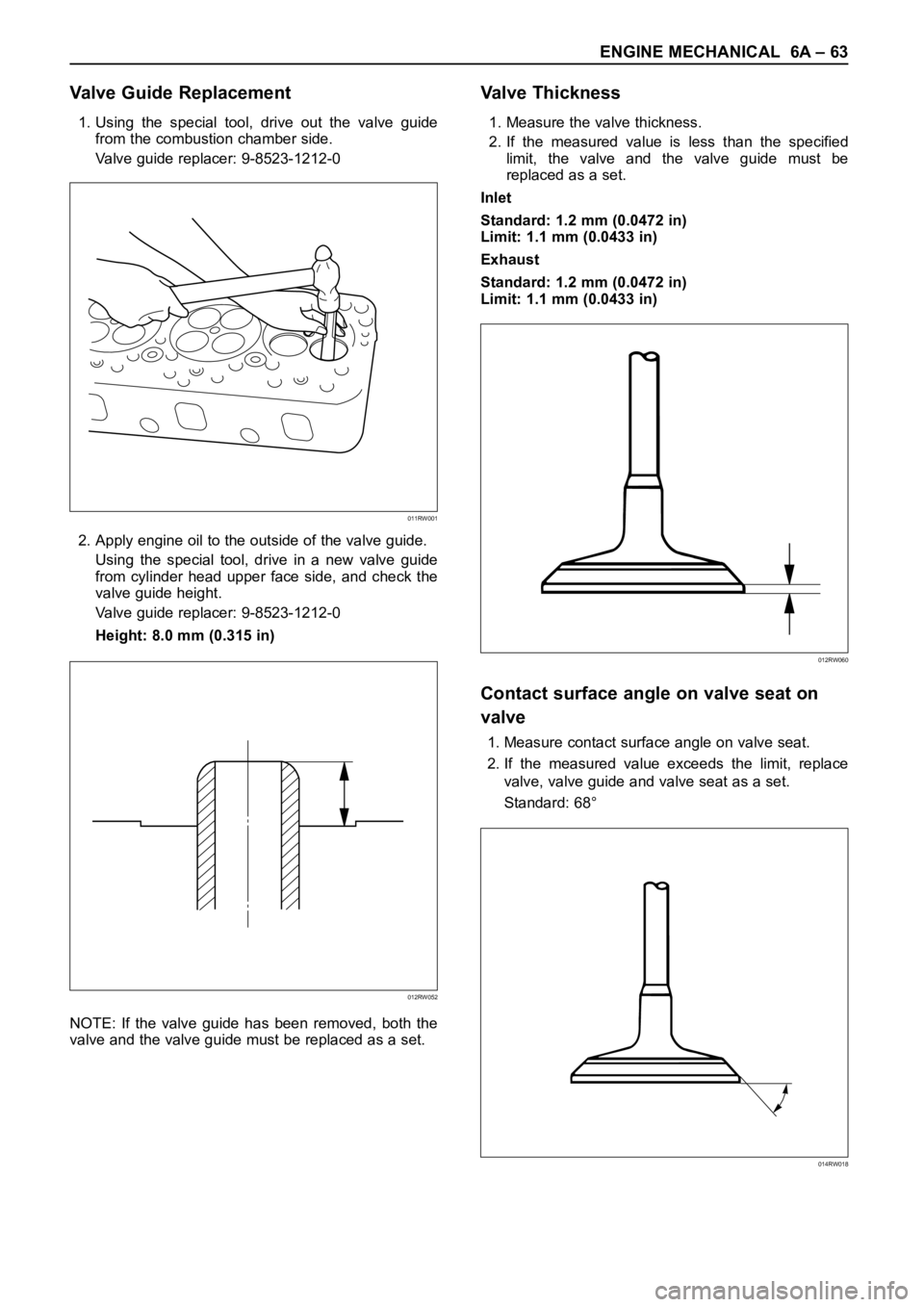
1. Using the special tool, drive out the valve guide
from the combustion chamber side.
Valve guide replacer: 9-8523-1212-0
2. Apply engine oil to the outside of the valve guide.
Using the special tool, drive in a new valve guide
from cylinder head upper face side, and check the
valve guide height.
Valve guide replacer: 9-8523-1212-0
Height: 8.0 mm (0.315 in)
NOTE: If the valve guide has been removed, both the
valve and the valve guide must be replaced as a set.
Va l v e T h i c k n e s s
1. Measure the valve thickness.
2. If the measured value is less than the specified
limit, the valve and the valve guide must be
replaced as a set.
Inlet
Standard: 1.2 mm (0.0472 in)
Limit: 1.1 mm (0.0433 in)
Exhaust
Standard: 1.2 mm (0.0472 in)
Limit: 1.1 mm (0.0433 in)
Contact surface angle on valve seat on
valve
1. Measure contact surface angle on valve seat.
2. If the measured value exceeds the limit, replace
valve, valve guide and valve seat as a set.
Standard: 68°
011RW001
012RW052
012RW060
014RW018
Page 1800 of 6000

ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 67
VALVE CLEARANCE ADJUSTMENT
NOTE:
1. Valve clearance should be inspected and adjusted
while the engine is cool.
2. The tightening of the camshaft bearing cap and
camshaft carrier assembly should be checked
before inspecting and adjusting valve clearance.
INSPECTION
1. Remove cylinder head noise insulator cover and
cylinder head cover.
Refer to “Cylinder Head” in this manual.
2. Disconnect all harness connecters of the injector
and remove harness assembly.
3. Drain oil from oil rail assembly.
4. Remove injector clamp nuts and fixing bolts to take
out injector assembly.
5. Loosen oil rail bolts, remove oil rail assembly.
6. Set cylinder No.1 to the TDC at the compression
stroke. Make sure that there is play in cylinder No.1
tappets on inlet and exhaust sides and that there is
no play in cylinder No.4 tappets.
7. Measure valve clearance at No.1 TDC (Refer to the
black circles indicated in the illustration).
Standard Valve clearance:
Intake valve: 0.15 mm (0.0059 in) ± 0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
Exhaust valve: 0.25 mm (0.0098 in) ± 0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
8. Turn the crankshaft one turn to set No.4 cylinder
TDC at the compression stroke.
9. Measure valve clearance at No.4 TDC (Refer to the
black circles indicated in the illustration).
Standard Valve clearance:
Intake valve: 0.15 mm (0.0059 in) ± 0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
Exhaust valve: 0.25 mm (0.0098 in) ± 0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
10. If measured value is outside standard value,
readjust the valve clearance.
ADJUSTMENT
For valve clearance adjustment, follow the procedure
given below.
1. Set cylinder No.1 or No.4 to the TDC at the
compression stroke.
Set the valve clearance adjusting tool on the tappet
requiring adjustment.
After making sure of the correct setting of the
special tool, depress the tappet by turning the bolt.
Valve Clearance Adjusting Tool: 5-8840-2590-0
NOTE: Before depressing the tappet, set the tappet
notch in the direction where adjuster can be easily
taken out.
2. Take out the adjuster using a small screw driver and
finger magnet.
011RW045
011RW046
014RW150
Page 1808 of 6000
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 75
DISASSEMBLY
1. Cylinder Head
1) Refer to “Cylinder head” in this manual.
2. Crankshaft Front Oil Seal
1) Use a plastic hammer and a screwdriver to tap
around the oil seal to free it from the gear case
cover.
Take care not to damage the oil seal fitting
surfaces.
3. Crankshaft Timing Gear
4. Timing Gear Case
5. Flywheel
6. Cylinder Block Rear Plate
7. Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal
1) Use special tool to remove the crankshaft rear
oil seal.
Oil Seal Remover: 5-8840-2360-0
8. Crank Case
9. Piston Cooling Oil Pipe
10. Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly
11. Main Bearing Cap Assembly
12. Crankshaft
INSPECTION AND REPAIR
Make the necessary adjustments, repairs, and part
replacements if excessive wear or damage is
discovered during inspection.
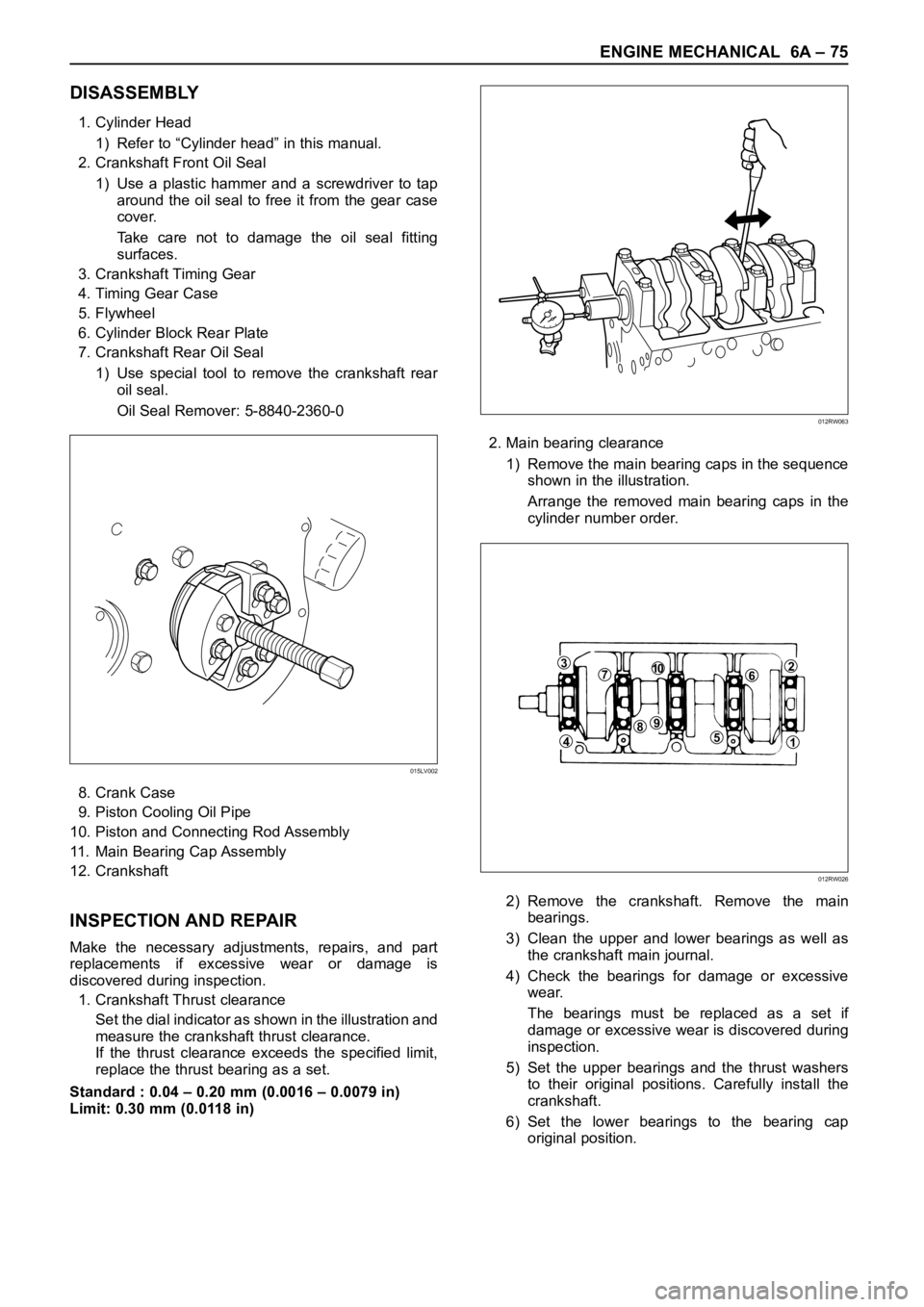
1. Crankshaft Thrust clearance
Set the dial indicator as shown in the illustration and
measure the crankshaft thrust clearance.
If the thrust clearance exceeds the specified limit,
replace the thrust bearing as a set.
Standard : 0.04 – 0.20 mm (0.0016 – 0.0079 in)
Limit: 0.30 mm (0.0118 in)2. Main bearing clearance
1) Remove the main bearing caps in the sequence
shown in the illustration.
Arrange the removed main bearing caps in the
cylinder number order.
2) Remove the crankshaft. Remove the main
bearings.
3) Clean the upper and lower bearings as well as
the crankshaft main journal.
4) Check the bearings for damage or excessive
wear.
The bearings must be replaced as a set if
damage or excessive wear is discovered during
inspection.
5) Set the upper bearings and the thrust washers
to their original positions. Carefully install the
crankshaft.
6) Set the lower bearings to the bearing cap
original position.
015LV002
012RW063
371062
51
984
012RW026
Page 1812 of 6000
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 79
Main Bearing Crankshaft
Bore Diameter mm(in) Main Journal Diameter mm(in)Crankshaft Oil Clearance
Grade Inside Diameter Grade Outside DiameterBearing mm(in)
1 or - 69.927 – 69.932 4 0.045 – 0.061
(2.7530 – 2.7532) (0.0018 – 0.0024)
1 73.992 – 74.000 2 or - - 69.922 – 69.927 4 0.050 – 0.066
(2.9131 – 2.9134) (2.7528 – 2.7530) (0.0020 – 0.0026)
3 or - - - 69.917 – 69.922 5 0.052 – 0.068
(2.7526 – 2.7528) (0.0020 – 0.0027)
1 or - 69.927 – 69.932 2 0.042 – 0.059
(2.7530 – 2.7532) (0.0017 – 0.0023)
2 73.983 – 73.992 2 or - - 69.922 – 69.927 3 0.044 – 0.061
(2.9127 – 2.9131) (2.7528 – 2.7530) (0.0017 – 0.0024)
3 or - - - 69.917 – 69.922 4 0.046 – 0.063
(2.7526 – 2.7528) (0.0018 – 0.0025)
1 or - 69.927 – 69.932 1 0.037 – 0.053
(2.7530 – 2.7532) (0.0015 – 0.0021)
3 73.975 – 73.983 2 or - - 69.922 – 69.927 2 0.039 – 0.055
(2.9124 – 2.9127) (2.7528 – 2.7530) (0.0015 – 0.0022)
3 or - - - 69.917 – 69.922 2 0.044 – 0.060
(2.7526 – 2.7528) (0.0017 – 0.0024)
REASSEMBLY
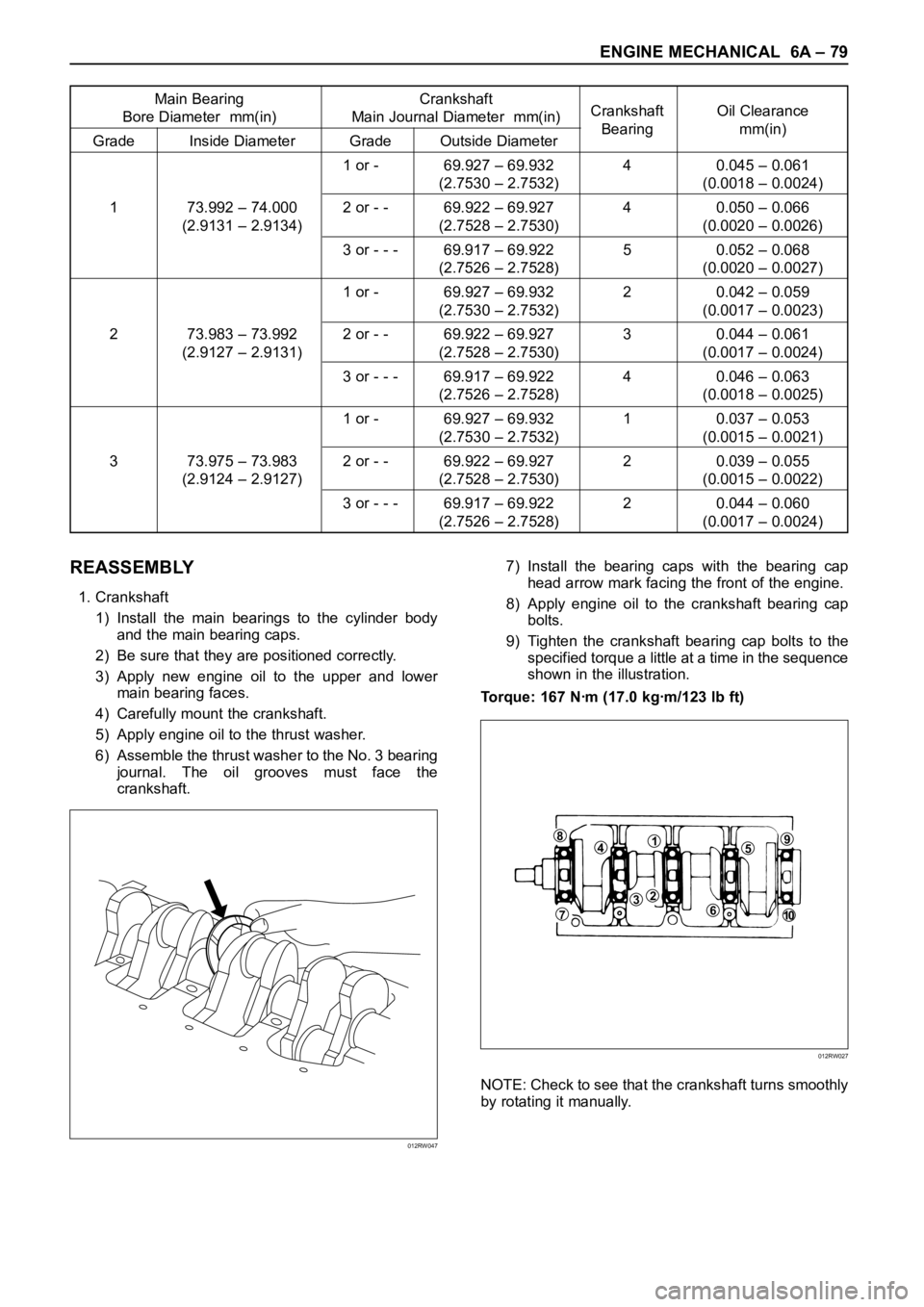
1. Crankshaft
1) Install the main bearings to the cylinder body
and the main bearing caps.
2) Be sure that they are positioned correctly.
3) Apply new engine oil to the upper and lower
main bearing faces.
4) Carefully mount the crankshaft.
5) Apply engine oil to the thrust washer.
6) Assemble the thrust washer to the No. 3 bearing
journal. The oil grooves must face the
crankshaft.7) Install the bearing caps with the bearing cap
head arrow mark facing the front of the engine.
8) Apply engine oil to the crankshaft bearing cap
bolts.
9) Tighten the crankshaft bearing cap bolts to the
specified torque a little at a time in the sequence
shown in the illustration.
Torque: 167 Nꞏm (17.0 kgꞏm/123 lb ft)
NOTE: Check to see that the crankshaft turns smoothly
by rotating it manually.
012RW047
84159
610
237
012RW027