torque SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 1997, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997Pages: 2053, PDF Size: 88.33 MB
Page 1085 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-102 ABS AND TCS
ACCELERATION SENSOR
Removal and Installation Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the acceleration sensor connector. It
is located at the rear of audio system.
3. Remove the acceleration sensor mounting bolts.
Installation Notice
SYSTEM FUSE
Removal and Installation Procedure
The ABS/TCS system fuse, EF11, is located in the
engine fuse block. Counting from the battery toward
the surge tank, it is the first system fuse in the row.
KAA4F410
KAA4F420
Tightening Torque 7 Nm (62 lb-in)
4. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
INDICATORS
The indicator lamps ABS and EBD and TCS are part of
the instrument cluster. Refer to Section 9E, instrumenta-
tion/ Driver information, for removal and replacement
details.
Page 1092 of 2053
PARKING BRAKE 4G-5
SSANGYONG MY2002
KAA4G040
KAA4G050
KAA4G060
KAA4G070
PARKING BRAKE LEVER
Removal and Installation Procedure
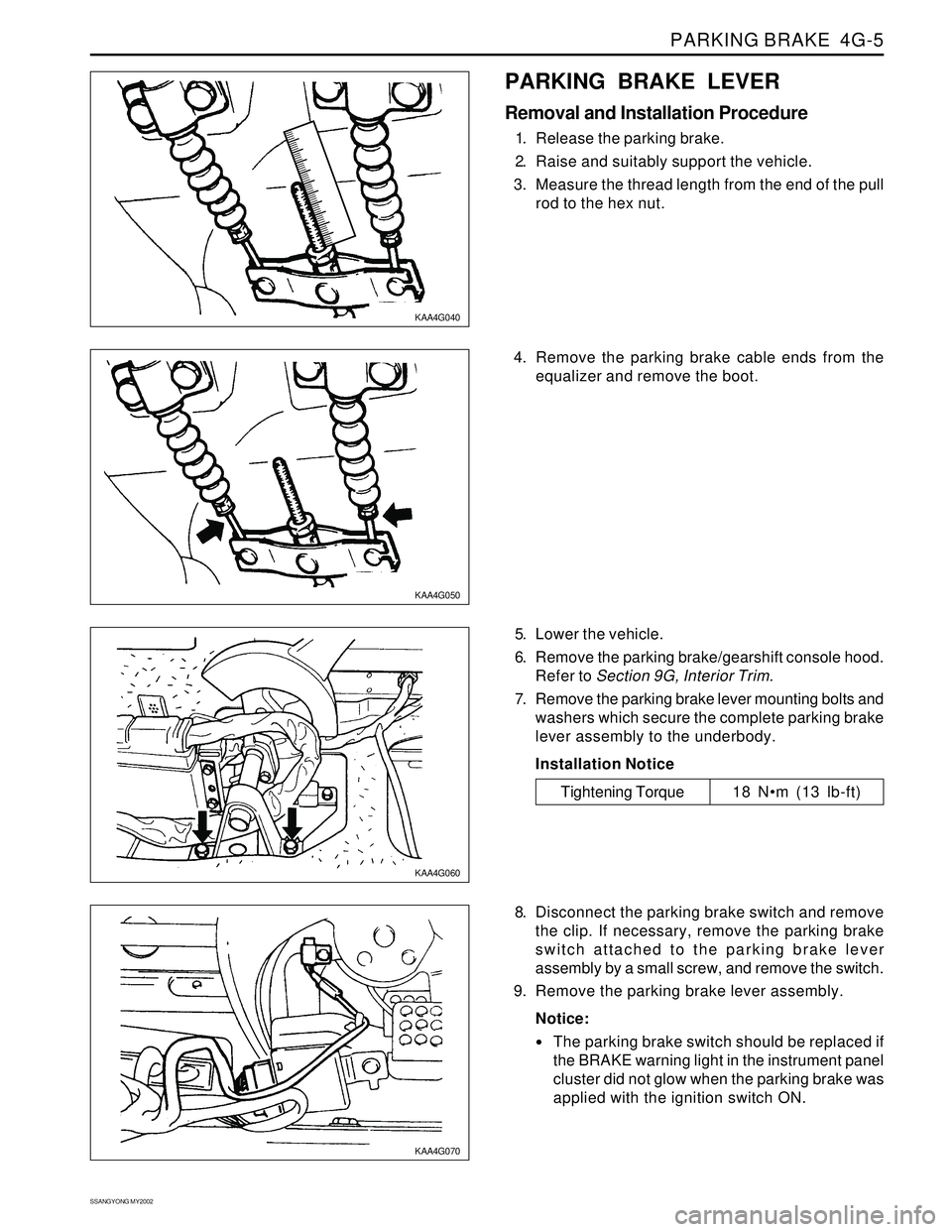
1. Release the parking brake.
2. Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
3. Measure the thread length from the end of the pull
rod to the hex nut.
5. Lower the vehicle.
6. Remove the parking brake/gearshift console hood.
Refer to Section 9G, Interior Trim.
7. Remove the parking brake lever mounting bolts and
washers which secure the complete parking brake
lever assembly to the underbody.
Installation Notice
8. Disconnect the parking brake switch and remove
the clip. If necessary, remove the parking brake
switch attached to the parking brake lever
assembly by a small screw, and remove the switch.
9. Remove the parking brake lever assembly.
Notice:
The parking brake switch should be replaced if
the BRAKE warning light in the instrument panel
cluster did not glow when the parking brake was
applied with the ignition switch ON.
Tightening Torque 18 Nm (13 lb-ft) 4. Remove the parking brake cable ends from the
equalizer and remove the boot.
Page 1093 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4G-6 PARKING BRAKE
KAA4G020
KAA4G080
KAA4G050
PARKING BRAKE CABLE
Removal and Installation Procedure
1. Release the parking brake.
2. Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
3. Remove the clip that holds the cable into the rear
knuckle assembly.
6. Remove the parking brake cable ends from the
equalizer.
Tightening Torque 9 Nm (80 lb-in) 5. Remove the bolts securing the parking brake cable
to a holding bracket attached to the trailing link
brackets on both the driver and passenger sides
of the vehicle.
Installation Notice
Page 1096 of 2053
5A-2 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
SSANGYONG MY2002
OPERATORS INTERFACES
There are three operator interfaces as the following;
•Gear Shift Control Lever
Driving Mode Selector
Indicator Light
Gear Shift Control lever
The transmission uses a conventional shift control lever.
The gear shift control lever can be moved from one
position to another within the staggered configuration
of the shift control lever gate to positively indicate the
gear selection.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
BTRA M74 4WD AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
The BTR Automotive Model 74 Four Speed Automatic
Transmission is an electronically controlled overdrive
four speed unit with a lock-up torque converter. The
lock-up torque converter results in lower engine speeds
at cruise and eliminates unnecessary slippage. These
features benefit the customer through improved fuel
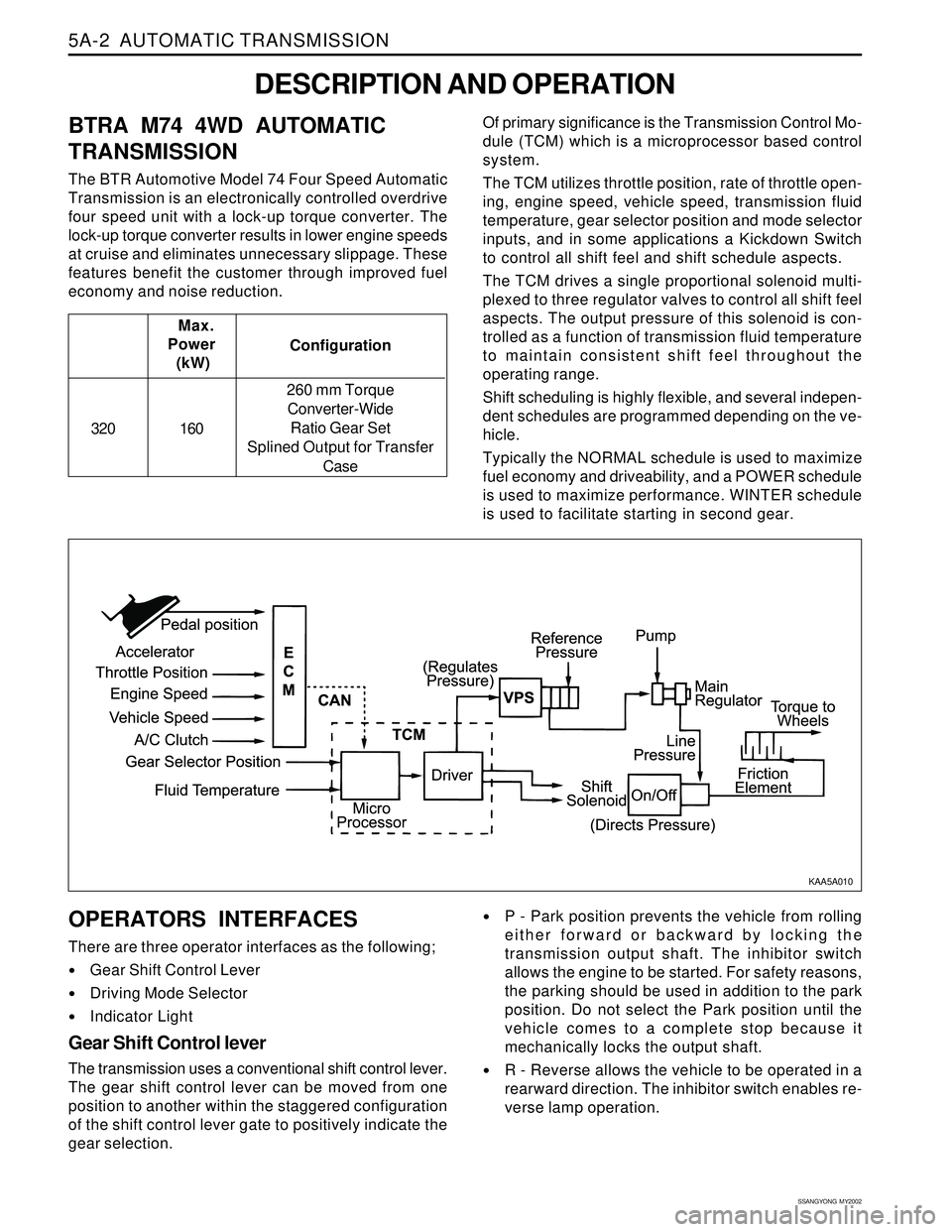
economy and noise reduction.Of primary significance is the Transmission Control Mo-
dule (TCM) which is a microprocessor based control
system.
The TCM utilizes throttle position, rate of throttle open-
ing, engine speed, vehicle speed, transmission fluid
temperature, gear selector position and mode selector
inputs, and in some applications a Kickdown Switch
to control all shift feel and shift schedule aspects.
The TCM drives a single proportional solenoid multi-
plexed to three regulator valves to control all shift feel
aspects. The output pressure of this solenoid is con-
trolled as a function of transmission fluid temperature
to maintain consistent shift feel throughout the
operating range.
Shift scheduling is highly flexible, and several indepen-
dent schedules are programmed depending on the ve-
hicle.
Typically the NORMAL schedule is used to maximize
fuel economy and driveability, and a POWER schedule
is used to maximize performance. WINTER schedule
is used to facilitate starting in second gear. Configuration Max.
Power
(kW)
320 160260 mm Torque
Converter-Wide
Ratio Gear Set
Splined Output for Transfer
Case
P - Park position prevents the vehicle from rolling
either forward or backward by locking the
transmission output shaft. The inhibitor switch
allows the engine to be started. For safety reasons,
the parking should be used in addition to the park
position. Do not select the Park position until the
vehicle comes to a complete stop because it
mechanically locks the output shaft.
R - Reverse allows the vehicle to be operated in a
rearward direction. The inhibitor switch enables re-
verse lamp operation.
KAA5A010
Page 1097 of 2053

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-3
SSANGYONG MY2002
N - Neutral allows the engine to be started and oper-
ated while driving the vehicle. The inhibitor switch
allows the engine to be started. There is no power
transferred through the transmission in Neutral. But
the final drive is not locked by the parking pawl, so
thewheels are free to rotate.
D - Overdrive range is used for all normal driving
conditions. 4th gear (overdrive gear) reduces the
fuel consumption and the engine noise. Engine
braking is applied with reduced throttle.
First to second (1 → 2), first to third (1 → 3), second
to third (2 → 3), second to fourth (2 → 4), third to
fourth (3 → 4), fourth to third (4 → 3), fourth to
second (4 → 2), third to second (3 → 2), third to
first (3 → 1) and second to first (2 → 1) shifts are
all available as a function of vehicle speed, throttle
position and the time change rate of the throttle
position.
Downshifts are available for safe passing by
depress-ing the accelerator. Lockup clutch may be
enabled in 3rd and 4th gears depending on vehicle
type.
3 - Manual 3 provides three gear ratios (first through
third) and prevents the transmission from operating
in 4th gear. 3rd gear is used when driving on long
hill roads or in heavy city traffic. Downshifts are
available by depressing the accelerator.
2 - Manual 2 provides two gear ratios (first and
second). It is used to provide more power when
climbing hills or engine braking when driving down
a steep hill or starting off on slippery roads.
1 - Manual 1 is used to provide the maximum engine
braking when driving down the severe gradients.When NORMAL mode is selected upshifts will occur
to maximize fuel economy. When POWER mode is se-
lected, upshifts will occur to give maximum
performance and the POWER mode indicator light is
switched ON.
When WINTER mode is selected, starting in second
gear is facilitated, the WINTER mode indicator light is
switched ON and the POWER mode indicator light is
switched OFF.
Indicator Light
The indicator light is located on the instrument panel.
Auto shift indicator light comes ON when the ignition
switch ON and shows the gear shift control lever
position.
POWER mode indicator light comes ON when the
POWER mode is selected and when the kickdown
switch is depressed.
WINTER mode indicator light comes ON when the
WINTER mode is selected.
CONTROL SYSTEMS
BTRA M74 4WD automatic transmission consists of
two control systems. One is the electronic control
system that monitors vehicle parameters and adjusts
the transmission performance. Another is the hydraulic
control system that implements the commands of the
electronic control system commands.
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The electronic control system comprises of sensors, a
TCM and seven solenoids. The TCM reads the inputs
and activates the outputs according to values stored
in Read Only Memory (ROM).
The TCM controls the hydraulic control system. This
control is via the hydraulic valve body, which contains
seven electromagnetic solenoids. Six of the seven
solenoids are used to control the line pressure, operate
the shift valves and the torque converter lock-up clutch,
and to turn ON and OFF the two regulator valves that
control the shift feel.
The seventh solenoid is the proportional or Variable
Pressure Solenoid (VPS) which works with the two regu-
lator valves to control shift feel.
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
The TCM is an in-vehicle micro-processor based trans-
mission management system. It is mounted under the
driver’s side front seat in the vehicle cabin.
The TCM contains:
Processing logic circuits which include a central mi-
croprocessor controller and a back-up memory
system.
Input circuits.
Driving Mode Selector
The driving mode selector consists of a driving mode
selector switch and indicator light. The driving mode
selector is located on the center console and allows
the driver to select the driving mode.
The driving modes available to be selected vary with
vehicle types. Typically the driver should have the
option to select among NORMAL, POWER and
WINTER modes.
KAA5A020
Page 1098 of 2053
5A-4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
SSANGYONG MY2002
Output circuits which control external devices such
as the Variable Pressure Solenoid (VPS) driver, On/
Off solenoid drivers, a diagnostics output and the
driving mode indicator light.
Processing Logic
Shift schedule and calibration information is stored in
an Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EPROM).
Throttle input calibration constants and the diagnostics
information are stored in Electrically Erasable Program-
mable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) that retains the
memory even when power to the TCM is disconnected.
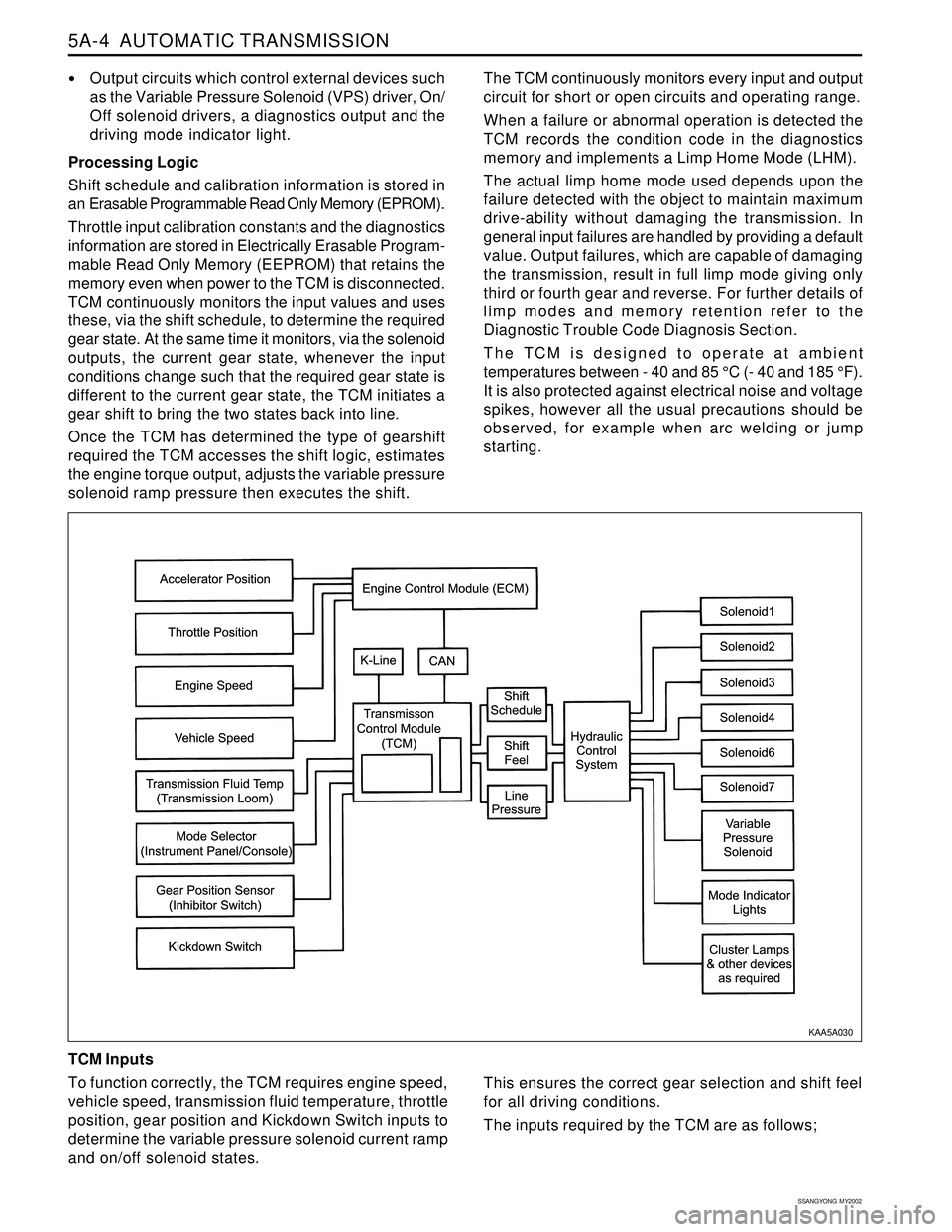
TCM continuously monitors the input values and uses
these, via the shift schedule, to determine the required
gear state. At the same time it monitors, via the solenoid
outputs, the current gear state, whenever the input
conditions change such that the required gear state is
different to the current gear state, the TCM initiates a
gear shift to bring the two states back into line.
Once the TCM has determined the type of gearshift
required the TCM accesses the shift logic, estimates
the engine torque output, adjusts the variable pressure
solenoid ramp pressure then executes the shift.The TCM continuously monitors every input and output
circuit for short or open circuits and operating range.
When a failure or abnormal operation is detected the
TCM records the condition code in the diagnostics
memory and implements a Limp Home Mode (LHM).
The actual limp home mode used depends upon the
failure detected with the object to maintain maximum
drive-ability without damaging the transmission. In
general input failures are handled by providing a default
value. Output failures, which are capable of damaging
the transmission, result in full limp mode giving only
third or fourth gear and reverse. For further details of
limp modes and memory retention refer to the
Diagnostic Trouble Code Diagnosis Section.
The TCM is designed to operate at ambient
temperatures between - 40 and 85 °C (- 40 and 185 °F).
It is also protected against electrical noise and voltage
spikes, however all the usual precautions should be
observed, for example when arc welding or jump
starting.
TCM Inputs
To function correctly, the TCM requires engine speed,
vehicle speed, transmission fluid temperature, throttle
position, gear position and Kickdown Switch inputs to
determine the variable pressure solenoid current ramp
and on/off solenoid states.
KAA5A030
This ensures the correct gear selection and shift feel
for all driving conditions.
The inputs required by the TCM are as follows;
Page 1099 of 2053
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-5
SSANGYONG MY2002
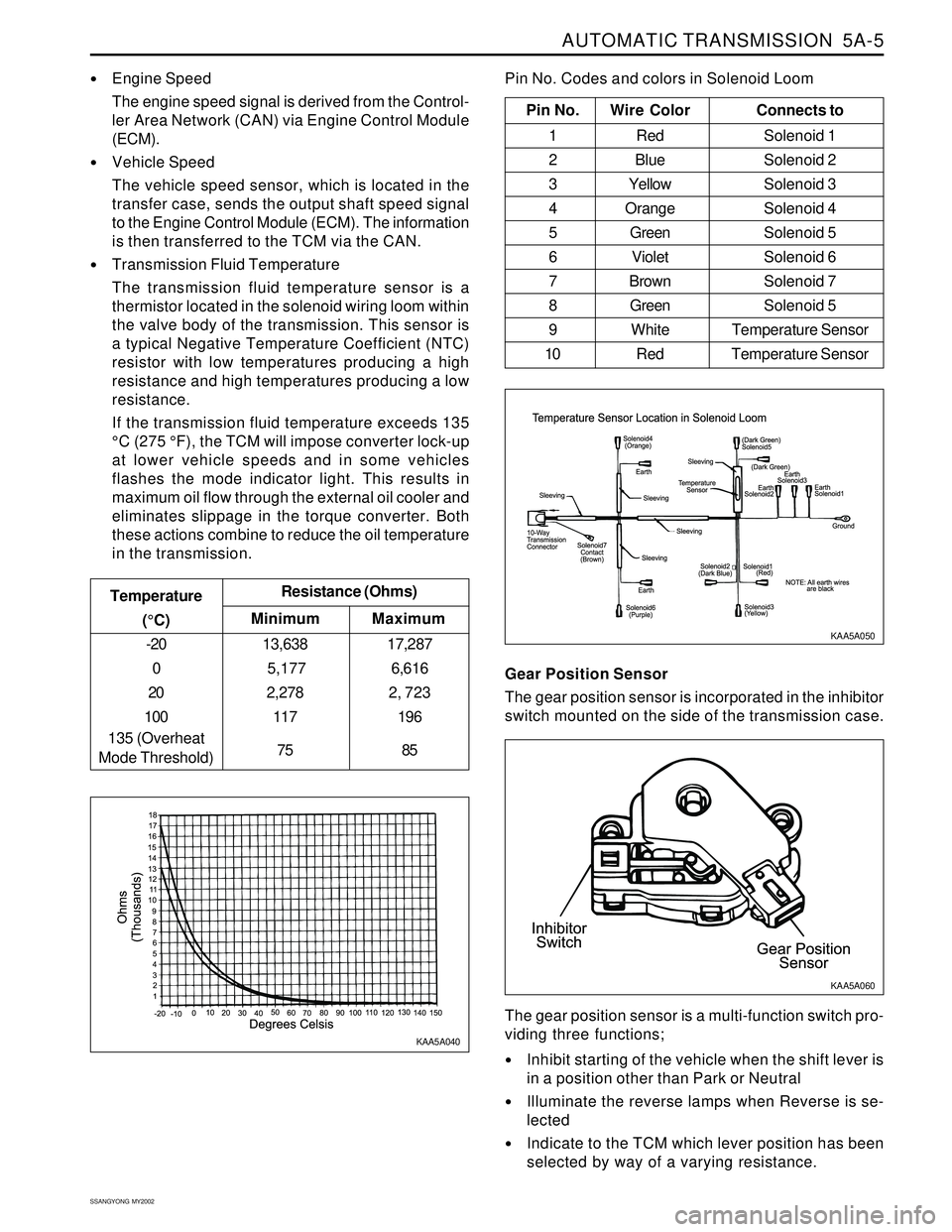
Engine Speed
The engine speed signal is derived from the Control-
ler Area Network (CAN) via Engine Control Module
(ECM).
Vehicle Speed
The vehicle speed sensor, which is located in the
transfer case, sends the output shaft speed signal
to the Engine Control Module (ECM). The information
is then transferred to the TCM via the CAN.
Transmission Fluid Temperature
The transmission fluid temperature sensor is a
thermistor located in the solenoid wiring loom within
the valve body of the transmission. This sensor is
a typical Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC)
resistor with low temperatures producing a high
resistance and high temperatures producing a low
resistance.
If the transmission fluid temperature exceeds 135
°C (275 °F), the TCM will impose converter lock-up
at lower vehicle speeds and in some vehicles
flashes the mode indicator light. This results in
maximum oil flow through the external oil cooler and
eliminates slippage in the torque converter. Both
these actions combine to reduce the oil temperature
in the transmission.
Minimum Temperature
(°C)Resistance (Ohms)
-20
0
20
100
135 (Overheat
Mode Threshold)13,638
5,177
2,278
117
75
Maximum
17,287
6,616
2, 723
196
85
Pin No. Wire ColorConnects to
1 Red Solenoid 1
2 BlueSolenoid 2
3 YellowSolenoid 3
4 OrangeSolenoid 4
5 GreenSolenoid 5
6 VioletSolenoid 6
7 BrownSolenoid 7
8 GreenSolenoid 5
9 White Temperature Sensor
10 Red Temperature Sensor
Pin No. Codes and colors in Solenoid Loom
KAA5A040KAA5A050
Gear Position Sensor
The gear position sensor is incorporated in the inhibitor
switch mounted on the side of the transmission case.
Inhibit starting of the vehicle when the shift lever is
in a position other than Park or Neutral
Illuminate the reverse lamps when Reverse is se-
lected
Indicate to the TCM which lever position has been
selected by way of a varying resistance. The gear position sensor is a multi-function switch pro-
viding three functions;
KAA5A060
Page 1103 of 2053

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-9
SSANGYONG MY2002
The DLC connector is located within the driver’s
compartment, directly below the instrument panel on
the driver’s side.
HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The hydraulic controls are located in the valve body,
pump body and main case.
The valve body contains the following;
Manual valve
Three shift valves
Sequence valve
Solenoid supply pressure regulator valve
Line pressure control valve
Clutch apply feed regulator valve
Band apply feed regulator valve
Solenoid S1 to S6
Reverse lockout valveThe pump cover contains the following;
Primary regulator valve for line pressure
Converter clutch regulator valve
Converter clutch control valve
Solenoid S7
The main case contains the following;
B1R exhaust valve
All upshifts are accomplished by simultaneously
switching on a shift valve(s), switching VPS pressure
to the band and/or clutch regulator valve, and then
sending the VPS a ramped current. The shift is
completed by switching the regulators OFF and at the
same time causing the VPS to reach maximum
pressure.
All downshifts are accomplished by switching VPS pres-
sure to the band and/or clutch regulator valve and send-
ing a ramped current to the VPS. The shift is completed
by simultaneously switching the regulators OFF,
switching the shift valves and at the same time causing
the VPS to return to stand-by pressure.
The primary regulator valve is located in the pump
cover and supplies four line pressures; high and low
for forward gears, and high and low for reverse. This
pressure has no effect on shift quality and merely
provides static clutch capacity during steady state
operation. Low pressure can be obtained by activating
an ON/OFF solenoid with high line pressure being the
default mode.
Torque converter lock-up is initiated by toggling the
converter clutch control valve with an ON/OFF solenoid.
The actual apply and release of the clutch is regulated
by the VPS via the converter clutch regulator valve.
The solenoid supply pressure regulator valve provides
reference pressure for all the solenoids.
KAA5A080
Page 1108 of 2053
5A-14 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
SSANGYONG MY2002
Converter Clutch Regulator Valve
The converter clutch regulator valve regulates the pres-
sure of the oil which applies the converter clutch. Input
oil from the line 500 circuit is regulated within the valve,
with the output pressure being variable according to
the signal pressure from the S5 circuit. Converter clutch
apply and release application is smoothed by
electronically varying the S5 circuit pressure.
Converter Clutch Control Valve
The converter clutch control valve is a two position
valve which applies or releases the converter clutch.
The switching of this valve is governed by the signal
pressure from S7.
When the valve is in the OFF or released position, con-
verter feed oil from the PRV is directed to the release
side of the converter clutch. After flowing through the
converter, oil returns to the converter clutch control
valve and is then directed to the oil cooler.
When the valve is in the ON or applied position, regu-
lated oil from the converter clutch regulator valve is
directed to the apply side of the converter clutch. This
oil remains within the converter because the converter
clutch piston is sealed against the flat friction surface
of the converter cover. To provide oil flow to the cooler
the converter clutch control valve directs converter feed
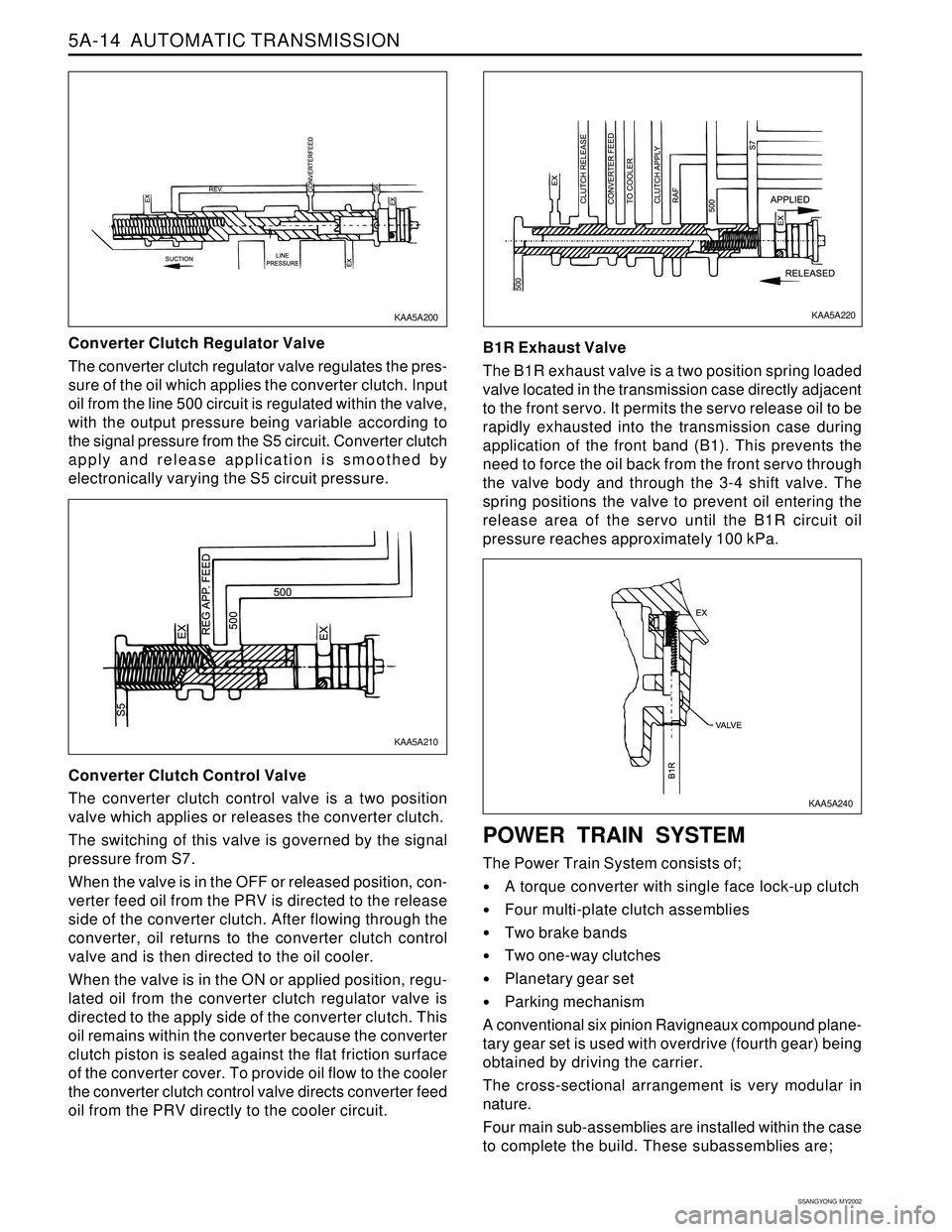
oil from the PRV directly to the cooler circuit.B1R Exhaust Valve
The B1R exhaust valve is a two position spring loaded
valve located in the transmission case directly adjacent
to the front servo. It permits the servo release oil to be
rapidly exhausted into the transmission case during
application of the front band (B1). This prevents the
need to force the oil back from the front servo through
the valve body and through the 3-4 shift valve. The
spring positions the valve to prevent oil entering the
release area of the servo until the B1R circuit oil
pressure reaches approximately 100 kPa.
POWER TRAIN SYSTEM
The Power Train System consists of;
A torque converter with single face lock-up clutch
Four multi-plate clutch assemblies
Two brake bands
Two one-way clutches
Planetary gear set
Parking mechanism
A conventional six pinion Ravigneaux compound plane-
tary gear set is used with overdrive (fourth gear) being
obtained by driving the carrier.
The cross-sectional arrangement is very modular in
nature.
Four main sub-assemblies are installed within the case
to complete the build. These subassemblies are;
KAA5A220KAA5A200
KAA5A210
KAA5A240
Page 1110 of 2053

5A-16 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
SSANGYONG MY2002
Torque Converter
The torque converter consists of a turbine, stator pump,
impeller and a lock-up damper and piston assembly.
As in conventional torque converters, the impeller is
attached to the converter cover, the turbine is splined
to the input shaft and the stator is mounted on the
pump housing via a one way clutch (sprag).
The addition of the damper and piston assembly en-
ables the torque converter to lock-up under favorable
conditions. Lock-up is only permitted to occur in third
and fourth gears under specified throttle and vehicle
speed conditions.
Lock-up is achieved by applying hydraulic pressure
to the damper and piston assembly which couples the
turbine to the converter cover, locking-up the converter
and eliminating unwanted slippage. Whenever lock-
up occurs, improved fuel consumption is achieved.
Torsional damper springs are provided in the damper
and piston assembly to absorb any engine torque
fluctuations during lock-up.
Clutch Packs
There are four clutch packs. All clutch packs are com-
posed of multiple steel and friction plates.
C1 CLUTCH: When applied, this clutch pack allows
the input shaft to drive the planet carrier. This occurs
in third and fourth gears.
C2 CLUTCH: When applied this clutch pack allows
the input shaft to drive the forward sun gear via the 3-
4 OWC. This occurs in all forward gears.
C3 CLUTCH: When applied this clutch pack allows
the input shaft to drive the reverse sun gear. This only
occurs in reverse gear.
C4 CLUTCH: When applied this clutch provides engine
braking on overrun. This occurs in Manual 1, 2 and 3
and also Drive 2 and Drive 3 to prevent objectionable
free wheel coasting.
KAA5A260
KAA5A270