engine ACURA NSX 1991 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ACURA, Model Year: 1991, Model line: NSX, Model: ACURA NSX 1991Pages: 1640, PDF Size: 60.48 MB
Page 1431 of 1640
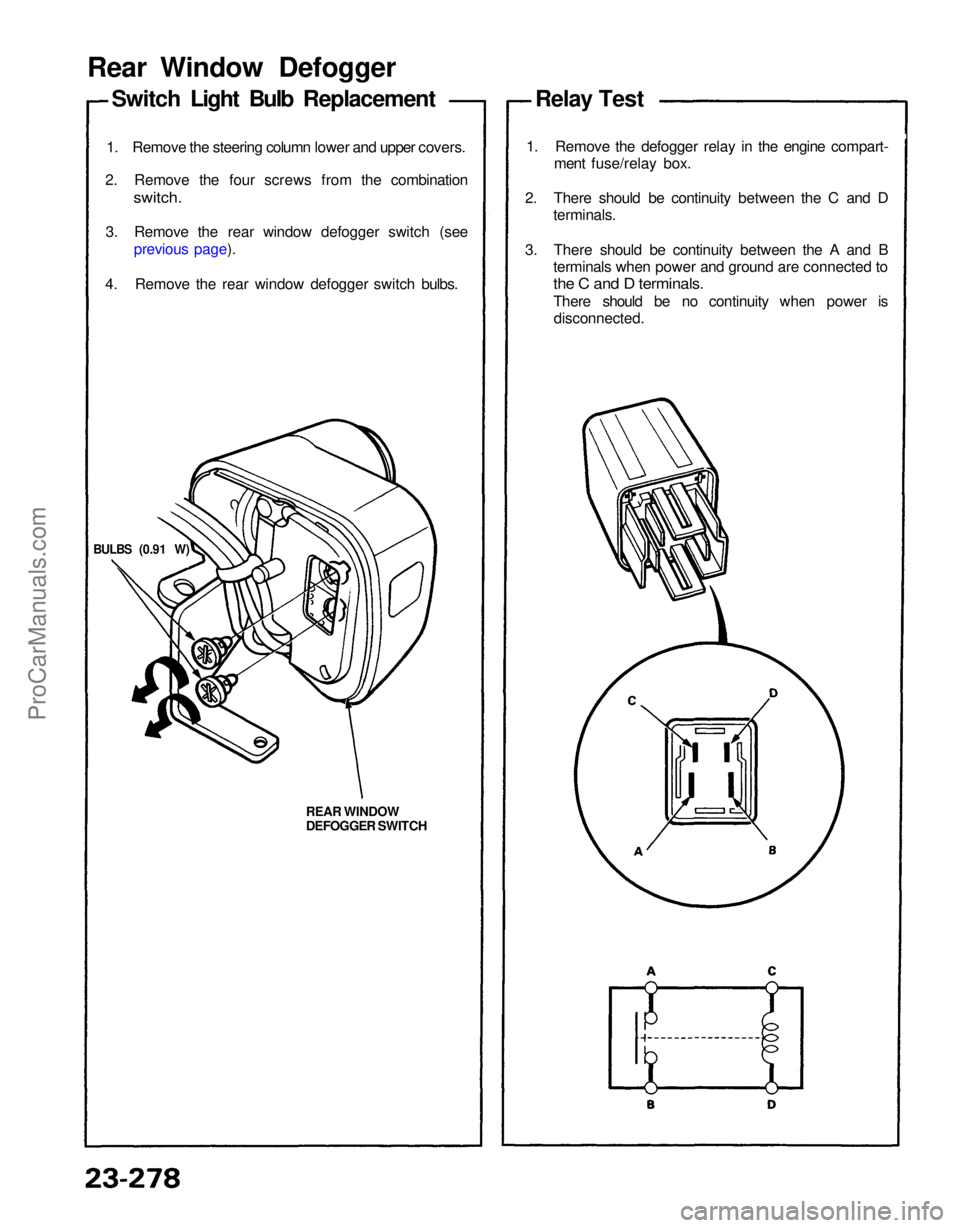
Rear Window Defogger
Switch Light Bulb Replacement
1. Remove the steering column lower and upper covers.
2. Remove the four screws from the combination
switch.
3. Remove the rear window defogger switch (see previous page).
4. Remove the rear window defogger switch bulbs.
BULBS (0.91 W)
REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER SWITCH Relay Test
1. Remove the defogger relay in the engine compart- ment fuse/relay box.
2. There should be continuity between the C and D terminals.
3. There should be continuity between the A and B terminals when power and ground are connected to
the C and D terminals.
There should be no continuity when power isdisconnected.ProCarManuals.com
Page 1448 of 1640
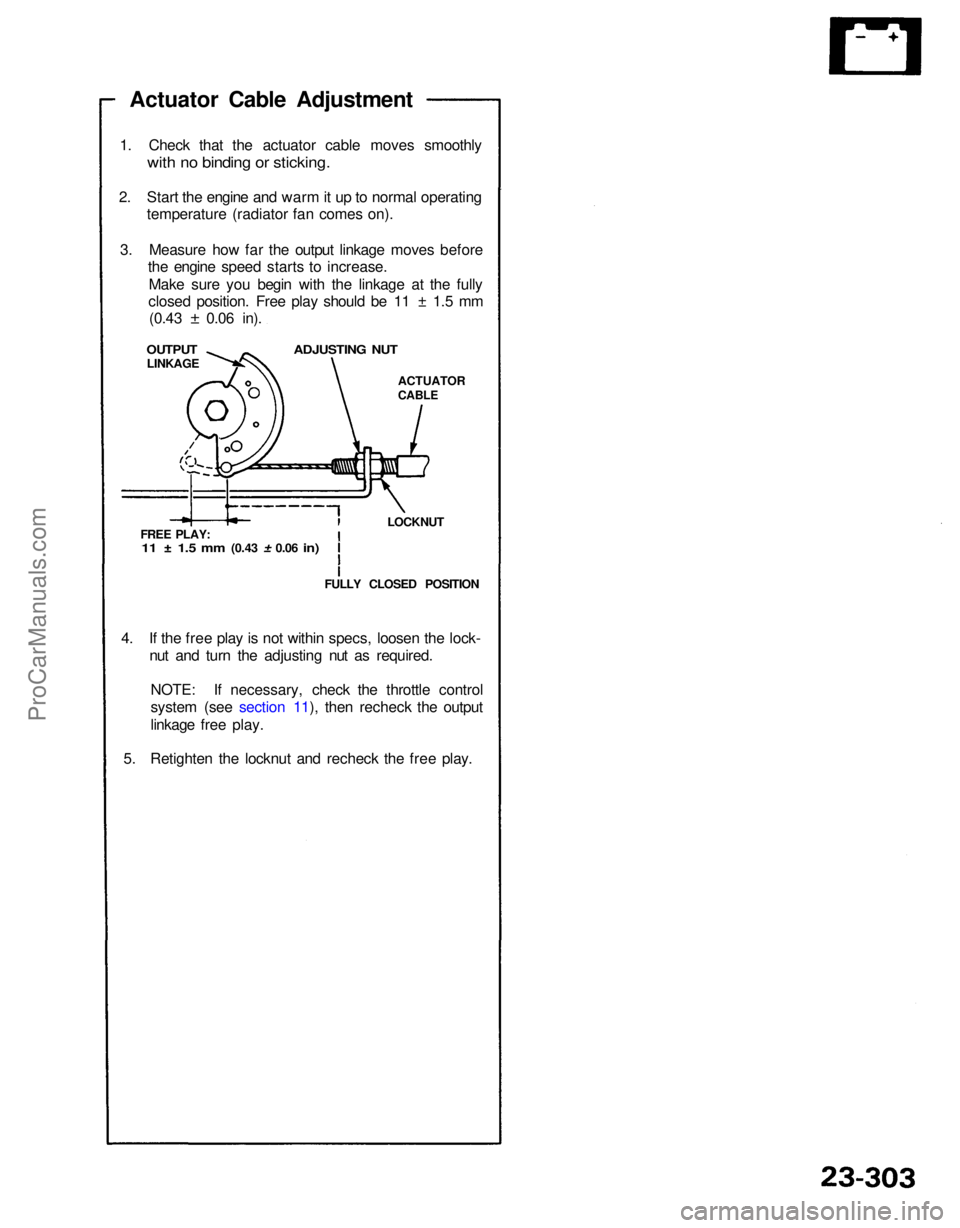
Actuator Cable Adjustment
1. Check that the actuator cable moves smoothly
with no binding or sticking.
2. Start the engine and warm it up to normal operating temperature (radiator fan comes on).
3. Measure how far the output linkage moves before the engine speed starts to increase.
Make sure you begin with the linkage at the fully
closed position. Free play should be 11 ± 1.5 mm (0.43
±
0.06 in).
OUTPUT
LINKAGE
ADJUSTING NUT
ACTUATOR
CABLE
LOCKNUT
FREE PLAY:
11 ± 1.5 mm
(0.43
±
0.06
in)
FULLY CLOSED POSITION
4. If the free play is not within specs, loosen the lock- nut and turn the adjusting nut as required.
NOTE: If necessary, check the throttle control
system (see section 11), then recheck the output
linkage free play.
5. Retighten the locknut and recheck the free play.ProCarManuals.com
Page 1454 of 1640
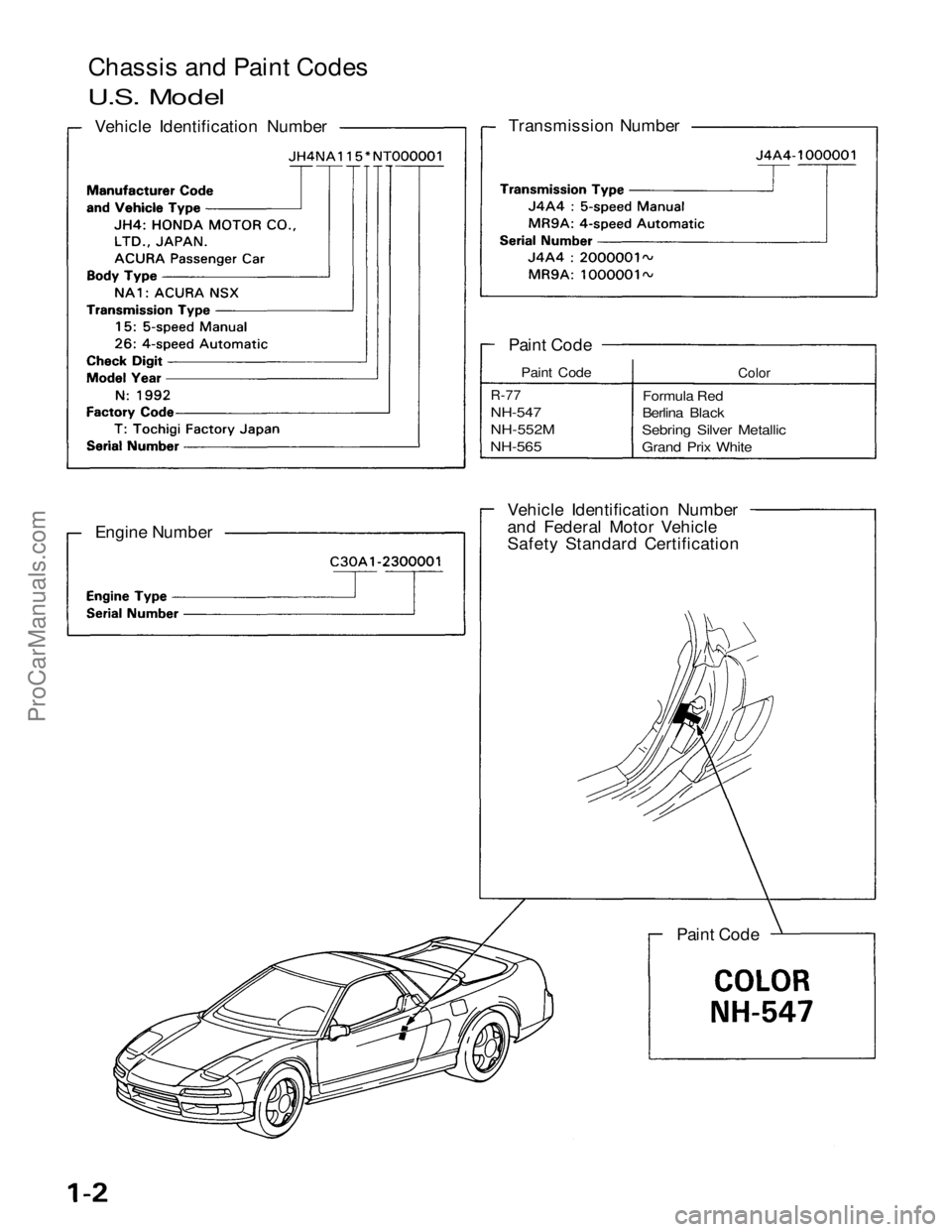
Chassi
s
and Paint Codes
Vehicle Identification Number
Transmission Number
Vehicle Identification Number
and Federal Motor Vehicle
Safety Standard Certification Paint Code
Engine Number
Paint Code
Paint Code
R-77
NH-547
NH-552M
NH-565
Color
Formula Red
Berlina Black
Sebring Silver Metallic
Grand Prix White
U.S. Model
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1455 of 1640
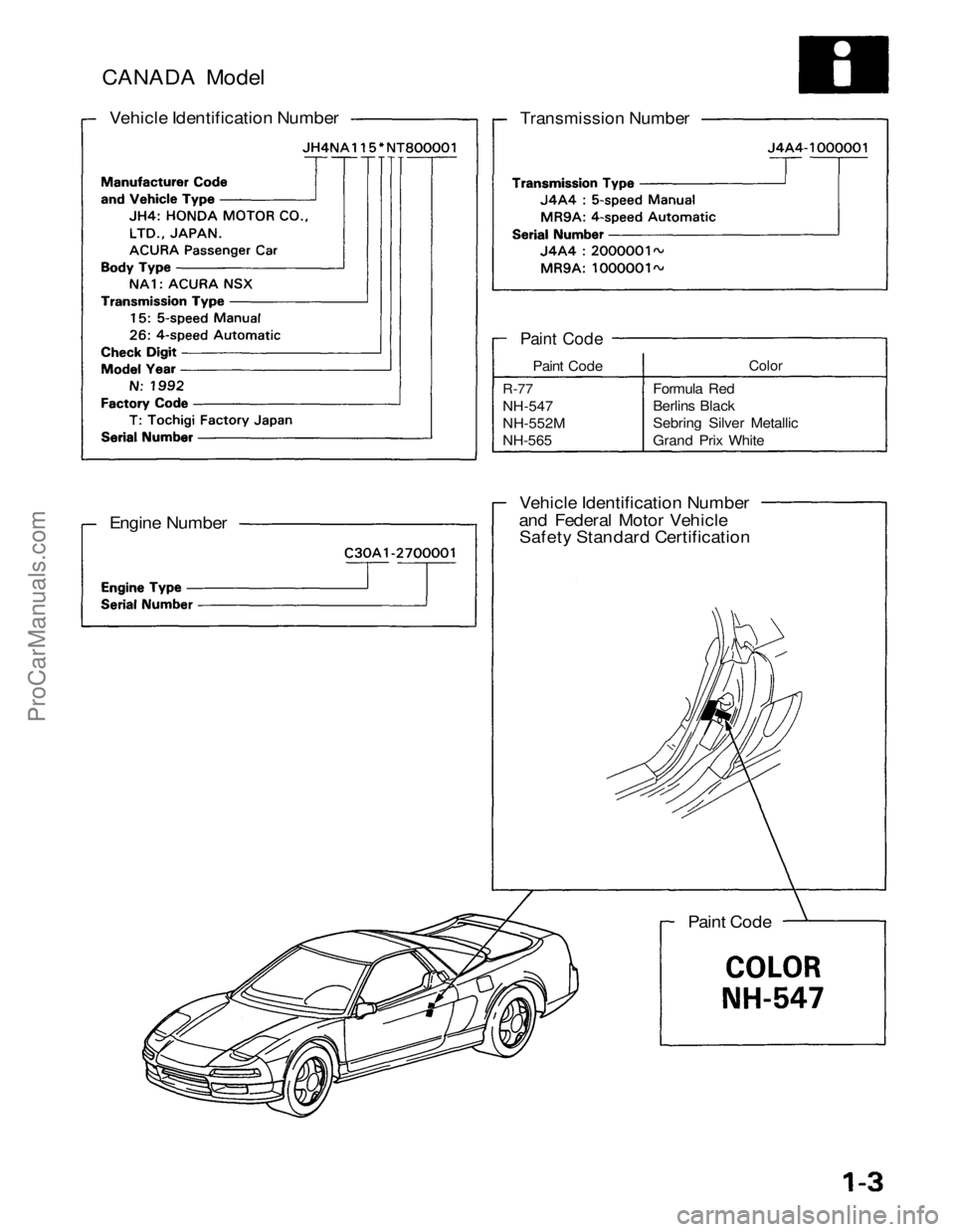
CANADA Model
Vehicle Identification Number
Transmission Number
Engine Number
Vehicle Identification Number
and Federal Motor Vehicle
Safety Standard Certification
Paint Code
Paint Code
R-77
NH-547
NH-552M
NH-565
Paint Code
Color
Formula Red
Berlins Black
Sebring Silver Metallic
Grand Prix WhiteProCarManuals.com
Page 1461 of 1640
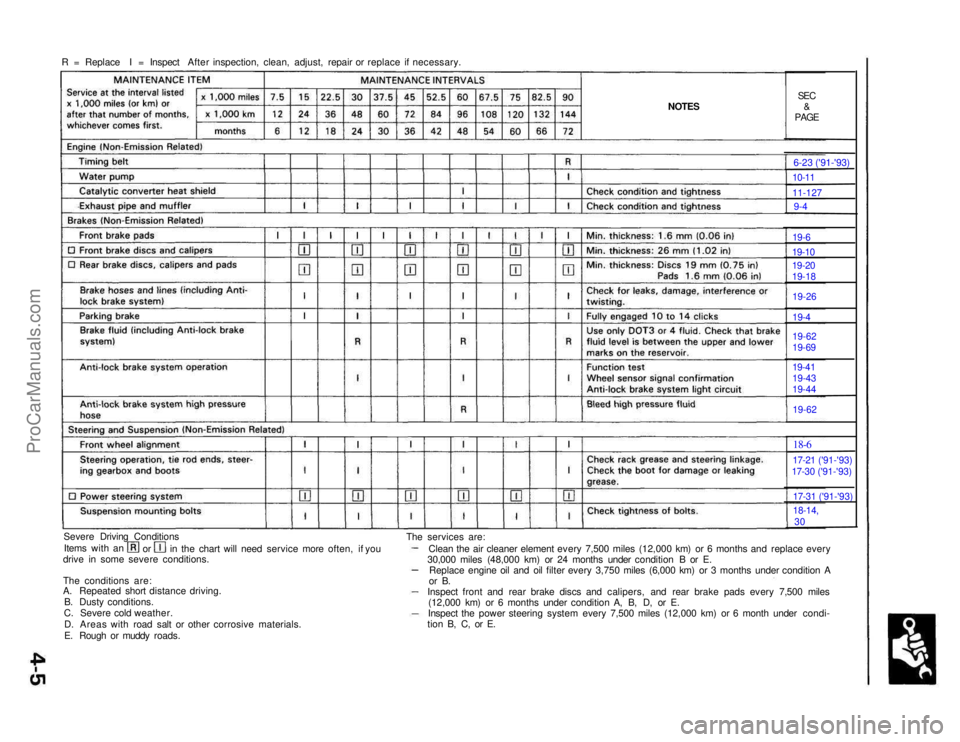
R = Replace I = Inspect After inspection, clean, adjust, repair or replace if necessary.
NOTES
SEC
&
PAGE
Severe Driving Conditions Items with an orin the chart will need service more often, if you
drive in some severe conditions.
The conditions are:
A. Repeated short distance driving.
B. Dusty conditions.
C. Severe cold weather.
D. Areas with road salt or other corrosive materials.
E. Rough or muddy roads. The services are:
Clean the air cleaner element every 7,500 miles (12,000 km) or 6 months and replace every
30,000 miles (48,000 km) or 24 months under condition B or E. Replace engine oil and oil filter every 3,750 miles (6,000 km) or 3 months under condition A
or B.
Inspect front and rear brake discs and calipers, and rear brake pads every 7,500 miles (12,000 km) or 6 months under condition A, B, D, or E.
Inspect the power steering system every 7,500 miles (12,000 km) or 6 month under condi-
tion B, C, or E. 6-23 ('91-'93)10-11
11-127
9-4
19-6
19-10
19-20
19-18
19-26
19-4
19-62
19-69
19-41
19-43
19-44
19-62
18-6
17-21 ('91-'93)
17-30 ('91-'93)
17-31 ('91-'93)
18-14,
30
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1462 of 1640
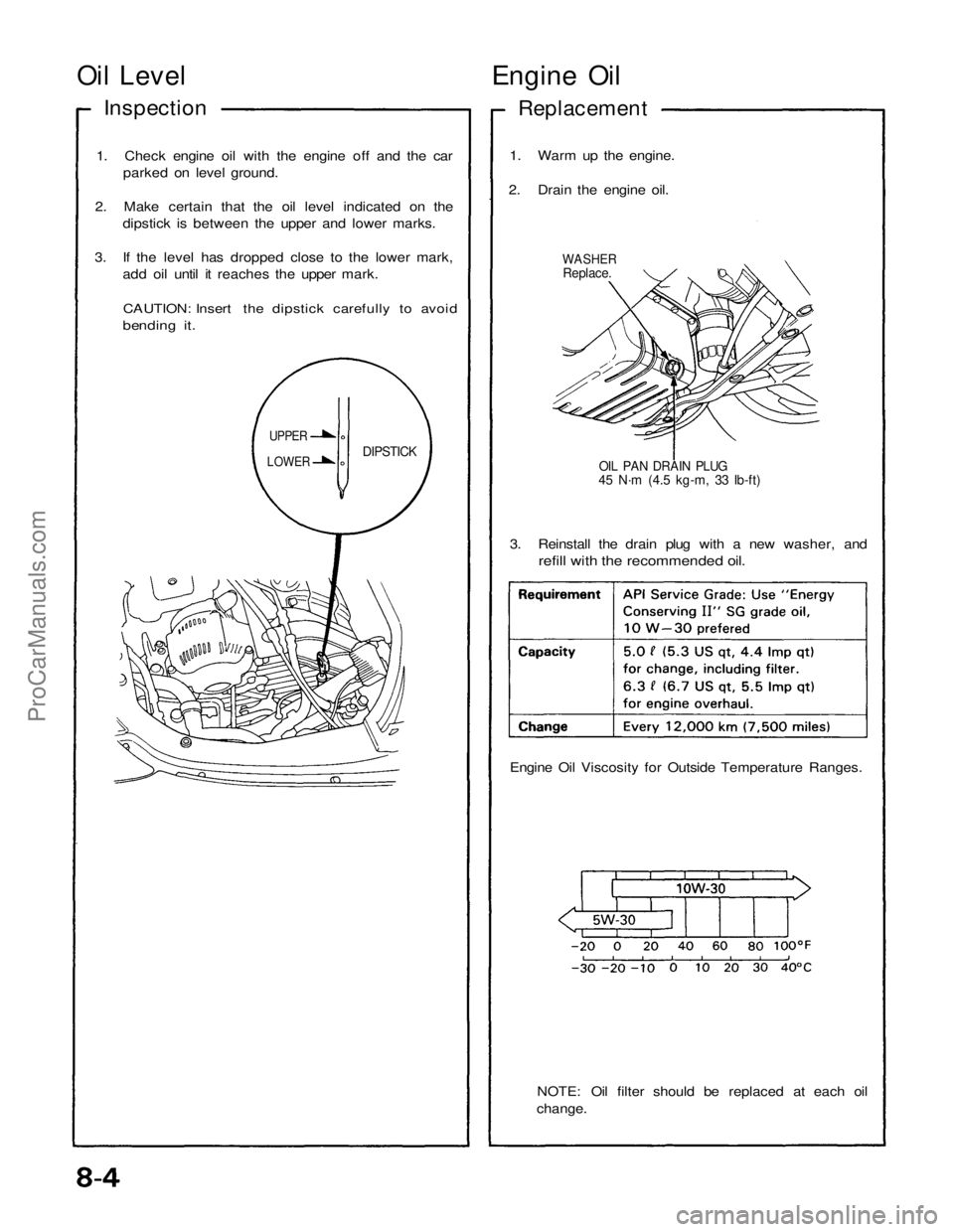
Oil Level
Engine Oil
Inspection
Replacement
1. Check engine oil with the engine off and the car parked on level ground.
2. Make certain that the oil level indicated on the dipstick is between the upper and lower marks.
3. If the level has dropped close to the lower mark, add oil until it reaches the upper mark.
CAUTION: Insert the dipstick carefully to avoid
bending it.
1. Warm up the engine.
2. Drain the engine oil.
WASHER
Replace.
OIL PAN DRAIN PLUG
45 N·m (4.5 kg-m, 33 Ib-ft)
DIPSTICK
UPPER
LOWER
3. Reinstall the drain plug with a new washer, and
refill with the recommended oil.
Engine Oil Viscosity for Outside Temperature Ranges.
NOTE: Oil filter should be replaced at each oil
change.ProCarManuals.com
Page 1477 of 1640
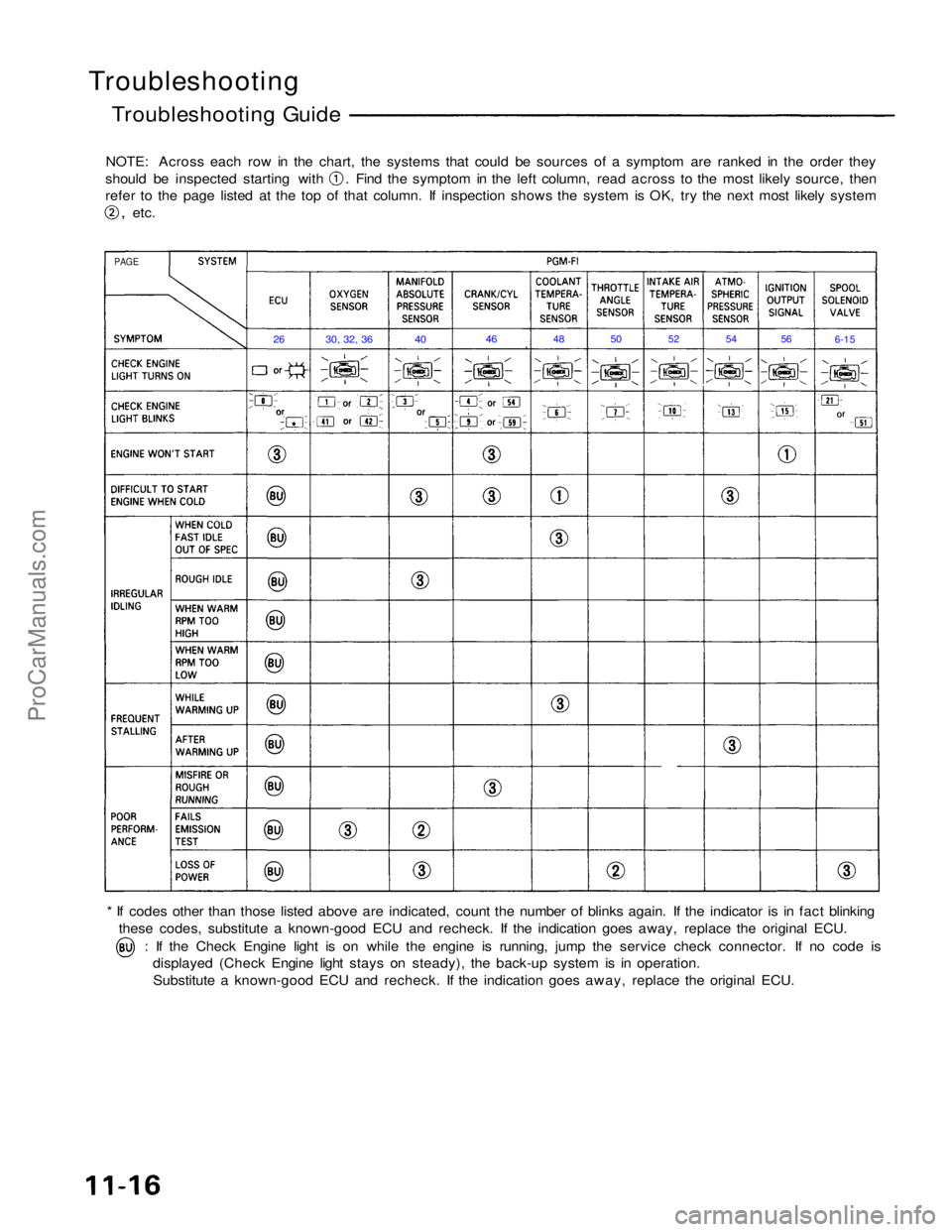
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Guide
NOTE: Across each row in the chart, the systems that could be sources of a symptom are ranked in the order they should be inspected starting with . Find the symptom in the left column, read across to the most likely source, then
refer to the page listed at the top of that column. If inspection shows the system is OK, try the next most likely system
,
etc.
* If codes other than those listed above are indicated, count the number of blinks again. If the indicator is in fact blinking these codes, substitute a known-good ECU and recheck. If the indication goes away, replace the original ECU. : If the Check Engine light is on while the engine is running, jump the service check connector. If no code is
displayed (Check Engine light stays on steady), the back-up system is in operation.
Substitute a known-good ECU and recheck. If the indication goes away, replace the original ECU.
PAGE
26
30, 32, 36
40
46
48
50
52
54
56
6-15ProCarManuals.com
Page 1479 of 1640

How to Read Flowcharts
A flowchart is designed to be used from start to final repair. It's like a map showing you the shortest distance. But beware: if you
go off the "map" anywhere but a "stop" symbol, you can easily get lost.
Describes the conditions or situation to start a troubleshooting flowchart.
(bold type)
Asks you to do something; perform a test, set up a condition, etc.
Asks you about the result of an action, then sends you in the appropriate troubleshooting direction.
The end of a series of actions and decisions, describes a final repair action and sometimes directs
(bold type) you to an earlier part of the flow to confirm your repair.
NOTE: The term "Intermittent Failure" is used in these charts. It simply means a system may have had a failure, but it checks
out OK through all your tests. You may need to road test the car to reproduce the failure or if the problem was a loose
connection, you may have unknowingly solved it while doing the tests. In any event, if the Check Engine light on the
dash does not come on, check for poor connections or loose wires at all connectors related to the circuit that you are
troubleshooting. Most of the troubleshooting flowcharts have you reset the ECU and try to duplicate the problem code. If the problem
is internittent and you can't duplicate the code, do not continue through the flowchart. To do so will only result in con-
fusion and, possibly, a needlessly replaced ECU. "Open" and "Short" are common electrical terms. An open is a break in a wire or at a connection. A short is an ac-
cidental connection of a wire to ground or to another wire. In simple electronics, this usually means something won't
work at all. In complex electronics (like ECUs), this can sometimes mean something works, but not the way it's sup-
posed to. If the electrical readings are not as specified when using the ECU test harness, check the test harness connections
before proceeding.ProCarManuals.com
Page 1480 of 1640

PGM-FI Control System
System Description
INPUTS ELECTRONIC CONTROL UNIT OUTPUTSCRANK/CYL SensorsMAP Sensor
TW Sensor
TA Sensor
Throttle Angle Sensor Oxygen SensorsEGR Valve Lift Sensor
Vehicle Speed Sensor
Ignition Timing Adjuster
Knock Sensers
A/T Fl Signals
TCS Signals
Starter Signal
Alternator FR Signal
Air Conditioning Signal
A/T Shift Position Signal M/T Neutral Switch Signal
M/T Clutch Switch Signal
Battery Voltage (IGN. 1)
Fuel Pump Terminal Voltage
VTEC Oil Pressure Switch
Signals
Injector Timing and Duration
Electronic Idle Control
Other Control Functions Ignition Timing Control
ECU Back-up Functions Injectors
Main Relay (Fuel Pump)
Fuel Pump Relay
Check Engine Light
EACV
A/C Compressor Clutch Relay
Igniter Unit
Purge Cut-Off Solenoid Valve
EGR Control Solenoid Valve
Chamber Volume Control Solenoid Valve
Radiator Fan Relay
Engine Compartment Fan Relay
VTEC Spool Valves
TCS Control Signals
Injector Tinning and Duration
The ECU contains memories for the basic discharge durations at various engine speeds and manifold pressures. The
basic discharge duration, after being read out from the memory, is further modified by signals sent from various sensors
to obtain the final discharge duration.
Electronic Air Control
Electronic Air Control Valve (EACV)
When the engine is cold, the A/C compressor is on, the transmission is in gear (A/T only) or the alternator is charging, the ECU
controls current to the EACV to maintain correct idle speed.
Ignition Timing Control
The ECU contains memories for basic ignition timing at various engine speeds and manifold pressures. Ignition timing
is also adjusted for coolant temperature.
A Knock Control System is also used. When detonation is detected by the knock sensor, the ignition timing is
retarded.
Other Control Functions
1. Starting Control
When the engine is started, the ECU provides a rich mixture.
2. Fuel Pump Control
When the ignition switch is initially turned on, the ECU supplies ground to the main relay which supplies current to
the fuel pump for two seconds to pressurize the fuel system.
When the engine is running, the ECU supplies ground to the mam relay which supplies current to the fuel pump.
When the engine is not running and the ignition is on, the ECU cuts ground to the main relay which cuts current
to the fuel pump.
Excellent engine performance is achieved through the use of VTEC (Variable Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Con-
trol System), intake manifold chamber control and discharge volume control of the fuel pump.
3. Fuel Cut-off Control During deceleration with the throttle valve closed, current to the injectors is cut off to improve fuel economy at
speeds over 1,500 rpm.
Fuel cut-off action also takes place
when
engine speed exceeds,
8,300
rpm, regardless
of the
position
of the
throttle valve, to protect the engine from over-revving.ProCarManuals.com
Page 1481 of 1640

4. A/C Compressor Clutch Relay
When the ECU receives a demand for cooling from the air conditioning system (compressor control unit), it delays
the compressor from being energized, and enriches the mixture to assure smooth transition to the A/C mode.
5. Purge Cut-off Solenoid Valve
When the coolant temperature is below 70 °C (158 °F), the ECU supplies a ground to the purge cut-off solenoid valve
which cuts vacuum to the purge control valve.
6. Chamber Volume Control Solenoid Valve (CVCSV)
When the engine rpm is below 4,800 rpm the CVCSV is activated by a signal from the ECU, intake air flows through
a smaller chamber, then high torque is delivered. At speeds higher than 4,800 rpm, both solenoid valves are deac-
tivated by the ECU, and intake air flows through the a larger chamber in order to increase airflow.
7. EGR Control Solenoid Valve (EGR CSV)
When the EGR is required for control of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) emissions, the ECU supplies ground to the EGR CSV
which supplies regulated vacuum to the EGR valve.
ECU Back-up Functions
1. Fail-Safe Function
When an abnormality occurs in a signal from a sensor, the ECU ignores that signal and assumes a pre-programmed
value that allows the engine to continue to run.
2. Back-up Function
When an abnormality occurs in the ECU itself, the injectors are controlled by a back-up circuit independent of the
system in order to permit minimal diving.
3. Self-diagnosis Function (Check Engine light)
When an abnormality occurs in a signal from a sensor, the ECU lights the Check Engine light and stores the failure
code in erasable memory. When the ignition is initially turned on, the ECU supplies ground for the Check Engine light
for two seconds.ProCarManuals.com