air condition DATSUN PICK-UP 1977 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1977, Model line: PICK-UP, Model: DATSUN PICK-UP 1977Pages: 537, PDF Size: 35.48 MB
Page 77 of 537

Condition
Seized
valve
seat
Excessively
worn
cylinder
and
piston
Faulty
connecting
rod
Faulty
crankshaft
bearing
Engine
Mechanical
Probable
cause
Improper
valve
clearance
Weakened
valve
spring
Thin
valve
head
edge
Narrow
valve
seat
Overheating
Over
speeding
Stuck
valve
guide
Shortage
of
engine
oil
Dirty
engine
oil
Poor
quality
of
oiL
Overheating
Wrong
assembly
of
piston
with
connecting
rod
Improper
piston
ring
clearance
Broken
piston
ring
Dirty
aii
cleaner
Mixture
too
rich
Engine
over
run
Stuck
choke
valve
Overchoking
Shortage
of
engine
oil
Low
oil
pressure
Poor
quality
of
engine
oil
Rough
surface
of
craokshaft
Clogged
oil
passage
Bearing
worn
or
eccentric
Bearingimproperly
assembled
Loose
bearing
Connecting
rod
alignment
incorrect
Shortage
of
engine
oil
Low
oil
pressure
Poor
quality
of
engine
oil
Craokshaft
journal
worn
or
out
of
round
Clogged
oil
passage
in
crankshaft
Bearing
worn
or
eccentric
Bearing
improperly
assembled
Eccentric
craokshaft
or
bearing
EM
32
Corrective
action
Adjust
Replace
Replace
valve
Reface
Repair
or
replace
Drive
at
proper
speeds
Repair
Add
or
replace
oil
Clean
crankcase
replace
oil
and
oil
niter
element
Use
right
oil
Repair
or
replace
Repair
or
replace
Adjust
Replace
Clean
Adjust
Drive
at
proper
speeds
Clean
and
adjust
Start
correct
way
Add
oiL
Correct
Use
proper
oil
Grind
and
replace
bearing
Clean
Replace
Correct
Replace
Repair
or
replace
Add
or
replace
Correct
Use
proper
oil
Repair
Clean
Replace
Correct
Replace
Page 92 of 537
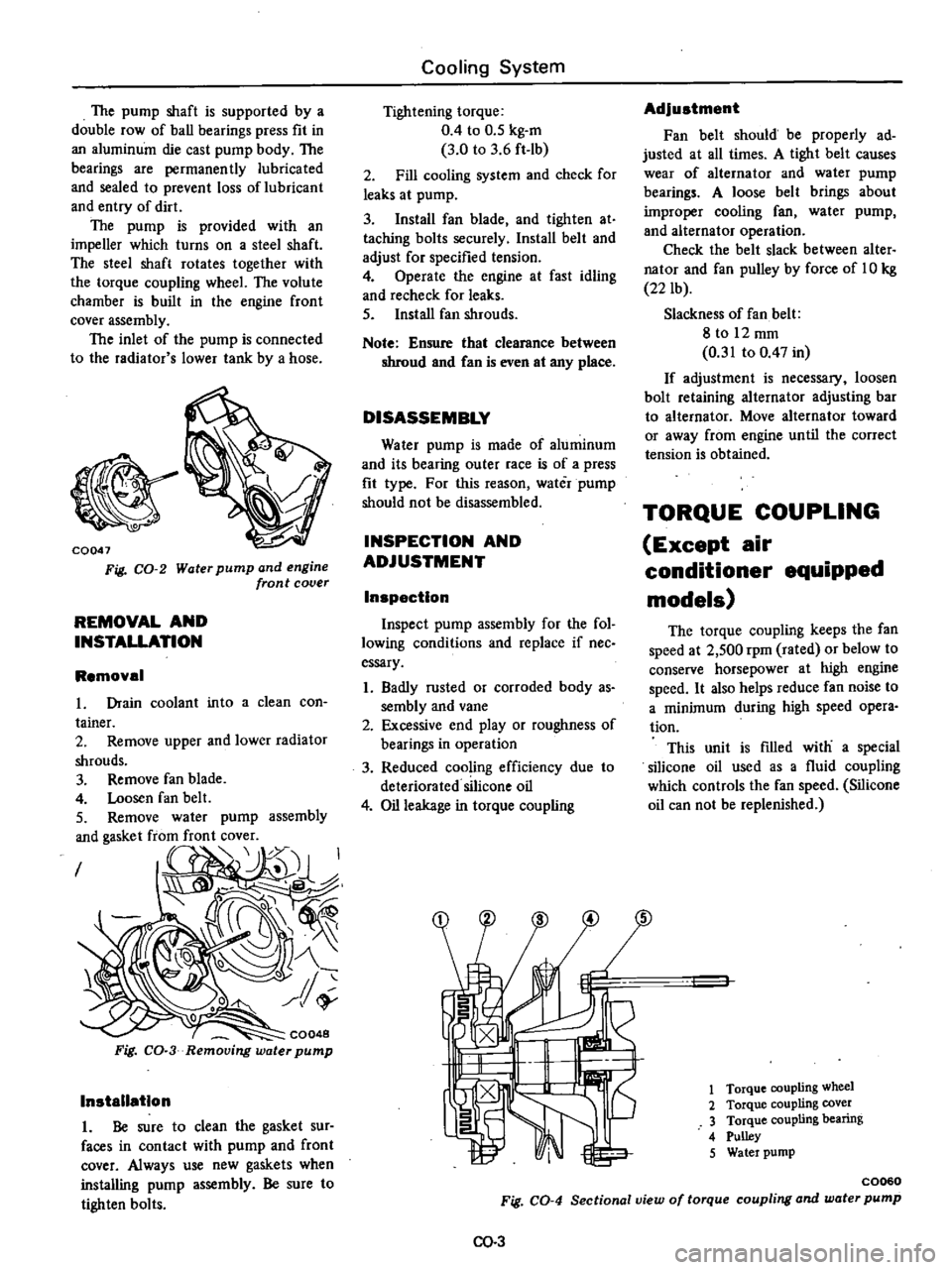
The
pump
shaft
is
supported
by
a
double
row
of
ball
bearings
press
fit
in
an
aluminum
die
cast
pump
body
The
bearings
are
permanently
lubricated
and
sealed
to
prevent
loss
of
lubricant
and
entry
of
dirt
The
pump
is
provided
with
an
impeller
which
turns
on
a
steel
shaft
The
steel
shaft
rotates
together
with
the
torque
coupling
wheeL
The
volute
chamber
is
built
in
the
engine
front
cover
assembly
The
inlet
of
the
pump
is
connected
to
the
radiator
s
lower
tank
by
a
hose
i
o
CQ047
Fig
CO
2
Water
pump
and
engine
front
cover
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
Removal
in
to
a
clean
con
assembly
I
CQ048
Fig
CO
3
Removing
water
pump
Installation
1
Be
sure
to
clean
the
gasket
sur
faces
in
contact
with
pump
and
front
cover
Always
use
new
gaskets
when
installing
pump
assembly
Be
sure
to
tighten
bolts
Cooling
System
Tightening
torque
0
4
to
0
5
kg
m
3
0
to
3
6
ft
lb
2
Fill
cooling
system
and
check
for
leaks
at
pump
3
Install
fan
blade
and
tighten
at
taching
bolts
securely
Install
belt
and
adjust
for
specified
tension
4
Operate
the
engine
at
fast
idling
and
recheck
for
leaks
5
Install
fan
shrouds
Note
Ensure
that
clearance
between
shroud
and
Can
is
even
at
any
place
DISASSEMBLY
Water
pump
is
made
of
aluminum
and
its
bearing
outer
race
is
of
a
press
fit
type
For
this
reason
water
pump
should
not
be
disassembled
INSPECTION
AND
ADJUSTMENT
Inspection
Inspect
pump
assembly
for
the
fol
lowing
conditions
and
replace
if
nee
essary
1
Badly
rusted
or
corroded
body
as
sembly
and
vane
2
Excessive
end
play
or
roughness
of
bearings
in
operation
3
Reduced
cooling
efficiency
due
to
deteriorated
silicone
oil
4
Oil
leakage
in
torque
coupling
Adjustment
Fan
belt
should
be
properly
ad
justed
at
all
times
A
tight
belt
causes
wear
of
alternator
and
water
pump
bearings
A
loose
belt
brings
about
improper
cooling
fan
water
pump
and
alternator
operation
Check
the
belt
slack
between
alter
nator
and
fan
pulley
by
force
of
10
kg
22
lb
Slackness
of
fan
belt
8
to
12
mm
0
31
to
0
47
in
If
adjustment
is
necessary
loosen
bolt
retaining
alternator
adjusting
bar
to
alternator
Move
alternator
toward
or
away
from
engine
until
the
correct
tension
is
obtained
TORQUE
COUPLING
Except
air
conditioner
equipped
models
The
torque
coupling
keeps
the
fan
speed
at
2
500
rpm
rated
or
below
to
conserve
horsepower
at
high
engine
speed
It
also
helps
reduce
fan
noise
to
a
minimum
during
high
speed
opera
tion
This
unit
is
filled
with
a
special
silicone
oil
used
as
a
fluid
coupling
which
controls
the
fan
speed
Silicone
oil
can
not
be
replenished
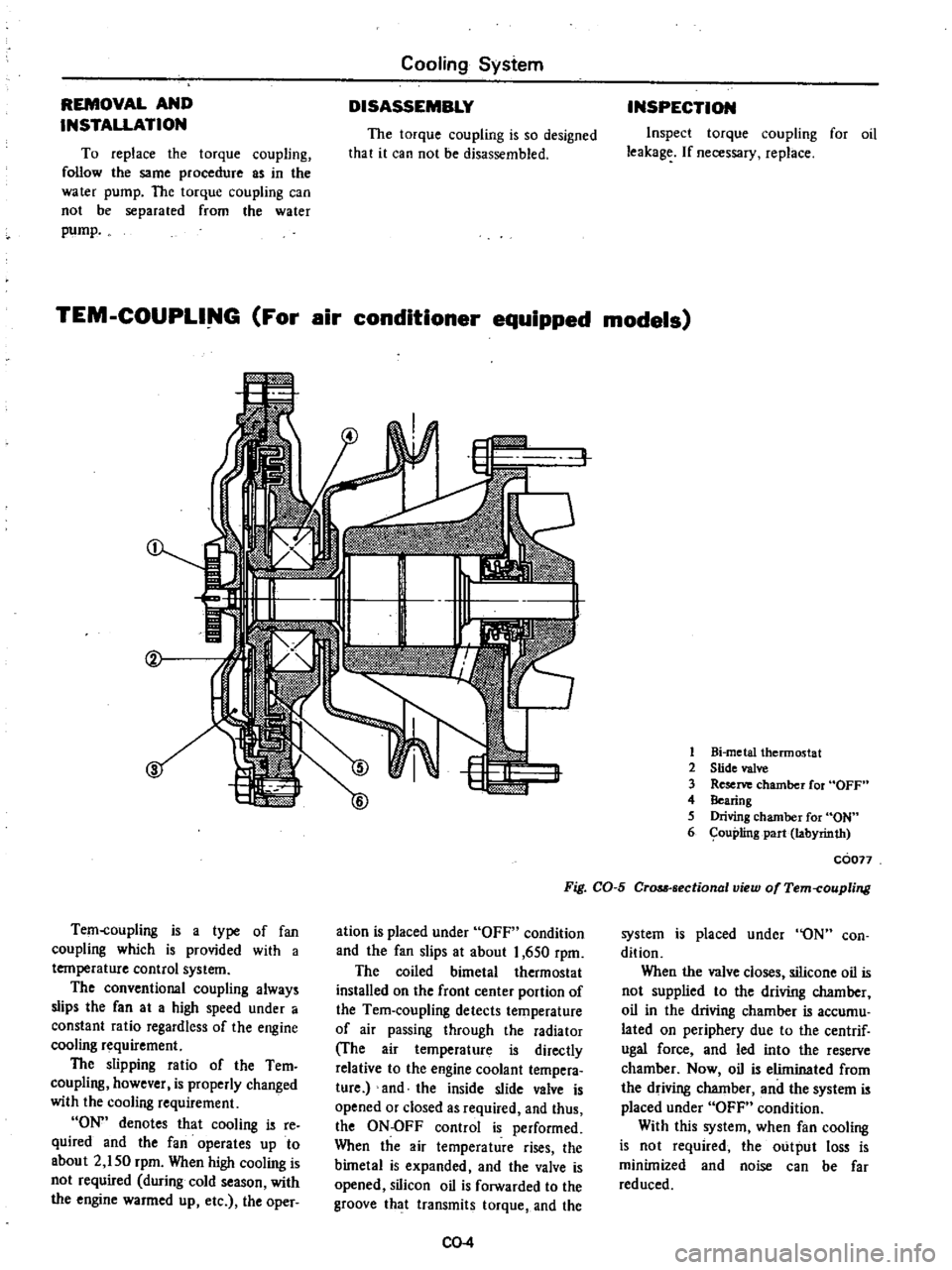
1
Torque
coupling
wheel
2
Torque
coupling
cover
3
Torque
coupling
bearing
4
Pulley
5
Water
pump
C0060
Fig
CO
4
Sectional
view
of
torque
coupling
and
water
pump
00
3
Page 93 of 537
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
To
replace
the
torque
coupling
follow
the
same
procedure
as
in
the
water
pump
The
torque
coupling
can
not
be
separated
from
the
water
pump
Cooling
System
DISASSEMBLY
The
torque
coupling
is
so
designed
that
it
can
not
be
disassembled
INSPECTION
Inspect
torque
coupling
for
oil
leakage
If
necessary
replace
TEM
COUPLl
G
For
air
conditioner
equipped
models
Tem
coupling
is
a
type
of
fan
coupling
which
is
provided
with
a
temperature
control
system
The
conventional
coupling
always
slips
the
fan
at
a
high
speed
under
a
constant
ratio
regardless
of
the
engine
cooling
requirement
The
slipping
ratio
of
the
Tern
coupling
however
is
properly
changed
with
the
cooling
requirement
ON
denotes
that
cooling
is
re
quired
and
the
fan
operates
up
to
about
2
150
rpm
When
high
cooling
is
not
required
during
cold
season
with
the
engine
warmed
up
etc
the
oper
w
6
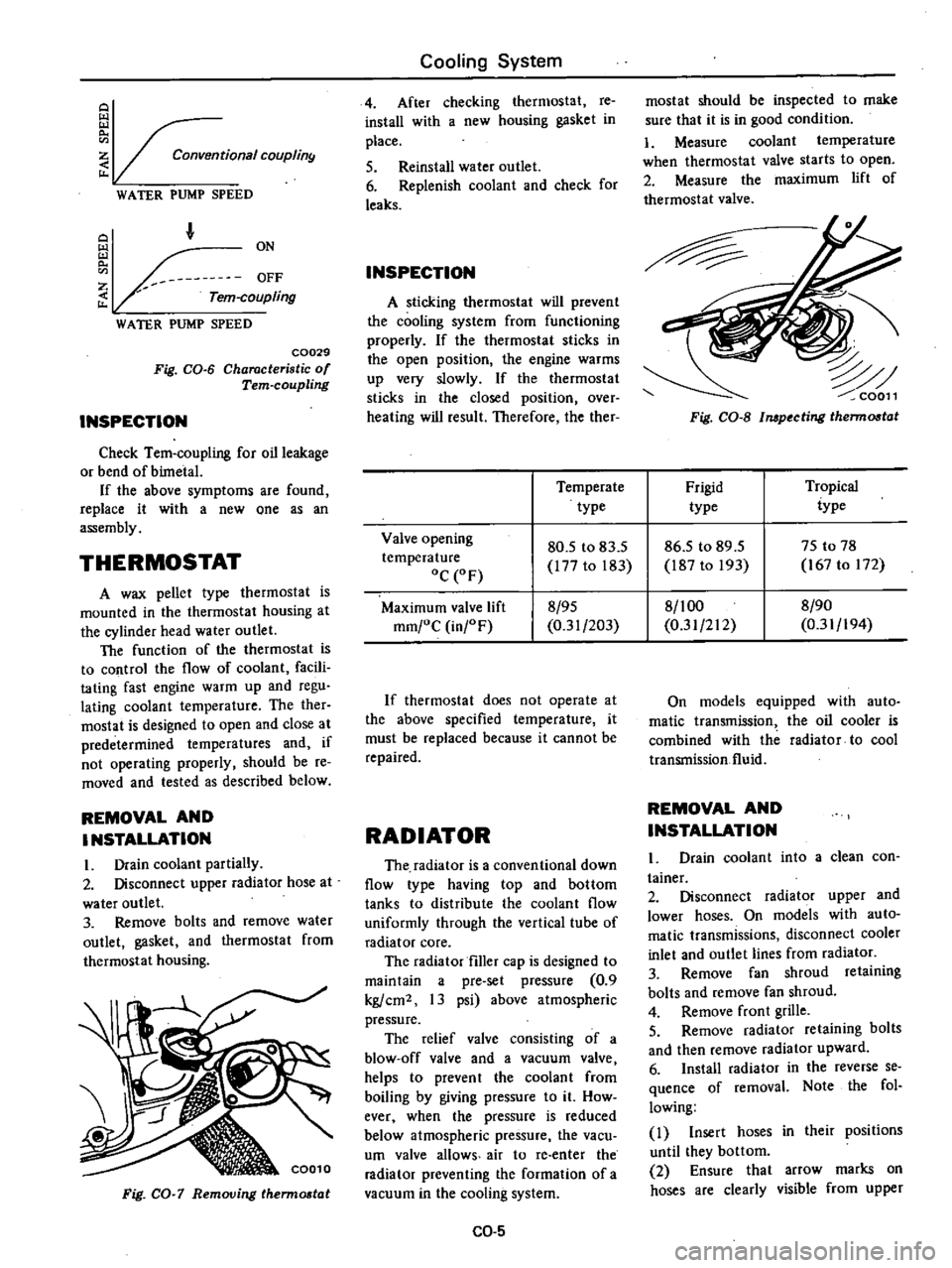
I
1
Bi
metal
thermostat
2
Slide
valve
3
Reserve
chamber
for
OFF
4
Bearing
5
Driving
chamber
for
ON
6
ouplingpart
labyrinth
coon
Fig
CO
5
CrQM
sectional
view
of
Tem
coupling
ation
is
placed
under
OFF
condition
and
the
fan
slips
at
about
1
650
rpm
The
coiled
bimetal
thermostat
installed
on
the
front
center
portion
of
the
Tem
coupling
detects
temperature
of
air
passing
through
the
radiator
The
air
temperature
is
directly
relative
to
the
engine
coolant
tempera
ture
and
the
inside
slide
valve
is
opened
or
closed
as
required
and
thus
the
ON
OFF
control
is
performed
When
the
air
temperature
rises
the
bimetal
is
expanded
and
the
valve
is
opened
silicon
oil
is
forwarded
to
the
groove
that
transmits
torque
and
the
CO
4
system
is
placed
under
ON
con
dition
When
the
valve
closes
silicone
oil
is
not
supplied
to
the
driving
chamber
oil
in
the
driving
chamber
is
accumu
lated
on
periphery
due
to
the
centrif
ugal
force
and
led
into
the
reserve
chamber
Now
oil
is
eliminated
from
the
driving
chamber
and
the
system
is
placed
under
OFF
condition
With
this
system
when
fan
cooling
is
not
required
the
output
loss
is
minimized
and
noise
can
be
far
reduced
Page 94 of 537
Conventional
COUplin9
WATER
PUMP
SPEED
F
Z
Tern
coupling
WATER
PUMP
SPEED
C0029
Fig
CO
6
Characteristic
of
Tern
coupling
INSPECTION
Check
Tem
coupling
for
oil
leakage
or
bend
of
bimetal
If
the
above
symptoms
are
found
replace
it
with
a
new
one
as
an
assembly
THERMOSTAT
A
wax
pellet
type
thermostat
is
mounted
in
the
thermostat
housing
at
the
cylinder
head
water
outlet
The
function
of
the
thermostat
is
to
control
the
flow
of
coolant
facili
tating
fast
engine
warm
up
and
regu
lating
coolant
temperature
The
ther
mostat
is
designed
to
open
and
close
at
predetermined
temperatures
and
if
not
operating
properly
should
be
re
moved
and
tested
as
described
below
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
I
Drain
coolant
partially
2
Disconnect
upper
radiator
hose
at
water
outlet
3
Remove
bolts
and
remove
water
outlet
gasket
and
thermostat
from
thermostat
housing
Fig
CO
7
Removing
therm06t
t
Cooling
System
4
After
checking
thermostat
re
install
with
a
new
housing
gasket
in
place
5
Reinstall
water
outlet
6
Replenish
coolant
and
check
for
leaks
INSPECTION
A
sticking
thermostat
will
prevent
the
cooling
system
from
functioning
properly
If
the
thermostat
sticks
in
the
open
position
the
engine
warms
up
very
slowly
If
the
thermostat
sticks
in
the
closed
position
over
heating
will
result
Therefore
the
ther
mostat
should
be
inspected
to
make
sure
that
it
is
in
good
condition
1
Measure
coolant
temperature
when
thermostat
valve
starts
to
open
2
Measure
the
maximum
lift
of
thermostat
valve
Fig
CO
S
Impecting
therm06t
t
Temperate
Frigid
Tropical
type
type
iype
Valve
opening
80
5
to
83
5
86
5
to
89
5
75
to
78
temperature
177
to
183
187
to
193
167
to
172
oC
OF
Maximum
valve
lift
8
95
8
1
00
8
90
mm
oC
in
F
0
31
203
0
31
212
0
31
194
If
thermostat
does
not
operate
at
the
above
specified
temperature
it
must
be
replaced
because
it
cannot
be
repaired
RADIATOR
The
radiator
is
a
conventional
down
flow
type
having
top
and
bottom
tanks
to
distribute
the
coolant
flow
uniformly
through
the
vertical
tube
of
radiator
core
The
radiator
filler
cap
is
designed
to
maintain
a
pre
set
pressure
0
9
kg
cm2
13
psi
above
atmospheric
pressure
The
relief
valve
consisting
of
a
blow
off
valve
and
a
vacuum
valve
helps
to
prevent
the
coolant
from
boiling
by
giving
pressure
to
it
How
ever
when
the
pressure
is
reduced
below
atmospheric
pressure
the
vacu
um
valve
allows
air
to
re
enter
the
radiator
preventing
the
formation
of
a
vacuum
in
the
cooling
system
CO
5
On
models
equipped
with
auto
matic
transmission
the
oil
cooler
is
combined
with
the
radiator
to
cool
transmission
fluid
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
Drain
coolant
into
a
clean
con
tainer
2
Disconnect
radiator
upper
and
lower
hoses
On
models
with
auto
matic
transmissions
disconnect
cooler
inlet
and
outlet
lines
from
radiator
3
Remove
fan
shroud
retaining
bolts
and
remove
fan
shroud
4
Remove
front
grille
5
Remove
radiator
retaining
bolts
and
then
remove
radiator
upward
6
Install
radiator
in
the
reverse
se
quence
of
removal
Note
the
fol
lowing
I
Insert
hoses
in
their
positions
until
they
bottom
2
Ensure
that
arrow
marks
on
hoses
are
clearly
visible
from
upper
Page 95 of 537
r
direction
when
hoses
are
assembled
3
Ensure
that
clearance
between
radiator
hose
and
any
adjacent
parts
is
30
mm
I
181
in
minimum
On
mod
els
equipped
with
air
conditions
a
minimum
clearance
of
18
mm
0
709
in
should
exist
between
compressor
and
hose
4
Ensure
that
clearance
between
shroud
and
fan
is
even
at
any
place
Note
Be
careful
not
to
damage
radia
tor
fins
and
core
tube
when
in
stalling
INSPECTION
Radiator
cap
should
be
checked
for
working
pressure
at
regular
tune
up
intervals
First
check
rubber
seal
on
cap
for
tears
cracks
or
deterioration
Cooling
System
after
cleaning
it
Then
install
radiator
cap
on
a
tester
If
cap
does
not
hold
or
will
not
release
at
the
specified
pres
sure
replace
cap
Fig
CO
9
Telting
radiator
cap
Also
inspect
radiator
for
leakage
using
cap
tester
and
applying
a
pres
sure
of
1
6
kg
cm
22
8
psi
If
a
leakage
is
detected
repair
or
replace
radiator
Fig
CO
IO
Testing
cooling
6ystem
pUS
ure
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
Thermostat
Valve
opening
temperature
oC
F
Maximum
valve
lift
mm
oC
inj
F
Radia
tor
Type
Manual
transmission
Automatic
transmission
Cap
relief
pressure
Cooling
system
Leakage
testing
pressure
Capacity
Manual
transmission
Automatic
transmission
Fan
Number
of
blades
x
outer
diameter
Without
air
conditioner
mm
in
With
air
conditioner
mm
in
kg
em
psi
kg
em
psi
liters
US
qt
Imp
qt
liters
US
qt
Imp
qt
CO
6
Temperate
Frigid
type
Tropical
type
type
80
5
to
83
5
86
5
to
89
5
75
to
78
177
to
183
187
to
193
167
to
172
8
95
8
100
8
90
0
31
203
0
31
212
0
31
194
Corrugated
fin
type
Corrugated
fin
type
equipped
with
oil
cooler
0
9
1
3
1
6
22
8
with
heater
8
0
8
Ii
7
7
8
8
Y
6
J
i
without
heater
74
7J
i6
1i
7
2
7
X
6
X
7
x
380
15
8
x
380
15
Page 96 of 537
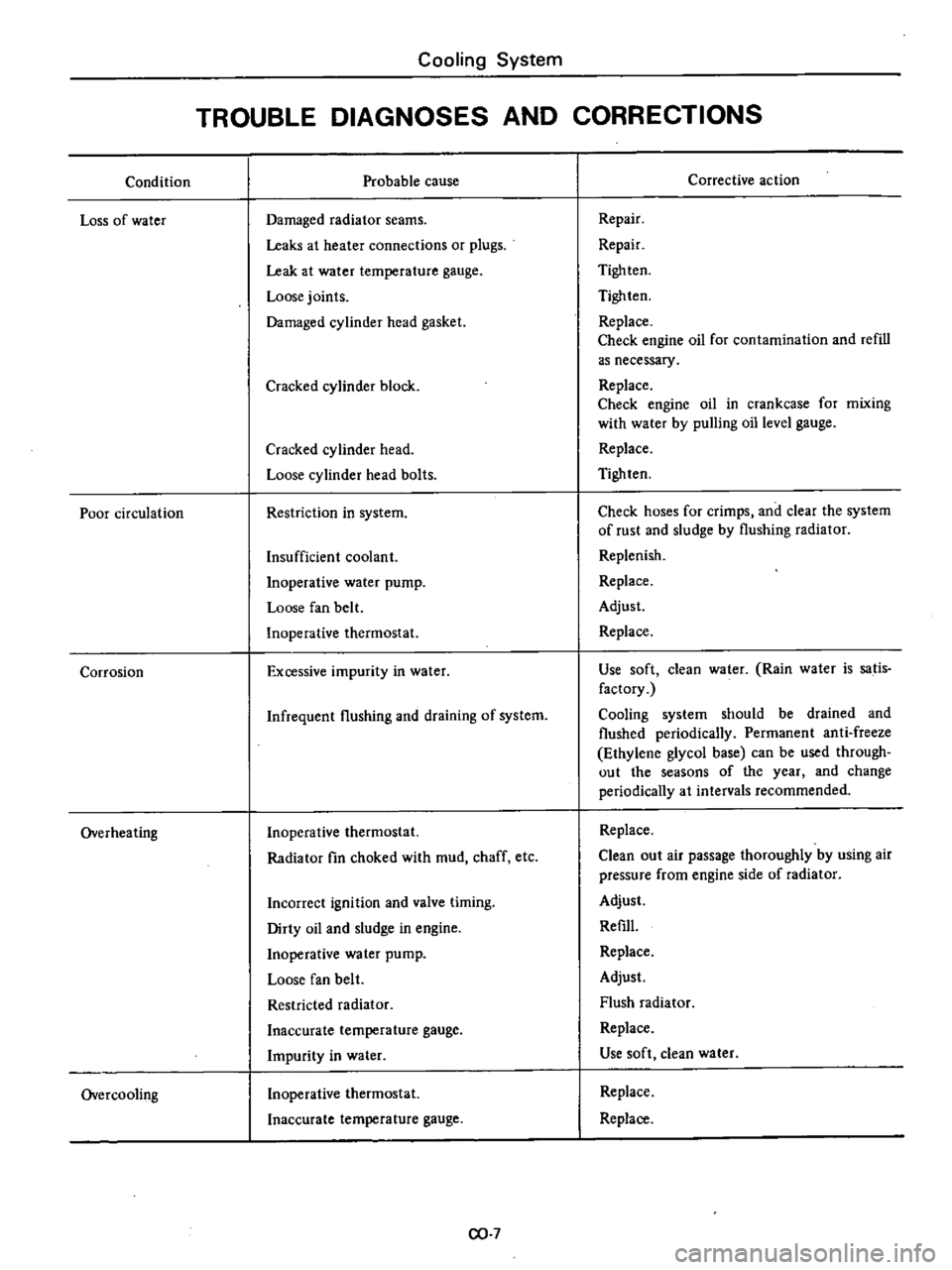
Condition
Loss
of
water
Poor
circulation
Corrosion
Overheating
Overcooling
Cooling
System
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
Probable
cause
Damaged
radiator
seams
Leaks
at
heater
connections
or
plugs
Leak
at
water
temperature
gauge
Loose
joints
Damaged
cylinder
head
gasket
Cracked
cylinder
block
Cracked
cylinder
head
Loose
cylinder
head
bolts
Restriction
in
system
Insufficient
coolant
Inoperative
water
pump
Loose
fan
belt
Inoperative
thermostat
Excessive
impurity
in
water
Infrequent
flushing
and
draining
of
system
Inoperative
thermostat
Radiator
fin
choked
with
mud
chaff
etc
Incorrect
ignition
and
valve
timing
Dirty
oil
and
sludge
in
engine
Inoperative
water
pump
Loose
fan
belt
Restricted
radiator
Inaccurate
temperature
gauge
Impurity
in
water
Inoperative
thermostat
Inaccurate
temperature
gauge
CO
7
Corrective
action
Repair
Repair
Tigh
ten
Tighten
Replace
Check
engine
oil
for
contamination
and
refill
as
necessary
Replace
Check
engine
oil
in
crankcase
for
mixing
with
water
by
pulling
oil
level
gauge
Replace
Tighten
Check
hoses
for
crimps
and
clear
the
system
of
rust
and
sludge
by
flushing
radiator
Replenish
Replace
Adjust
Replace
Use
soft
clean
water
Rain
water
is
satis
factory
Cooling
system
should
be
drained
and
flushed
periodically
Permanent
anti
freeze
Ethylene
glycol
base
can
be
used
through
out
the
seasons
of
the
year
and
change
periodically
at
intervals
recommended
Replace
Clean
out
air
passage
thoroughly
by
using
air
pressure
from
engine
side
of
radiator
Adjust
Refill
Replace
Adjust
Flush
radiator
Replace
Use
soft
clean
water
Replace
Replace
Page 99 of 537

Engine
Fuel
@
1
Fresh
air
duct
Except
for
Canada
2
Air
inlet
pipe
3
Vacuum
motor
assembly
4
Air
control
valve
5
Hot
air
pipe
6
Idle
compensator
7
Blow
by
gas
fiI
teT
8
Temperature
sensor
assembly
9
Altitude
compensator
California
models
EF713
Fig
EF
1
Automatic
temperature
control
air
cleaner
OPERATION
The
automatic
temperature
control
system
of
the
air
cleaner
is
controlled
by
the
inlet
air
temperature
and
the
load
condition
of
the
engine
The
inlet
air
temperature
is
detected
by
the
sensor
and
the
vacuum
motor
is
actu
ated
by
the
engine
intake
vacuum
Under
hood
air
Sensor
vacuum
at
Air
control
valve
Sensor
operation
temperature
vacuum
motor
side
operation
Below
60
mmHg
Open
cold
air
Below
300C
2
36
inHg
860
F
Close
Above
210
mmHg
Close
hot
air
8
27
inHg
30
to
540C
Half
open
Open
86
to
1290
F
cold
air
hot
air
Above
55
oC
Open
cold
air
Open
1310F
A
T
C
AIR
CLEANER
HOT
AIR
OPERATION
When
the
under
hood
air
tempera
ture
is
low
the
sensor
air
bleed
valve
remains
in
the
closed
position
and
establishes
vacuum
passage
between
the
intake
manifold
and
vacuum
motor
With
this
condition
the
vacu
urn
at
the
intake
manifold
side
actu
ates
the
air
control
valve
attached
to
the
vacuum
motor
diaphragm
to
intro
duce
hot
air
into
the
air
cleaner
through
the
hot
air
duct
on
the
ex
haust
manifold
EF
3
Page 102 of 537

r
AIR
CLEANER
1
Loosen
bolts
securing
air
cleaner
to
air
cleaner
bracket
2
Loosen
air
cleaner
lock
bolt
and
remove
air
cleaner
from
carburetor
Disconnect
the
following
hoses
when
dismounting
air
cleaner
Under
hood
air
inlet
hose
Hot
air
inlet
hose
Vacuum
hose
Sensor
to
intake
manifold
Vacuum
hose
Sensor
to
vacuum
motor
Vacuum
hose
Idle
compensator
to
intake
manifold
Hose
Air
pump
to
air
cleaner
Hose
AB
valve
to
air
cleaner
Hose
Carburetor
to
air
cleaner
Blow
by
hose
Air
cleaner
to
rocker
cover
Hose
Air
control
vaive
to
air
cleaner
California
models
only
3
To
install
reverse
the
removal
procedure
INSPECTION
1
AIR
CLEANER
ELEMENT
Viscous
paper
type
air
cleaner
ele
ment
does
not
require
any
cleaning
operation
until
it
is
replaced
periodi
cally
Brushing
or
blasting
operation
will
cause
clogging
and
result
in
enrich
ment
of
carburetor
mixture
and
should
never
be
conducted
For
reo
placement
interval
of
air
cleaner
ele
ment
refer
to
Maintenance
Sched
ule
2
HOT
AIR
CONTROL
SYSTEM
In
warm
weather
it
is
difficult
to
find
out
malfunction
of
hot
air
control
system
In
cold
wea
thee
however
malfunction
of
air
control
valve
due
to
disconnection
or
deterioration
of
vacu
um
hose
between
intake
manifold
and
vacuum
motor
and
insufficient
dura
bility
of
air
control
valve
will
cause
insufficient
automatic
control
opera
tion
for
intake
air
and
result
in
engine
disorder
including
I
Stall
or
hesitation
of
engine
oper
ation
2
Increase
in
fuel
consumption
3
uck
of
power
Engine
Fuel
These
phenomena
reveal
malfunc
tion
of
hot
air
control
system
If
these
phenomena
should
occur
check
hot
air
control
system
as
described
in
the
following
before
carrying
out
inspec
tion
of
carburetor
2
1
Vacuum
hose
Intake
manifold
to
3
way
connec
tor
3
way
connector
to
temperature
sensor
3
way
connector
to
idle
com
pensator
temperature
sensor
to
vacu
um
motor
I
Check
that
vacuum
hoses
are
se
curely
connected
in
correct
postion
2
Check
each
hose
for
cracks
or
distortion
hose
clip
for
condition
Note
Vacuum
hose
position
R
H
side
of
Nissan
mark
on
the
top
of
sensor
is
for
intake
manifold
L
U
side
of
the
mark
is
for
vacuum
motor
2
2
Vacuum
motor
I
With
engine
stopped
disconnect
fresh
air
duct
Place
a
mirror
at
the
end
of
air
cleaner
inlet
pipe
as
shown
and
check
to
see
if
air
con
trol
valve
is
in
correct
position
EF213
Fig
EF
11
Inspecting
valve
position
Air
control
valve
is
in
correct
posi
tion
if
its
under
hood
air
inlet
is
open
and
hot
air
inlet
is
closed
Check
air
control
valve
linkage
for
condition
2
Disconnect
vacuum
motor
inlet
vacuum
hose
and
connect
another
hose
to
the
inlet
to
apply
vacuum
to
vacuum
motor
Vacuum
can
be
ap
plied
by
breathing
in
the
hose
end
as
shown
Place
a
mirror
at
the
end
of
air
cleaner
inlet
pipe
and
check
to
see
if
air
control
valve
is
in
correct
position
EF
6
EF217
Fig
EF
12
Inspecting
valve
position
Correct
position
of
air
control
valve
is
the
reverse
of
paragraph
J
above
Air
control
valve
is
in
correct
position
if
under
hood
air
inlet
is
closed
and
hot
air
inlet
is
open
3
With
hot
air
inlet
in
open
posi
tion
as
described
in
paragraph
2
above
pinch
vacuum
hose
with
fingers
and
cut
off
air
from
vacuum
hose
In
this
condition
check
that
air
control
valve
maintains
the
condition
de
scribed
in
step
2
for
more
than
30
seconds
and
that
hot
air
inlet
is
open
If
diaphragm
spring
actuates
the
air
control
valve
by
its
spring
force
to
open
under
hood
air
inlet
within
30
seconds
replace
vacuum
motor
as
an
assembly
since
this
may
be
resulted
from
air
leak
at
vacuum
motor
dia
phragm
2
3
Temperature
ensor
Check
temperature
sensor
for
func
tion
by
proceeding
as
follows
Be
sure
to
keep
engine
cold
before
starting
test
I
With
engine
off
check
air
control
valve
for
condition
In
this
case
under
hood
air
inlet
is
open
Use
a
mirror
for
inspection
as
2
2
1
above
2
Start
engine
and
keep
idling
Immediately
after
engine
starting
check
air
control
valve
for
correct
position
as
described
above
In
this
case
correct
position
of
air
control
valve
is
the
reverse
of
2
2
I
under
hood
air
inlet
is
closed
and
hot
air
inlet
is
open
3
Check
that
air
control
valve
grad
ually
opens
to
under
hood
air
inlet
side
as
engine
warms
up
When
en
vironmental
temperature
around
tern
perature
sensor
is
low
spend
more
time
for
engine
warming
up
operation
Page 104 of 537
Engine
Fuel
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
Remove
air
cleaner
cover
2
Remove
hose
connecting
idle
compensator
and
3
way
connector
3
Loosen
screws
securing
idle
com
pensator
to
air
cleaner
then
remove
idle
compensator
Notes
a
When
removing
idle
compensator
remove
gasket
and
plate
b
When
removing
screw
securing
idle
compensator
to
air
cleaner
be
care
ful
not
to
miss
the
saew
4
To
install
reverse
the
removal
procedure
INSPECTION
I
Check
tha
t
valve
IS
m
closed
position
when
bi
metal
temperature
is
lower
than
operating
temperature
To
check
breathe
air
into
tube
or
suck
DESCRIPTION
The
fuel
fJlter
is
a
cartridge
type
It
uses
a
paper
element
which
can
be
checked
for
condition
from
the
out
side
EF718
Fig
EF
15
Location
of
idle
compenl
otor
air
If
excessive
air
leakage
is
found
at
the
valve
replace
idle
compensator
as
an
assembly
Note
that
two
idle
com
pensators
are
mounted
to
air
cleaner
and
that
it
is
necessary
to
plug
the
valve
of
one
of
these
idle
compensa
tors
so
as
to
prevent
air
leak
while
checking
the
other
one
@
CD
I
tl
1
Orifice
2
Rubber
valve
EF225
Fig
EF
16
Checking
idle
compelll
lor
FUEL
FILTER
1
Body
2
Paper
element
3
Cover
1
EFOO5
Fig
EF
18
Sectional
view
of
cartridge
type
fuel
filter
EF
8
Note
When
checking
idle
compensa
tor
on
vehicle
disconnect
hose
leading
to
idle
compensator
and
connect
other
hose
then
carry
out
check
as
descn
bed
above
2
When
bi
metal
temperature
is
above
the
specified
operating
tempera
ture
visually
check
to
see
if
the
valve
is
in
open
position
If
valve
is
not
open
replace
idle
compensator
as
an
assembly
Watcr
temperature
Observe
valve
11t
No
1
Bknctal
60
to
70De
140
to
1580F
NO
2
Bi
metal
70
to
900C
158to
1940F
EF226
Fig
EF
17
Checking
idle
compensator
3
Others
I
Check
hoses
for
correct
installa
tion
distortion
or
cracks
2
Check
rubber
valve
seat
of
idle
compensator
for
sticking
or
any
other
faulty
conditions
REMOVAL
Disconnect
inlet
and
outlet
fuel
lines
from
fuel
fJlter
and
remove
fuel
fJlter
Note
Before
disconnecting
fuel
lines
use
a
container
to
receive
the
fuel
remaining
in
lines
Page 107 of 537
3
Check
diaphragm
for
small
holes
carcks
or
wear
4
Check
rocker
arm
for
wear
at
the
mating
portion
with
camshaft
5
Check
rocker
arm
pin
for
wear
A
worn
pin
may
cause
oil
leakage
6
Check
all
other
components
for
any
abnormalities
and
replace
if
neces
sary
DESCRIPTION
INSPECTION
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
DESCRIPTION
The
electric
fuel
pump
is
adopted
on
air
conditioner
equipped
models
Engine
Fuel
ASSEMBLY
Reverse
the
order
of
disassembly
Closely
observe
the
following
instruc
tions
L
Use
new
gaskets
2
Lubricate
rocker
ann
rocker
arm
link
and
rocker
arm
pin
before
installa
tion
3
To
test
the
function
proceed
as
follows
Position
fuel
pump
assembly
about
I
meter
3
3
ft
above
fuel
level
of
fuel
strainer
and
connect
a
pipe
from
strainer
to
fuel
pump
Operate
rocker
arm
by
hand
If
fuel
is
drawn
up
soon
after
rocker
arm
is
released
fuel
pump
is
functioning
properly
ELECTRIC
FUEL
PUMP
CONTENTS
EF
11
EF
11
EF
12
DISASSEMBL
Y
ASSEMBL
Y
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
EF
12
EF
12
The
silicon
transistor
type
fuel
pump
consists
of
a
transistor
diodes
a
sole
I
Tr
lOsistor
6
Ou
tIet
valve
2
Plunger
7
Return
spring
3
Diaphragm
8
Filter
4
Diode
9
Magnet
5
Magnet
coil
10
Inlet
valve
INSPECTION
I
Disconnect
fuel
hose
at
pump
outlet
2
Connect
a
suitable
hose
approxi
mately
6
mm
0
24
in
inner
dia
meter
to
pump
outlet
ev
J
J
Note
If
diameter
is
too
small
the
following
proper
delivery
capacity
cannot
be
obtained
even
if
pump
functions
properly
EF
11
EF
13
noid
a
pump
mechanism
and
filter
parts
I
T
nsistor
2
Re
ist
f
I
3
Dinde
4
Signal
coil
5
Main
coil
6
Resistor
3
7
Zener
dlOdl
8
Resistor
2
EF719
Fig
EF
22
Construction
of
electric
fuel
pump
3
With
hose
outlet
in
a
higher
posi
tion
than
pump
operate
pump
and
check
delivery
capacity
for
more
than
15
seconds
4
The
capacity
should
be
I
400
cc