lock INFINITI M35 2006 Factory Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: INFINITI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: M35, Model: INFINITI M35 2006Pages: 5621, PDF Size: 65.56 MB
Page 941 of 5621

BL-2Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45 CHANGE SETTINGS FUNCTION ....................... 60
INTELLIGENT KEY REGISTRATION .................. 60
STEERING LOCK UNIT REGISTRATION .......... 60
CAN Communication System Description .............. 60
CAN Communication Unit ....................................... 60
Schematic ............................................................... 61
Wiring Diagram — I/KEY— .................................... 63
Terminals and Reference Value for Intelligent Key
Unit ......................................................................... 74
Terminals and Reference Value for BCM ................ 77
Terminals and Reference Value for IPDM E/R ........ 77
Trouble Diagnosis Procedure ................................. 78
WORK FLOW ...................................................... 78
CONSULT-II Functions (INTELLIGENT KEY) ........ 80
CONSULT-II Inspection Procedure ......................... 80
BASIC OPERATION ............................................ 80
CONSULT-II Application Items ............................... 81
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC RESULTS ........................... 81
DATA MONITOR .................................................. 82
WORK SUPPORT ............................................... 83
ACTIVE TEST ..................................................... 84
Trouble Diagnosis Symptom Chart ......................... 86
ALL FUNCTIONS OF INTELLIGENT KEY SYS-
TEM DOES NOT OPERATE ............................... 86
DOOR LOCK/UNLOCK FUNCTION MALFUNC-
TION .................................................................... 86
REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY FUNCTION MAL-
FUNCTION .......................................................... 87
TRUNK OPEN FUNCTION MALFUNCTION ...... 88
HAZARD AND BUZZER REMINDER FUNC-
TION MALFUNCTION ......................................... 89
HAZARD AND HORN REMINDER FUNCTION
MALFUNCTION ................................................... 89
POWER WINDOW DOWN FUNCTION MAL-
FUNCTION .......................................................... 90
WARNING FUNCTION MALFUNCTION ............. 90
Check CAN Communication System ...................... 92
Check Power Supply and Ground Circuit ............... 93
Check Key Slot ....................................................... 94
Check Door Switch ..............................................
... 96
Check Trunk Room Lamp Switch ........................... 99
Check Door Request Switch .................................101
Check Trunk Opener Request Switch ..................103
Check Unlock Sensor ...........................................105
Check Intelligent Key Warning Buzzer .................107
Check Outside Key Antenna (Driver Side and Pas-
senger Side) .........................................................108
Check Outside Key Antenna (Trunk Room) .........110
Check Inside Key Antenna ...................................112
Check Park Position Switch ..................................115
Check Ignition Switch Position .............................117
Check Remote Keyless Entry Receiver ................117
Check Trunk Lid Opener Cancel Switch ...............121
Check Key Slot Illumination ..................................123
Check Horn Function ............................................124
Check Combination Meter Display Function .........124
Check Warning Chime Function ...........................125
Removal and Installation of Intelligent Key Unit ...125
REMOVAL ........................................................
.125INSTALLATION ..................................................125
Intelligent Key Battery Replacement .....................126
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY OF INTELLI-
GENT KEY .........................................................126
INTELLIGENT KEY BATTERY INSPECTION ...126
INTELLIGENT KEY SYSTEM/ENGINE START
FUNCTION ..............................................................127
Component Parts and Harness Connector Location .127
System Description ...............................................128
PRECAUTIONS FOR INTELLIGENT KEY SYS-
TEM ...................................................................129
Operation Description ...........................................129
SYSTEM DIAGRAM ..........................................129
OPERATION WHEN INTELLIGENT KEY IS
CARRIED ...........................................................129
OPERATION WHEN KEY SLOT IS USED ........130
PUSH-BUTTON IGNITION SWITCH OPERA-
TION PROCEDURE ..........................................130
CAN Communication System Description ............131
CAN Communication Unit .....................................131
Schematic .............................................................132
Wiring Diagram —ENG/ST— ................................134
Terminals and Reference Value for Intelligent Key
Unit ........................................................................143
Terminals and Reference Value for Steering Lock
Unit ........................................................................146
Terminals and Reference Value for BCM ..............147
Terminals and Reference Value for IPDM E/R ......147
Terminals and Reference Value for PDU ..............148
Work Flow .............................................................149
CONSULT-II Functions (INTELLIGENT KEY) .......151
CONSULT-II Inspection Procedure .......................151
BASIC OPERATION ..........................................151
CONSULT-II Application Items ..............................152
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC RESULTS .........................152
DATA MONITOR ................................................153
WORK SUPPORT .............................................154
ACTIVE TEST ....................................................155
DTC B2013 STRG COMM 1 .................................157
DIAGNOSIS DESCRIPTION .............................157
TERMINALS AND REFERENCE VALUE FOR
INTELLIGENT KEY UNIT ..................................157
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC LOGIC ..............................157
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE .............................157
DTC B2551 STEERING LOCK UNIT ....................159
DIAGNOSIS DESCRIPTION .............................159
TERMINALS AND REFERENCE VALUE ..........159
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC LOGIC .............................
.160
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE .............................160
DTC B2552 INTELLIGENT KEY ...........................163
DIAGNOSIS DESCRIPTION .............................163
DTC B2553 IGN POWER CIRCUIT ......................163
DIAGNOSIS DESCRIPTION .............................163
TERMINAL AND REFERENCE VALUE FOR
INTELLIGENT KEY UNIT ..................................163
CONSULT-II DATA MONITOR STANDARD
VALUE ...............................................................163
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC LOGIC ..............................164
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE .............................164
Page 942 of 5621

BL-3
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
BL
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45 DTC B2554 ACC POWER CIRCUIT ....................164
DIAGNOSIS DESCRIPTION .............................164
TERMINALS AND REFERENCE VALUE FOR
INTELLIGENT KEY UNIT .................................165
CONSULT-II DATA MONITOR STANDARD
VALUE ...............................................................165
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC LOGIC .............................165
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE ............................166
DTC B2555 STOP LAMP CIRCUIT .....................167
DIAGNOSIS DESCRIPTION .............................167
TERMINALS AND REFERENCE VALUE FOR
INTELLIGENT KEY UNIT INPUT ......................167
CONSULT-II DATA MONITOR STANDARD
VALUE ...............................................................167
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC LOGIC .............................167
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE ............................168
DTC B2556 ENG START SW ..............................168
DIAGNOSIS DESCRIPTION .............................168
TERMINALS AND REFERENCE VALUE FOR
INTELLIGENT KEY UNIT .................................168
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC LOGIC .............................168
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE ............................169
DTC B2557 VEHICLE SPEED .............................169
DIAGNOSIS DESCRIPTION .............................169
TERMINALS AND REFERENCE VALUE FOR
INTELLIGENT KEY UNIT .................................170
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC LOGIC .............................170
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE ............................170
DTC B2558 SHIFT POSITION .............................172
DIAGNOSIS DESCRIPTION .............................172
TERMINALS AND REFERENCE VALUE FOR
INTELLIGENT KEY UNIT .................................172
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC LOGIC .............................172
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE ............................172
DTC B2559 PDU ..................................................174
DIAGNOSIS DESCRIPTION .............................174
DTC B2560 START POW SUP CIRC ..................174
DIAGNOSIS DESCRIPTION .............................174
TERMINALS AND REFERENCE VALUE .........175
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC LOGIC .............................175
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE ............................175
DTC B2562 LOW VOLTAGE ................................177
DIAGNOSIS DESCRIPTION .............................177
TERMINALS AND REFERENCE VALUE FOR
INTELLIGENT KEY UNIT .................................177
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC LOGIC .............................177
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE ............................177
DTC B2563 HI VOLTAGE ....................................178
DIAGNOSIS DESCRIPTION .............................178
TERMINAL AND REFERENCE VALUE FOR
INTELLIGENT KEY UNIT .................................178
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC LOGIC .............................178
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE ............................179
Trouble Diagnosis Symptom Chart 1 ...................179
CONDITIONS OF VEHICLE (OPERATING CON-
DITIONS) ..........................................................179
Trouble Diagnosis Symptom Chart 2 ...................180
CONDITIONS OF VEHICLE (OPERATING CON-
DITIONS) ..........................................................180Trouble Diagnosis Symptom Chart 3 ....................180
CONDITIONS OF VEHICLE (OPERATING CON-
DITIONS) ...........................................................180
Check CAN Communication System ....................181
Check Push-Button Ignition Switch ......................181
Check Inside Key Antenna ...................................183
Check Remote Keyless Entry Receiver ................185
Check Key Switch Built In Key Slot ......................186
Check NATS Antenna Amp. Built In Key Slot .......188
DOOR ......................................................................190
Fitting Adjustment .................................................190
FRONT DOOR ..................................................190
REAR DOOR .....................................................190
STRIKER ADJUSTMENT ..................................191
Removal and Installation of Front Door ................191
REMOVAL ........................................................
.191
INSTALLATION .................................................192
Removal and Installation of Rear Door .................192
REMOVAL ........................................................
.192
INSTALLATION .................................................193
Door Weatherstrip ................................................194
FRONT DOOR ..................................................194
REMOVAL ........................................................
.194
INSTALLATION .................................................194
REAR DOOR .....................................................195
REMOVAL ........................................................
.195
INSTALLATION .................................................195
FRONT DOOR LOCK .............................................196
Component Structure ............................................196
Removal and Installation ......................................196
REMOVAL ........................................................
.196
INSTALLATION .................................................199
REAR DOOR LOCK ...............................................200
Component Structure ............................................200
Removal and Installation ......................................200
REMOVAL ........................................................
.200
INSTALLATION .................................................202
TRUNK LID .............................................................203
Fitting Adjustment .................................................203
Removal and Installation of Trunk Lid Assembly ..204
REMOVAL ........................................................
.204
INSTALLATION .................................................205
Removal and Installation of Trunk Lid Stay ..........205
REMOVAL ........................................................
.205
INSTALLATION .................................................205
Removal and Installation of Trunk Lid Lock ..........206
REMOVAL .......................................................
. .206
INSTALLATION .................................................206
Removal and Installation of Trunk Lid Striker .......207
REMOVAL ........................................................
.207
INSTALLATION .................................................207
Removal and Installation of Trunk Lid Weatherstrip .208
REMOVAL ........................................................
.208
INSTALLATION .................................................208
TRUNK LID OPENER .............................................209
Component Parts and Harness Connector Location .209
System Description ...............................................210
TRUNK LID OPENER OPERATION .................210
Wiring Diagram —TLID— .....................................211
Page 943 of 5621

BL-4Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45 Terminals and Reference Value for BCM ..............213
CONSULT-II Function (BCM) ................................214
CONSULT-II INSPECTION PROCEDURE ........214
DATA MONITOR ................................................215
ACTIVE TEST ...................................................215
Trouble Diagnosis .................................................216
TRUNK DOSE NOT OPEN WITH TRUNK LID
OPENER SWITCH / WITH INTELLIGENT KEY .216
VEHICLE SECURITY (THEFT WARNING) SYSTEM .220
Component Parts and Harness Connector Location .220
System Description ...............................................222
DESCRIPTION ..................................................222
POWER SUPPLY AND GROUND CIRCUIT .....223
INITIAL CONDITION TO ACTIVATE THE SYS-
TEM ...................................................................223
VEHICLE SECURITY SYSTEM ALARM OPER-
ATION ................................................................224
VEHICLE SECURITY SYSTEM DEACTIVATION .224
PANIC ALARM OPERATION .............................224
CAN Communication System Description ............224
CAN Communication Unit .....................................224
Schematic .............................................................225
Wiring Diagram —VEHSEC— ..............................226
Terminals and Reference Value of BCM ...............232
Terminals and Reference Value of IPDM E/R .......232
CONSULT-II Function (BCM) ................................233
CONSULT-II APPLICATION ITEM .....................234
Trouble Diagnosis Work Flow ...............................235
Preliminary Check ................................................235
Trouble Diagnosis Symptom Chart .......................237
Diagnostic Procedure 1 ........................................238
DOOR SWITCH CHECK ...................................238
HOOD SWITCH CHECK ...................................241
TRUNK ROOM LAMP SWITCH CHECK ..........243
Diagnostic Procedure 2 ........................................245
SECURITY INDICATOR LAMP CHECK ............245
Diagnostic Procedure 3 ........................................246
FRONT DOOR KEY CYLINDER SWITCH
CHECK ..............................................................246
Diagnostic Procedure 4 ........................................246
VEHICLE SECURITY HORN ALARM CHECK . 246
Diagnostic Procedure 5 ........................................247
VEHICLE SECURITY HEADLAMP ALARM
CHECK ..............................................................247
Diagnostic Procedure 6 ........................................247
DOOR LOCK AND UNLOCK SWITCH CHECK .247
Diagnostic Procedure 7 ........................................247
VEHCLE SECURITY HAZARD LAMP ALARM
CHECK ..............................................................247
IVIS (INFINITI VEHICLE IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM-
NATS) ......................................................................248
Component Parts and Harness Connector Location .248
System Description ...............................................250
DESCRIPTION ..................................................250
PRECAUTIONS FOR KEY REGISTRATION ....250
SECURITY INDICATOR ....................................250
Operation Description ...........................................251
SYSTEM DIAGRAM ..........................................251
OPERATION WHEN INSERTING TO KEY SLOT .251OPERATION WHEN INTELLIGENT KEY IS
CARRIED ...........................................................251
PUSH-BUTTON IGNITION SWITCH OPERA-
TION PROCEDURE ..........................................251
ECM Re-Communicating Function .......................252
Schematic .............................................................254
Wiring Diagram — NATS — ..................................256
Terminals and Reference Value for Intelligent Key
Unit ........................................................................264
Terminals and Reference Value for Steering Lock
Unit ........................................................................266
Terminals and Reference Value for BCM ..............266
Terminals and Reference Value for IPDM E/R ......267
Terminals and Reference Value for PDU ..............267
CONSULT-II ..........................................................268
CONSULT-II INSPECTION PROCEDURE ........268
CONSULT-II DIAGNOSTIC TEST MODE FUNC-
TION ..................................................................270
HOW TO READ SELF-DIAGNOSTIC RESULTS .270
“NATS V5.0” SELF-DIAGNOSTIC RESULTS
ITEM CHART .....................................................271
“NATS BCM OR S/ENT” SELF-DIAGNOSTIC
RESULTS ITEM CHART ....................................271
“NATS I-KEY” SELF-DIAGNOSTIC RESULTS
ITEM CHART .....................................................272
Work Flow .............................................................272
Trouble Diagnoses Flow Chart for IVIS (NATS) ....275
Symptom Chart for Security Indicator ...................277
CONDITIONS OF VEHICLE (OPERATING CON-
DITIONS) ...........................................................277
Check Security Indicator Harness .........................277
DTC P1612 CHAIN of ECM-IMMU .......................278
DTC P1611 ID DISCORD, IMM-ECM ...................280
Removal and Installation of Key Slot ....................280
REMOVAL ..........................................................280
INSTALLATION ..................................................280
INTEGRATED HOMELINK TRANSMITTER ...........281
Wiring Diagram —TRNSCV— ..............................281
Trouble Diagnoses ................................................282
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE .............................282
BODY REPAIR ........................................................284
Body Exterior Paint Color ......................................284
Body Component Parts .........................................285
UNDERBODY COMPONENT PARTS ...............285
BODY COMPONENT PARTS ............................287
Corrosion Protection ..........................................
...289
DESCRIPTION ..................................................289
UNDERCOATING ..............................................290
Body Sealing .........................................................291
DESCRIPTION ..................................................291
Body Construction .................................................294
BODY CONSTRUCTION ...................................294
Body Alignment .....................................................295
BODY CENTER MARKS ...................................295
PANEL PARTS MATCHING MARKS .................296
DESCRIPTION ..................................................297
ENGINE COMPARTMENT ................................298
UNDERBODY ....................................................300
PASSENGER COMPARTMENT ........................302
Page 945 of 5621

BL-6
PRECAUTIONS
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
PRECAUTIONSPFP:00001
Precautions for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) “AIR BAG” and “SEAT
BELT PRE-TENSIONER”
NIS001WA
The Supplemental Restraint System such as “AIR BAG” and “SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER”, used along
with a front seat belt, helps to reduce the risk or severity of injury to the driver and front passenger for certain
types of collision. This system includes seat belt switch inputs and dual stage front air bag modules. The SRS
system uses the seat belt switches to determine the front air bag deployment, and may only deploy one front
air bag, depending on the severity of a collision and whether the front occupants are belted or unbelted.
Information necessary to service the system safely is included in the SRS and SB section of this Service Man-
ual.
WAR NING :
To avoid rendering the SRS inoperative, which could increase the risk of personal injury or death
in the event of a collision which would result in air bag inflation, all maintenance must be per-
formed by an authorized NISSAN/INFINITI dealer.
Improper maintenance, including incorrect removal and installation of the SRS, can lead to per-
sonal injury caused by unintentional activation of the system. For removal of Spiral Cable and Air
Bag Module, see the SRS section.
Do not use electrical test equipment on any circuit related to the SRS unless instructed to in this
Service Manual. SRS wiring harnesses can be identified by yellow and/or orange harnesses or
harness connectors.
Precautions for Procedures without Cowl Top CoverNIS001WB
When performing the procedure after removing cowl top cover, cover
the lower end of windshield with urethane, etc.
Precautions Necessary for Steering Wheel Rotation after Battery DisconnectNIS001WC
NOTE:
Before removing and installing any control units, first turn the push-button ignition switch to the LOCK
position, then disconnect both battery cables.
After finishing work, confirm that all control unit connectors are connected properly, then re-connect both
battery cables.
Always use CONSULT-II to perform self-diagnosis as a part of each function inspection after finishing
work. If a DTC is detected, perform trouble diagnosis according to self-diagnosis results.
This vehicle is equipped with a push-button ignition switch and a steering lock unit.
If the battery is disconnected or discharged, the steering wheel will lock and cannot be turned.
If turning the steering wheel is required with the battery disconnected or discharged, follow the procedure
below before starting the repair operation.
OPERATION PROCEDURE
1. Connect both battery cables.
NOTE:
Supply power using jumper cables if battery is discharged.
2. Carry the Intelligent Key or insert it to the key slot and turn the push-button ignition switch to ACC position.
(At this time, the steering lock will be released.)
3. Disconnect both battery cables. The steering lock will remain released with both battery cables discon-
nected and the steering wheel can be turned.
4. Perform the necessary repair operation.
PIIB3706J
Page 946 of 5621

PRECAUTIONS
BL-7
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
BL
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
5. When the repair work is completed, re-connect both battery cables. With the brake pedal released, turn
the push-button ignition switch from ACC position to ON position, then to LOCK position. (The steering
wheel will lock when the push-button ignition switch is turned to LOCK position.)
6. Perform self-diagnosis check of all control units using CONSULT-II.
Precautions for WorkNIS001WD
After removing and installing the opening/closing parts, be sure to carry out fitting adjustments to check
their operational.
Check the lubrication level, damage, and wear of each part. If necessary, grease or replace it.
Page 948 of 5621

SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
BL-9
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
BL
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSISPFP:00000
Work FlowNIS001WG
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs.Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to BL-13, "
Diagnostic Worksheet" . This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to
obtain all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer
is concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard sur-
faces=higher pitch noise/softer surfaces=lower pitch noises/edge to surface=chirping
Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch
dependent on materials/often brought on by activity.
Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
Knock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
Tick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
Buzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may
judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
SBT842
Page 949 of 5621

BL-10
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
If possible, drive the vehicle with the customer until the noise is duplicated. Note any additional information on
the Diagnostic Worksheet regarding the conditions or location of the noise. This information can be used to
duplicate the same conditions when you confirm the repair.
If the noise can be duplicated easily during the test drive, to help identify the source of the noise, try to dupli-
cate the noise with the vehicle stopped by doing one or all of the following:
1) Close a door.
2) Tap or push/pull around the area where the noise appears to be coming from.
3) Rev the engine.
4) Use a floor jack to recreate vehicle “twist”.
5) At idle, apply engine load (electrical load, half-clutch on M/T model, drive position on A/T model).
6) Raise the vehicle on a hoist and hit a tire with a rubber hammer.
Drive the vehicle and attempt to duplicate the conditions the customer states exist when the noise occurs.
If it is difficult to duplicate the noise, drive the vehicle slowly on an undulating or rough road to stress the
vehicle body.
CHECK RELATED SERVICE BULLETINS
After verifying the customer concern or symptom, check ASIST for Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) related
to that concern or symptom.
If a TSB relates to the symptom, follow the procedure to repair the noise.
LOCATE THE NOISE AND IDENTIFY THE ROOT CAUSE
1. Narrow down the noise to a general area. To help pinpoint the source of the noise, use a listening tool
(Chassis Ear: J-39570, Engine Ear and mechanics stethoscope).
2. Narrow down the noise to a more specific area and identify the cause of the noise by:
removing the components in the area that you suspect the noise is coming from.
Do not use too much force when removing clips and fasteners, otherwise clips and fastener can be broken
or lost during the repair, resulting in the creation of new noise.
tapping or pushing/pulling the component that you suspect is causing the noise.
Do not tap or push/pull the component with excessive force, otherwise the noise will be eliminated only
temporarily.
feeling for a vibration with your hand by touching the component(s) that you suspect is (are) causing the
noise.
placing a piece of paper between components that you suspect are causing the noise.
looking for loose components and contact marks.
Refer to BL-11, "
Generic Squeak and Rattle Troubleshooting" .
REPAIR THE CAUSE
If the cause is a loose component, tighten the component securely.
If the cause is insufficient clearance between components:
–separate components by repositioning or loosening and retightening the component, if possible.
–insulate components with a suitable insulator such as urethane pads, foam blocks, felt cloth tape or ure-
thane tape. A Nissan Squeak and Rattle Kit (J-43980) is available through your authorized Nissan Parts
Department.
CAUTION:
Do not use excessive force as many components are constructed of plastic and may be damaged.
NOTE:
Always check with the Parts Department for the latest parts information.
The following materials are contained in the Nissan Squeak and Rattle Kit (J-43980). Each item can be
ordered separately as needed.
URETHANE PADS [1.5 mm (0.059 in) thick]
Insulates connectors, harness, etc.
76268-9E005: 100
135 mm (3.945.31 in)/76884-71L01: 6085 mm (2.363.35 in)/76884-
71L02: 15
25 mm (0.590.98 in)
INSULATOR (Foam blocks)
Insulates components from contact. Can be used to fill space behind a panel.
73982-9E000: 45 mm (1.77 in) thick, 50
50 mm (1.971.97 in)/73982-
50Y00: 10 mm (0.39 in) thick, 50
50 mm (1.971.97 in)
Page 950 of 5621

SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
BL-11
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
BL
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
INSULATOR (Light foam block)
80845-71L00: 30 mm (1.18 in) thick, 30
50 mm (1.181.97 in)
FELT CLOTHTAPE
Used to insulate where movement does not occur. Ideal for instrument panel applications.
68370-4B000: 15
25 mm (0.590.98 in) pad/68239-13E00: 5 mm (0.20 in) wide tape roll
The following materials, not found in the kit, can also be used to repair squeaks and rattles.
UHMW (TEFLON) TAPE
Insulates where slight movement is present. Ideal for instrument panel applications.
SILICONE GREASE
Used in place of UHMW tape that will be visible or not fit. Will only last a few months.
SILICONE SPRAY
Use when grease cannot be applied.
DUCT TAPE
Use to eliminate movement.
CONFIRM THE REPAIR
Confirm that the cause of a noise is repaired by test driving the vehicle. Operate the vehicle under the same
conditions as when the noise originally occurred. Refer to the notes on the Diagnostic Worksheet.
Generic Squeak and Rattle TroubleshootingNIS001WH
Refer to Table of Contents for specific component removal and installation information.
INSTRUMENT PANEL
Most incidents are caused by contact and movement between:
1. The cluster lid A and instrument panel
2. Acrylic lens and combination meter housing
3. Instrument panel to front pillar garnish
4. Instrument panel to windshield
5. Instrument panel mounting pins
6. Wiring harnesses behind the combination meter
7. A/C defroster duct and duct joint
These incidents can usually be located by tapping or moving the components to duplicate the noise or by
pressing on the components while driving to stop the noise. Most of these incidents can be repaired by apply-
ing felt cloth tape or silicon spray (in hard to reach areas). Urethane pads can be used to insulate wiring har-
ness.
CAUTION:
Do not use silicone spray to isolate a squeak or rattle. If you saturate the area with silicone, you will
not be able to recheck the repair.
CENTER CONSOLE
Components to pay attention to include:
1. Shifter assembly cover to finisher
2. A/C control unit and cluster lid C
3. Wiring harnesses behind audio and A/C control unit
The instrument panel repair and isolation procedures also apply to the center console.
DOORS
Pay attention to the:
1. Finisher and inner panel making a slapping noise
2. Inside handle escutcheon to door finisher
3. Wiring harnesses tapping
4. Door striker out of alignment causing a popping noise on starts and stops
Tapping or moving the components or pressing on them while driving to duplicate the conditions can isolate
many of these incidents. You can usually insulate the areas with felt cloth tape or insulator foam blocks from
the Nissan Squeak and Rattle Kit (J-43980) to repair the noise.
Page 951 of 5621

BL-12
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
TRUNK
Trunk noises are often caused by a loose jack or loose items put into the trunk by the owner.
In addition look for:
1. Trunk lid dumpers out of adjustment
2. Trunk lid striker out of adjustment
3. The trunk lid torsion bars knocking together
4. A loose license plate or bracket
Most of these incidents can be repaired by adjusting, securing or insulating the item(s) or component(s) caus-
ing the noise.
SUNROOF/HEADLINING
Noises in the sunroof/headlining area can often be traced to one of the following:
1. Sunroof lid, rail, linkage or seals making a rattle or light knocking noise
2. Sunvisor shaft shaking in the holder
3. Front or rear windshield touching headlining and squeaking
Again, pressing on the components to stop the noise while duplicating the conditions can isolate most of these
incidents. Repairs usually consist of insulating with felt cloth tape.
SEATS
When isolating seat noise it's important to note the position the seat is in and the load placed on the seat when
the noise is present. These conditions should be duplicated when verifying and isolating the cause of the
noise.
Cause of seat noise include:
1. Headrest rods and holder
2. A squeak between the seat pad cushion and frame
3. The rear seatback lock and bracket
These noises can be isolated by moving or pressing on the suspected components while duplicating the con-
ditions under which the noise occurs. Most of these incidents can be repaired by repositioning the component
or applying urethane tape to the contact area.
UNDERHOOD
Some interior noise may be caused by components under the hood or on the engine wall. The noise is then
transmitted into the passenger compartment.
Causes of transmitted underhood noise include:
1. Any component mounted to the engine wall
2. Components that pass through the engine wall
3. Engine wall mounts and connectors
4. Loose radiator mounting pins
5. Hood bumpers out of adjustment
6. Hood striker out of adjustment
These noises can be difficult to isolate since they cannot be reached from the interior of the vehicle. The best
method is to secure, move or insulate one component at a time and test drive the vehicle. Also, engine RPM
or load can be changed to isolate the noise. Repairs can usually be made by moving, adjusting, securing, or
insulating the component causing the noise.
Page 955 of 5621
BL-16
HOOD
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
1. Check the clearance and the surface height between the hood and each part by visual and tactile feeling.
(Fitting standard dimension in the table below should be satisfied.)
* Unit: mm (in)
2. In case out of specification, adjust them according to the procedures shown below.
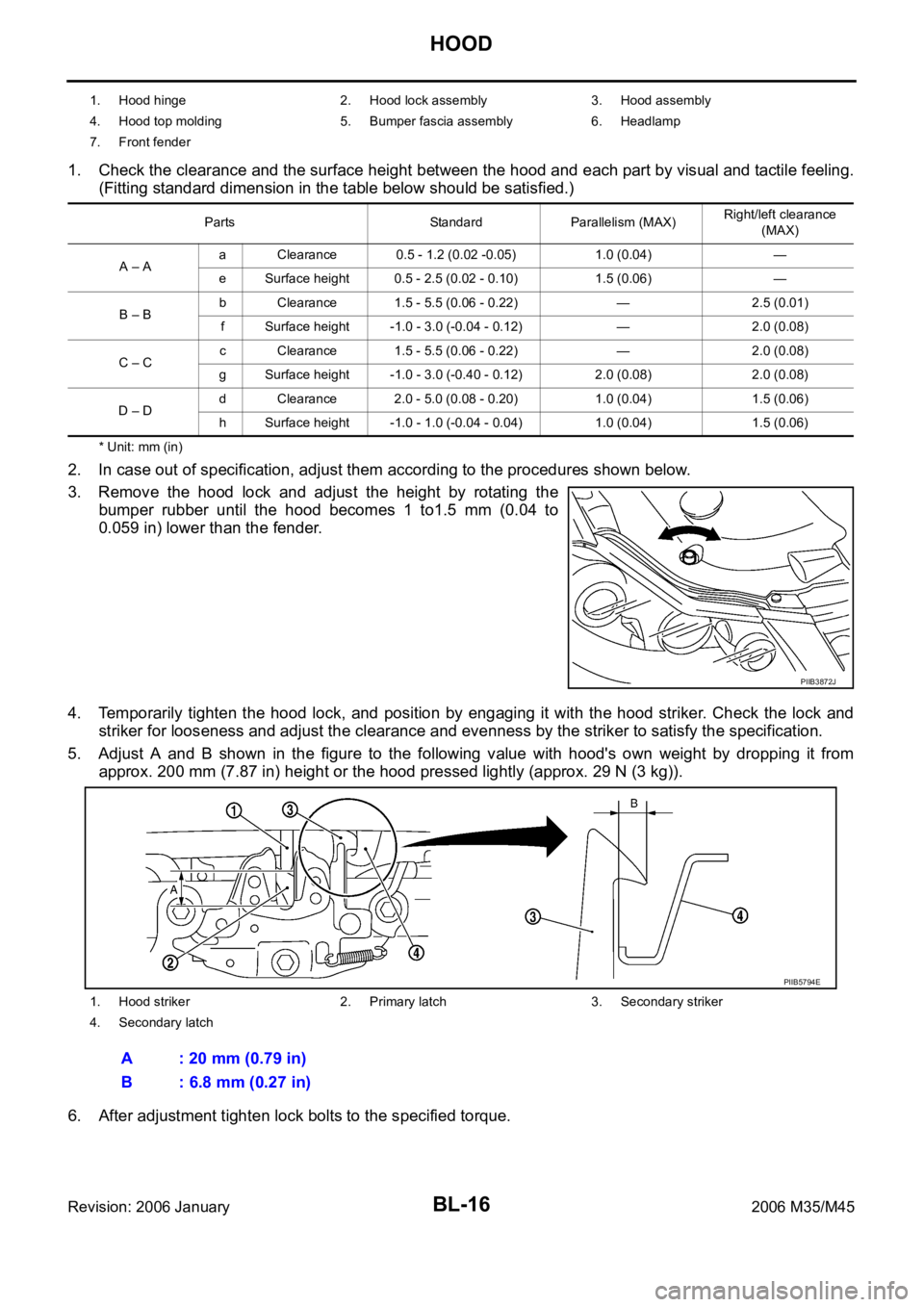
3. Remove the hood lock and adjust the height by rotating the
bumper rubber until the hood becomes 1 to1.5 mm (0.04 to
0.059 in) lower than the fender.
4. Temporarily tighten the hood lock, and position by engaging it with the hood striker. Check the lock and
striker for looseness and adjust the clearance and evenness by the striker to satisfy the specification.
5. Adjust A and B shown in the figure to the following value with hood's own weight by dropping it from
approx. 200 mm (7.87 in) height or the hood pressed lightly (approx. 29 N (3 kg)).
6. After adjustment tighten lock bolts to the specified torque.
1. Hood hinge 2. Hood lock assembly 3. Hood assembly
4. Hood top molding 5. Bumper fascia assembly 6. Headlamp
7. Front fender
Parts Standard Parallelism (MAX)Right/left clearance
(MAX)
A – Aa Clearance 0.5 - 1.2 (0.02 -0.05) 1.0 (0.04) —
e Surface height 0.5 - 2.5 (0.02 - 0.10) 1.5 (0.06) —
B – Bb Clearance 1.5 - 5.5 (0.06 - 0.22) — 2.5 (0.01)
f Surface height -1.0 - 3.0 (-0.04 - 0.12) — 2.0 (0.08)
C – Cc Clearance 1.5 - 5.5 (0.06 - 0.22) — 2.0 (0.08)
g Surface height -1.0 - 3.0 (-0.40 - 0.12) 2.0 (0.08) 2.0 (0.08)
D – Dd Clearance 2.0 - 5.0 (0.08 - 0.20) 1.0 (0.04) 1.5 (0.06)
h Surface height -1.0 - 1.0 (-0.04 - 0.04) 1.0 (0.04) 1.5 (0.06)
PIIB3872J
1. Hood striker 2. Primary latch 3. Secondary striker
4. Secondary latch
A : 20 mm (0.79 in)
B : 6.8 mm (0.27 in)
PIIB5794E