relay ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 2276 of 6020

6E–106 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
10 Repair the open circuit between the fuel pump relayand battery.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
11 Using the DVM and check the fuel pump power supply circuit.
1. Ignition “On”, engine “Off”.
2. Disconnect the fuel pump connector.
3. Check the circuit for open or short to ground circuit.
Was the DVM indicated specified value?
10 - 14.5V Go to Step 13Go to Step 12
12 Repair the open or short to ground circuit between the fuel pump relay and fuel pump.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
13 Using the DVM and check the fuel pump ground circuit.
1. Ignition “Off”, engine “Off”.
2. Disconnect the fuel pump connector.
3. Check the circuit for open circuit.
Was the DVM indicated specified value?
Continuity Go to Step 15Go to Step 14
14 Repair the open circuit between the fuel pump and body ground.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
15 Replace the fuel pump. Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 16
16 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 17
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
V
1
F2
F-2
Ω
4
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2279 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–109
• The fuel injector(s).
4. Fuel pressure that drops off during acceleration, cruise, or hard cornering may case a lean condition.
A lean condition can cause a loss of power, surging,
or misfire. A lean condition can be diagnosed using a
Tech 2 Scan Tool.
Following are applicable to the vehicle with
closed Loop System:
If an extremely lean condition occurs, the oxygen
sensor(s) will stop toggling. The oxygen sensor
output voltage(s) will drop below 500 mV. Also, the
fuel injector pulse width will increase.
Important: Make sure the fuel system is not
operating in the “Fuel Cut-Off Mode.”
When the engine is at idle, the manifold pressure is
low (high vacuum). This low pressure (high vacuum)
is applied to the fuel pressure regulator diaphragm.
The low pressure (high vacuum) will offset the
pressure being applied to the fuel pressure regulator
diaphragm by the spring inside the fuel pressure
regulator. When this happens, the result is lower fuel
pressure. The fuel pressure at idle will vary slightly
as the barometric pressure changes, but the fuel
pressure at idle should always be less than the fuel
pressure noted in step 2 with the engine OFF.
16.Check the spark plug associated with a particular
fuel injector for fouling or saturation in order to
determine if that particular fuel injector is leaking. If
checking the spark plug associated with a particular
fuel injector for fouling or saturation does not
determine that a particular fuel injector is leaking,
use the following procedure:
• Remove the fuel rail, but leave the fuel lines and injectors connected to the fuel rail. Refer to Fuel
Rail Assembly in On-Vehicle Service .
• Lift the fuel rail just enough to leave the fuel injector nozzles in the fuel injector ports.
Caution: In order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury that may result from fuel
spraying on the engine, verify that the fuel rail is
positioned over the fuel injector ports and verify
that the fuel injector retaining clips are intact.
• Pressurize the fuel system by connecting a 20 amp fused jumper between B+ and the fuel
pump relay connector.
• Visually and physically inspect the fuel injector nozzles for leaks.
17.A rich condition may result from the fuel pressure being above 376 kPa (55 psi). A rich condition may
cause a 45 to set. Driveability conditions associated with rich conditions can include hard starting
(followed by black smoke) and a strong sulfur smell
in the exhaust.
20.This test determines if the high fuel pressure is due to a restricted fuel return line or if the high fuel
pressure is due to a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
21.A lean condition may result from fuel pressure below 333 kPa (48 psi). A lean condition may cause a 44 to
set. Driveability conditions associated with lean
conditions can include hard starting (when the
engine is cold), hesitation, poor driveability, lack of
power, surging, and misfiring.
22.Restricting the fuel return line causes the fuel pressure to rise above the regulated fuel pressure.
Command the fuel pump ON with the scan tool. The
fuel pressure should rise above 376 kPa (55 psi) as
the fuel return line becomes partially closed.
NOTE: Do not allow the fuel pressure to exceed 414
kPa (60 psi). Fuel pressure in excess of 414 kPa (60
psi) may damage the fuel pressure regulator. Caution: To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury:
• It is necessary to relieve fuel system pressure before connecting a fuel pressure gauge.
Refer to Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure,
below.
• A small amount of fuel may be released when disconnecting the fuel lines. Cover fuel line
fittings with a shop towel before
disconnecting, to catch any fuel that may leak
out. Place the towel in an approved container
when the disconnect is completed.
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
1. Remove the fuel cap.
2. Located on the intake manifold which is at the top right part of the engine.
3. Start the engine and allow it to stall.
4. Crank the engine for an additional 3 seconds.
Fuel Pressure Gauge Installation
1. Remove the fuel pressure fitting cap.
2. Install fuel pressure gauge 5-8840-0378-0 to the fuel feed line located on the upper right side of the
engine.
3. Reinstall the fuel pump relay.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2440 of 6020

6E–270 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
FUEL PRESSURE RELIEF
Caution: To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system
pressure before servicing the fuel system
components.
Caution: After relieving the fuel system pressure, a
small amount of fuel may be released when
servicing fuel lines or connections. Reduce the
chance of personal injury by covering the fuel line
fitting with a short towel before disconnecting the
fittings. The towel will absorb any fuel that may leak
out. When the disconnect is completed, place the
towel in an approved container.
1. Remove the fuel filler cap.
2. Remove the fuel pump relay from the underhood relay box.
3. Start the engine and allow it to stall.
4. Crank the engine for about 30 seconds.
5. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY
Removal Procedure
NOTE:
• Use care when removing the fuel rail assembly in order to prevent damage to the injector al connector
terminal and the injector spray tips.
• Fitting should be capped and holes plugged during servicing to prevent dirt and other contaminants from
entering open lines and passage.
Important: An eight-digit identification number is
stamped on side of the fuel injector. Refer to this
number when you service the fuel rail or when a
replacement part is required.
1. Disconnect 4 injector connectors.
2. Lift side-clip up on the fuel rail.
3. Disconnect fuel pressure regulator hose.
4. Disconnect wiring harness from the bands on the fuel rail.
5. Remove the intake pipe.
6. Loosen flare nut.
A. Lift up the injectors carefully to separate them from intake manifold.
B. Lift up the fuel rail with injectors as assembly. Do not separate the fuel injectors from fuel rail.
C. If an injector become separated from fuel rail, injector backup O-ring and injector retainer clip
must be replaced.
D. Drain residual fuel from fuel rail into an approved container.
7. If removal of fuel pressure regulator is necessary, Refer to Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal
Procedure .
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2443 of 6020
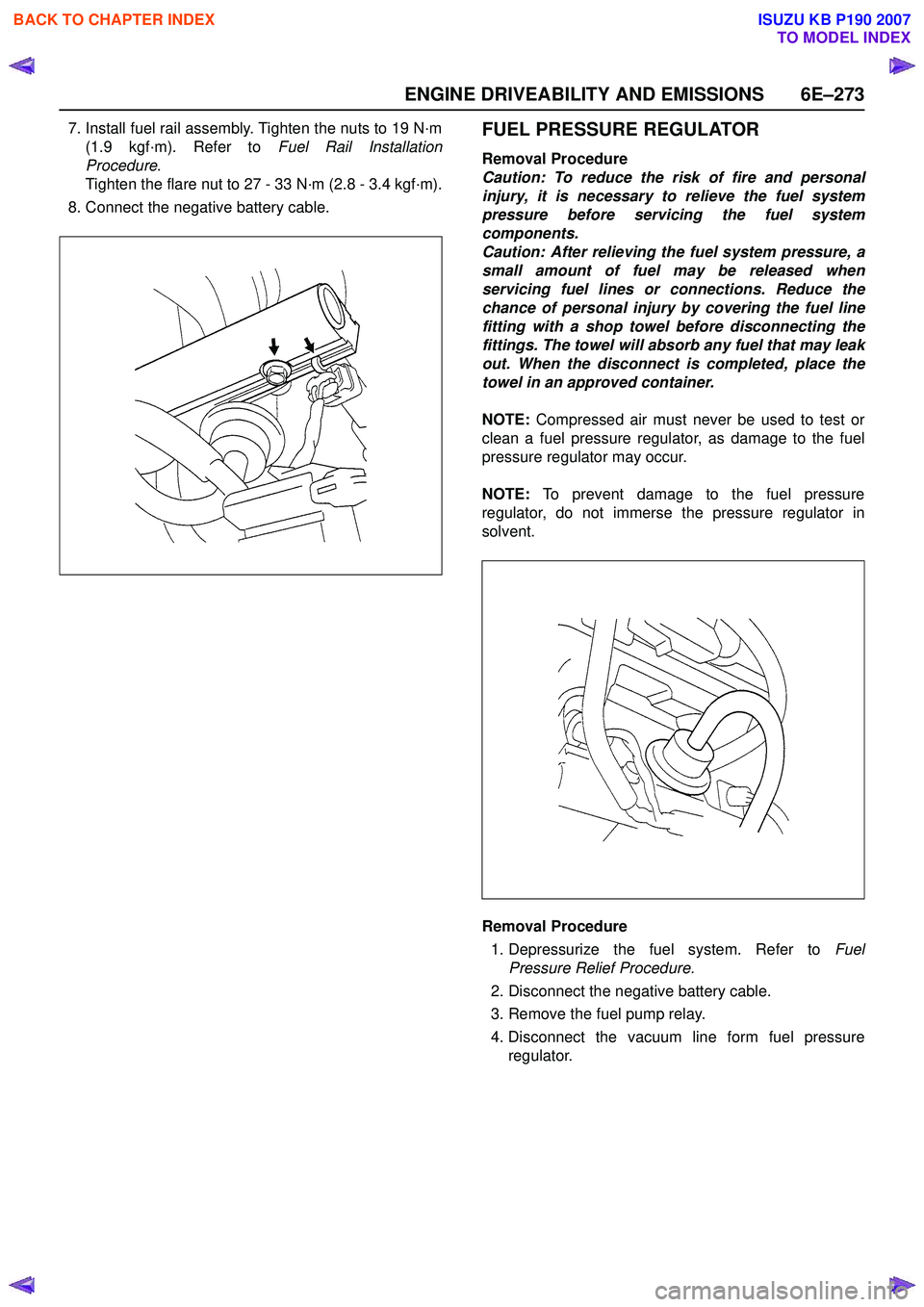
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–273
7. Install fuel rail assembly. Tighten the nuts to 19 N·m(1.9 kgf·m). Refer to Fuel Rail Installation
Procedure .
Tighten the flare nut to 27 - 33 N·m (2.8 - 3.4 kgf·m).
8. Connect the negative battery cable.FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
Removal Procedure
Caution: To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system
pressure before servicing the fuel system
components.
Caution: After relieving the fuel system pressure, a
small amount of fuel may be released when
servicing fuel lines or connections. Reduce the
chance of personal injury by covering the fuel line
fitting with a shop towel before disconnecting the
fittings. The towel will absorb any fuel that may leak
out. When the disconnect is completed, place the
towel in an approved container.
NOTE: Compressed air must never be used to test or
clean a fuel pressure regulator, as damage to the fuel
pressure regulator may occur.
NOTE: To prevent damage to the fuel pressure
regulator, do not immerse the pressure regulator in
solvent.
Removal Procedure
1. Depressurize the fuel system. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Relief Procedure.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Remove the fuel pump relay.
4. Disconnect the vacuum line form fuel pressure regulator.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2444 of 6020
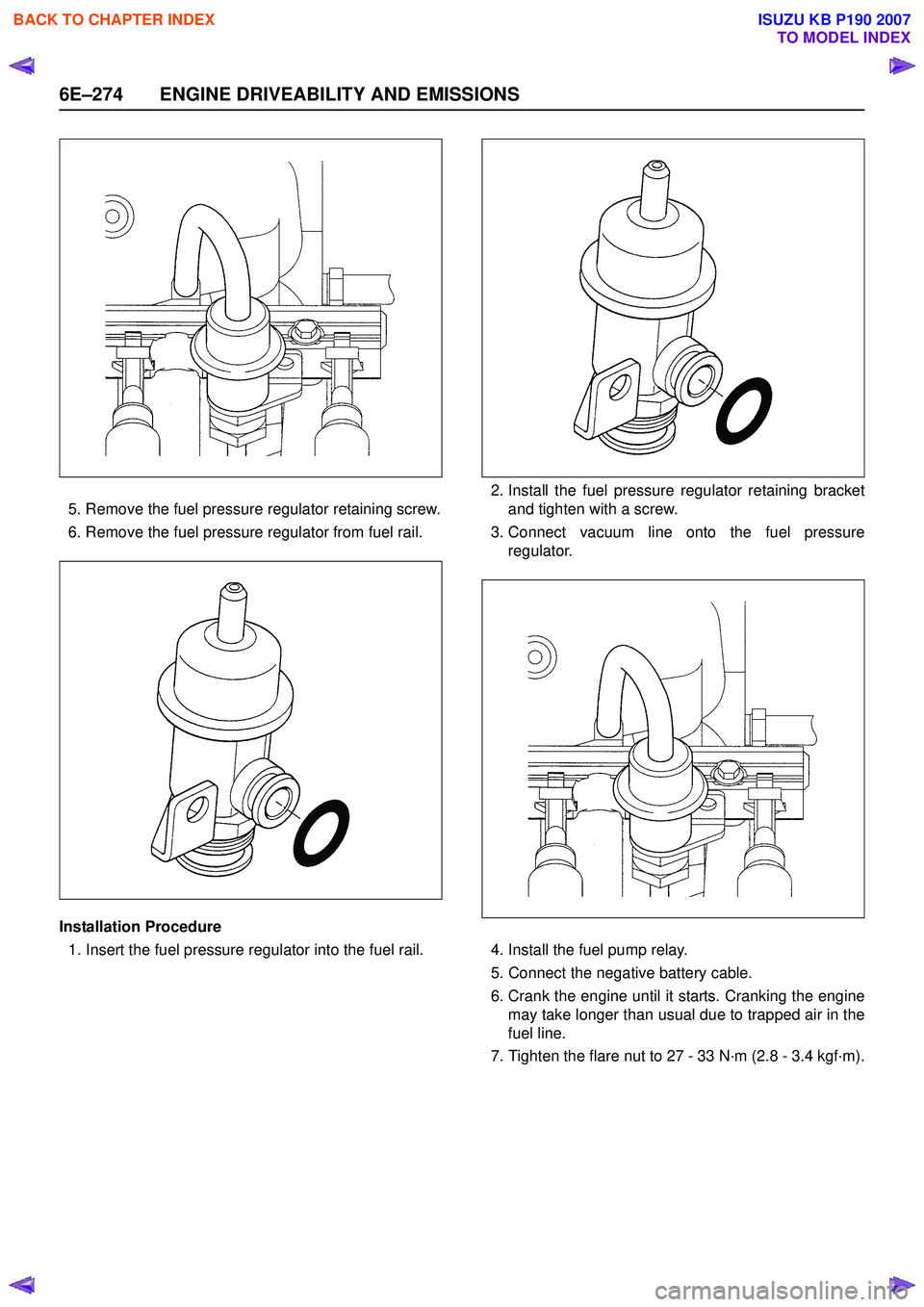
6E–274 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
5. Remove the fuel pressure regulator retaining screw.
6. Remove the fuel pressure regulator from fuel rail.
Installation Procedure 1. Insert the fuel pressure regulator into the fuel rail. 2. Install the fuel pressure regulator retaining bracket
and tighten with a screw.
3. Connect vacuum line onto the fuel pressure regulator.
4. Install the fuel pump relay.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
6. Crank the engine until it starts. Cranking the engine may take longer than usual due to trapped air in the
fuel line.
7. Tighten the flare nut to 27 - 33 N·m (2.8 - 3.4 kgf·m).
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2517 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–38
2.15 Engine Compression Test
A compression pressure test of the engine cylinders determines the condition of the rings, the valves and the head
gasket.
Preliminary Steps
1 Ensure the battery is fully charged.
2 Remove the spark plugs from all cylinders, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
NOTE
DTCs will set when the fuel system or the ignition
system is disabled and the engine is cranked.
Disregard DTCs that set under this condition.
3 Disable the fuel system by removing the fuel pump relay, refer to 8A Electrical Body & Chassis.
4 Start the engine to use any residual fuel from the fuel lines.
4 Disable the ignition coils by removing fuses 34 and 35, refer to 8A Electrical Body & Chassis .
5 Using Tech 2, command the throttle plate to wide open throttle.
Engine Cylinder Compression Test
1 Install the compression tester to cylinder number 1.
2 W hile observing the compression tester reading, turn the ignition to the START position for several seconds and then allow the ignition to return to the ON position.
3 Record the highest compression reading obtained.
4 Repeat the engine compression test for each cylinder.
Test Result Evaluation
Normal engine compression pressure builds quickly and evenly to over 965 kPa. In addition, the lowest reading of an
engine cylinder should not be less than 70 percent of the highest reading. If any cylinder fails the compression test,
adding 15 ml of engine oil to the suspected cylinder may help isolate the following fault condition.
1 A fault condition in the piston rings will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression tends to build-up with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression improves with the addition of engine oil.
2 A fault condition in an intake or exhaust valve will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression does not build with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression does not improve with the addition of engine oil.
3 A fault condition in the cylinder head gasket will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression does not build with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression does not improve with the addition of engine oil.
• The suspected cylinders are positioned adjacent to each other.
• The engine oil may be contaminated with engine coolant.
• The engine coolant may be contaminated with engine oil.
Once the fault has been identified, refer to the relevant service procedure and reinstall the removed components.
Using Tech 2, clear DTCs.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2822 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–45
Page 6A1–45
2.15 Engine Compression Test
A compression pressure test of the engine cylinders determines the condition of the rings, the valves and the head
gasket.
Preliminary Steps
1 Ensure the battery is fully charged.
2 Remove the spark plugs from all cylinders, refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
NOTE
DTCs will set when the fuel system or the ignition
system is disabled and the engine is cranked.
Disregard DTCs that set under this condition.
3 Disable the fuel system by removi ng the fuel pump relay, refer to Section 8A Electrical Body & Chassis .
4 Start the engine to use any resi dual fuel from the fuel lines.
4 Disable the ignition coils by removing fuses 34 and 35, refer to Section 8A Electrical Body & Chassis .
5 Using Tech 2, command the throttle plate to wide open throttle.
Engine Cylinder Compression Test
1 Install the compression tester to cylinder number 1.
2 While observing the compression tester reading, turn t he ignition to the START position for several seconds and
then allow the ignition to return to the ON position.
3 Record the highest compression reading obtained.
4 Repeat the engine compression test for each cylinder.
Test Result Evaluation
Normal engine compression pressure builds quickly and evenly to over 965 kPa. In addition, the lowest reading of an
engine cylinder should not be less than 70 per cent of the highest reading. If any cylinder fails the compression test,
adding 15 ml of engine oil to the suspected cylinder may help isolate the following fault condition.
1 A fault condition in the piston rings will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression tends to build-up with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression improves with the addition of engine oil.
2 A fault condition in an intake or exhaus t valve will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression does not build with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression does not improve with the addition of engine oil.
3 A fault condition in the cylinder head gasket will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression does not build with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression does not improve with the addition of engine oil.
• The suspected cylinders are pos itioned adjacent to each other.
• The engine oil may be contaminated with engine coolant.
• The engine coolant may be cont aminated with engine oil.
Once the fault has been identified, refe r to the relevant service procedure and reinstall the removed components.
Using Tech 2, clear DTCs.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3210 of 6020

Fuel System – V6 Page 6C – 8
3 System Checks
3.1 Fuel Pump Flow Test
If a reduction of the fuel supply is suspected, perform the following checks.
1 Ensure there is sufficient fuel in the tank.
2 W ith the engine running, check the fuel lines from the fuel tank to the injectors for evidence of leakage.
Retighten, if the lines or the connections are loose.
Also, check the fuel lines for restrictions such as
squashed or clogged fuel line.
3 Depressurize the fuel system, refer to 3.4 Fuel System Depressurisation.
4 Disconnect the fuel line at the fuel rail.
5 Connect a hose from the fuel line and place the open end into a clean container.
6 Connect the fuel pump relay terminals (2) with a jumper wire (1) as shown, then turn the ignition to the
ON position to operate the fuel pump, then check the
fuel pump flow rate.
Do not generate any sparks when connecting
the jumper wire.
Fuel delivery test time ....................................... 15.0 Sec
Fuel delivery rate .....................................0.38 Litres Min
NOTE
If the fuel flow rate is below the minimum value,
conduct a fuel pressure test, refer to 3.2
Fuel Pressure Test.
Figure 6C – 4
3.2 Fuel Pressure Test
To reduce the risk of fire or personal injury,
depressurise the fuel system before servicing
any fuel system components, refer to 3.4
Fuel System Depressurisation.
Gauge Installation
1 Turn the ignition switch off.
2 Depressurise the fuel system, refer to 3.4 Fuel System Depressurisation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3211 of 6020
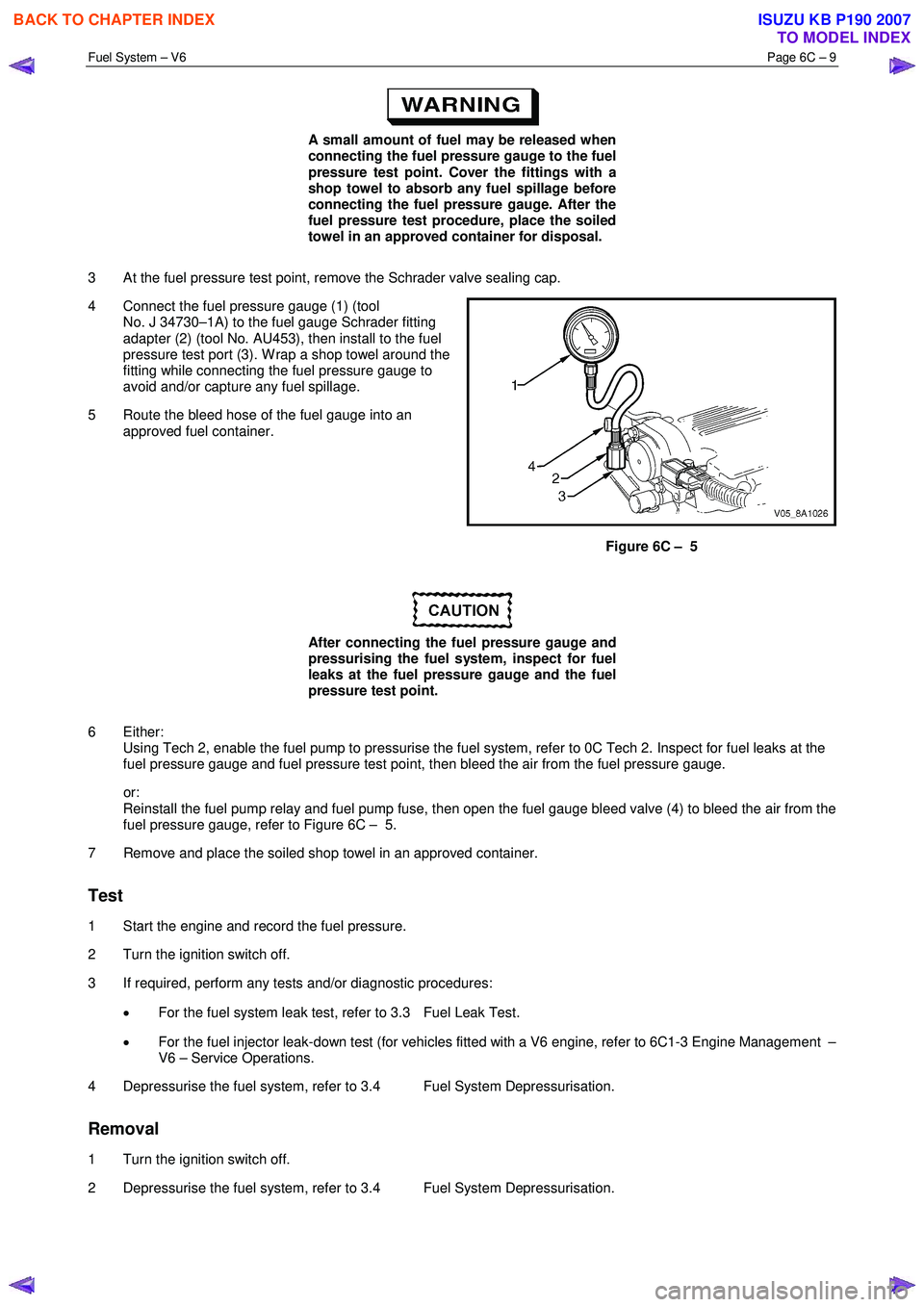
Fuel System – V6 Page 6C – 9
A small amount of fuel may be released when
connecting the fuel pressure gauge to the fuel
pressure test point. Cover the fittings with a
shop towel to absorb any fuel spillage before
connecting the fuel pressure gauge. After the
fuel pressure test procedure, place the soiled
towel in an approved container for disposal.
3 At the fuel pressure test point, remove the Schrader valve sealing cap.
4 Connect the fuel pressure gauge (1) (tool No. J 34730–1A) to the fuel gauge Schrader fitting
adapter (2) (tool No. AU453), then install to the fuel
pressure test port (3). W rap a shop towel around the
fitting while connecting the fuel pressure gauge to
avoid and/or capture any fuel spillage.
5 Route the bleed hose of the fuel gauge into an approved fuel container.
Figure 6C – 5
After connecting the fuel pressure gauge and
pressurising the fuel system, inspect for fuel
leaks at the fuel pressure gauge and the fuel
pressure test point.
6 Either: Using Tech 2, enable the fuel pump to pressurise the fuel system, refer to 0C Tech 2. Inspect for fuel leaks at the
fuel pressure gauge and fuel pressure test point, then bleed the air from the fuel pressure gauge.
or: Reinstall the fuel pump relay and fuel pump fuse, then open the fuel gauge bleed valve (4) to bleed the air from the
fuel pressure gauge, refer to Figure 6C – 5.
7 Remove and place the soiled shop towel in an approved container.
Test
1 Start the engine and record the fuel pressure.
2 Turn the ignition switch off.
3 If required, perform any tests and/or diagnostic procedures:
• For the fuel system leak test, refer to 3.3 Fuel Leak Test.
• For the fuel injector leak-down test (for vehicles fitted with a V6 engine, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
4 Depressurise the fuel system, refer to 3.4 Fuel System Depressurisation.
Removal
1 Turn the ignition switch off.
2 Depressurise the fuel system, refer to 3.4 Fuel System Depressurisation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3213 of 6020
Fuel System – V6 Page 6C – 11
Figure 6C – 6
5 Replace any faulty components and repeat step 2 to step 5 inclusive.
6 Replace all engine components removed to perform the fuel leak test, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
3.4 Fuel System Depressurisation
To reduce the risk of fire or personal injury,
depressurise the fuel system before servicing
any fuel system components.
1 Turn the ignition switch off.
2 Remove the fuel pump fuse and fuel pump relay, refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis.
3 Loosen the fuel filler cap to relieve the fuel tank vapour pressure.
4 W ith the throttle closed, crank the engine.
NOTE
The engine may start and operate until the fuel
remaining in the fuel delivery system depletes.
5 W hen the engine stops, crank the engine for another 10 seconds to ensure the fuel feed line pressure has been fully relieved.
6 Clean the area around the fuel pressure test point.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007