check engine ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 1960 of 6020

ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-343
Excessive Smoke (Black Smoke)
ChecksAction
Definition:
Black smoke under load, idle or start up hot or cold.
Preliminary Check • Ensure the vehicle has an actual problem.
• Inspect the ECM grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Remove the air cleaner and check for dirt, or for air ducts being plugged or restricted. Replace as necessary.
• Inspect the fuel quality (cetane index).
• Inspect the engine oil level and quality.
• Inspect the programmed fuel injector ID code for each cylinder.
• Inspect the Scan Tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the Service Bulletin.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the Scan Tool
Data List in this section.
• Compare the Coolant Temperature with the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) parameters on a cold engine condition. If the difference among
temperature reading is more than 5 °C (9 °F) on a cold engine, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT may indicate
a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
• Observe the MAF parameter for a skewed or slow MAF sensor.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure (FRP) Sensor parameter with the engine OFF. The FRP Sensor should read 0.9 to 1.0 volt with the key ON and engine OFF after the
engine has stopped running for a minimum of 1 minute. If not, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure and Desired Fuel Rail Pressure parameter between idle and W.O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) in Neutral. Fuel Rail Pressure
parameter should follow within ±5 MPa ( ±725 psi) quick enough.
• Observe the Barometric Pressure (BARO) parameter. The BARO parameter should indicate near surrounding barometric pressure. Refer to Altitude vs. Barometric
Pressure. (Standard output)
• Observe the Boost Pressure and BARO with ignition ON and engine OFF. Both parameters should be within the 7.0 kPa (1.0 psi) each other. (High output)
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Fuel injectors. Remove the injectors and visually inspect.
• Perform the Cylinder Balance Test with a scan tool.
• Perform the Pilot Injection Control with a scan tool.
• Observe the Fuel Compensation for each cylinder at idle on the scan tool.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Air cleaner, air intake ducts and charge air cooler for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• A restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Intake throttle valve for a stuck condition.
• A restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• A restriction or damaged at MAF sensor.
• A worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor wheel. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1961 of 6020

6E-344 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Engine Mechanical ChecksInspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Inspect for poor cylinder compression.
• Improper mechanical timing (timing gear and timing chain).
• Improper valve gap.
• Broken or weak valve springs.
• Worn camshaft lobes.
• Any excessive oil entering combustion chamber.
Additional Checks • EGR system operating correctly. Refer to EGR Control System Check in this
section.
• Excessive blow-by gasses.
Checks
Action
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1962 of 6020

ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-345
Excessive Smoke (White Smoke)
ChecksAction
Difinition:
White smoke under load, idle or start up hot or cold.
Preliminary Check • Ensure the vehicle has an actual problem.
• Inspect the ECM grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Inspect the fuel quality (cetane index).
• Inspect the programmed fuel injector ID code for each cylinder.
• Inspect the Scan Tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the Service Bulletin.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the Scan Tool
Data List in this section.
• Compare the Coolant Temperature with the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) parameters on a cold engine condition. If the difference among
temperature reading is more than 5 °C (9 °F) on a cold engine, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT may indicate
a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure (FRP) Sensor parameter with the engine OFF. The FRP Sensor should read 0.9 to 1.0 volt with the key ON and engine OFF after the
engine has stopped running for a minimum of 1 minute. If not, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure and Desired Fuel Rail Pressure parameter between idle and W.O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) in Neutral. Fuel Rail Pressure
parameter should follow within ± 5 MPa ( ± 725 psi) quick enough.
• Observe the Accelerator Pedal Position (APP). APP parameter should change linearly from 0 to 100% according to the accelerator pedal operation.
• Observe the Boost Pressure and Barometric Pressure (BARO) with ignition ON and engine OFF. Both parameters should be within the 7.0 kPa (1.0 psi) each other.
• Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is tight and the sensor rotor is not damaged.
Fuel System Checks • If excessive smoke is present, check for a stuck open fuel injector. Inspect for fuel
leakage into the combustion chamber.
• Fuel injectors. Remove the injectors and visually inspect.
• Perform the Cylinder Balance Test with a scan tool.
• Perform the Pilot Injection Control with a scan tool.
• Observe the Fuel Compensation for each cylinder at idle on the scan tool.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Air cleaner, air intake ducts and charge air cooler for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• A restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Intake throttle valve for a stuck condition.
• A restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• A restriction or damaged at MAF sensor.
• Perform the Swirl Control Solenoid Test with a scan tool. Inspect the diaphragm valve operation when it commanded ON/ OFF.
• A worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor wheel. Oil leak from turbocharger. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical
section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1963 of 6020

6E-346 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Engine Mechanical ChecksInspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Poor cylinder compression.
• Improper mechanical timing (timing gear and timing chain).
• Improper valve gap.
• Broken or weak valve springs.
• Worn camshaft lobes.
• Thermostat working (open stuck).
• Any excessive oil entering combustion chamber.
Electrical System Checks • Glow plug control (preheating) system operation. Refer to Glow Control System
Check in this section.
Checks
Action
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1966 of 6020

ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-349
4. In order to get programming approval, the on-screen displays a message to user. Get
programming approval from the TIS 2000 using
the following procedure:
a. Connect a scan tool to the terminal that installed TIS 2000 with the latest software and
the hardware key is plugged into port.
b. Turn ON the scan tool and keep at title screen.
c. Launch the TIS application.
d. Select the Security Access at the main screen.
e. Highlight the “Tech 2” on the Diagnostic Tool Selection screen and click “Next”.
f. Click “Close” on the Security Access Enabled screen.
g. Turn OFF the scan tool.
h. Disconnect the scan tool from the terminal.
5. Install a scan tool to the vehicle.
6. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
7. Select Diagnostics > appropriate vehicle identification > 4JK1 or 4JJ1 > Programming >
Program ECU.
8. Verify the VIN on the screen if programmed at previously described SPS. If not programmed or
incorrect VIN, input correct VIN.
9. Input 24 digits of each fuel injector ID code.
10. After complete the programming, turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
11. Start the engine and let idle.
12. Inspect for a proper engine running condition and for no DTC's. Refer to the Diagnostic System
Check - Engine Controls if needed.
G. Supply Pump Relearn 1. Install a scan tool.
2. Start the engine and let idle until engine coolant temperature reads 65 °C (149 °F) or higher while
observing the Supply Pump Status parameter with
a scan tool. The scan tool parameter changes
status Not Learn > Learning > Learned.
3. If the ECM has correctly learned the fuel supply pump current adjustment, the Supply Pump Status
parameter on the scan tool will repeatedly indicate
Learning and Learned.Service Programming System (SPS)
Description
The service programming system (SPS) allows a
technician to program a control module through the
data link connector (DLC). The information transfer
circuit that is used at the DLC is the same serial data
circuit used by the scan tool for retrieving DTCs,
displaying data, clearing DTCs etc. This procedure
offers the ability to install software/ calibrations
matched to a particular vehicle.
Most control modules have two types of memory. The
software/ calibrations reside in the flash memory. The
two types of memory are listed below:
• Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM)
This type of memory allows selected portions of
memory to be programmed while other portions
remain unchanged.
Certain learned values reside in the EEPROM,
such as:
- The vehicle identification number (VIN)
- The software/ calibrations identification numbers
- The control module security information
• Flash Read Only Memory-Flash Memory Flash memory has increased memory storage
capacity. During programming, all information
within this type of memory is erased, and then
replaced with entirely new information.
Service Programming Methods
The two methods of programming an ECM are listed
below:
• Remote Programming
• Pass Thru Programming
For information on programming an ECM using one of
the methods listed above, refer to Service
Programming System (SPS) (Remote Procedure) or
Service Programming System (SPS) (Pass-Thru
Procedure).
Before Programming a Control Module
Important: DO NOT program an existing ECM with the
identical software/ calibration package. This procedure is not
a short cut to correct the driveability condition. This is an
ineffective repair. An ECM should only be programmed when
the following occurs:
• When a service procedure instructs you to replace the ECM.
• An updated software/ calibrations is released.
Ensure that the following conditions are met before
programming an ECM:
• The scan tool PCMCIA card is programmed with the latest software.
• The TIS 2000 is installed with the latest software.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1999 of 6020
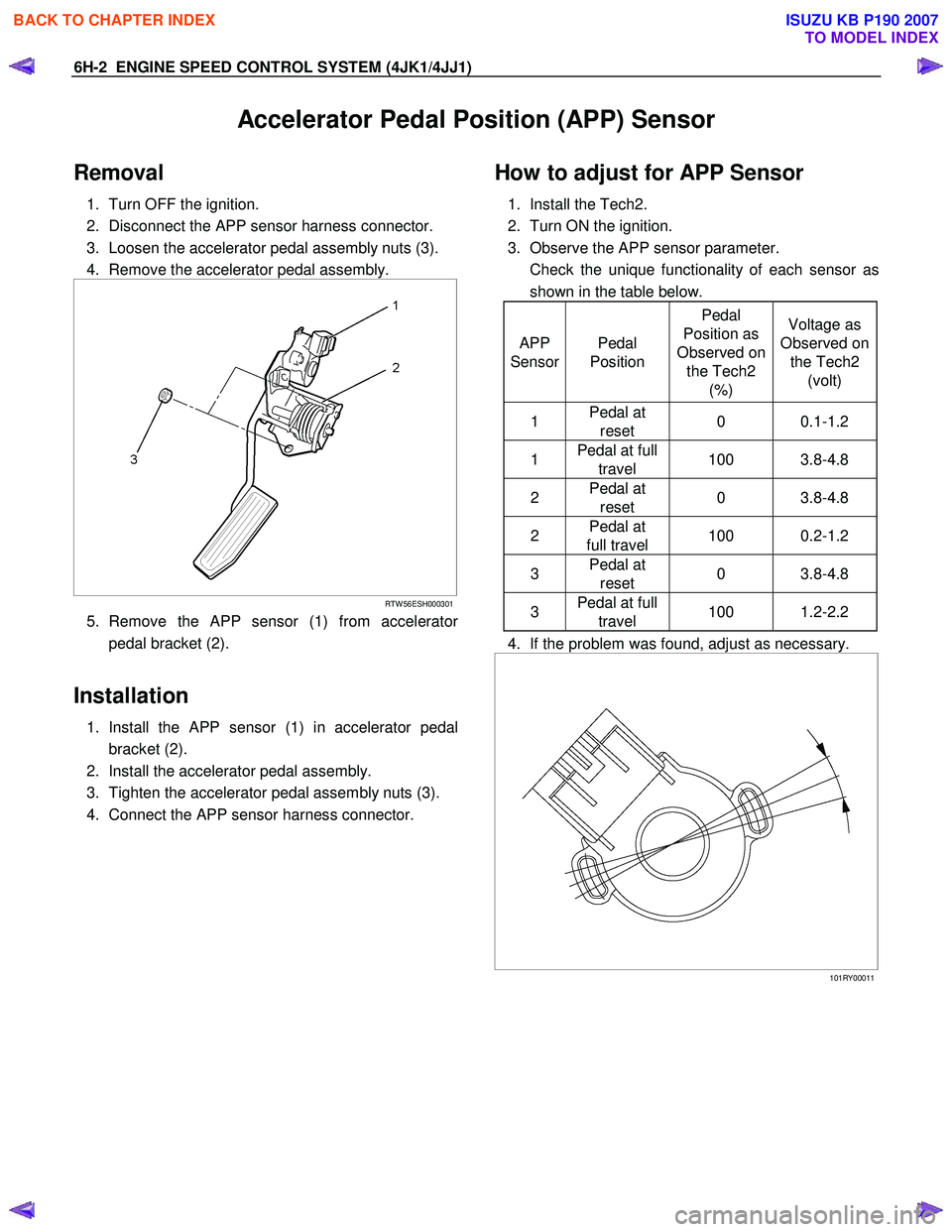
6H-2 ENGINE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
Removal
1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Disconnect the APP sensor harness connector.
3. Loosen the accelerator pedal assembly nuts (3).
4. Remove the accelerator pedal assembly.
RTW 56ESH000301
5. Remove the APP sensor (1) from accelerator
pedal bracket (2).
Installation
1. Install the APP sensor (1) in accelerator pedal
bracket (2).
2. Install the accelerator pedal assembly.
3. Tighten the accelerator pedal assembly nuts (3).
4. Connect the APP sensor harness connector.
How to adjust for APP Sensor
1. Install the Tech2.
2. Turn ON the ignition.
3. Observe the APP sensor parameter.
Check the unique functionality of each sensor as shown in the table below.
APP
Sensor Pedal
Position Pedal
Position as
Observed on the Tech2 (%) Voltage as
Observed on the Tech2 (volt)
1 Pedal at
reset 0 0.1-1.2
1 Pedal at full
travel 100 3.8-4.8
2 Pedal at
reset 0 3.8-4.8
2 Pedal at
full travel 100 0.2-1.2
3 Pedal at
reset 0 3.8-4.8
3 Pedal at full
travel 100 1.2-2.2
4. If the problem was found, adjust as necessary.
101RY00011
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2001 of 6020

ENGINE DIAGNOSIS (C24SE) 6-1
SECTION 6
ENGINE DIAGNOSIS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAGE
Engine Diagnosis .............................................................................................................. 6- 2
Hard Starting ................................................................................................................. 6- 2
Engine Compression Test Procedure ......................................................................... 6- 3
Rough Engine Idling or Engine Stalling...................................................................... 6- 4
Rough Engine Running ................................................................................................ 6- 5
Hesitation ..................................................................................................................... . 6- 6
Engine Lacks Power ..................................................................................................... 6- 7
Engine Noisy ................................................................................................................. 6 - 8
Abnormal Noise Due to Hydraulic Lash Adjustor ...................................................... 6- 9
Troubleshooting Procedure ......................................................................................... 6- 9
Abnormal Combustion ................................................................................................. 6-11
Engine Oil Consumption Excessive............................................................................ 6-12
Fuel Consumption Excessive ...................................................................................... 6-13
Oil Problems.................................................................................................................. 6-13
Engine Oil Pressure Check .......................................................................................... 6-13
Malfunction Indicator Lamp ......................................................................................... 6-14
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2002 of 6020
6-2 ENGINE DIAGNOSIS (C24SE)
Engine Diagnosis
Hard Starting
1.Starting Motor Does Not Turn Over
Trouble Shooting Procedure
Turn on headlights and starter switch.
Condition Possible cause Correction
Headlights go out or dim
considerably Battery run down or under
charged Recharge or replace battery
Terminals poorly connected Clean battery posts and terminals
and connect properly
Starting motor coil circuit shorted Overhaul or replace
Starting motor defective Overhaul or replace
2.Ignition Trouble - Starting Motor Turns Over But Engine Does Not Start
Spark Test Disconnect a high tension cable from any spark plug.
Connect the spark plug tester (use commercially
available tool), crank the engine, and check if a spark is
generated in the spark plug tester. Before cranking the
engine, make sure that the spark plug tester is properly
grounded. To avoid electrical shock, do not touch the
high tension cable while the engine is running.
Condition Possible cause Correction
Spark jumps across gap Spark plug defective Clean, adjust spark gap or replace
Spark plug wire in correct Connect properly or replace
Ignition timing incorrect Refer to Ignition System
Fuel not reaching fuel injector(s)
or engine Refer to item 3 (Trouble in fuel
system)
Valve timing incorrect Adjust
Engine lacks compression Refer to item 4 (Engine lacks
compression)
No sparking takes place Ignition coil disconnected or
broken Connect properly or replace
Electronic Ignition System with
module Replace
Poor connections in engine
harness Correct
Engine Control Module cable
disconnected or defective Correct or replace
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2003 of 6020
ENGINE DIAGNOSIS (C24SE) 6-3
3.Trouble in Fuel System Condition Possible cause Correction
Starting motor turns over and
spark occurs but engine does not
start. Fuel tank empty Fill
Water in fuel system Clean
Fuel filter clogged Replace filter
Fuel pipe clogged Clean or replace
Fuel pump defective Replace
Fuel pump circuit open Correct or replace
Evaporative Emission Control
system circuit clogged Correct or replace
Multiport Fuel Injection System
faulty Refer to "Electronic Fuel Injection"
section
4.Engine Lacks Compression
Condition Possible cause Correction
Engine lacks compression Spark plug loosely fitted or spark
plug gasket defective Tighten to specified torque or
replace gasket
Spark plug wire incorrect Connect properly or replace
Valve timing incorrect Adjust
Cylinder head gasket defective Replace gasket
Valve incorrectly seated Lap valve
Valve stem seized Replace valve and valve guide
Valve spring weakened Replace
Cylinder or piston rings worn Overhaul engine
Piston ring seized Overhaul engine.
Engine Compression Test Procedure
1. Start and run the engine until the engine
reaches normal operating temperature.
2. Turn the engine off.
3. Remove all the spark plugs.
4. Remove ignition coil fuse (15A) and disable the ignition system.
5. Remove the fuel pump relay from the relay and fuse box. 6. Engage the starter and check that the cranking
speed is approximately 300 rpm.
7. Install cylinder compression gauge into spark plug hole.
8. With the throttle valve opened fully, keep the starter engaged until the compression gauge
needle reaches the maximum level. Note the
reading.
9. Repeat the test with each cylinder. The pressure difference between the individual
cylinders should not exceed 100kPa (14.5 psi).
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2006 of 6020

6-6 ENGINE DIAGNOSIS (C24SE)
Hesitation
Condition Possible cause Correction
Hesitation on acceleration Throttle Position Sensor
adjustment incorrect Replace throttle valve assembly
Throttle Position Sensor circuit
open or shorted Correct or replace
Excessive play in accelerator
linkage Adjust or replace
Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) Sensor circuit open or
shorted Correct or replace
MAP Sensor defective Replace
Intake Air Temperature (IAT)
Sensor circuit open or shorted Correct or replace
Knock Sensor (KS) Circuit open or
shorted Correct or replace
KS
defective Replace
KS Module circuits open or
shorted Correct or replace
KS Module defective Replace
IAT Sensor defective Replace
Hesitation at high speeds
(Fuel pressure too low) Fuel tank strainer clogged Clean or replace
Fuel pipe clogged Clean or replace
Fuel filter clogged Replace
Defective fuel pump system Check and replace
Fuel Pressure Control Valve
leaking Replace
Hesitation at high speeds
(Fuel injector not working
normally) Power supply or ground circuit for
Multiport Fuel Injection System
shorted or open Check and correct or replace
Cable of Multiport Fuel Injection
System disconnected or defective Correct or replace
Hesitation at high speeds
Engine Control Module defective Replace
Throttle Position Sensor circuit
open or shorted Correct or replace
Throttle Position Sensor defective Replace
Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor circuit open or shorted Correct or replace
Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor defective Replace
MAP Sensor cable open or
shorted Correct or replace
MAP Sensor defective Replace
IAT Sensor circuit open or shorted Correct or replace
IAT Sensor defective Replace
KS Circuit open or shorted Correct or replace
KS defective Replace
KS Module circuit open or shorted Correct or replace
KS Module defective Replace
Throttle valve not wide opened Check and correct or replace
Air Cleaner Filter clogged Replace filter element
Power supply voltage too low Check and correct or replace
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007