check engine ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 3603 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-16
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the generator is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the following:
1 Tighten all fasteners to the correct torque specification.
2 Reconnect the battery ground lead.
3 Start the engine.
4 Check the generator warning indicator operation.
5 Check the drive belt is correctly routed and aligned.
6 Check the generator output. Refer to 3.3 On-vehicle Testing.
7 Check the voltage regulator operation. Refer to 3.3 On-vehicle Testing.
8 Turn the ignition switch off.
Generator mounting bolts ........................... (1) 58.0 Nm
Generator mounting bolts ........................... (2) 58.0 Nm
Generator mounting bolts ........................... (4) 58.0 Nm
Battery harness to P-9 pin B nut
torque specification ...................................7.1 – 13.3 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3609 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–1
6D1-2
Starting System – V6
ATTENTION
Before performing any service operation or other procedure described in this Section, refer to 1.1
WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES for correct workshop practices with regard to safety and/or property
damage.
1 General Information ............................................................................................................ ...................3
1.1 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES .................................................................................................... ................... 3
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements ............................................................................. .... 3
WARNING defined ............................................................................................................................................. 3
CAUTION defined .............................................................................................................................................. 3
NOTE defined..................................................................................................................................................... 3
1.2 Components .......................................................................................................................................................... 4
Starting System Components ............................................................................................................................... 4
Starter Motor and Solenoid Switch Components................................................................................... ............. 4
Solenoid Switch.................................................................................................................................................. 4
Planetary Drive Train.......................................................................................................... ................................ 4
Armature ............................................................................................................................................................ 4
Brushes .............................................................................................................................................................. 4
1.3 System Operation .................................................................................................................................................. 5
Operation ...................................................................................................................... ..................................... 5
Sequence of Operation .......................................................................................................... ............................ 6
2 Diagnostics .............................................................................................................................................7
2.1 Diagnostic General Information............................................................................................................................ 7
Basic Diagnostic Tools Required ......................................................................................................................... 7
2.2 Tech 2 Data List ............................................................................................................... ...................................... 7
2.3 Diagnostic Systems Check ....................................................................................................... ............................ 7
2.4 Wiring Diagram ...................................................................................................................................................... 8
2.5 Starting System Inoperative / Malfunctioning ................................................................................... ................ 10
Circuit Description ............................................................................................................................................ 10
Diagnostic Table Notes ......................................................................................................... ........................... 10
Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................................... 10
Diagnostic Table – Slow Cranking, Solenoid Clicks or Chatters.................................................................. ..... 14
3 Minor Service Operations ....................................................................................................................15
3.1 Safety Precautions............................................................................................................................................... 15
3.2 Maintenance ......................................................................................................................................................... 15
Regular Checks ................................................................................................................. ................................... 15
3.3 On-Vehicle Testing ............................................................................................................. ................................. 15
Engine Compartment Relay And Fuse Panel ........................................................................................ ........... 16
Bad Connection Test ........................................................................................................................................ 16
Starter Motor Ground Test ...................................................................................................... ......................... 17
Switching Circuit Test ....................................................................................................................................... 17
Cranking Voltage Test .......................................................................................................... ............................ 18
Current Draw Test ............................................................................................................................................ 18
4 Major Service Operations ....................................................................................................................19
4.1 Starter Motor ........................................................................................................................................................ 19
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 19
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3615 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–7
2 Diagnostics
2.1 Diagnostic General Information
NOTE
There is a minimum battery voltage threshold
value. If the battery voltage is below the set value,
the ECU will inhibit cranking. Refer to 6C1-1
Engine Management – V6 – General Information
for further information.
Basic Diagnostic Tools Required
Use of incorrect electrical circuit diagnostic
tools when performing the cruise control
diagnostic procedures could result in
incorrect diagnostic results or damage to
components.
The following electrical circuit testing tools are required to perform the diagnostic procedures detailed in this Section:
• digital multimeter with 10 meg ohms impedance, and
• connector test adapter kit Tool No. KM609.
For further information on the use of these tools, refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis.
2.2 Tech 2 Data List
The Tech 2 displays the status of certain starting system parameters.
To view the data list:
1 Connect Tech 2 to the DLC.
2 On Tech 2 select: Engine / V6 Engine / Data Display / Data List / Electrical / Theft Data .
Tech 2 Parameter Units Displayed Typical Display Values
Crank Request Inactive / Active Inactive
Starter Relay Off / On Off
2.3 Diagnostic Systems Check
Step Action Yes No
1
Is the fault specifically isolated to this system / module?
Go to Step 2 Go to 0D Vehicle
Diagnostics
2 1 Connect Tech 2 to the DLC.
2 Ignition ON, engine OFF.
3 On Tech 2 select:
Engine / V6 Engine / Diagnostic Trouble codes / Read
DTC’s.
Are there any set DTC’s? Go to the
appropriate DTC
table in 6C1-2 Engine
Management – V6 – Diagnostics. Refer to 2.5
Starting
System Inoperative / Malfunctioning
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3618 of 6020
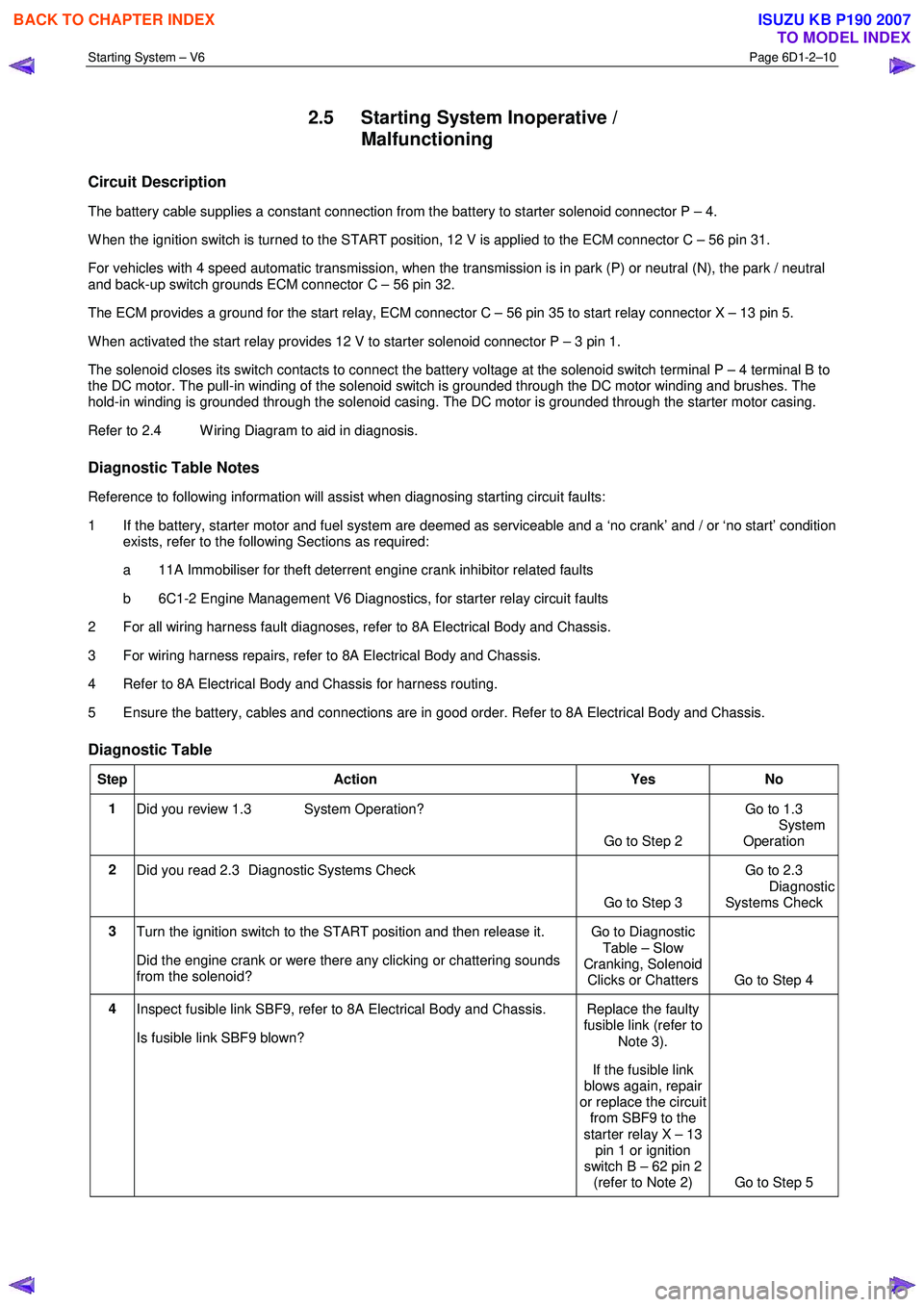
Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–10
2.5 Starting System Inoperative /
Malfunctioning
Circuit Description
The battery cable supplies a constant connection from the battery to starter solenoid connector P – 4.
W hen the ignition switch is turned to the START position, 12 V is applied to the ECM connector C – 56 pin 31.
For vehicles with 4 speed automatic transmission, when the transmission is in park (P) or neutral (N), the park / neutral
and back-up switch grounds ECM connector C – 56 pin 32.
The ECM provides a ground for the start relay, ECM connector C – 56 pin 35 to start relay connector X – 13 pin 5.
W hen activated the start relay provides 12 V to starter solenoid connector P – 3 pin 1.
The solenoid closes its switch contacts to connect the battery voltage at the solenoid switch terminal P – 4 terminal B to
the DC motor. The pull-in winding of the solenoid switch is grounded through the DC motor winding and brushes. The
hold-in winding is grounded through the solenoid casing. The DC motor is grounded through the starter motor casing.
Refer to 2.4 W iring Diagram to aid in diagnosis.
Diagnostic Table Notes
Reference to following information will assist when diagnosing starting circuit faults:
1 If the battery, starter motor and fuel system are deemed as serviceable and a ‘no crank’ and / or ‘no start’ condition exists, refer to the following Sections as required:
a 11A Immobiliser for theft deterrent engine crank inhibitor related faults
b 6C1-2 Engine Management V6 Diagnostics, for starter relay circuit faults
2 For all wiring harness fault diagnoses, refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis.
3 For wiring harness repairs, refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis.
4 Refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis for harness routing.
5 Ensure the battery, cables and connections are in good order. Refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Did you review 1.3 System Operation?
Go to Step 2 Go to 1.3
System
Operation
2 Did you read 2.3 Diagnostic Systems Check
Go to Step 3 Go to 2.3
Diagnostic Systems Check
3 Turn the ignition switch to the START position and then release it.
Did the engine crank or were there any clicking or chattering sounds
from the solenoid? Go to Diagnostic
Table – Slow
Cranking, Solenoid Clicks or Chatters Go to Step 4
4 Inspect fusible link SBF9, refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis.
Is fusible link SBF9 blown? Replace the faulty
fusible link (refer to
Note 3).
If the fusible link
blows again, repair
or replace the circuit from SBF9 to the
starter relay X – 13 pin 1 or ignition
switch B – 62 pin 2 (refer to Note 2) Go to Step 5
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3620 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–12
Step Action Yes No
10
1 Connect Tech 2 to the DLC.
2 Ignition on, engine off.
3 On Tech 2 select: Engine / V6 Engine / Data Display / Data List /
Electrical/Theft Data.
4 On Tech 2 scroll to Crank Request.
5 W hile monitoring Tech 2, turn the ignition switch to START.
Does Tech 2 display the following:
Inactive with the ignition switch in the ON position, Active with the
ignition switch in the START position? Go to Step 15 Go to Step 11
11 1 Disconnect the ECM connector C – 56.
2 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, back probe between the harness connector C56 – X2 pin 31 and ground.
3 W ith the aid of an assistant, monitor the voltage on the multimeter and turn the ignition switch to START.
• W ith the ignition switch in the START position, the
multimeter should display battery voltage
• W ith the ignition switch in the ON position, the multimeter
should display 0 V
Does the multimeter display as described? Refer to 6C1 - 3
Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations
for further diagnosis.
Go to Step 21 Go to Step 12
12 Test the ignition switch, refer to 3B Steering.
Is the ignition switch serviceable?
Go to Step 13 Replace the faulty
ignition switch. Refer to 3B
Steering
Go to Step 21
13 Check for short to ground or open circuit from the ignition switch start
terminal to the ECM connector C – 56 pin 31.
W as the circuit serviceable? Go to Step 14 Repair as required
(refer to Note 2).
Go to Step 21
14 Check for short to ground or open circuit from the ignition switch
terminal B1 to the fuse SBF5.
W as the circuit serviceable? Go to Step 2 Repair as required
(refer to Note 2).
Go to Step 21
15 NOTE
This procedure is only required on vehicles fitted with
manual transmissions. If the vehicle is fitted with an
automatic transmission, go to Step 16
1 Scroll to Starter Relay
2 W hile monitoring Tech 2, turn the ignition switch to START.
Does Tech 2 display the following:
Off with the ignition switch in the ON position,
On with the ignition switch in the START position?
Go to Step 21 Go to Step 16
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3621 of 6020
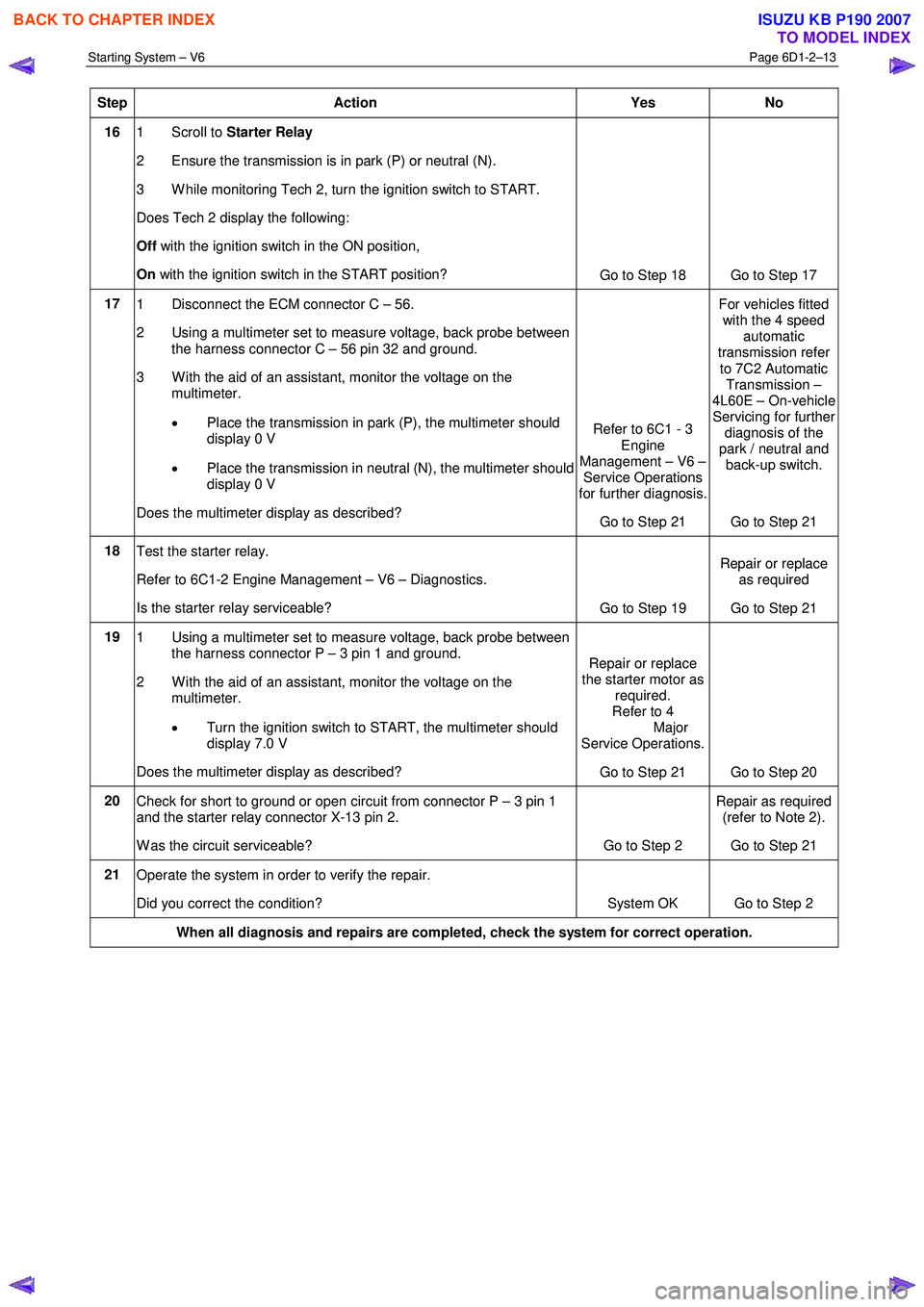
Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–13
Step Action Yes No
16 1 Scroll to Starter Relay
2 Ensure the transmission is in park (P) or neutral (N).
3 W hile monitoring Tech 2, turn the ignition switch to START.
Does Tech 2 display the following:
Off with the ignition switch in the ON position,
On with the ignition switch in the START position?
Go to Step 18 Go to Step 17
17 1 Disconnect the ECM connector C – 56.
2 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, back probe between the harness connector C – 56 pin 32 and ground.
3 W ith the aid of an assistant, monitor the voltage on the multimeter.
• Place the transmission in park (P), the multimeter should
display 0 V
• Place the transmission in neutral (N), the multimeter should
display 0 V
Does the multimeter display as described? Refer to 6C1 - 3
Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations
for further diagnosis.
Go to Step 21 For vehicles fitted
with the 4 speed automatic
transmission refer
to 7C2 Automatic Transmission –
4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing for further
diagnosis of the
park / neutral and back-up switch.
Go to Step 21
18 Test the starter relay.
Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics.
Is the starter relay serviceable? Go to Step 19 Repair or replace
as required
Go to Step 21
19 1 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, back probe between
the harness connector P – 3 pin 1 and ground.
2 W ith the aid of an assistant, monitor the voltage on the multimeter.
• Turn the ignition switch to START, the multimeter should
display 7.0 V
Does the multimeter display as described? Repair or replace
the starter motor as required.
Refer to 4
Major
Service Operations.
Go to Step 21 Go to Step 20
20 Check for short to ground or open circuit from connector P – 3 pin 1
and the starter relay connector X-13 pin 2.
W as the circuit serviceable? Go to Step 2 Repair as required
(refer to Note 2).
Go to Step 21
21 Operate the system in order to verify the repair.
Did you correct the condition? System OK Go to Step 2
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3626 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–18
Cranking Voltage Test
1 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, attach
the multimeter’s negative lead to ground and the
multimeter’s positive lead to starter solenoid
connector P – 3 pin 1 (3) of the solenoid switch.
Do not crank the engine for more than
30 seconds at a time. Allow 2 minutes for
the starter motor to cool down between
tests.
3 Crank the engine.
4 Record the voltage that displayed during cranking.
Minimum cranking
voltage.................................................................9.0 V
5 Remove and repair or replace the starter motor and solenoid switch if the voltage is below the
specifications and cranks poorly. Refer to 4
Major Service Operations. Figure 6D1-2 – 7
Current Draw Test
1 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, attach the multimeter’s positive lead to the positive battery post.
2 Attach the same multimeter’s negative lead to the negative battery post.
3 Using a multimeter set to measure current, attach the multimeter’s positive lead to the battery post.
4 Connect the negative lead of the multimeter set to measure current to a battery loading device, for example a carbon pile.
5 Connect the free lead of the battery loading device to the negative battery terminal.
6 Set the battery loading device to maximum resistance (open).
7 Crank the engine.
8 Record the voltage that displayed during cranking.
9 W ith the ignition in the OFF position, adjust the battery loading device so the reading of the multimeter set to measure voltage matches the reading recorded in the last step.
10 Record the current draw from the battery loading device.
11 Set the battery loading device back to ‘open’.
12 Check the current draw is within specifications.
Cranking current range ................................ 100 – 140 A
13 Remove and repair or replace the starter motor and solenoid switch if the current draw is outside the specification. Refer to 4 Major Service Operations.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3629 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–21
10 Unclip the oil level sensor harness from the heat shield
(1).
11 Remove the heat shield attaching screw (2).
12 Remove the lower starter motor attaching bolt (3).
13 Remove the heat shield.
14 Remove the upper starter motor retaining bolt (3).
15 Remove the starter motor from the engine block and lower the starter motor as far as possible to gain
access to the wiring harness connections.
Figure 6D1-2 – 12
16 Remove the wiring harness connector P – 3 (1) from the solenoid switch (2).
17 Remove the flange nut (3) and battery connector P – 4 (4) from the solenoid switch.
18 Remove the starter motor from the vehicle.
Figure 6D1-2 – 13
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the starter motor is the reverse of the removal procedure noting the following:
1 Tighten all fasteners to the correct torque specification.
Solenoid switch connector P – 4 nut (B+)
torque specification ............................................10.0 Nm
Starter motor heat shield lower bolts
torque specification ............................................23.0 Nm
Starter motor heat shield upper screw
torque specification .....................................3.0 – 5.0 Nm
Starter motor mounting bolt
torque specification ............................................45.0 Nm
Knock sensor bolt
torque specification ............................................23.0 Nm
2 Check the starter motor operates correctly.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3640 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–32
7 Special Tools
Tool Number Illustration Description Tool Classification
KM609
Connector Test Adaptor Kit
Used when carrying out electrical
diagnostic circuit checks.
Previously released
Desirable
3588
(J39200)
Digital Multimeter
Must have at least 10 M Ω input
impedance and be capable of reading
frequencies.
Previously released.
Available
EN – 46114 Engine Lifting Brackets
Available
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3647 of 6020

Battery Page 6D1-3–7
3 Diagnosis
3.1 Diagnostic Procedures
Introduction
This test is used to aid in diagnosing faults with the vehicle where the battery seems to be at fault.
W ith the increased use of electronic sensors and computer control, the battery is much more than just a component used
to start a car. Low battery voltage can:
• affect the operation of the vehicle control modules and cause driveability problems, and
• cause the control modules to set diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
For example if a control module senses low battery voltage, it may increase fuel injector timing to increase engine rpm to
increase the generator output.
Therefore consider the state of charge of the battery any time a customer complains of a driveability related problem.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
1 Checks the operator understands the safety precautions for working with batteries.
2 Checks if the vehicle is fitted with a battery of the correct specification.
3 Checks if the battery appears serviceable by performing the battery inspection procedure.
4 Checks if the battery loses charge over an extended period. If so the likely problem is excess current draw while the vehicles ignition is in the off position.
5 Checks the state of charge of the battery.
6 Checks if the battery is capable of delivering the required load by performing the load test procedure.
Diagnostic Table Notes
1 For all wiring harness fault diagnosis, refer to 8A Electrical Body & Chassis.
2 For wiring harness repairs, refer to 8A Electrical Body & Chassis.
3 Refer to 6D1 – 3 Battery – V6.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Have you read and understood the safety precautions for working with
batteries? Go to Step 2 Refer to 2
Safety Precautions
2 Check the battery fitted is the correct specification recommended for
the vehicle? Refer to 5 Specifications.
Is the battery the correct specification? Go to Step 3 Replace the battery
with the correct
specification
3 Perform the battery inspection, refer to 3.2 Battery Inspection.
Does the battery appear serviceable? Go to Step 4 Replace the battery,
refer to 4.1
Battery
4 Does the customer complain the battery loses charge if the engine is
not started for an extended period? Preform the battery
current draw test, refer to 3.5
Battery
Current Draw Test Go to Step 5
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007