engine JAGUAR X308 1998 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1998, Model line: X308, Model: JAGUAR X308 1998 2.GPages: 2490, PDF Size: 69.81 MB
Page 43 of 2490
Safety Standard
Canister PurgeCANPControls pu
rging of the EVAP canister
Carbon dioxideCO2Colorless gas with
a density of a
pproximately 1.5 ti mes that of air
Carbon mon
oxide
COPoi
sonous gas produced as the re
sult of incomplete combustion
Case G
round
CSE GNDControl modu
le casing ground
Catal
ytic converter
In
-line exhaust system device used to reduce the level of engine exhaust
emissions
Ce
lsius
CSI ter
m for the Centigrade scale, with
freezing point at zero and boiling point
at 100В°
Central
Processor Unit
CPUTh
e section of a computer that contai
ns the arithmetic, logic and control
circuits. It performs arithm etic operations, controls instruction processing, and
provides timing signals and other housekeeping operations
Cl
osed Loop
CL
Cl
osed Loop System
CLSControl
system with one
or more feedback loops
Col
umn/Mirror Control
Module
C/MC
M
Control ModuleCMA
self-contained group of electrical/electronic components, designed as a
single replaceable un it, and controlling one or more processes
Controll
er Area Network
CANA
communication system which allows control modules to be linked together
in a network.
Crankshaft Posi
tion
Sensor
CKPSGenerates crankshaft positi on informa
tion in conjunct
ion with the CKPTR (also
generates speed information in certain applications)
Crankshaft Posi
tion
Timing Ring
CKPT
R
Toothe
d ring which
triggers the CKPS
Crankcase Ventila
tion
System
CVSys
tem which scavenges camshaft cover and crankcase emissions and feeds
them into the inlet manifold
Cubic ce nt
imeter
cm
3
Curb weightWe
ight of vehicle with fuel, lubrican
ts and coolant, but excluding driver,
passengers or payload
D
Dat
a Link Connector
DLCConne
ctor providing access and/or control of the vehicle information,
operating conditions, and diagnostic information
De
gree
deg, В°Angle or tempe
rature
D
epartment of
Transportation (US)
DO
T
D
epartment of Transport
(UK)
DTp
De
utsche In
stitut fГјr
Normung
DINGerman stand
ards regulation body
Di
agnostic Module
DMSuppl
emental Restraint System (non-c
ontrolling) module for diagnostics
overview
Di
agnostic Test Mode
DTMA le
vel of capability in an OBD system.
May include different functional states
to observe signals, a base level to re ad DTCs, a monitor level which includes
information on signal levels, bi-directional control with on /off board aids, and
the ability to interface with remote diagnosis
Diagnostic Trouble CodeDTCAn al
pha/numeric identifier for a fault
condition identified by the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) system
D
ial test indicator
DTIA mechan
ical measuring
instrument, with a rotary indicating pointer
connected to a linear operating probe
D
ifferential pressure
Pressure di
fference betwee
n two regions e.g. between intake manifold and
atmospheric pressures
D
ifferential Pressure
Feedback EGR
DP
FE
An
EGR system that monito
rs differential EGR pressure across a remote orifice
to control EGR flow
D
irect current
dcCurrent which f
lows in on
e direction only, though it may have appreciable
pulsations in its magnitude
Du
al linear switch
DLSJ
-gate switch connected to the TCM on SC vehicles
E
EGR
Temperature EGRT
Sensor
EGRTSens
ing EGR function based on temperature change
EGR Vacu
um Regulator
EVRControls EGR
flow by changi
ng vacuum to the EGR valve
EGR Valve
Position
EVPAn EGR
system that direct
ly monitors EGR valve position to control EGR flow
Electrically E
rasable
Programmable Read-Only
Memory
EEP
ROM
Page 44 of 2490
Electrically Programmable
R
ead-Only memory
EPROM
Ele
c
tronic Secondary Air
Injection
EAIRA p
ump-driven system for providing seco
ndary air using an electric air pump
Engine C
ontrol Module
ECM
End of dashEODR
e
ferring to a vehicle fascia, eg EOD air vent
Engine
C
oolant Level
ECL
Engine
C
oolant
Temperature
ECT
ECT Sen s
or
ECTSTherm
i
stor which provides engine coolant temperature signal to the ECM to
trigger enrichment circuits which increase injector 'on' time for cold start and
warm-up
Engine s
peed
RP
M
Environ m
ental Protection
Agency
EPA
Evaporative EmissionEVAPSy stem designed to prevent fu
el vapor from escaping into the atmosphere.
Typically includes a charcoal filled canister to absorb fuel vapor
Evaporative Emission
Control ValveEVAPP
Exhaust G
as Recirculation
EGRSys
t
em which reduces NOx emissions by adding exhaust gases to the
incoming fuel/air charge
Exhaus t G
as Recirculation
Solenoid Vacuum Valve
EGRS
Exhaus t G
as Recirculation
Temperature Sensor
EGRT Sen s
or
Exhaus
t G
as Recirculation
Valve
EGRV
F
F a
n Control
FCEngine
cooling fan control
F
e
deral Motor Vehicle
Safety Standard (US)
FMV S
S
Fi
gur
e
Fi
g.Illustrati
on reference
Flash
E
lectrically Erasable
Programmable Read-Only
Memory
FEE PR
OM
Flash
E
rasable
Programmable Read-Only
Memory
FEP R
OM
Flywhee
l
Sensor
CKFSSens
or moun
ted so as to be
triggered by each flywheel ring gear tooth to give
an engine speed signal
Fue l
Injectors
FISol
e
noid operated devices that spray a metered quantity of fuel into the inlet
ports
F u
el Pressure Regulator
Control
FP RCControls fuel pressure regu l
ator; used primarily to
give extra fuel at cold
start-up
Fue l
Pump
FP
Fue
l
Pump Monitor
FP
MMonitors operation of fuel pump
Fue l
Pump Relay
FP
R
Fu
el rich/lean
Q
u
alitative evaluation
of air/fuel ratio based on a ratio known as
stoichiometry, or 14.7:1 (Lambda)
F u
ll Scale Deflection
FSDTh
e
maximum indication point on
an analogue meter or gauge
G
Gene
rator
GENRot
a
ting machine which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy
G
r
amme centimeter
gcm
Gramm
e
(force)
gf
Gramm
e
(mass)
g
GroundGNDEle
c
trical conductor used
as a common return for an electrical circuit or
circuits, and with a relative zero potential
H
Hard f a
ult
A
fau
lt currently present in the system
HeadlampHL
Heat
ed Oxygen
Sensor
HO2SElectrically
h
eated oxygen sensor which induces fueling corrections
Hertz (frequency)HzFrequ
e
ncy, one cycle per second
High
Moun
ted Stoplamp
HMSL
Page 45 of 2490
High
tension (electrical)
ht
Hourh
Hydro
carbon
HC
I
Idl
e Air Control
IACEl
ectrical control of throttle bypass air
Idl
e Air Control Valve
IACVStepper motor dri
ven device which vari
es the volume of air by-passing the
throttle to maintain the programmed idle speed
Ignitionign
Ignition am
plifier
IAD
evice which amplifies the i
gniti
on system output
Ignition groundIGN GND
In
ertia Fuel Shut-off
IFSAn
inertia system that shuts off the fuel supply when activated by pre-
determined force limits brough t about by (e.g.) collision
In
ertia Fuel Shut-off
Switch
IFSSShut
s down fuel and ignition systems in the event of a vehicle impact
Inta
ke air
Air drawn t
hrough a cleaner and distri
buted to each cylinder for use in
combustion
InputI/PAn
electrical input signal to a controlling device
Inta
ke Air Temperature
IATTem
perature of intake air
Inta
ke Air Temperature
Sensor
IATSDe
vice used to measure IAT
Inta
ke Air Temperature
Sensor Ignition
IATSITherm
istor which signals the ECM to retard
the ignition timing in response to
high inlet air temperatures
Inta
ke Air Temperature
Sensor Injection
IATSFTher
mistor which inputs air density information to the ECM
Internal diameteri.
dia
Inte
rnational Standards
Organization
ISO
K
Kilogramme (mass)kg
Kilogram
me (force)
kg
f
Ki
logramme force per
square centimeter
kg
f/cm2
Kilom
eter
km
Ki
lometer per hour
km
/h
Kilopasc
al
kP
a
KilovoltkV
Knock
Sensor
KSSens
or which detects the onset of detonation, and signals the ECM to retard
the ignition
L
Le
ft-hand
LH
Left-hand drive veh
icle
LHD
Le
ft-hand thread
LH Thd
Ligh
t Emitting Diode
LEDLigh
t-emitting semiconductor diode used
in alphanumeric displays and as an
indicator lamp
Liqu
id Crystal Display
LCDOp
tical digital display system, applied voltage to which varies the way the
crystals reflect light, thereby modifying the display
LiterL
Low ten
sion
ltPrim
ary circuit of the ignition system, linking the battery to the primary
winding in the ignition coil
M
Malfu
nction Indicator
Lamp
MILA
required on-board indicator to aler
t the driver of an emission related
malfunction
Mani
fold Absolute
Pressure
MAPAbsolute pressure o
f the intake manifold air
Mani
fold Absolute
Pressure Sensor
MAPSSensor loca
ted in the ECM and
ported to the intake manifold
Manifol
d Surface
Temperature
MST
Mass Ai
r Flow
MAFSy
stem which provides inform
ation on the mass flow rate of the intake air to
the engine
Mass Ai
r Flow Sensor
MAFSHot-wi
re sensor which monitors air flow
into the intake manifold for fueling
and ignition control
Maxim
um
max.
Page 47 of 2490
Mem
ory
Pulse Width ModulationPW
M
A
method of control in an electronic co
ntrol system in which the duration of
pulses in a pulse train is proportional to the amplitude of the modulating
signal
R
Ran
dom Access Memory
RAMF
ast access memory store which is accessible for entry or extraction of data
Re
ad-Only Memory
RO
M
F
ast access memory in which data
is fixed and may not be changed
Re
servoir
RESContaine
r, usually for oils,
coolants or hydraulic fluids
Re
turn
RTNA
dedicated sensor ground circuit
R
evolutions Per Minute
RP
M
Shaft speed o
f a device, us
ually an engine or motor
R
ight-hand
RH
Right-hand drive veh
icle
RHD
S
Scan T
ool
STDe
vice that interfaces with and comm
unicates information on a data link
Se
at Control Module
SCMModule
controlling the seat motor systems (not electric raise/lower-only
seats)
Secon
dary Air
Air pro
vided to the exhaust system
Secon
dary Air Injection
AIRSy
stem used for a period of time each
time the engine is started, unless
certain temperature criter ia are met. Pumps air directly into the exhaust
system which generates extra heat and reduces the time taken for the
catalytic converters to reach operating temperature
Secon
dary Air Injection
Bypass
AIRBVents secon
dary air to atmosphere
Secon
dary Air Injection
Check Valve
AIRCValve wh
ich prevents back-flow of exhaust gas to the AIR system when the
system is inoperative
Secon
dary Air Injection
Diverter
AIRDD
iverts secondary air to either
the catalyst or exhaust manifold
Secon
dary Air Injection
Magnetic Clutch
AIRP
C
Clu
tch mounted on the AIRP drive shaft
Secon
dary Air Injection
Pump
AIRPMe
chanically driven rotary vane
pump, driven through the AIRPC
Secon
dary Air Injection
Relay
AIRRCont
rols the injection of air into the exhaust system
Secon
dary Air Injection
Switchin
g Va
lve
AIRSV
acuum operated valve backing-up the AIRC
Secu
rity and Locking
Control Module
SLCMModul
e controlling the vehicle's security and closure-locking functions
SensorSGeneri
c name for a device
that senses either the absolute value or a change
in a physical quantity su ch as temperature, pressure or flow rate, and
converts that change into an electrical quantity signal
Servic
e Repair Operation
(number)
SRONu
mber generated by Jaguar Methods
and Techniques system which relates
to the time allowed to complete a repair operation. Further information on the
system can be found in the separate Jaguar Publications (for each model
range) entitled 'Repair Operation Times'
Shif
t signal
SDA
shift process signal to the TCM on SC vehicles
Shif
t Solenoid
SSControls shi
fting in an automatic transmission
Si
gnal return
SIG RTN
Slidin
g Roof Control
Module
SRCM
Society of Automotive
Engineers
SAE
Speed
Control Control
Module
SCCMModule con
trolling Speed Control System
Square c
entimeter
cm
2
Stan
dard
std
Stan
dard Corporate
Protocol
SCPA
high-speed, serial communications system linking all body system control
modules. Control messages and data ar e passed between modules at up to
786 messages per second
SuperchargerSCAn in
take system which utilizes a supercharger (mechanically driven device
that pressurizes intake air, thereby in creasing density of charge air and the
consequent power output from a given displacement)
Supercharger
Bypass
SCB
SwitchSW
T
Page 48 of 2490
Tacho
meter
TACHA
ci
rcuit that provides input for
an electronic tachometer display
Thermal Vacuu
m Valve
TVVControls vacuum l
e
vels or
routing based on temperature
Throttle
Body
TBDe
vi
ce containing the throttle
Throttl
e
Position
TP
Throttl
e
Position Sensor
TPSInterprets throttl
e
position and movement to iden tify idle, acceleration and
full-power demands
Top Dead CenterTDC
Torque Converter C
lutch
TCC
To
tal
indicator reading
TIRThe t
o
tal indicated movement on a DTI with the test piece rotated through
360В°
Transm
ission Control
Module
TCMControls
the shifting pattern
of the (automatic) transmission
Transm
ission Control
Switch
TCSModifi es
the operation of electronically controlled transmissions
Transmission Oil
TemperatureTOTIndi
cat
es temperature of transmission fluid
Transmission RangeTRThe ran
g
e in which the transmission is operating
Transmission Spe
e
d
Sensor
TSSIndi cat
es rotational speed of transmission output shaft or turbine shaft
V
Vacuu
m
Solenoid Valve
VSVVacuu
m
operated valve used in the speed control system
Vacuu
m
Solenoid Valve
(atm)
VSV VAVacuu m
atmospheric valve used in the speed control system
Vacuu
m
Solenoid Valve
(rel)
VSV VRVacuu m
release valve used in the speed control system
Vacuu
m
Solenoid Valve
(vac)
VSV VVVacuu m
valve used in the speed control system
Variable Valve TimingVVTA
s
ystem by which the relationship of the crankshaft and camshaft may be
altered during engine running
Vehi cl
e Battery Adapter
VBAProvide
s
electrical power to the PDU
and supplies a battery reference level
Vehicl
e Condition Monitor
VCMInst
rum
ent panel display which warns of faults
Ve
hic
le Emission Control
Information Label
VECI Label
Vehi cl
e Identification
Number
VINN u
mber assigned to the vehicle by the manufacturer, primarily for licensing
and identification purposes
Vehi cl
e Interface Adapter
VIAExtends the
PDU ca
pability and provid
es a parallel interface to vehicle
harnesses and ECMs
Vehicle Spe e
d Sensor
VSSSens
or which provides ve
hicle speed information
Viscosity In
dexVI
Voltage RegulatorVRDe
vice which regulates the variable output voltage of a generator
W
Wat
tWSI unit of power (1 hp = 7
45.7 watts)
W
i
de Open Throttle
WO
TFu
ll throttle position
Page 49 of 2490
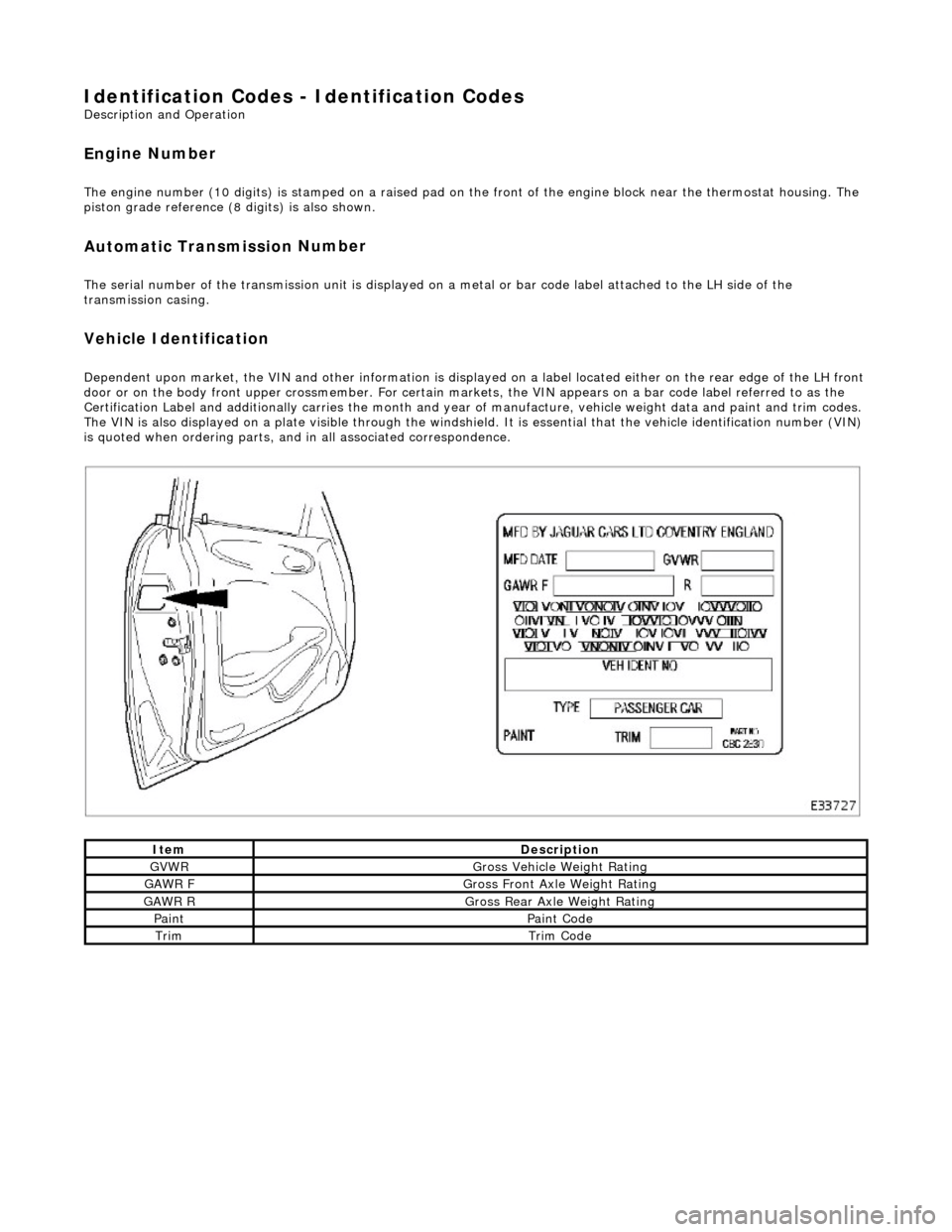
Identification
Codes -
Identification Codes
Descr
iption and Operation
En
gine Number
The en
gine number (10 digits) is stamped on a raised pad on th
e front of the engine block near the thermostat housing. The
piston grade reference (8 digits) is also shown.
Automatic Transmission
Number
The
serial number of the transmission unit is displayed on
a metal or bar code label attached to the LH side of the
transmission casing.
Veh
icle Identification
Dependent
upon market, the VIN and other info
rmation is displayed on a label located ei ther on the rear edge of the LH front
door or on the body front upper crossmember. For certain mark ets, the VIN appears on a bar code label referred to as the
Certification Label and additionally carries the month and year of manufacture, vehicle weight data and paint and trim codes.
The VIN is also displayed on a plate visible through the windshie ld. It is essential that the vehicle identification number (VIN)
is quoted when ordering parts, and in all associated correspondence.
ItemDe
scription
GVW
R
G
ross Vehicle Weight Rating
GAW
R F
Gros
s Front Axle Weight Rating
GAW
R R
Gros
s Rear Axle Weight Rating
Pai
nt
Pai
nt Code
TrimTrim
Code
Page 50 of 2490
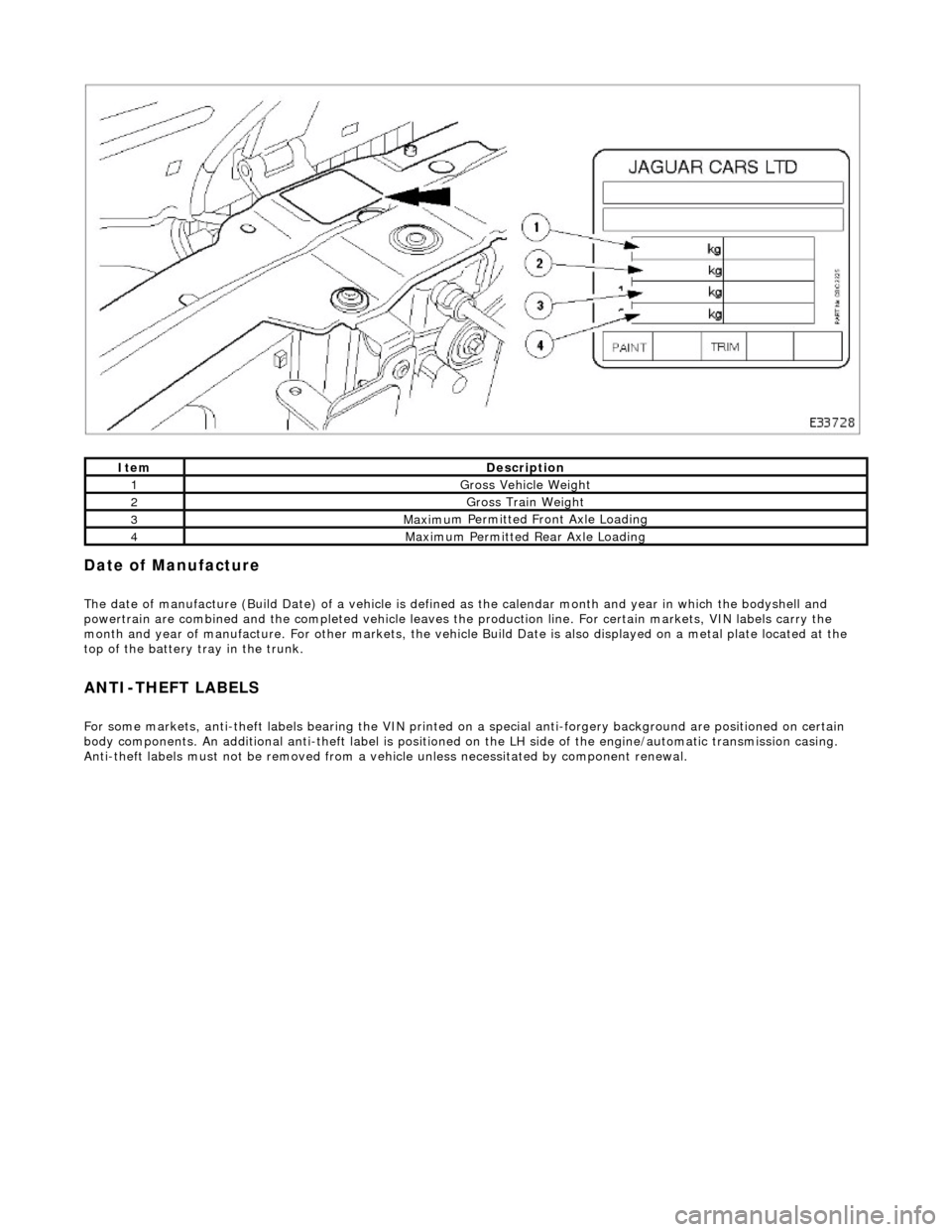
Date of
Manufacture
T
h
e date of manufacture (Build Date) of a vehicle is define
d as the calendar month and year in which the bodyshell and
powertrain are combined and the completed vehicle leaves the production line. For certain markets, VIN labels carry the
month and year of manufacture. For other markets, the vehicle Build Date is also displayed on a metal plate located at the
top of the battery tray in the trunk.
ANTI-T
HEFT LABELS
F
or
some markets, anti-theft labels bearing the VIN printed on
a special anti-forgery background are positioned on certain
body components. An additional anti-theft label is positioned on the LH side of the engine/automatic transmission casing.
Anti-theft labels must not be removed from a vehicle unless necessitated by component renewal.
ItemDe scrip
tion
1Gross Vehic
l
e Weight
2Gross Trai
n W
eight
3Maxim
u
m Permitted Front Axle Loading
4Maxim
u
m Permitted Rear Axle Loading
Page 54 of 2490

Wh en t
he vehicle is being reco
vered by rear suspended tow:
пЃ¬The ignition key must be remo ved from the ig
nition switch to lock the stee
ring with the front wheels facing straight
ahead.
пЃ¬The re ar
wheels must be
correctly positioned in the lifting cradle and securely tied down.
Em
ergency Towing
WARNING: IF THE
ENGINE IS NOT
RUNNING, THE STEERING WILL BECOME HEAVY AND THE FORCE NECESSARY TO
EFFECTIVELY APPLY THE BRAKES WILL BE GREATLY INCREASED.
• CAUTIONS:
A vehicle with a defective transmission must be towed by rear suspended tow.
The vehicle towing point is not suit able for use with a solid tow-bar.
Do not use the crossbeam tie bar as a towing location.
When the vehicle is being towed on its own wheels:
пЃ¬Loc a
l regulations for the towing of ve
hicles must be followed. In some co untries the registration number of the
towing vehicle and an 'On Tow' sign or warning triangle must be displayed at the rear of the towed vehicle.
пЃ¬The gear s
elector lever
must be in Neutral.
пЃ¬The
ignition switch must be in positi
on II to release the steering lock and make the direction indicators, horn and
stop lamps operate.
пЃ¬A di
stance of 0.8 km (0.5 mi
le) must not be exceeded.
пЃ¬A spe
ed of 48 km/h (30 mph) must not be exceeded.
пЃ¬The tow rope must be attached using th
e towi
ng location provided; refer to Front Towing Point in this section.
Rear Su
spended
Tow
Page 56 of 2490
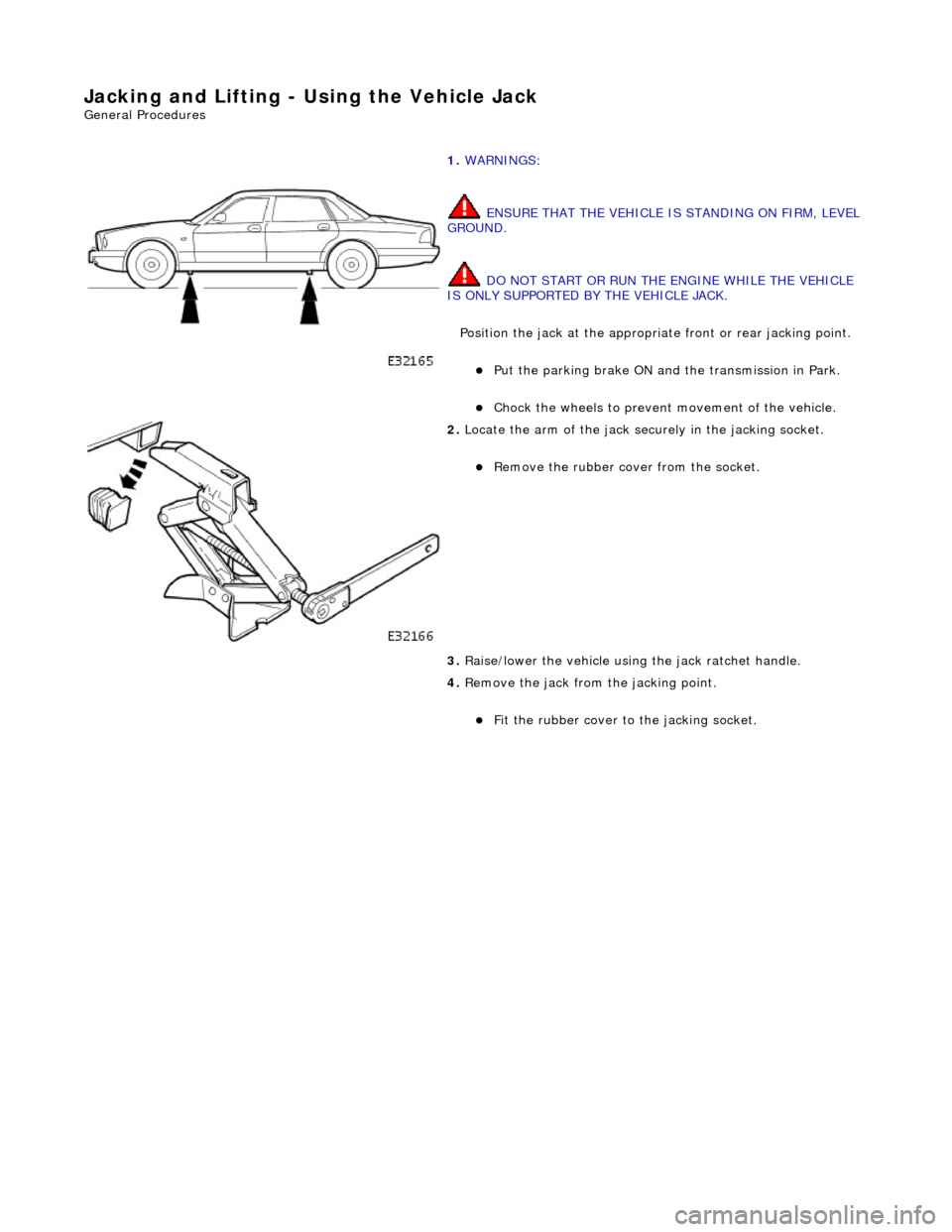
Jacking and Lifting - Using the Vehicle Jack
Gene
ral Procedures
1.
WARN
INGS:
ENSURE THAT THE VEHICLE IS STANDING ON FIRM, LEVEL
GROUND.
DO NOT START OR RUN THE ENGINE WHILE THE VEHICLE
IS ONLY SUPPORTED BY THE VEHICLE JACK.
Position the jack at the appropri ate front or rear jacking point.
пЃ¬Put the parkin
g brake ON and
the transmission in Park.
пЃ¬Chock the wh
eels to prevent movement of the vehicle.
2.
Locat e
the arm of the jack securely in the jacking socket.
пЃ¬R
e
move the rubber cover from the socket.
3. Raise/lower the vehicle using the jack ratchet handle.
4. Remove the jack from the jacking point.
пЃ¬Fi
t the rubber cover to the jacking socket.
Page 67 of 2490
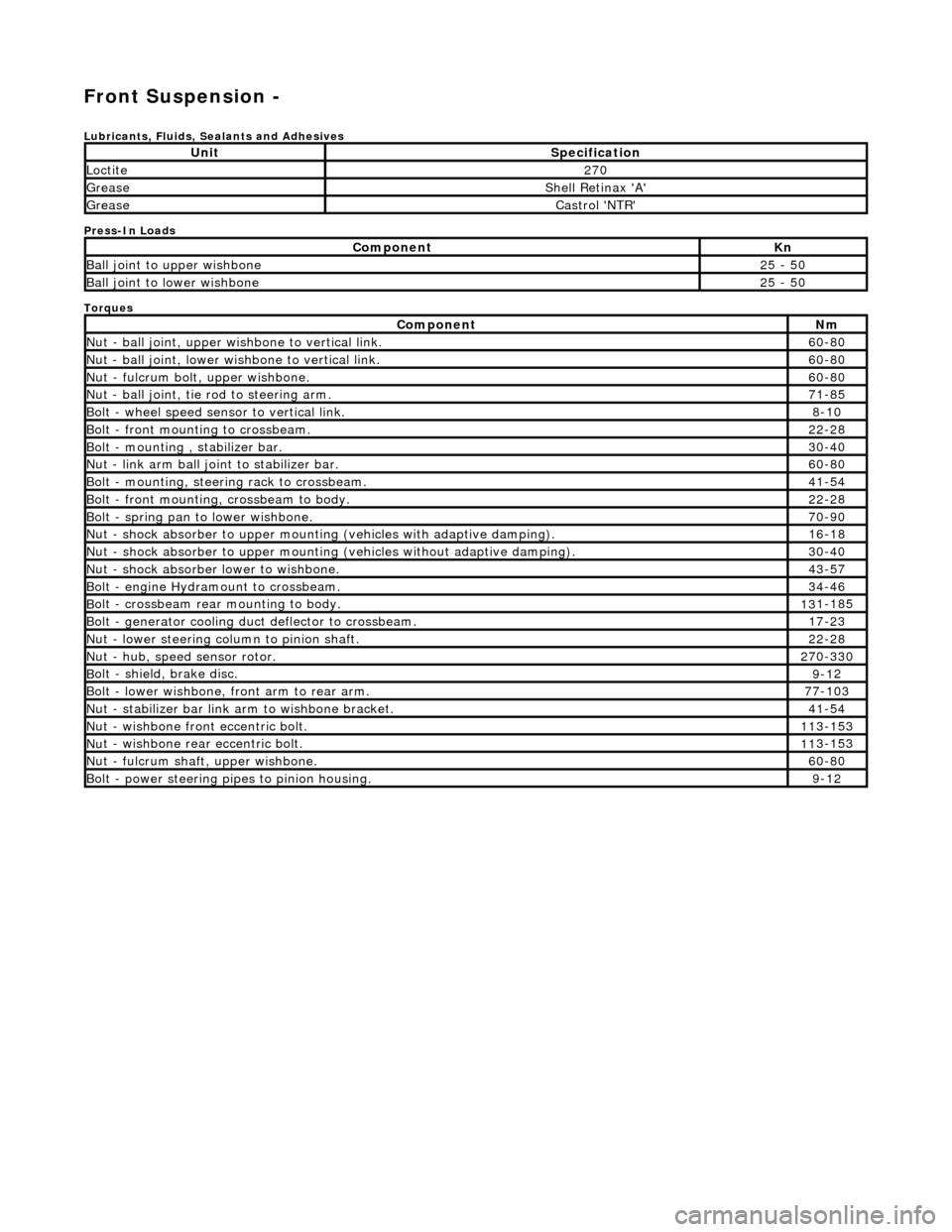
Front Suspension -
Lubri
cants, Fluids, Sealants and Adhesives
Press-In Loads
Torques
UnitS
pecification
Loctite27
0
Greas
e
Shell Retin
ax 'A'
Greas
e
Castro
l 'NTR'
Com
ponent
Kn
Ball join
t to upper wishbone
25
- 50
B
all joint to lower wishbone
25
- 50
Com
ponent
Nm
N
ut - ball joint, upper wishbone to vertical link.
60
-80
N
ut - ball joint, lower wishbone to vertical link.
60
-80
Nu
t - fulcrum bolt, upper wishbone.
60
-80
N
ut - ball joint, tie rod to steering arm.
71
-85
Bol
t - wheel speed sensor to vertical link.
8-1
0
Bol
t - front mounting to crossbeam.
22
-28
Bolt
- mounting , stabilizer bar.
30
-40
N
ut - link arm ball joint to stabilizer bar.
60
-80
Bolt
- mounting, steering rack to crossbeam.
41
-54
B
olt - front mounting, crossbeam to body.
22
-28
Bol
t - spring pan to lower wishbone.
70
-90
N
ut - shock absorber to upper mounting
(vehicles with adaptive damping).
16
-18
Nu
t - shock absorber to upper mounting (vehicles without adaptive damping).
30
-40
N
ut - shock absorber lower to wishbone.
43
-57
B
olt - engine Hydramount to crossbeam.
34
-46
B
olt - crossbeam rear mounting to body.
13
1-185
Bol
t - generator cooling du
ct deflector to crossbeam.
17
-23
N
ut - lower steering column to pinion shaft.
22
-28
N
ut - hub, speed sensor rotor.
27
0-330
B
olt - shield, brake disc.
9-1
2
Bol
t - lower wishbone, front arm to rear arm.
77
-103
Nu
t - stabilizer bar link arm to wishbone bracket.
41
-54
N
ut - wishbone front
eccentric bolt.
11
3-153
Nu
t - wishbone rear
eccentric bolt.
11
3-153
N
ut - fulcrum shaft, upper wishbone.
60
-80
Bolt -
power steering pi
pes to pinion housing.
9-1
2