Connector JAGUAR X308 1998 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1998, Model line: X308, Model: JAGUAR X308 1998 2.GPages: 2490, PDF Size: 69.81 MB
Page 204 of 2490
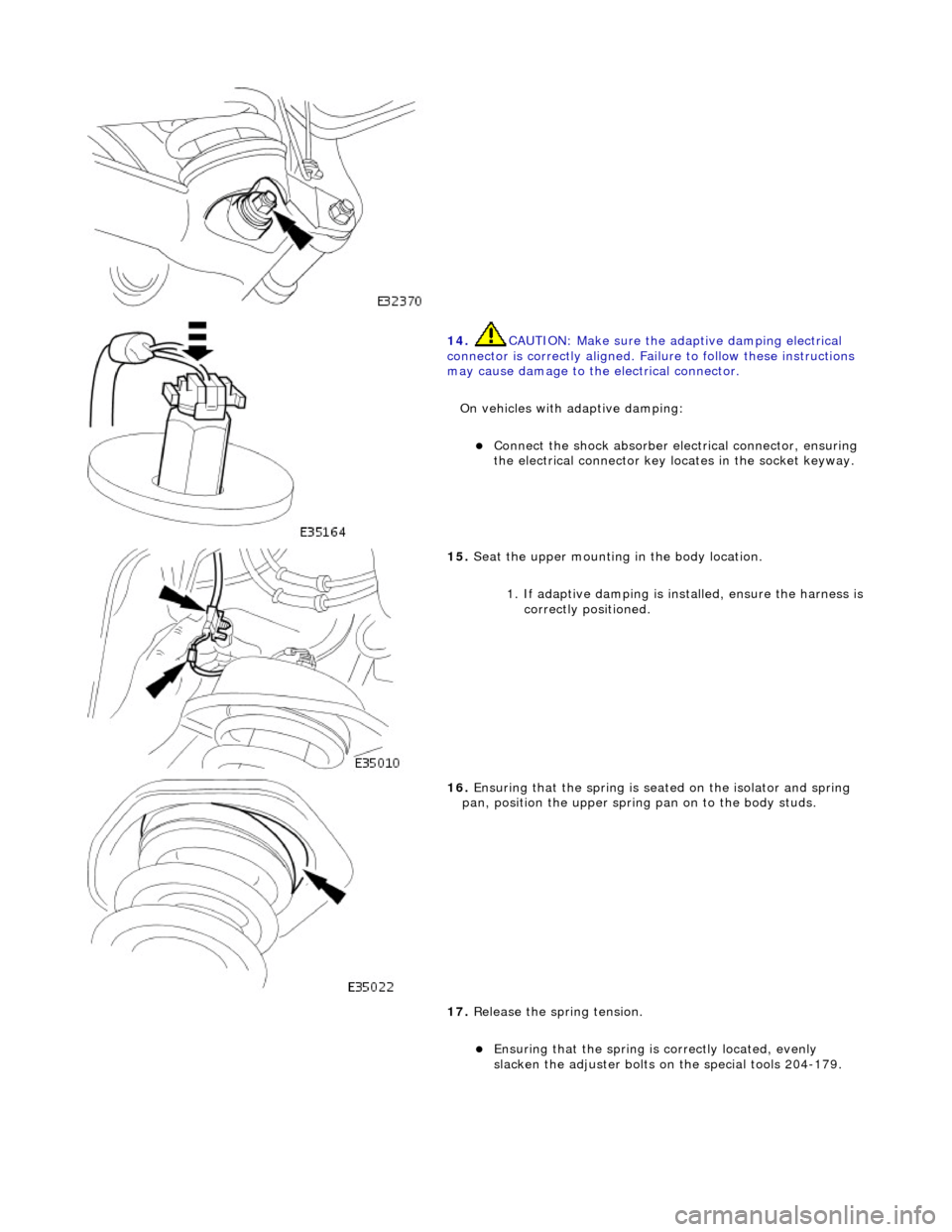
14. CAUTI
ON: Make sure the adaptive damping electrical
connector is correctly aligned. Failu re to follow these instructions
may cause damage to the electrical connector.
On vehicles with adaptive damping:
пЃ¬Conne ct
the shock absorber elec
trical connector, ensuring
the electrical connector key locates in the socket keyway.
15 . Seat
the upper mounting in the body location.
1. If adaptive damping is installed, ensure the harness is
correctly positioned.
16 . Ensuri
ng that the spri
ng is seated on the isolator and spring
pan, position the u pper spring pan on to the body studs.
17. Release the spring tension.
пЃ¬Ensuring that the spri
ng is
correctly located, evenly
slacken the adjuster bolts on the special tools 204-179.
Page 206 of 2490
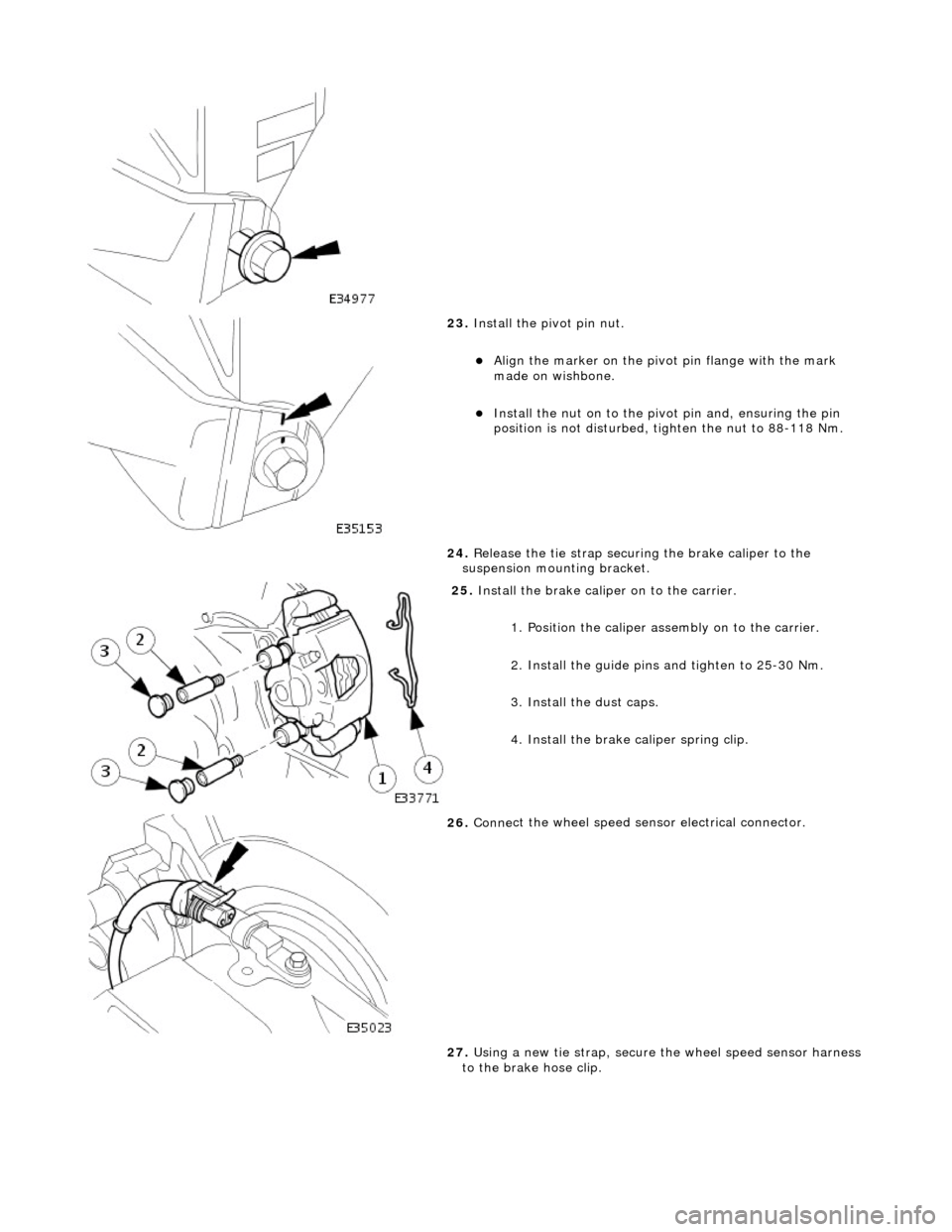
23. Inst
all the pivot pin nut.
пЃ¬Ali
g
n the marker on the pivo
t pin flange with the mark
made on wishbone.
пЃ¬Inst al
l the nut on to the pivot pin and, ensuring the pin
position is not dist urbed, tighten the nut to 88-118 Nm.
24. Release the tie strap securing the brake caliper to the
suspension mounting bracket.
25 . Install
the brake caliper on to the carrier.
1. Position the caliper asse mbly on to the carrier.
2. Install the guide pins and tighten to 25-30 Nm.
3. Install the dust caps.
4. Install the brake caliper spring clip.
26 . Conne
ct the wheel speed sensor electrical connector.
27. Using a new tie strap, secure the wheel speed sensor harness
to the brake hose clip.
Page 239 of 2490
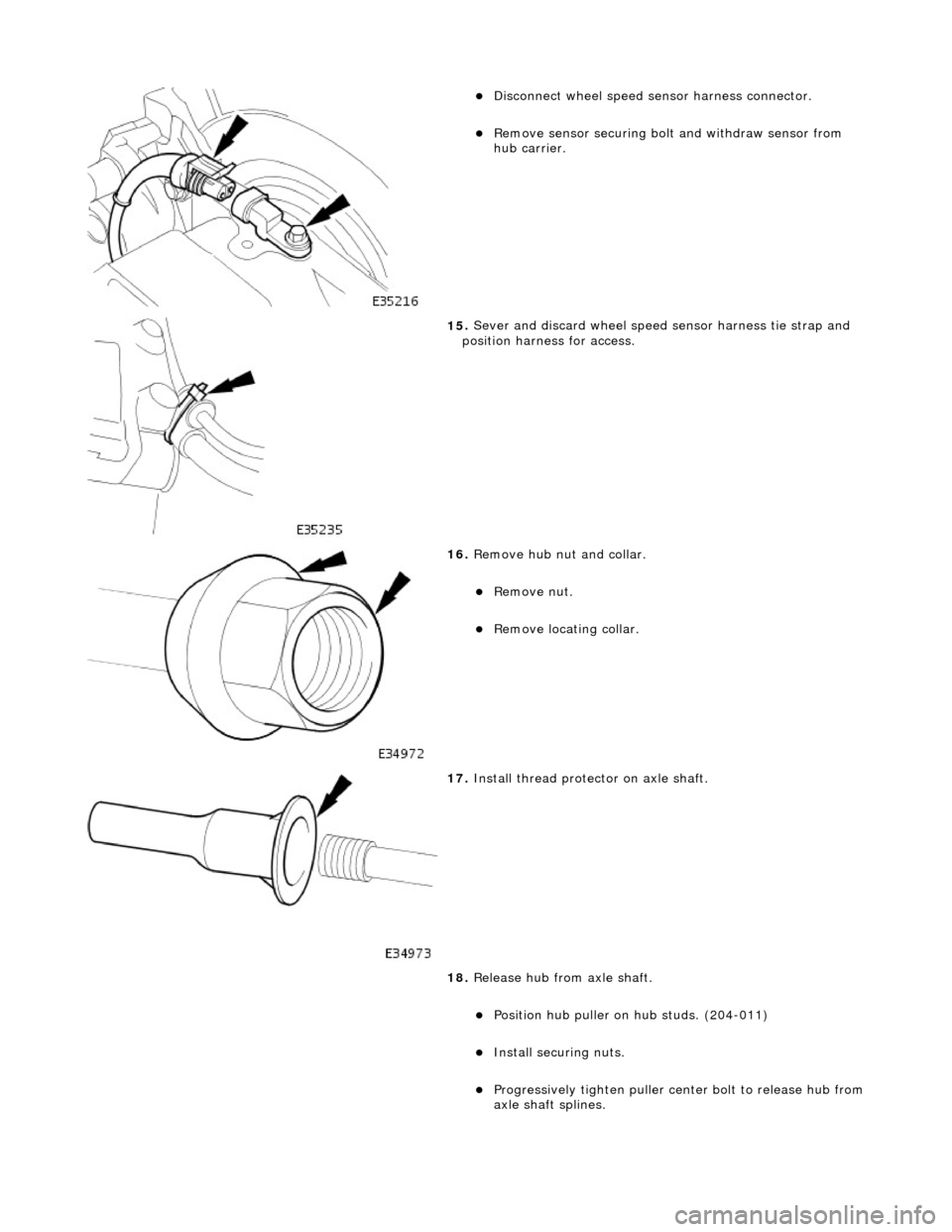
пЃ¬Disc
onnect wheel speed sensor harness connector.
пЃ¬R
emove sensor securing bolt
and withdraw sensor from
hub carrier.
15
.
Sever and discard wheel speed sensor harness tie strap and
position harness for access.
16
.
Remove hub nut and collar.
пЃ¬Re
move nut.
пЃ¬Re
move locating collar.
17
.
Install thread protec tor on axle shaft.
18. Release hub from axle shaft.
пЃ¬Position hu
b puller on hub studs. (204-011)
пЃ¬Inst
all securing nuts.
пЃ¬Progres
sively tighten
puller center bolt to release hub from
axle shaft splines.
Page 250 of 2490
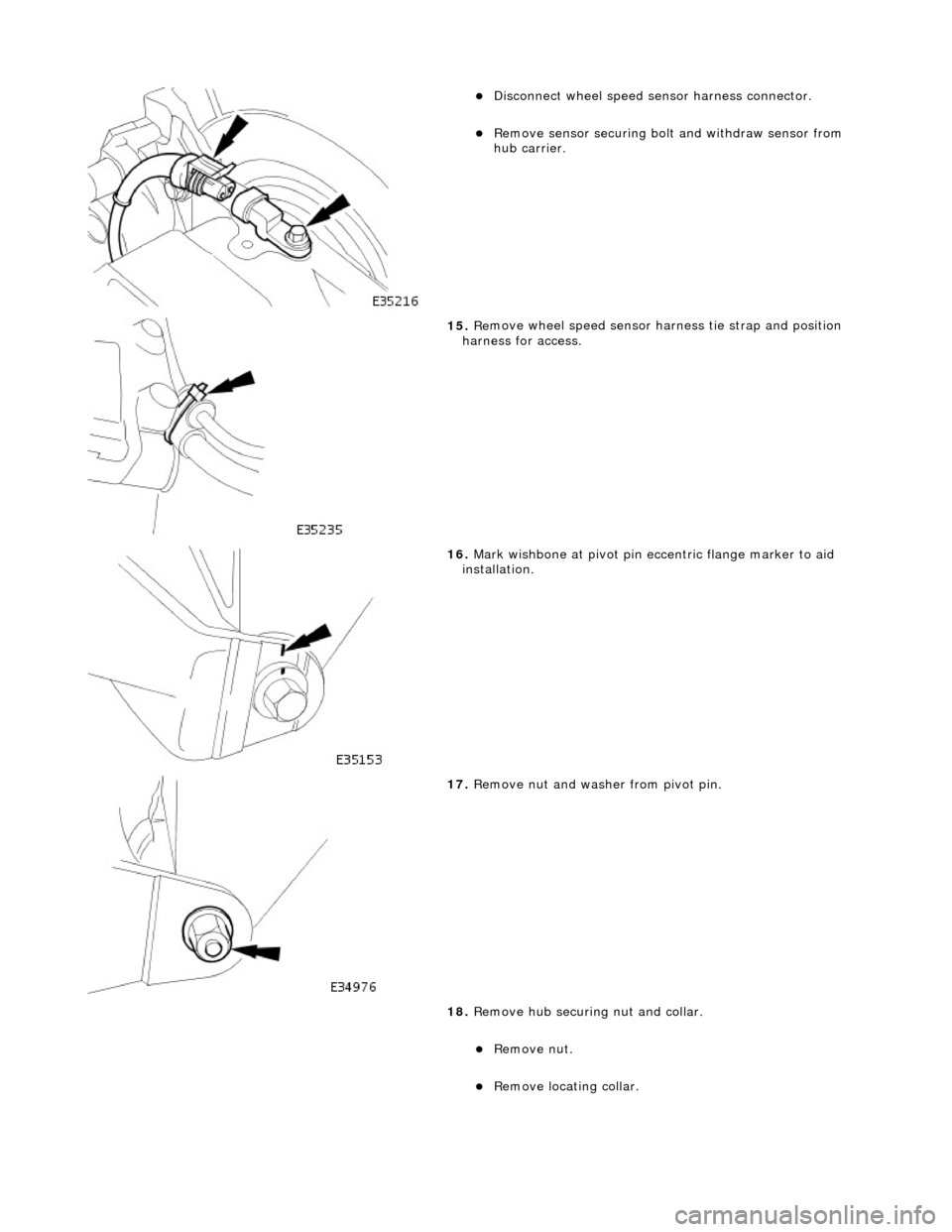
пЃ¬Disconne
ct wheel speed sensor harness connector.
пЃ¬Re
move sensor securing bolt
and withdraw sensor from
hub carrier.
15 . Re
move wheel speed sensor harness tie strap and position
harness for access.
16 . Mark wi
shbone at pivot pin eccentric flange marker to aid
installation.
17 . Remove n
ut and washer from pivot pin.
18. Remove hub securing nut and collar.
пЃ¬Remo
ve nut.
пЃ¬Remove l
ocating collar.
Page 274 of 2490
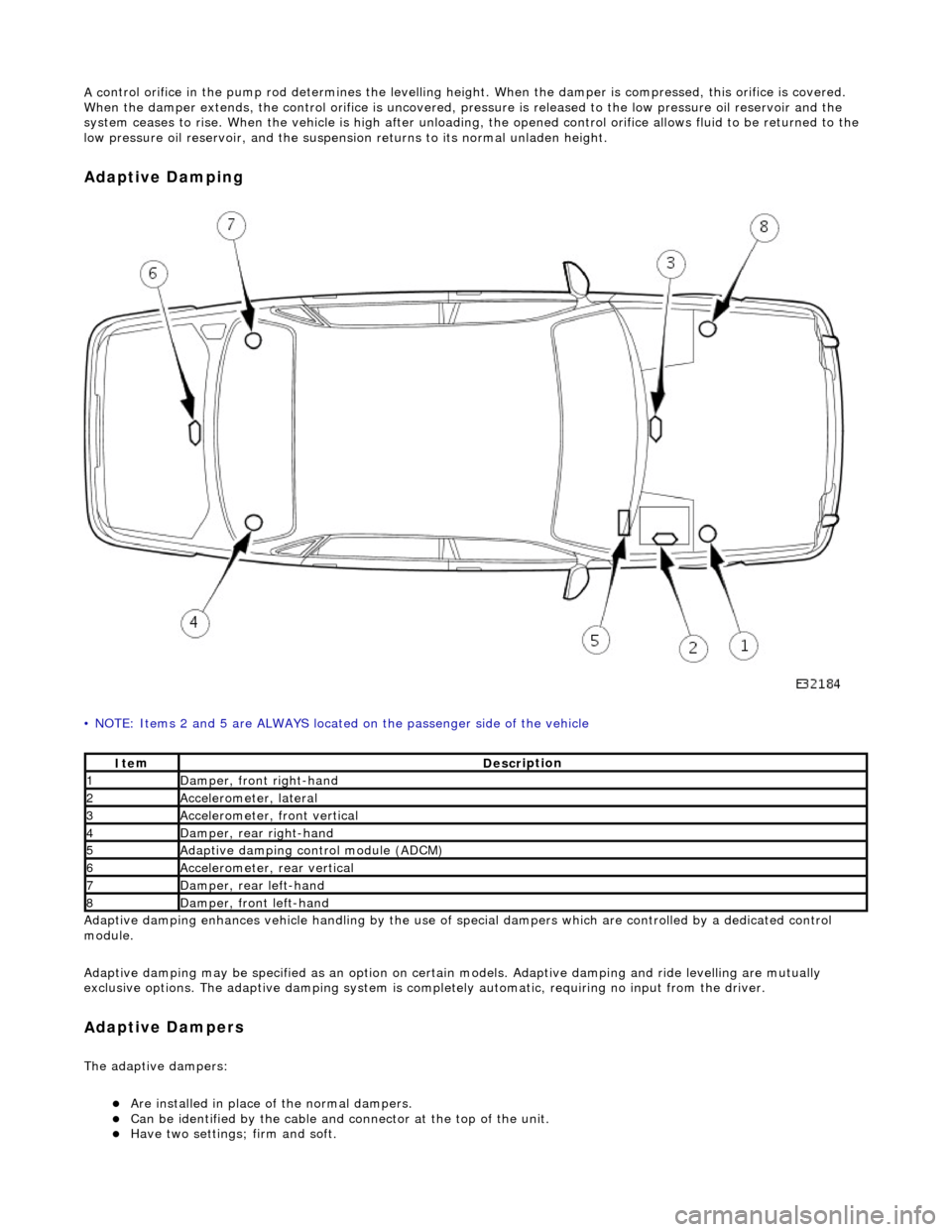
A c
ontrol orifice in the pump rod determines the levelling height. When the damper is compressed, this orifice is covered.
When the damper extends, the control orif ice is uncovered, pressure is released to the low pressure oil reservoir and the
system ceases to rise. When the vehicle is high after unloading, the opened control or ifice allows fluid to be returned to the
low pressure oil reservoir, and the suspensi on returns to its normal unladen height.
Ad
aptive Damping
•
NOTE: Items 2 and 5 are ALWAYS located
on the passenger side of the vehicle
Adaptive damping enhances vehicle handli ng by the use of special dampers which are controlled by a dedicated control
module.
Adaptive damping may be specified as an option on certai n models. Adaptive damping and ride levelling are mutually
exclusive options. The adaptive damping system is completely automatic, requiring no input from the driver.
A d
aptive Dampers
The adaptiv
e dampers:
пЃ¬Are inst
alled in place of the normal dampers.
пЃ¬Can be identified
by the cable and connector at the top of the unit.
пЃ¬Have two settings; fi
rm and so
ft.
It
e
m
De
scr
iption
1Dam
p
er, front right-hand
2Accel
e
rometer, lateral
3Accel
e
rometer,
front vertical
4D
a
mper, rear right-hand
5Adaptive dampin
g control module (A
DCM)
6Accel
e
rometer, rear vertical
7D
amper, rear l
eft-hand
8Dam
p
er, front left-hand
Page 275 of 2490
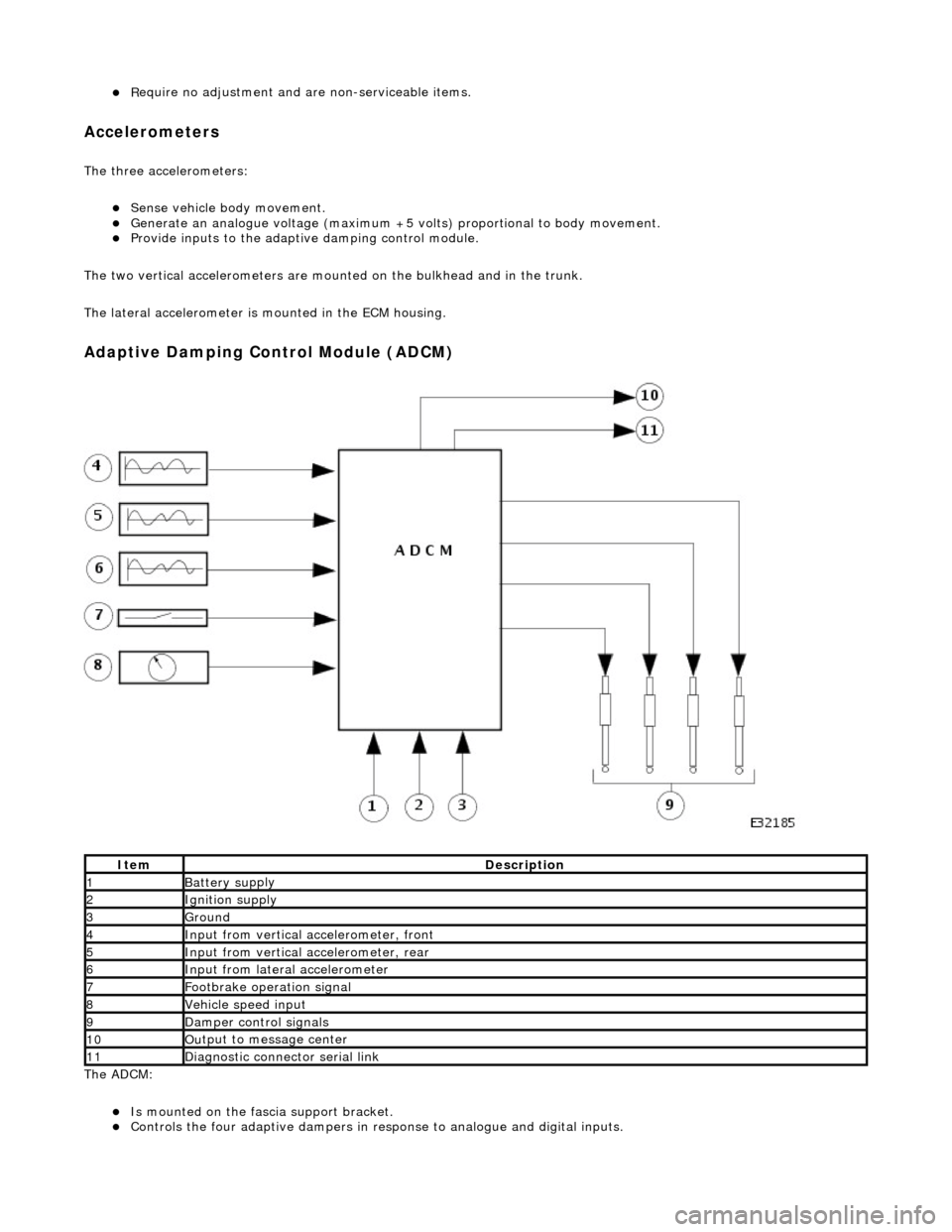
пЃ¬R
equire no adjustment and are non-serviceable items.
Accelerometers
The three accelerometers:
пЃ¬Sense veh
icle body movement.
пЃ¬Gen
erate an analogue voltag
e (maximum +5 volts) proportional to body movement.
пЃ¬Pr
ovide inputs to the adapti
ve damping control module.
The two vertical acce lerometers are mounted on the bulkhead and in the trunk.
The lateral accelerometer is mounted in the ECM housing.
Ada
ptive Damping Control Module (ADCM)
The ADCM
:
пЃ¬Is
mounted on the fascia support bracket.
пЃ¬Controls the four adaptiv
e dampers in re
sponse to analogue and digital inputs.
It
em
De
scription
1Battery su
pply
2Ignition su
pply
3Ground
4Input from verti
cal accelerometer, front
5Input from verti
cal accelerometer, rear
6Input from later
al accelerometer
7F
ootbrake operation signal
8Vehi
cle speed input
9D
amper control signals
10Ou
tput to message center
11D
iagnostic connector serial link
Page 276 of 2490
пЃ¬Is hard-wi
red to the instrume
nt cluster message center.
пЃ¬Is hard
-wired to the J1962 diagnostic connector.
Op
era
tion
Th
e
system selects the soft or
firm damper setting according to the current ro ad and driving conditions, to optimise vehicle
ride and handling.
With the vehicle stationary, the dampers are in the firm setting, but will normally switch to the soft setting when the vehicle
exceeds 8 km/h (5 mile/h); all dampers are switched simultaneously.
Sudden movement of the vehicle body, in response to road inputs, is detected by the vertical accelerometers, and the ADCM
switches the dampers to the firm setting to give improved damping of the resultant oscillations.
When cornering forces are detected by th e lateral accelerometer, the ADCM switches the dampers to the firm setting to
reduce the roll rate an d improve wheel control.
After the event has passed, the dampers revert to the soft setting.
When the footbrake is applied, the ADCM re ceives a signal and calculates the rate of vehicle deceleration. If the deceleration
rate is greater than a certain threshold, the dampers are switched to the firm setting to reduce the pitch rate and improve
wheel control.
If a system failure occurs, the ADCM grounds the output line to the instrument cluster message center, which displays a
text warning SUSPENSION FAULT and illuminates the amber warning lamp. Under fault conditions the system always fails to
the firm setting, so that the vehicle will be safe to drive un der all road and driving conditions.
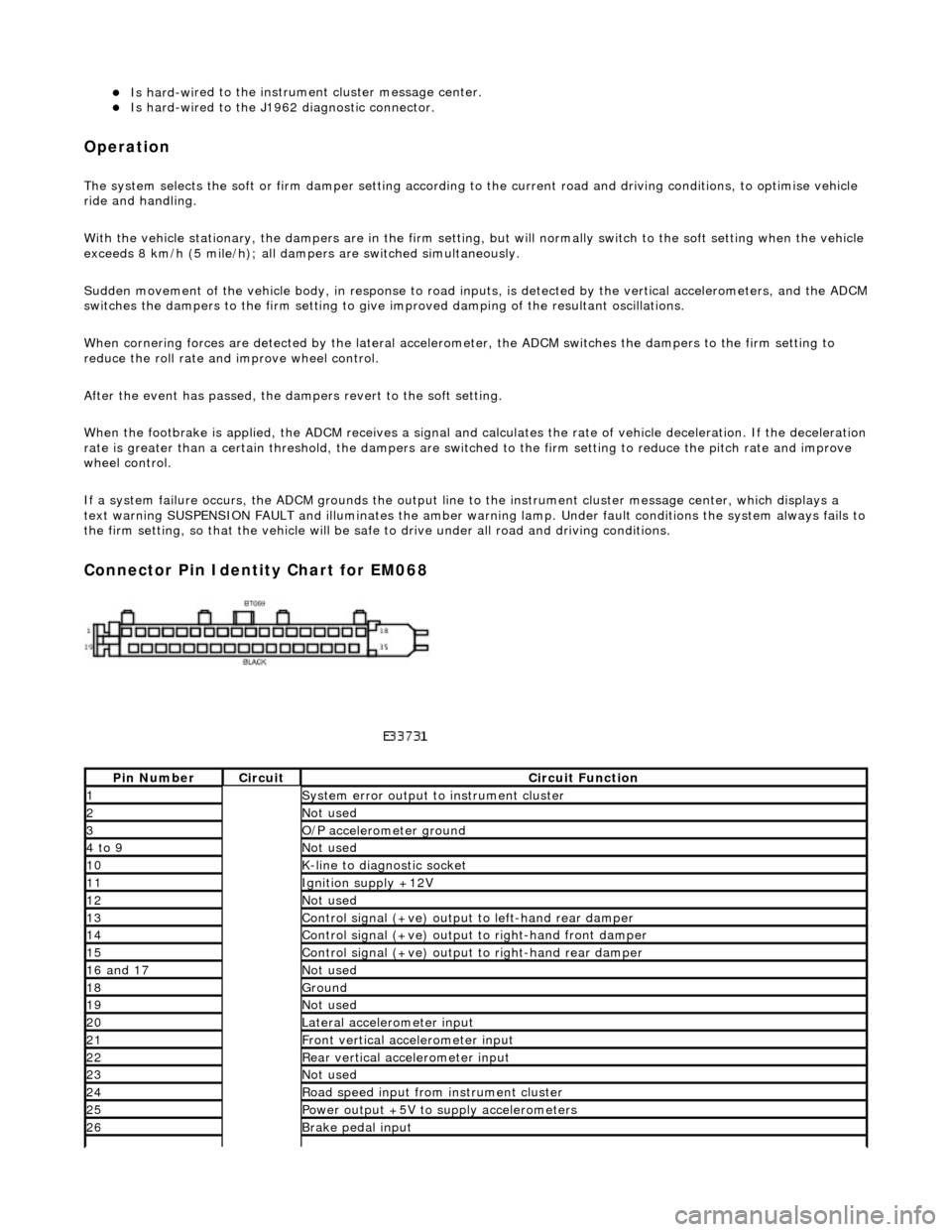
Connector Pin Identity Chart for EM068
Pin
Number
Ci
rcui
t
Circuit Functi
on
1System erro
r output to instrument
cluster
2Not
used
3O/
P a
ccelerometer ground
4 to
9
Not
used
10K-
li
ne to diagnostic socket
11Ignition su
pply +12V
12Not
used
13Control signal (+ve) output
to l
eft-hand rear damper
14Control signal (+ve) output
to right-hand front damp
er
15Control signal (+ve) output
to right-hand rear
damper
16
a
nd 17
No
t
used
18Ground
19No
t
used
20Lateral
accelerometer i
nput
21Front vertical ac
celerometer in
put
22Rear vertical
acce
lerometer input
23No
t
used
24R
o
ad speed input from
instrument cluster
25Power output +5V to suppl y accelerometers
26Brake peda
l input
Page 278 of 2490

Vehicle Dynamic Suspension - Vehicle Dynamic Suspension
Diagn
osis and Testing
Refer to the PDU User Guide for details of diagnosing and testing the Adaptive Damping System. The PDU interrogates the
ADCM directly via the K and L lines to the J1962 diagnostic socket.
The PDU will give an indication of the integrity of each electron ic and electrical component. It will indicate, for example, that
the accelerometers are not broken, but not that they functionin g correctly when the vehicle is in motion. However, it is
exceptional for an accelero meter to function incorrectly in its dynamic mode if it is proved to be functioning when static.
Basic Checks
The accele
rometers have the following ch
aracteristics. At 0g (no movement of the body) each vertical accelerometer
outputs approximately 2.5V steady voltage; the lateral acce lerometer outputs approximately 1.5V. The voltage output due
to body movement is proportional to acceleration in the acceleration axis, up to approximately 4.5V and down to
approximately 0.5V.
Before changing any component, refer to the circuit diagrams and check the cont inuity of relevant harness circuits; in some
instances, the PDU will not different iate between a faulty component an d a damaged connection or wiring.
Check the following fuses:
пЃ¬En
gine compartment fuse
box, fuse F5 (10A).
пЃ¬Engine m
anagement fuse
box, fuse F1 (20A).
Check the following ADCM input/output lines:
пЃ¬Sy stem erro
r output from the ADCM
to the instrument cluster.
пЃ¬Vehicl
e speed output from the inst
rument cluster to the ADCM.
пЃ¬Foo
tbrake signal to the ADCM.
Check any relevant connections to confirm that the connection is electrically sound and that a terminal pin has not been
pushed back into the connector shell, ie. not ma king a connection to its mating pin or socket.
Page 301 of 2490
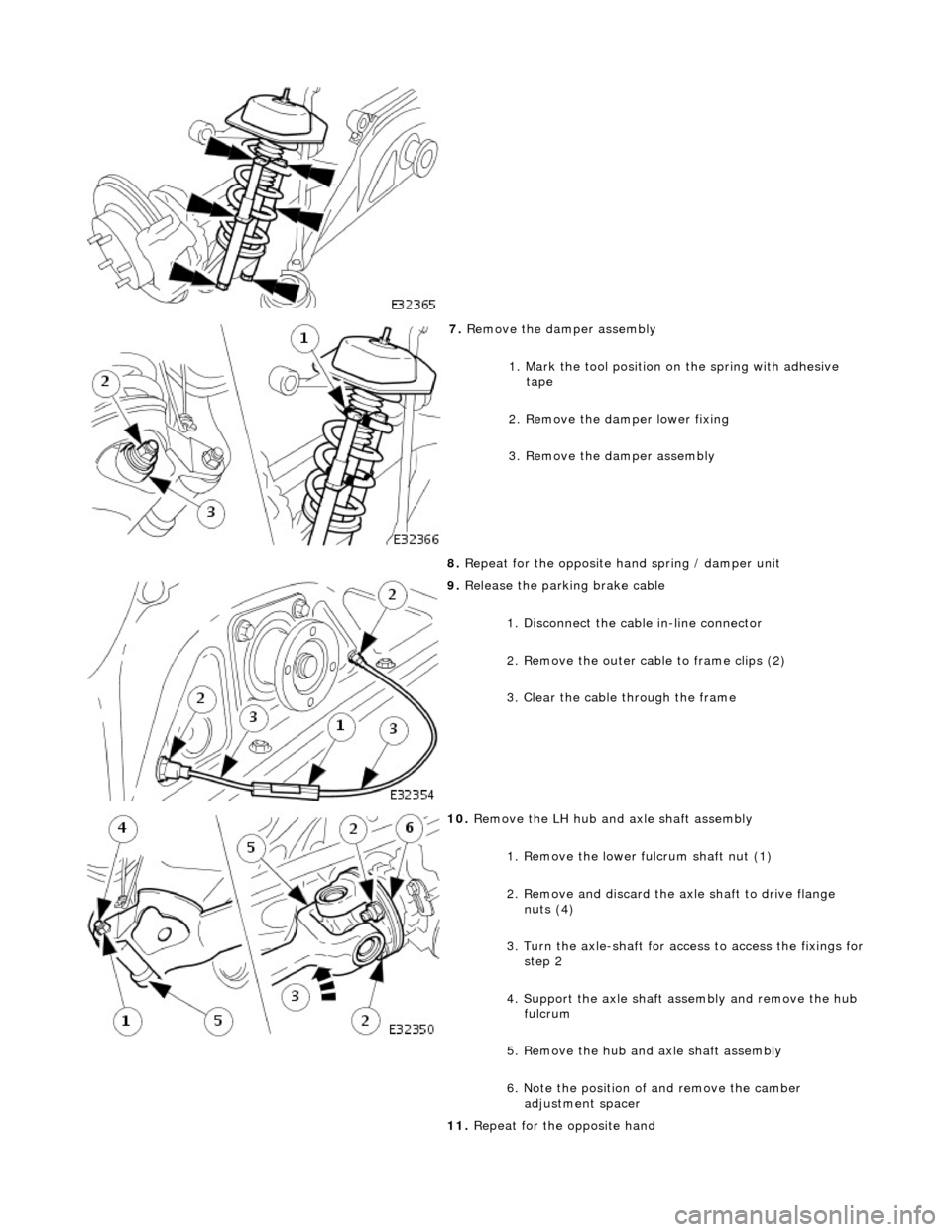
7. Re
move the damper assembly
1. Mark the tool position on the spring with adhesive
tape
2. Remove the damper lower fixing
3. Remove the damper assembly
8. Repeat for the opposite hand spring / damper unit
9. Relea
se the parking brake cable
1. Disconnect the cable in-line connector
2. Remove the outer cable to frame clips (2)
3. Clear the cable through the frame
10
.
Remove the LH hub and axle shaft assembly
1. Remove the lower fulcrum shaft nut (1)
2. Remove and discard the axle shaft to drive flange nuts (4)
3. Turn the axle-shaft for ac cess to access the fixings for
step 2
4. Support the axle shaft a ssembly and remove the hub
fulcrum
5. Remove the hub and axle shaft assembly
6. Note the position of and remove the camber adjustment spacer
11. Repeat for the opposite hand
Page 318 of 2490

Comp
onent Tests
Bra
k
e Booster
1.
1. Chec k all
hoses and connections. All unused vacuum connectors should be capped. Hoses and their connections
should be correctly secured and in good condition with no holes and no collapsed areas. Inspect the valve on the
brake booster for damage.
2. 2. Check the hydraulic brake system for leaks or low fluid.
3. 3. With the transmission in PARK, stop the engine and apply the parking brake. Pump the brake pedal several times
to exhaust all vacuum in the system.
4. 4. With the engine switched off and all vacuum in the system exhausted, appl y the brake pedal and hold it down.
Start the engine. If the vacuum system is operating, the brake pedal will tend to move downward under constant
foot pressure. If no motion is felt, the vacuum booster system is not functioning.
5. 5. Remove the vacuum hose from the brake booster. Manifold vacuum should be available at the brake booster end
of the hose with the engine at idle speed and the transm ission in PARK or NEUTRAL. Make sure that all unused
vacuum outlets are correctly capped, hose connectors are correctly secured and vacuum hoses are in good
condition. When it is established that manifold vacuum is available to the brake booster, connect the vacuum hose
to the brake booster and repeat Step 3. If no downward movement of the brake pedal is felt, install a new brake
booster.
6. 6. Operate the engine for a minimum of 10 seconds at a fast idle. Stop the engine and allow the vehicle to stand for
10 minutes. Then, apply th e brake pedal with approximately 89 N ( 20lb) of force. The pedal feel (brake
application) should be the same as that noted with the engine running. If the brake pedal feels hard (no power
assist), install a new valve and then re peat the test. If the brake pedal still feels hard, in stall a new brake booster.
If the brake pedal movement feels spongy, bleed the brak e system. For additional information, refer to General
Procedures in this section.
Bra k
e Master Cylinder
Usual
l
y, the first and strongest
indicator of anything wrong in the brake syst em is a feeling through the brake pedal. In
diagnosing the condition of the brake master cylinder, check pedal feel as evidence of a brake concern. Check for brake
warning lamp illumination and the brake fluid le vel in the brake master cylinder reservoir.
Normal Conditio
ns
The fo
llowing conditions are considered norm
al and are not indications that the brake master cylinder is in need of repair.
пЃ¬New bra
ke systems are designed to produc
e a pedal effort that is not as hard as in the past. Complaints of light
pedal efforts should be compared to the pedal effort s of another vehicle of the same model and year.
пЃ¬The fl
uid level will fall with brake pad wear.
Abnormal Conditions
•
NOTE: Prior to carrying out any diag
nosis, make sure the brake system warning indicator is functional.
Changes in the brake pedal feel or brake pedal travel are in dicators that something could be wrong in the brake system. The
diagnostic procedure and techniques use brake pedal feel, warning indicator illu mination and low brake fluid level as
indicators to diagnosing brake system co ncerns. The following conditions are cons idered abnormal and indicate that the
brake master cylinder is in need of repair:
пЃ¬Brake ped a
l goes down fast. Th
is could be caused by an ex ternal or internal leak.
пЃ¬Brake pedal goes down slowly
. This could be
caused by an internal or external leak.
пЃ¬Brak
e pedal is low or feels spongy. This condition may be ca
used by no fluid in the brake master cylinder, reservoir