Timing JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 1371 of 3039
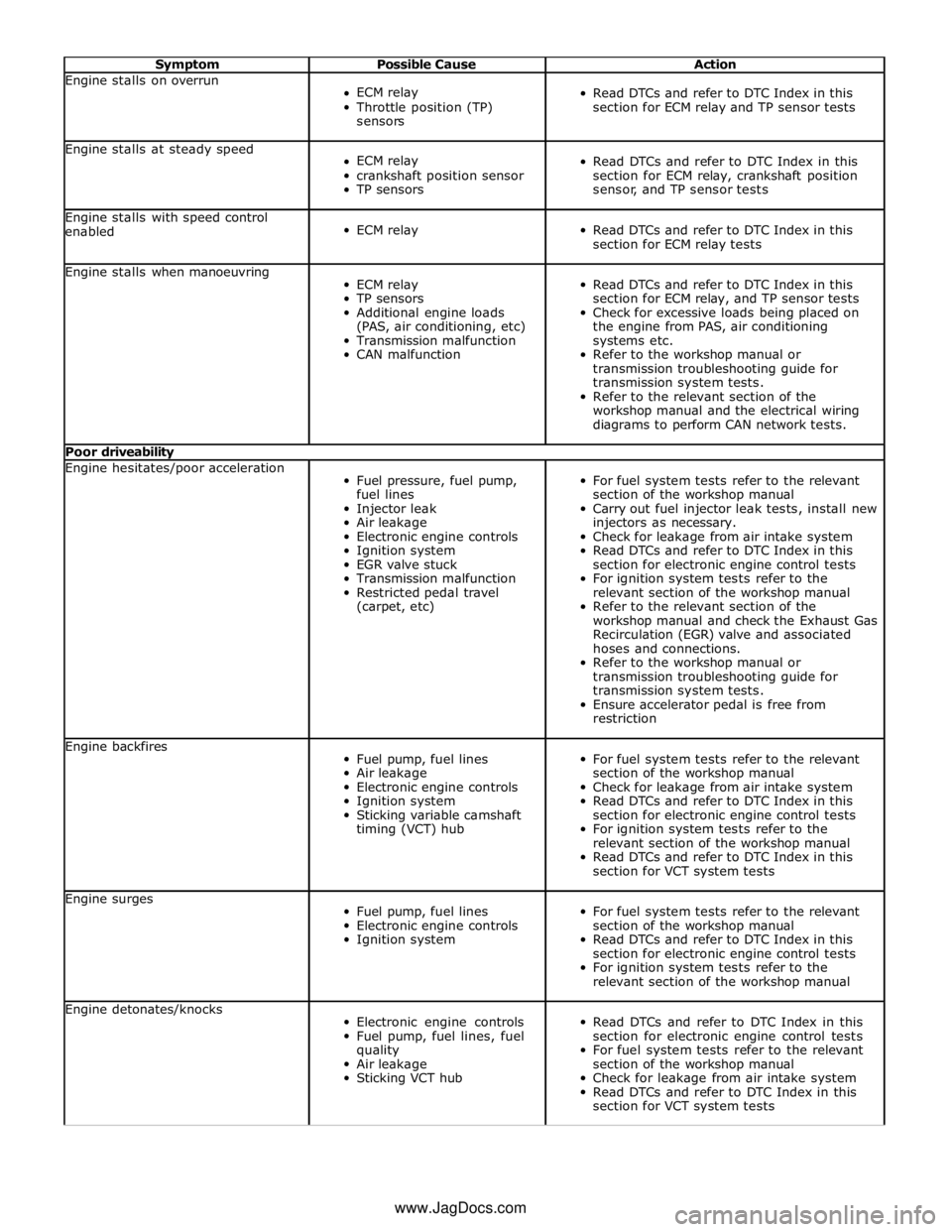
Symptom Possible Cause Action Engine stalls on overrun
ECM relay
Throttle position (TP)
sensors
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay and TP sensor tests Engine stalls at steady speed
ECM relay
crankshaft position sensor
TP sensors
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay, crankshaft position
sensor, and TP sensor tests Engine stalls with speed control
enabled
ECM relay
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay tests Engine stalls when manoeuvring
ECM relay
TP sensors
Additional engine loads
(PAS, air conditioning, etc)
Transmission malfunction
CAN malfunction
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay, and TP sensor tests
Check for excessive loads being placed on
the engine from PAS, air conditioning
systems etc.
Refer to the workshop manual or
transmission troubleshooting guide for
transmission system tests.
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and the electrical wiring
diagrams to perform CAN network tests. Poor driveability Engine hesitates/poor acceleration
Fuel pressure, fuel pump,
fuel lines
Injector leak
Air leakage
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
EGR valve stuck
Transmission malfunction
Restricted pedal travel
(carpet, etc)
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Carry out fuel injector leak tests, install new
injectors as necessary.
Check for leakage from air intake system
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) valve and associated
hoses and connections.
Refer to the workshop manual or
transmission troubleshooting guide for
transmission system tests.
Ensure accelerator pedal is free from
restriction Engine backfires
Fuel pump, fuel lines
Air leakage
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
Sticking variable camshaft
timing (VCT) hub
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Check for leakage from air intake system
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for VCT system tests Engine surges
Fuel pump, fuel lines
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual Engine detonates/knocks
Electronic engine controls
Fuel pump, fuel lines, fuel
quality
Air leakage
Sticking VCT hub
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Check for leakage from air intake system
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for VCT system tests www.JagDocs.com
Page 1404 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Variable Valve Timing (VVT)
Oil Control Solenoid LH
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
Refer to: Specifications (414-00, Specifications).
2. WARNING: Make sure to support the vehicle with axle stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
3. Refer to: Thermostat Housing - Vehicles With: Supercharger (303-03,
Removal and Installation).
4. NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur, but
the essential information is always correct.
Torque: 10 Nm
5. CAUTION: Evenly and progressively, remove the VVT
units from each side.
NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur,
but the essential information is always correct.
Page 1406 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Variable Valve Timing (VVT)
Oil Control Solenoid RH
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
Refer to: Specifications (414-00, Specifications).
2. WARNING: Make sure to support the vehicle with axle stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
3. Refer to: Thermostat Housing - Vehicles With: Supercharger (303-03,
Removal and Installation).
4. NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur, but
the essential information is always correct.
5. NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur,
but the essential information is always correct.
Torque: 10 Nm www.JagDocs.com
Page 1431 of 3039

transmission functions. The Mechatronic valve block comprises the following components:
TCM
Pressure regulator solenoids
Shift control solenoid
Damper
Hydraulic spool valves
Selector valve
Temperature sensor
Turbine speed sensor
Output shaft speed sensor.
Sensors
Speed Sensors
The turbine speed sensor and the output shaft speed sensor are Hall effect type sensors located in the Mechatronic valve block
and are not serviceable items. The TCM monitors the signals from each sensor to determine the input (turbine) speed and the output shaft speed.
The turbine speed is monitored by the TCM to calculate the slip of the torque converter clutch and internal clutch slip. This signal allows the TCM to accurately control the slip timing during shifts and adjust clutch application or release pressure for overlap shift control.
The output shaft speed is monitored by the TCM and compared to engine speed signals received on the CAN bus from the ECM. Using a comparison of the two signals the TCM calculates the transmission slip ratio for plausibility and maintains adaptive pressure control.
Temperature Sensor
The temperature sensor is also located in the Mechatronic valve block. The TCM uses the temperature sensor signals to determine the temperature of the transmission fluid. These signals are used by the TCM to control the transmission operation to promote faster warm-up in cold conditions or to assist with fluid cooling by controlling the transmission operation when high
fluid temperatures are experienced. If the sensor fails, the TCM will use a default value and a fault code will be stored in the TCM.
Damper
There is one damper located in the valve housing. The damper is used to regulate and dampen the regulated pressure supplied
via EPRS. The damper is load dependent through modulation of the damper against return spring pressure.
The damper comprises a piston, a housing bore and a spring. The piston is subject to the pressure applied by the spring. The
bore has a connecting port to the function to which it applies. Fluid pressure applied to the applicable component (i.e. a
clutch) is also subjected to the full area of the piston, which moves against the opposing force applied by the spring. The
movement of the piston creates an action similar to a shock absorber, momentarily delaying the build up of pressure in the
circuit. This results in a more gradual application of clutches improving shift quality.
Spool Valves
The valve block spool valves control various functions of the transmission. The spool valves are of conventional design and are
operated by fluid pressure.
Each spool valve is located in its spool bore and held in a default (unpressurized) position by a spring. The spool bore has a
number of ports which allow fluid to flow to other valves and clutches to enable transmission operation. Each spool has a
piston which is waisted to allow fluid to be diverted into the applicable ports when the valve is operated.
When fluid pressure moves a spool, one or more ports in the spool bore are covered or uncovered. Fluid is prevented from
flowing or is allowed to flow around the applicable waisted area of the spool and into another uncovered port. The fluid is
either passed through galleries to actuate another spool, operate a clutch or is returned to the fluid pan.
Page 1597 of 3039
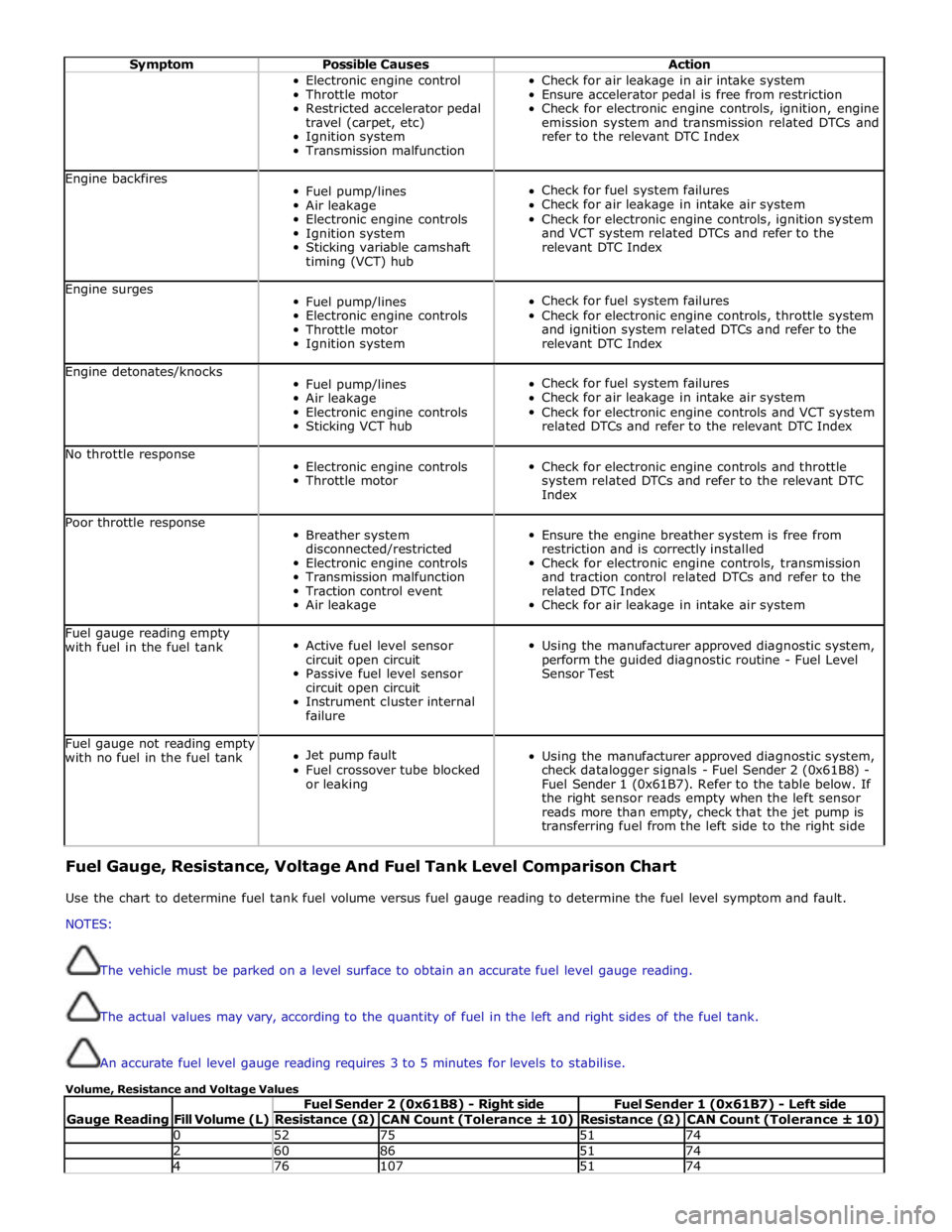
Symptom Possible Causes Action Electronic engine control
Throttle motor
Restricted accelerator pedal
travel (carpet, etc)
Ignition system
Transmission malfunction Check for air leakage in air intake system
Ensure accelerator pedal is free from restriction
Check for electronic engine controls, ignition, engine
emission system and transmission related DTCs and
refer to the relevant DTC Index Engine backfires
Fuel pump/lines
Air leakage
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
Sticking variable camshaft
timing (VCT) hub
Check for fuel system failures
Check for air leakage in intake air system
Check for electronic engine controls, ignition system
and VCT system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Engine surges
Fuel pump/lines
Electronic engine controls
Throttle motor
Ignition system
Check for fuel system failures
Check for electronic engine controls, throttle system
and ignition system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Engine detonates/knocks
Fuel pump/lines
Air leakage
Electronic engine controls
Sticking VCT hub
Check for fuel system failures
Check for air leakage in intake air system
Check for electronic engine controls and VCT system
related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC Index No throttle response
Electronic engine controls
Throttle motor
Check for electronic engine controls and throttle
system related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC
Index Poor throttle response
Breather system
disconnected/restricted
Electronic engine controls
Transmission malfunction
Traction control event
Air leakage
Ensure the engine breather system is free from
restriction and is correctly installed
Check for electronic engine controls, transmission
and traction control related DTCs and refer to the
related DTC Index
Check for air leakage in intake air system Fuel gauge reading empty
with fuel in the fuel tank
Active fuel level sensor
circuit open circuit
Passive fuel level sensor
circuit open circuit
Instrument cluster internal
failure
Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system,
perform the guided diagnostic routine - Fuel Level
Sensor Test Fuel gauge not reading empty
with no fuel in the fuel tank
Jet pump fault
Fuel crossover tube blocked
or leaking
Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system,
check datalogger signals - Fuel Sender 2 (0x61B8) -
Fuel Sender 1 (0x61B7). Refer to the table below. If
the right sensor reads empty when the left sensor
reads more than empty, check that the jet pump is
transferring fuel from the left side to the right side Fuel Gauge, Resistance, Voltage And Fuel Tank Level Comparison Chart
Use the chart to determine fuel tank fuel volume versus fuel gauge reading to determine the fuel level symptom and fault.
NOTES:
The vehicle must be parked on a level surface to obtain an accurate fuel level gauge reading.
The actual values may vary, according to the quantity of fuel in the left and right sides of the fuel tank.
An accurate fuel level gauge reading requires 3 to 5 minutes for levels to stabilise.
Volume, Resistance and Voltage Values
Gauge Reading
Fill Volume (L) Fuel Sender 2 (0x61B8) - Right side Fuel Sender 1 (0x61B7) - Left side Resistance (Ω) CAN Count (Tolerance ± 10) Resistance (Ω) CAN Count (Tolerance ± 10) 0 52 75 51 74 2 60 86 51 74 4 76 107 51 74
Page 1641 of 3039

6 Clockspring 7 APP (accelerator pedal position) sensor 8 Electric throttle actuator 9 Brake lamp/brake test switch 10 Adaptive speed control radar sensor 11 Diagnostic socket 12 Instrument cluster 13 TCM (transmission control module) 14 Adaptive speed control module
SPEED CONTROL System Operation
The speed control system uses inputs from the brake lamp/brake test switch, the APP sensor, the ECM and the ABS module.
Speed control is operated by the driver using only the steering wheel switches. When speed control is active, the ECM regulates the PWM (pulse width modulation) signals to the fuel injectors to adjust the fuel supply as required to maintain the
set speed.
During speed control operation, the ECM controls vehicle speed by adjusting fuel injection duration and timing. When the accelerator pedal is pressed with speed control active, the ECM outputs a calculated throttle angle signal in place of the actual throttle angle signals produced by the APP sensor. The calculated throttle angle is derived from fuel demand.
The minimum set speed for speed control is 18 mph (30 (km/h). Speed control is automatically suspended if the following
conditions apply:
Vehicle speed falls below 18 mph (30 km/h)
The brake pedal is pressed
The cancel button is pressed
Neutral, park or reverse gear is selected
The difference between actual speed and the set speed is too great
If the engine speed becomes near to the red line (maximum engine speed)
If the accelerator pedal is used to accelerate beyond the set speed for too long.
ADAPTIVE SPEED CONTROL
The adaptive speed control system comprises the following components:
Adaptive speed control sensor
Adaptive speed control module
Steering wheel control switches
ECM
Electric throttle actuator
ABS module and pump Adaptive speed control warning indicator.
The adaptive speed control system uses a forward looking radar sensor to scan the road ahead, looking for objects that are
moving at a different rate to itself. When a target is identified the adaptive speed control system will monitor the time gap
between it and the target vehicle. When that gap falls below a set driver selected level the adaptive speed control system will
intervene slowing the vehicle by backing off the throttle and/ or applying the brakes, until the correct gap is attained. The
driver can chose between four gap settings, 1, 1.4, 1.8 and 2.2 seconds.
The system will detect but not react to the following:
Vehicles in the oncoming lane
Stationary vehicles
Pedestrians
Vehicles not in the same lane.
Adaptive speed control is active when the vehicle is moving. Adaptive Speed Control only functions when a set speed is
entered in normal speed control mode. The adaptive speed control system only intervenes with the set speed when it detects
a target vehicle, and then only if the minimum time gap is breached.
It is important to note that the system is intended for use in limited driving situations, does not remove control and
responsibility from the driver, and at all times can be quickly overridden. The adaptive speed control system is not a collision
warning system and will not react to stationary objects. The system does not operate below a minimum speed of
approximately 30 km/h (20 mph) since it is unsuitable for use in cities or congested traffic. The system is best suited to main
roads/ highways with gradual bends.
The ECM, throttle body and throttle control are unchanged from those used for non adaptive speed control variants.
The adaptive speed control system is based on the use of a front mounted radar sensor. The sensor transmits a 1.5° wide
beam forward of the vehicle and detects the returning signals reflected off other vehicles and objects ahead.
The 1.5° wide radar beam is mechanically scanned at a rate of 10 sweeps/second across a total arc of 15° centered on the
Page 1794 of 3039
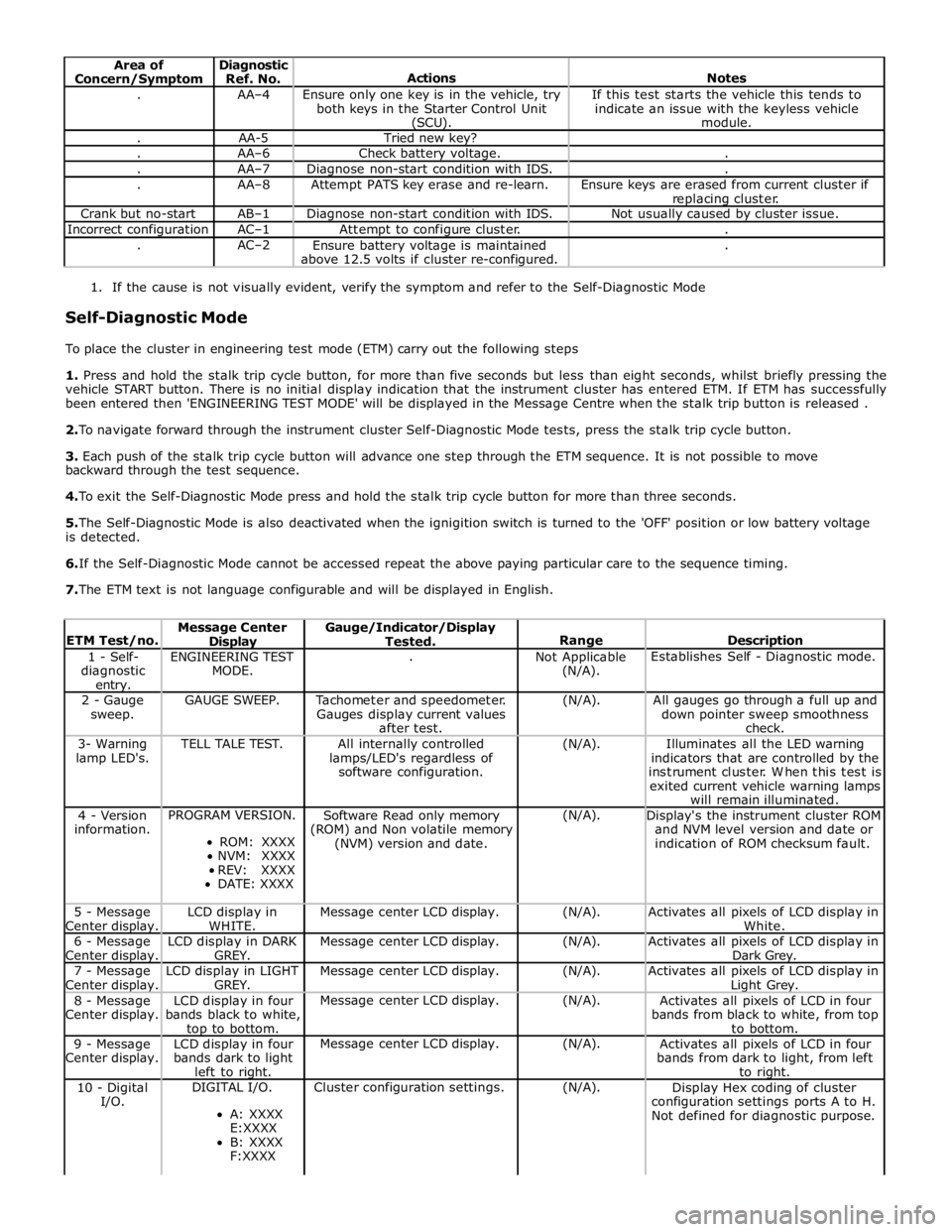
Area of
Concern/Symptom Diagnostic
Ref. No.
Actions
Notes . AA–4
Ensure only one key is in the vehicle, try
both keys in the Starter Control Unit (SCU). If this test starts the vehicle this tends to
indicate an issue with the keyless vehicle
module. . AA-5 Tried new key? . AA–6 Check battery voltage. . . AA–7 Diagnose non-start condition with IDS. . . AA–8 Attempt PATS key erase and re-learn.
Ensure keys are erased from current cluster if
replacing cluster. Crank but no-start AB–1 Diagnose non-start condition with IDS. Not usually caused by cluster issue. Incorrect configuration AC–1 Attempt to configure cluster. . . AC–2
Ensure battery voltage is maintained
above 12.5 volts if cluster re-configured. .
1. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Self-Diagnostic Mode
Self-Diagnostic Mode
To place the cluster in engineering test mode (ETM) carry out the following steps
1. Press and hold the stalk trip cycle button, for more than five seconds but less than eight seconds, whilst briefly pressing the
vehicle START button. There is no initial display indication that the instrument cluster has entered ETM. If ETM has successfully
been entered then 'ENGINEERING TEST MODE' will be displayed in the Message Centre when the stalk trip button is released .
2. To navigate forward through the instrument cluster Self-Diagnostic Mode tests, press the stalk trip cycle button.
3. Each push of the stalk trip cycle button will advance one step through the ETM sequence. It is not possible to move
backward through the test sequence.
4. To exit the Self-Diagnostic Mode press and hold the stalk trip cycle button for more than three seconds.
5. The Self-Diagnostic Mode is also deactivated when the ignigition switch is turned to the 'OFF' position or low battery voltage
is detected.
6. If the Self-Diagnostic Mode cannot be accessed repeat the above paying particular care to the sequence timing.
7. The ETM text is not language configurable and will be displayed in English.
ETM Test/no. Message Center Display Gauge/Indicator/Display
Tested.
Range
Description 1 - Self-
diagnostic entry. ENGINEERING TEST
MODE. .
Not Applicable
(N/A). Establishes Self - Diagnostic mode. 2 - Gauge
sweep. GAUGE SWEEP.
Tachometer and speedometer.
Gauges display current values
after test. (N/A).
All gauges go through a full up and
down pointer sweep smoothness
check. 3- Warning
lamp LED's. TELL TALE TEST.
All internally controlled
lamps/LED's regardless of
software configuration. (N/A).
Illuminates all the LED warning
indicators that are controlled by the
instrument cluster. When this test is
exited current vehicle warning lamps
will remain illuminated. 4 - Version
information. PROGRAM VERSION.
ROM: XXXX
NVM: XXXX
REV: XXXX
DATE: XXXX Software Read only memory
(ROM) and Non volatile memory
(NVM) version and date. (N/A).
Display's the instrument cluster ROM
and NVM level version and date or
indication of ROM checksum fault. 5 - Message
Center display. LCD display in
WHITE. Message center LCD display. (N/A).
Activates all pixels of LCD display in
White. 6 - Message
Center display. LCD display in DARK
GREY. Message center LCD display. (N/A).
Activates all pixels of LCD display in
Dark Grey. 7 - Message
Center display. LCD display in LIGHT
GREY. Message center LCD display. (N/A).
Activates all pixels of LCD display in Light Grey. 8 - Message
Center display. LCD display in four
bands black to white, top to bottom. Message center LCD display. (N/A).
Activates all pixels of LCD in four
bands from black to white, from top
to bottom. 9 - Message
Center display. LCD display in four
bands dark to light
left to right. Message center LCD display. (N/A).
Activates all pixels of LCD in four
bands from dark to light, from left
to right. 10 - Digital
I/O. DIGITAL I/O.
A: XXXX
E:XXXX
B: XXXX
F:XXXX Cluster configuration settings. (N/A).
Display Hex coding of cluster
configuration settings ports A to H.
Not defined for diagnostic purpose.
Page 1945 of 3039
player is only compatible with standard CD's. All other versions of CD player are compatible with standard CDs and CDs with MP3 or WMA (windows media audio) files.
A portable audio module allows for the connection of a range of portable audio devices to the car’s audio system. The portable
audio module is controlled through the IAM (integrated audio module) and Touch-screen with play back through the car’s
speaker system. The introduction of this system allows the user to import their personal portable media player to interface
with the car, including iPod and other MP3 players, or USB mass storage devices such as memory sticks. MP3 players can also
be controlled through the Touch-screen if they are configured as mass storage devices. Details of how to do this will be
contained in the manufacturers instructions.
The chosen audio device can be plugged into the car using an interface panel located in the floor console between the front
seats. The interface includes a 3.5mm auxiliary jack-plug socket, a 12-volt power supply, a dedicated iPod connector with
charging function, plus a USB2 connector which allows connectivity for a wide variety of USB devices. The USB port also
provides a charging function although it does not support a USB hub. The maximum charging current supplied is 500ma. The
user can connect an iPod and USB device at the same time, changing the source via the Touch-screen. The non selected source
will still charge.
The Jaguar Sound System is the basic audio system which comprises of an IAM (integrated audio module) with no external
amplifier and 8 speakers.
The Jaguar 320W Premium Sound System has the addition of an AUD 8 power amplifier and a 9 speaker system.
The Bowers & Wilkins 440w Surround Sound System additions include an AUD 12 power amplifier, a Dolby Pro-Logic 2 7.1
Surround Sound System, and 14 speakers.
DAB (digital audio broadcasting) is available for most European markets and gives access to digital radio channels for better
sound quality and enhanced functionality depending on local service availability. The DAB (digital audio broadcasting) module
is located in the luggage compartment. The system receives reception signals from the following sources to ensure optimum
signal strength.
DAB band L antenna located in the roof pod antenna module
DAB band III antenna located in the heated rear window.
For NAS vehicles the digital format adopted is satellite radio which specifically links to the Sirius network. The system operates
in the S-band frequency range, and as a result of the use of satellite transmission, has the ability to provide CD quality audio broadcasts over very large areas (typically continents). The satellite radio receiver is located in the luggage compartment. The
system receives reception signals from the satellite radio antenna located in the roof pod module.
Primary user control of the audio system is via the ICP (integrated control panel) and the Touch-screen which are located in the
center of the instrument panel. Control signals from the ICP (integrated control panel) are relayed on the medium speed CAN
(controller area network) bus to the ICM (information control module). The ICM (information control module) relays the control
signals to the rest of the audio system on the MOST (media oriented systems transport) ring. The ICM (information control
module) is the timing master for the MOST (media oriented systems transport) ring and also hosts a gateway function between
the medium speed CAN bus and the MOST (media oriented systems transport) ring. Audio output signals on the Jaguar 320W Premium Sound System and Bowers & Wilkins 440W Surround Sound System are sent on the MOST (media oriented systems
transport) ring from the IAM (integrated audio module) to the power amplifier for speaker output. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1948 of 3039

3 Satellite Radio digital receiver (Optional - NAS only) 4 Telephone control module (Optional) 5 Touch-screen 6 TV tuner (Optional) 7 Power amplifier (Not fitted to the Jaguar Sound System) 8 IAM (integrated audio module) 9 Portable audio module (Optional) 10 ICM (information control module)
AUDIO SYSTEM OPERATION System Operation
The components of the audio/infotainment system are all connected on the MOST (media orientated systems transport) ring.
The MOST (media orientated systems transport) ring is a fibre optic communications bus for multimedia applications. Audio
and control information is passed around the MOST (media orientated systems transport) ring and can be picked up by any of
the systems units. For example, radio station tuning/selection input by the vehicle user into the Touch-screen is sent along the
MOST (media orientated systems transport) ring and collected by the IAM (integrated audio module) which then selects the
requested radio station.
MOST (media orientated systems transport) technology uses a plastic optical fibre which forms a network connecting the audio
and multimedia system components. Each component in the ring is connected to the plastic optical fibre through a device
known as a FOT (fibre optical transceiver). Each FOT (fibre optical transceiver) has two optical connections; one connection is
sensitive to light and is the input, the second connection forms the light source and is the output. The system operates by
connecting the output from one FOT (fibre optical transceiver) to the input of another FOT (fibre optical transceiver).
The light signals are sent in one direction only and are formed in the following way:
Electrical signals are converted into an electrical current
The current then drives an LED (light emitting diode) in the FOT (fibre optical transceiver) to produce a high intensity
red light
The LED transmits the light through a fibre optic cable A photo diode in the FOT (fibre optical transceiver) at the opposite end of the fibre optic cable detects the light.
The following components may be connected to the MOST ring dependant on the vehicle equipment level:
IAM (integrated audio module)
Touch-screen
ICM (information control module)
DAB (digital audio broadcasting) radio receiver (Optional - Europe only)
Satellite radio digital receiver (Optional - NAS only)
Power amplifier (Not fitted to the Jaguar Sound System)
Portable audio module (Optional)
Telephone control module (Optional)
Navigation computer (Optional)
TV tuner (Optional)
NOTE: Do not view the red light directly
MOST is a synchronous network. A timing master supplies the clock information and all other devices on the network
synchronize their operation to this clock. The timing master for the MOST (media orientated systems transport) network on this
vehicle is the ICM (information control module). This unit also controls and manages the MOST (media orientated systems
transport) ring and the system components.
An Optical Bus tester is used in conjunction with the Jaguar diagnostic system to diagnose the MOST (media orientated
systems transport) system. The Optical Bus tester emits a visible, high intensity red light which can be connected into the ring
at any point to test the ring integrity. Disconnecting a MOST (media orientated systems transport) connector will reveal if the
high intensity red light is visible.
If a break occurs in the MOST (media orientated systems transport) ring fault codes are stored in the ICM (information control
module) which can be retrieved using the Jaguar diagnostic system equipment.
With reference to the audio system information and signal transfer the instrument cluster is the gateway between the high
and medium speed CAN bus communication protocols. The ICM (information control module) is the gateway between medium speed CAN and the MOST (media orientated systems transport) systems.
A typical example of information transfer is vehicle speed information from the ABS (anti-lock brake system) module used to
control the automatic volume control function. The vehicle speed information from the ABS module is sent on the high speed CAN network and collected by the instrument panel gateway. The signal is passed to the medium speed CAN network and onto the ICM (information control module) gateway. The ICM (information control module) calculates the volume adjustment
required. The corrected audio volume level signal is sent on the MOST (media orientated systems transport) network to the
IAM (integrated audio module) or Power amplifier (dependant on vehicle equipment level) for output to the speaker system.
Page 1953 of 3039
7 Triple TV antenna module 8 RF filter The diversity antenna module, located on the left hand side of the heated rear window, receives signals from four antennas
located in the heated rear window, where one antenna is dedicated as an AM antenna.
The diversity tuning system ensures that the strongest signals are used by the radio system to ensure the best possible FM
reception. Using the three remaining receiving antennas serves to eliminate multipath signal distortion. Typically, the signal
from the antenna with the least noise is chosen, and the other antennas are ignored.
The diversity antenna module is an interface between the antenna aerials in the heated rear window and audio system
modules/tuners. It provides antenna signals to the AM/FM tuner in the IAM, to the DAB receiver and to the VICS (vehicle
information and communication systems) or TMC (traffic message channel) in the navigation computer.
There are three different types of diversity antenna module fitted depending on the vehicle market and infotainment
equipment specification:
AM/FM with one co-axial output
AM/FM and VICS/TMC with two co-axial outputs
AM/FM, VICS/TMC and DAB band III with three co-axial outputs
The diversity antenna module receives a power supply from the IAM.
Vehicle or other component generated electromagnetic interference may cause unwanted disturbances in the radio and TV
reception signals. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the
circuit. It frequently affects the reception of AM radio in urban areas and can also affect FM radio and television reception,
although to a lesser extent.
The RF filters, which act as RF isolators, are located on both sides of the heated rear window and are used to reduce the
electromagnetic interference. The left hand side RF filter is connected across the heated rear window power supply and used to
separate the DC (direct current) interference from the RF signals. The right hand side RF filter is used in conjunction with the
TV antenna module (if fitted). If the TV system is not fitted the filter is linked directly to ground.
INFORMATION CONTROL MODULE
The ICM is located beneath the IAM in the center console. The unit performs a range of infotainment and some climate-control
functions.
The ICM, which is the timing master of the MOST system; supplies clock information to all other devices on the network which
synchronize their operation to this clock.
The unit also controls and manages the MOST ring and provides the allocations of channels, system power management,
functionality and co-ordination of the other system components.
The system becomes operational when the vehicle is unlocked and a 'wake up' signal is received by the ICM on the medium
speed CAN. The ICM 'wakes up' all the control modules on the MOST system ready for immediate operation by the vehicle user. If the ICM is replaced it must be configured as a new module using the Jaguar approved diagnostic equipment.
Calibration of the ICM using the Jaguar approved diagnostic equipment enables updates to be downloaded as new technology
becomes available or any fault concerns require software updates.