SUBARU FORESTER 2004 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: SUBARU, Model Year: 2004, Model line: FORESTER, Model: SUBARU FORESTER 2004Pages: 2870, PDF Size: 38.67 MB
Page 951 of 2870
ME(H4SO)-80
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
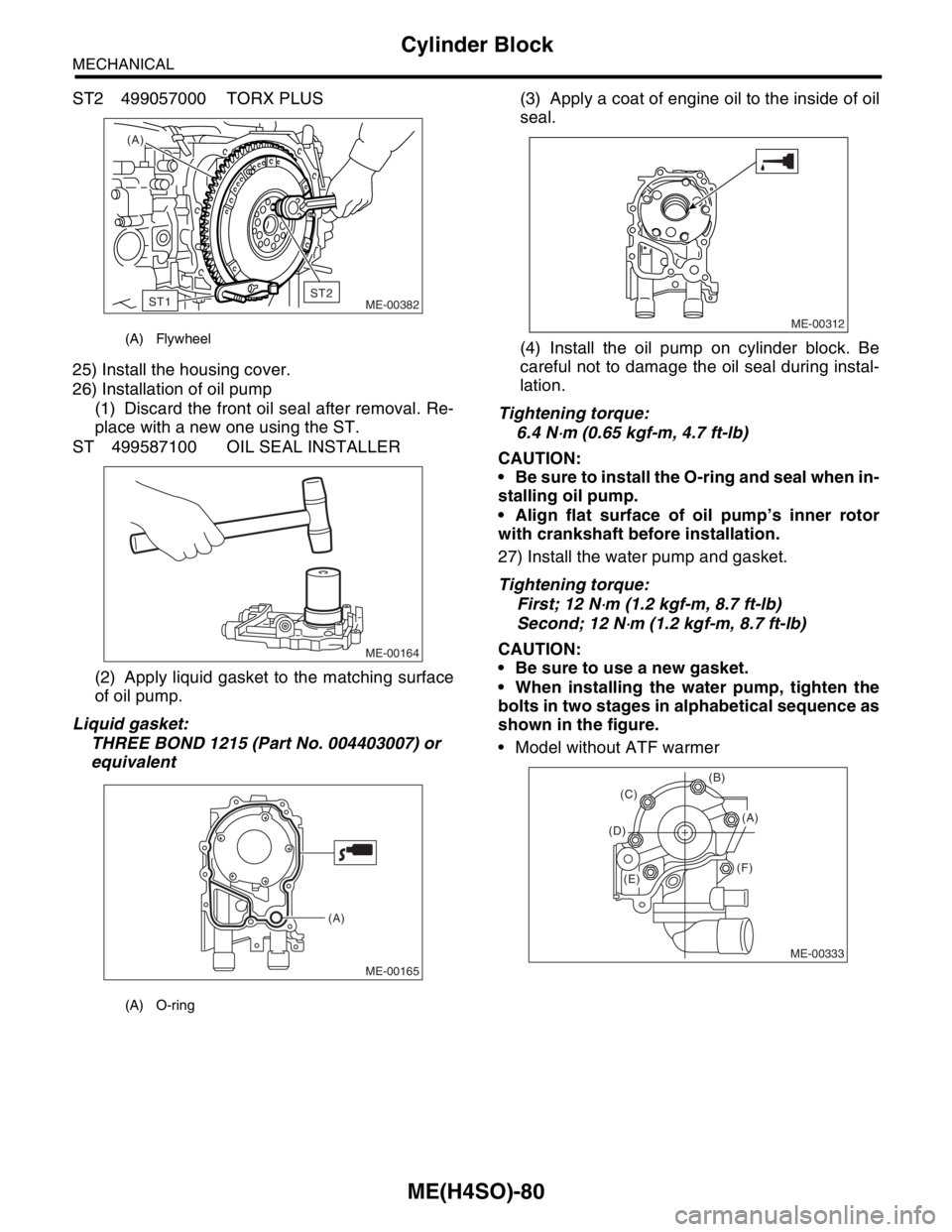
ST2 499057000 TORX PLUS
25) Install the housing cover.
26) Installation of oil pump
(1) Discard the front oil seal after removal. Re-
place with a new one using the ST.
ST 499587100 OIL SEAL INSTALLER
(2) Apply liquid gasket to the matching surface
of oil pump.
Liquid gasket:
THREE BOND 1215 (Part No. 004403007) or
equivalent(3) Apply a coat of engine oil to the inside of oil
seal.
(4) Install the oil pump on cylinder block. Be
careful not to damage the oil seal during instal-
lation.
Tightening torque:
6.4 N
⋅m (0.65 kgf-m, 4.7 ft-lb)
CAUTION:
Be sure to install the O-ring and seal when in-
stalling oil pump.
Align flat surface of oil pump’s inner rotor
with crankshaft before installation.
27) Install the water pump and gasket.
Tightening torque:
First; 12 N
⋅m (1.2 kgf-m, 8.7 ft-lb)
Second; 12 N
⋅m (1.2 kgf-m, 8.7 ft-lb)
CAUTION:
Be sure to use a new gasket.
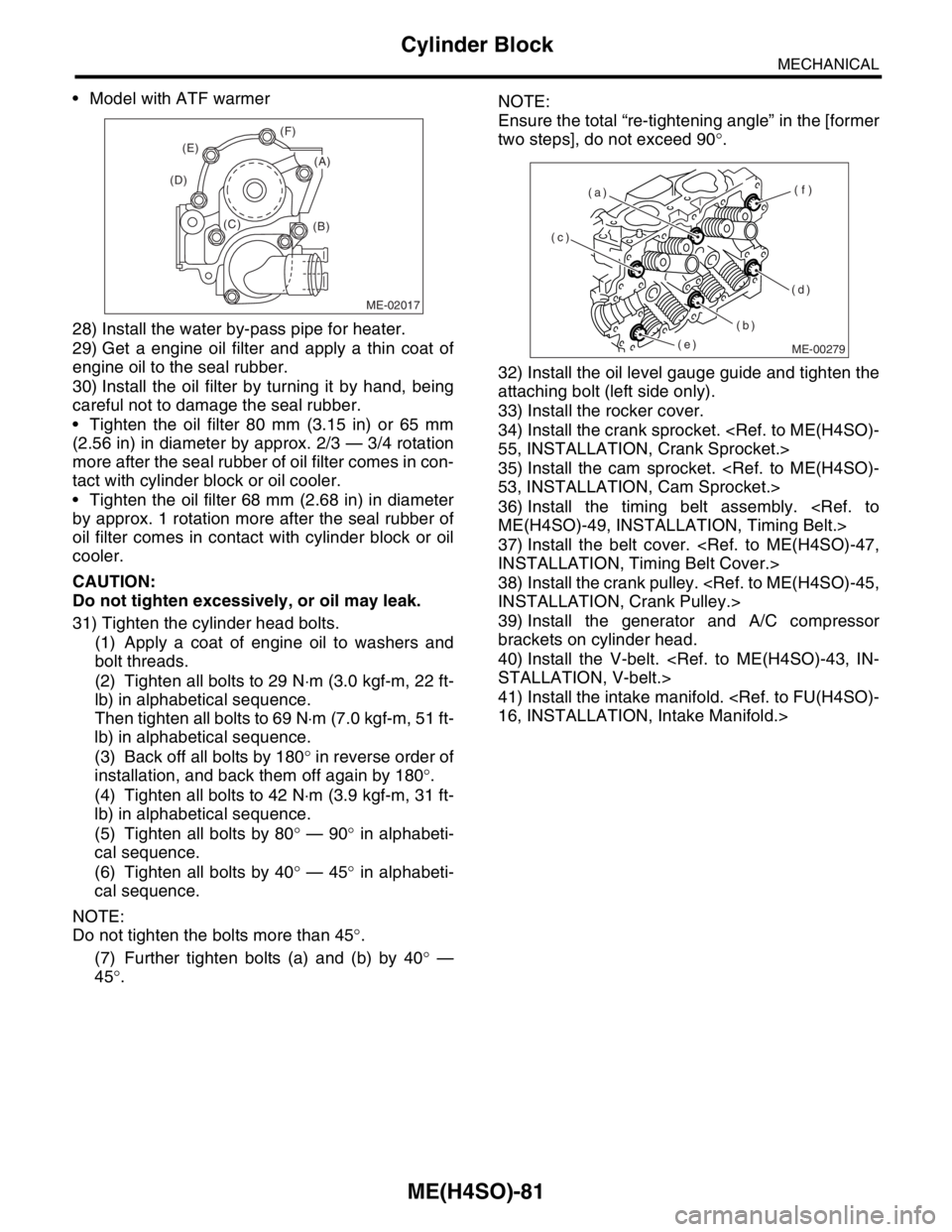
When installing the water pump, tighten the
bolts in two stages in alphabetical sequence as
shown in the figure.
Model without ATF warmer
(A) Flywheel
(A) O-ring
(A)
ME-00382
ST1ST2
ME-00164
ME-00165
(A)
ME-00312
ME-00333
(B)
(F) (D)(C)
(A)
(E)
Page 952 of 2870
ME(H4SO)-81
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
Model with ATF warmer
28) Install the water by-pass pipe for heater.
29) Get a engine oil filter and apply a thin coat of
engine oil to the seal rubber.
30) Install the oil filter by turning it by hand, being
careful not to damage the seal rubber.
Tighten the oil filter 80 mm (3.15 in) or 65 mm
(2.56 in) in diameter by approx. 2/3 — 3/4 rotation
more after the seal rubber of oil filter comes in con-
tact with cylinder block or oil cooler.
Tighten the oil filter 68 mm (2.68 in) in diameter
by approx. 1 rotation more after the seal rubber of
oil filter comes in contact with cylinder block or oil
cooler.
CAUTION:
Do not tighten excessively, or oil may leak.
31) Tighten the cylinder head bolts.
(1) Apply a coat of engine oil to washers and
bolt threads.
(2) Tighten all bolts to 29 N⋅m (3.0 kgf-m, 22 ft-
lb) in alphabetical sequence.
Then tighten all bolts to 69 N⋅m (7.0 kgf-m, 51 ft-
lb) in alphabetical sequence.
(3) Back off all bolts by 180° in reverse order of
installation, and back them off again by 180°.
(4) Tighten all bolts to 42 N⋅m (3.9 kgf-m, 31 ft-
lb) in alphabetical sequence.
(5) Tighten all bolts by 80° — 90° in alphabeti-
cal sequence.
(6) Tighten all bolts by 40° — 45° in alphabeti-
cal sequence.
NOTE:
Do not tighten the bolts more than 45°.
(7) Further tighten bolts (a) and (b) by 40° —
45°.NOTE:
Ensure the total “re-tightening angle” in the [former
two steps], do not exceed 90°.
32) Install the oil level gauge guide and tighten the
attaching bolt (left side only).
33) Install the rocker cover.
34) Install the crank sprocket.
35) Install the cam sprocket.
36) Install the timing belt assembly.
37) Install the belt cover.
38) Install the crank pulley.
39) Install the generator and A/C compressor
brackets on cylinder head.
40) Install the V-belt.
41) Install the intake manifold.
ME-02017
(B) (C) (D)(E)(F)
(A)
ME-00279
(c)
(b)(f)
(d) (a)
(e)
Page 953 of 2870
ME(H4SO)-82
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
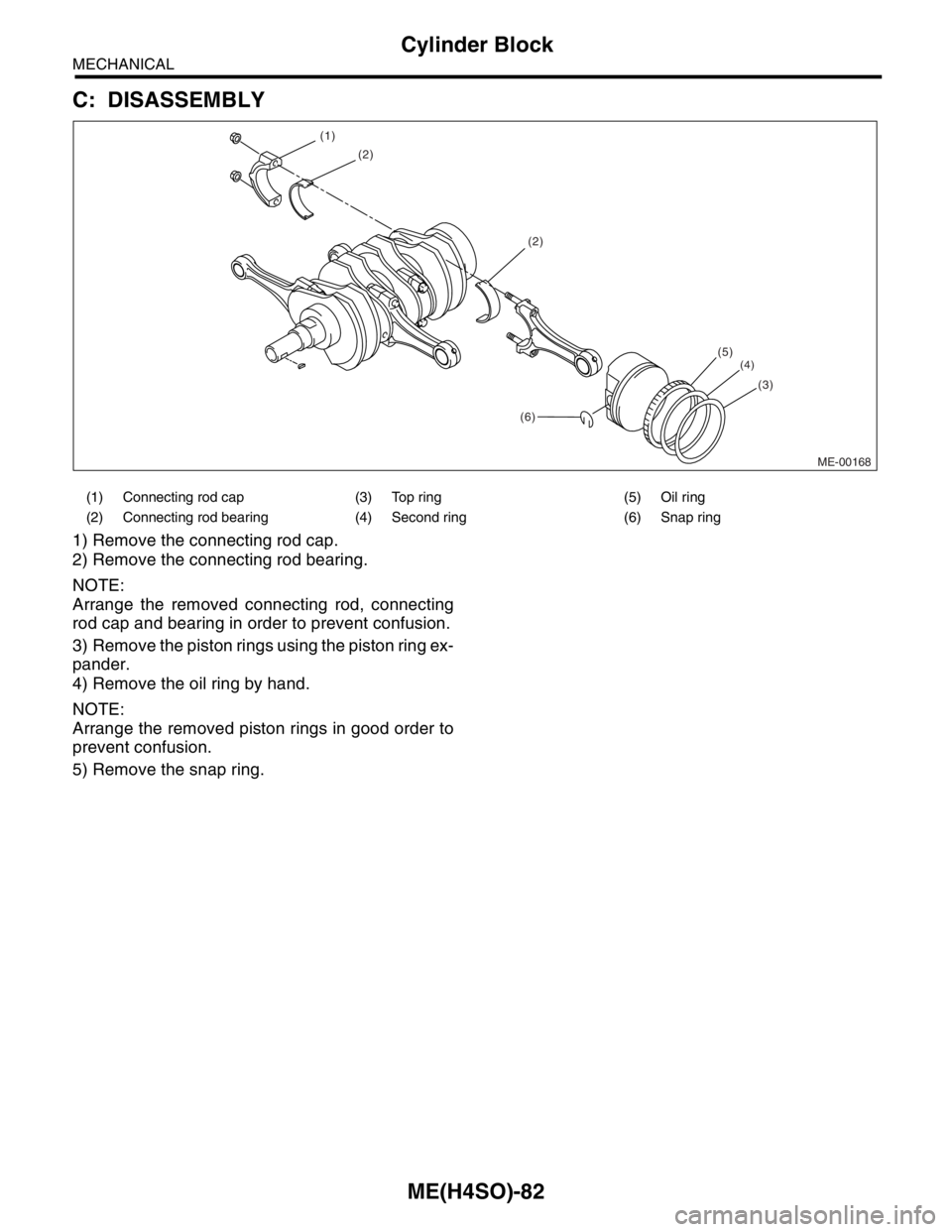
C: DISASSEMBLY
1) Remove the connecting rod cap.
2) Remove the connecting rod bearing.
NOTE:
Arrange the removed connecting rod, connecting
rod cap and bearing in order to prevent confusion.
3) Remove the piston rings using the piston ring ex-
pander.
4) Remove the oil ring by hand.
NOTE:
Arrange the removed piston rings in good order to
prevent confusion.
5) Remove the snap ring.
(1) Connecting rod cap (3) Top ring (5) Oil ring
(2) Connecting rod bearing (4) Second ring (6) Snap ring
ME-00168
(2)
(2)
(6)(5)
(4)
(3) (1)
Page 954 of 2870
ME(H4SO)-83
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
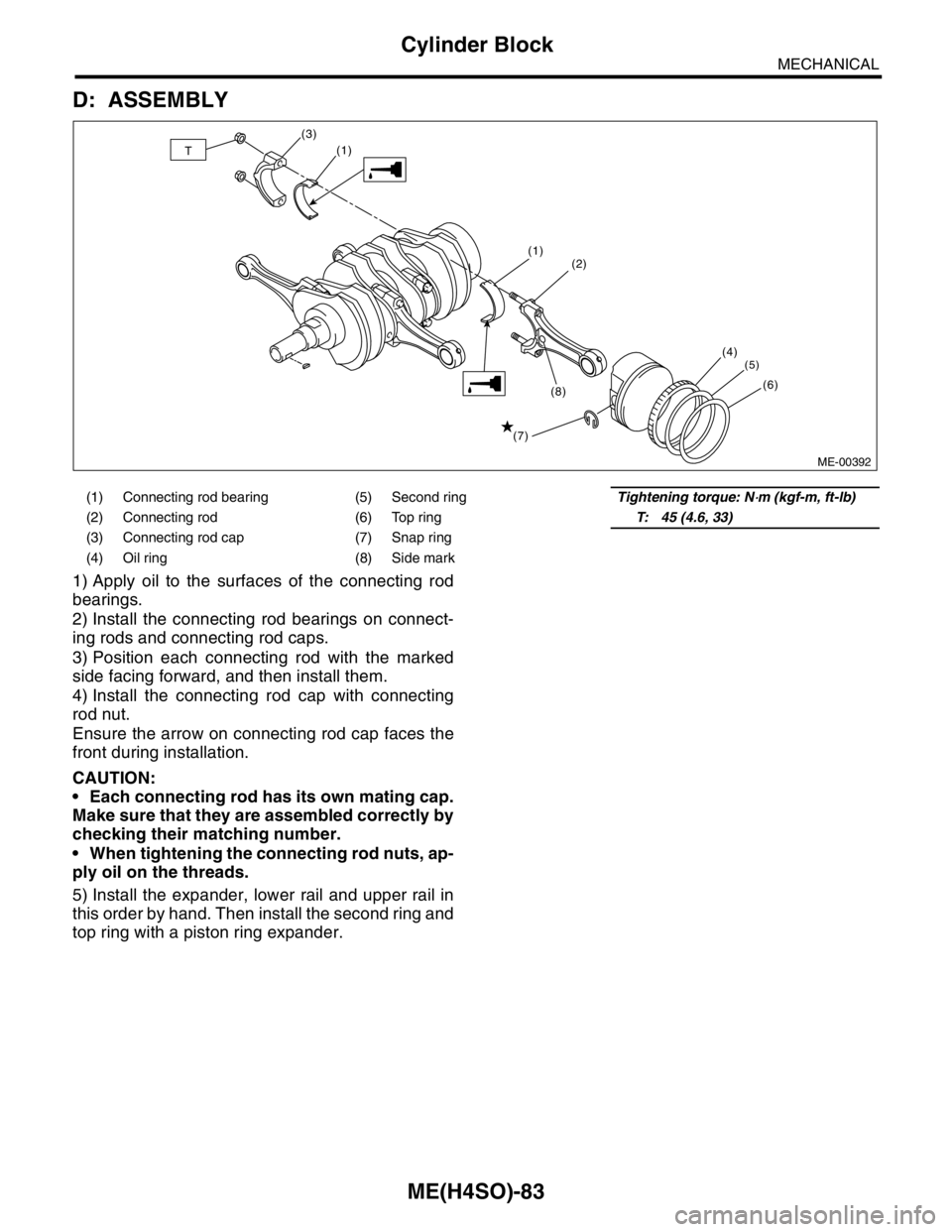
D: ASSEMBLY
1) Apply oil to the surfaces of the connecting rod
bearings.
2) Install the connecting rod bearings on connect-
ing rods and connecting rod caps.
3) Position each connecting rod with the marked
side facing forward, and then install them.
4) Install the connecting rod cap with connecting
rod nut.
Ensure the arrow on connecting rod cap faces the
front during installation.
CAUTION:
Each connecting rod has its own mating cap.
Make sure that they are assembled correctly by
checking their matching number.
When tightening the connecting rod nuts, ap-
ply oil on the threads.
5) Install the expander, lower rail and upper rail in
this order by hand. Then install the second ring and
top ring with a piston ring expander.
(1) Connecting rod bearing (5) Second ringTightening torque: N⋅m (kgf-m, ft-lb)
(2) Connecting rod (6) Top ringT: 45 (4.6, 33)
(3) Connecting rod cap (7) Snap ring
(4) Oil ring (8) Side mark
ME-00392
(2)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(1)
(1)
(7)(8) (3)T
Page 955 of 2870

ME(H4SO)-84
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
E: INSPECTION
1. CYLINDER BLOCK
1) Visually check for cracks and damage. Especial-
ly, inspect the important parts by means of red lead
check.
2) Check the oil passages for clogging.
3) Inspect the crankcase surface that mates with
cylinder head for warping by using a straight edge,
and correct by grinding if necessary.
Warping limit:
0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
Grinding limit:
0.1 mm (0.004 in)
Standard height of cylinder block:
201.0 mm (7.91 in)
2. CYLINDER AND PISTON
1) The cylinder bore size is stamped on cylinder
block’s front upper surface.
NOTE:
Measurement should be performed at a temper-
ature 20°C (68°F).
Standard sized pistons are classified into two
grades, “A” and “B”. These grades should be used
as a guide line in selecting a standard piston.Standard diameter:
2.0 L model
A: 92.005 — 92.015 mm (3.6222 — 3.6226
in)
B: 91.995 — 92.005 mm (3.6218 — 3.6222
in)
2.5 L model
A: 99.505 — 99.515 mm (3.9175 — 3.9179
in)
B: 99.495 — 99.505 mm (3.9171 — 3.9175
in)
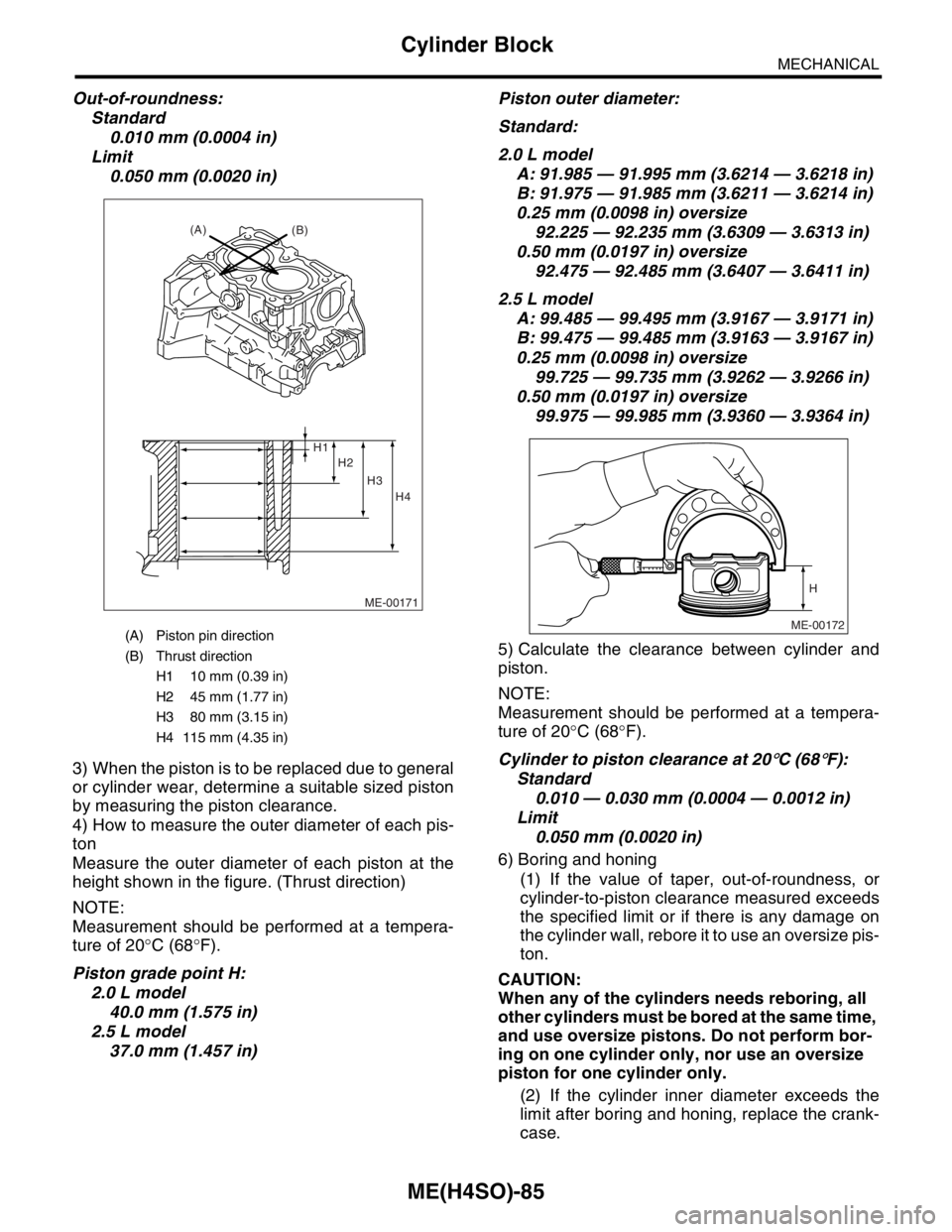
2) How to measure the inner diameter of each cyl-
inder
Measure the inner diameter of each cylinder in both
the thrust and piston pin directions at the heights
shown in the figure, using a cylinder bore gauge.
NOTE:
Measurement should be performed at a tempera-
ture 20°C (68°F).
Taper:
Standard
0.015 mm (0.0006 in)
Limit
0.050 mm (0.0020 in)
(A) Main journal size mark
(B) Cylinder block RH-LH combination mark
(C) #1 cylinder bore size mark
(D) #2 cylinder bore size mark
(E) #3 cylinder bore size mark
(F) #4 cylinder bore size mark
ME-00170 #5
#4
#3
#2
#1(A)(B)
(F)
(D)
A BA B
5 45 4
(C) (E)
Page 956 of 2870
ME(H4SO)-85
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
Out-of-roundness:
Standard
0.010 mm (0.0004 in)
Limit
0.050 mm (0.0020 in)
3) When the piston is to be replaced due to general
or cylinder wear, determine a suitable sized piston
by measuring the piston clearance.
4) How to measure the outer diameter of each pis-
ton
Measure the outer diameter of each piston at the
height shown in the figure. (Thrust direction)
NOTE:
Measurement should be performed at a tempera-
ture of 20°C (68°F).
Piston grade point H:
2.0 L model
40.0 mm (1.575 in)
2.5 L model
37.0 mm (1.457 in)Piston outer diameter:
Standard:
2.0 L model
A: 91.985 — 91.995 mm (3.6214 — 3.6218 in)
B: 91.975 — 91.985 mm (3.6211 — 3.6214 in)
0.25 mm (0.0098 in) oversize
92.225 — 92.235 mm (3.6309 — 3.6313 in)
0.50 mm (0.0197 in) oversize
92.475 — 92.485 mm (3.6407 — 3.6411 in)
2.5 L model
A: 99.485 — 99.495 mm (3.9167 — 3.9171 in)
B: 99.475 — 99.485 mm (3.9163 — 3.9167 in)
0.25 mm (0.0098 in) oversize
99.725 — 99.735 mm (3.9262 — 3.9266 in)
0.50 mm (0.0197 in) oversize
99.975 — 99.985 mm (3.9360 — 3.9364 in)
5) Calculate the clearance between cylinder and
piston.
NOTE:
Measurement should be performed at a tempera-
ture of 20°C (68°F).
Cylinder to piston clearance at 20
°C (68°F):
Standard
0.010 — 0.030 mm (0.0004 — 0.0012 in)
Limit
0.050 mm (0.0020 in)
6) Boring and honing
(1) If the value of taper, out-of-roundness, or
cylinder-to-piston clearance measured exceeds
the specified limit or if there is any damage on
the cylinder wall, rebore it to use an oversize pis-
ton.
CAUTION:
When any of the cylinders needs reboring, all
other cylinders must be bored at the same time,
and use oversize pistons. Do not perform bor-
ing on one cylinder only, nor use an oversize
piston for one cylinder only.
(2) If the cylinder inner diameter exceeds the
limit after boring and honing, replace the crank-
case.
(A) Piston pin direction
(B) Thrust direction
H1 10 mm (0.39 in)
H2 45 mm (1.77 in)
H3 80 mm (3.15 in)
H4 115 mm (4.35 in)
ME-00171
(A)
(B)
H2 H1
H3
H4
ME-00172
H
Page 957 of 2870
ME(H4SO)-86
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
NOTE:
Immediately after reboring, the cylinder diameter
may differ from its real diameter due to temperature
rise. Thus, pay attention to this when measuring
the cylinder diameter.
Limit of cylinder enlarging (boring):
0.5 mm (0.020 in)
3. PISTON AND PISTON PIN
1) Check the pistons and piston pins for damage,
cracks, and wear and the piston ring grooves for
wear and damage. Replace if defective.
2) Measure the piston-to-cylinder clearance at
each cylinder.
any of the clearances is not to specification, re-
place the piston or bore the cylinder to use an over-
size piston.
3) Make the sure that piston pin can be inserted
into piston pin hole with a thumb at 20°C (68°F).
Replace if defective.
Standard clearance between piston pin and
hole in piston:
Standard
0.004 — 0.008 mm (0.0002 — 0.0003 in)
Limit
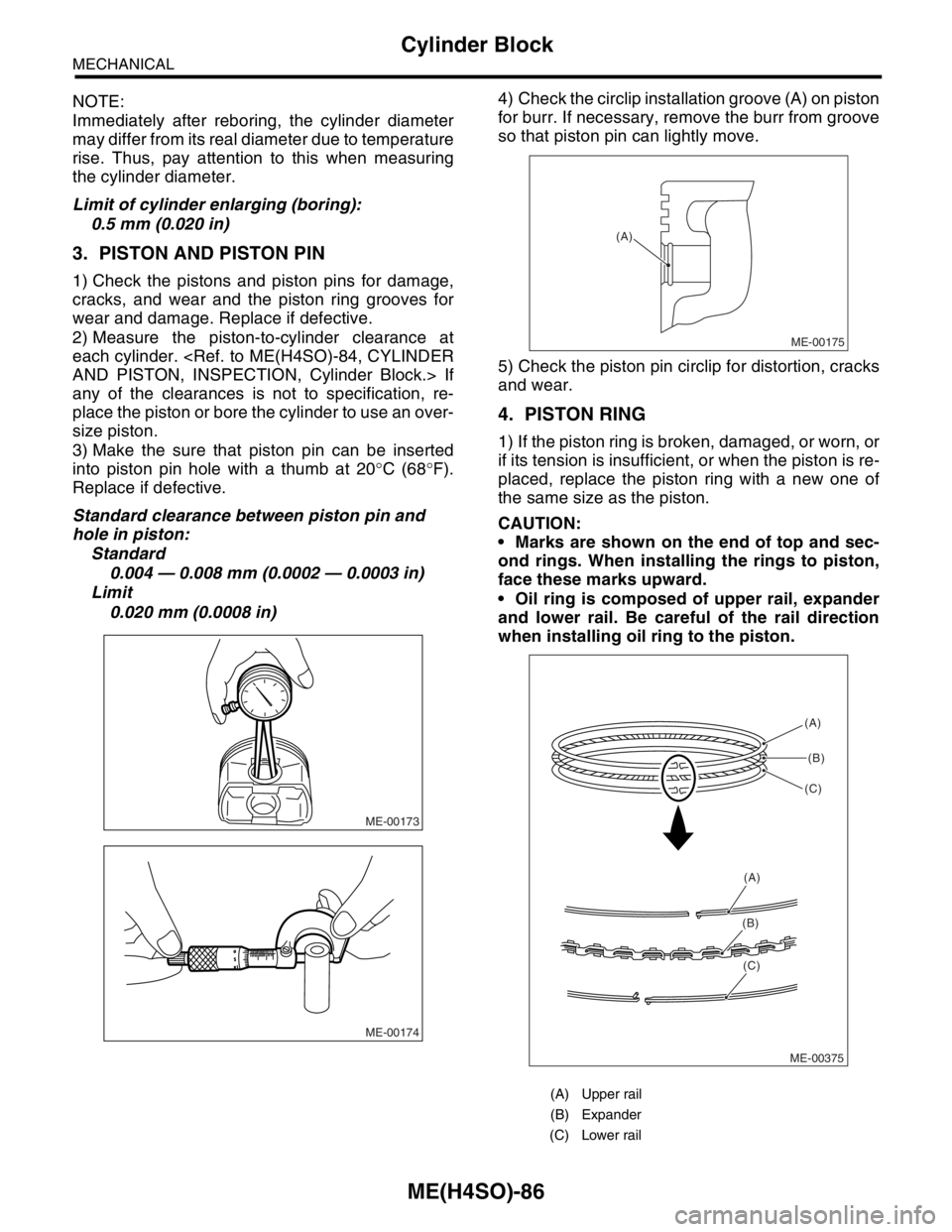
0.020 mm (0.0008 in)4) Check the circlip installation groove (A) on piston
for burr. If necessary, remove the burr from groove
so that piston pin can lightly move.
5) Check the piston pin circlip for distortion, cracks
and wear.
4. PISTON RING
1) If the piston ring is broken, damaged, or worn, or
if its tension is insufficient, or when the piston is re-
placed, replace the piston ring with a new one of
the same size as the piston.
CAUTION:
Marks are shown on the end of top and sec-
ond rings. When installing the rings to piston,
face these marks upward.
Oil ring is composed of upper rail, expander
and lower rail. Be careful of the rail direction
when installing oil ring to the piston.
ME-00173
ME-00174
(A) Upper rail
(B) Expander
(C) Lower rail
ME-00175
(A)
ME-00375(A)
(B)
(C)
(A)
(B)
(C)
Page 958 of 2870

ME(H4SO)-87
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
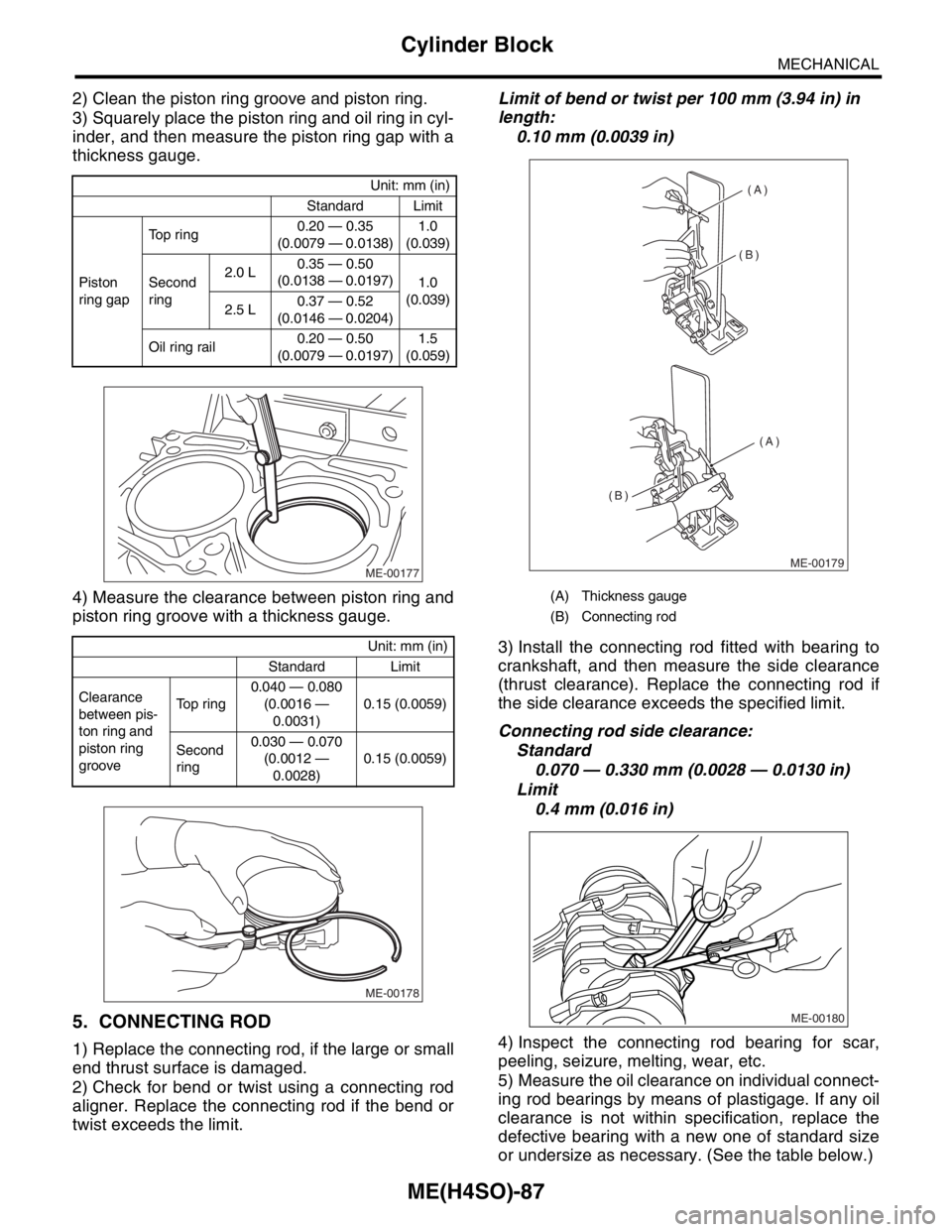
2) Clean the piston ring groove and piston ring.
3) Squarely place the piston ring and oil ring in cyl-
inder, and then measure the piston ring gap with a
thickness gauge.
4) Measure the clearance between piston ring and
piston ring groove with a thickness gauge.
5. CONNECTING ROD
1) Replace the connecting rod, if the large or small
end thrust surface is damaged.
2) Check for bend or twist using a connecting rod
aligner. Replace the connecting rod if the bend or
twist exceeds the limit.Limit of bend or twist per 100 mm (3.94 in) in
length:
0.10 mm (0.0039 in)
3) Install the connecting rod fitted with bearing to
crankshaft, and then measure the side clearance
(thrust clearance). Replace the connecting rod if
the side clearance exceeds the specified limit.
Connecting rod side clearance:
Standard
0.070 — 0.330 mm (0.0028 — 0.0130 in)
Limit
0.4 mm (0.016 in)
4) Inspect the connecting rod bearing for scar,
peeling, seizure, melting, wear, etc.
5) Measure the oil clearance on individual connect-
ing rod bearings by means of plastigage. If any oil
clearance is not within specification, replace the
defective bearing with a new one of standard size
or undersize as necessary. (See the table below.)
Unit: mm (in)
Standard Limit
Piston
ring gapTop ring0.20 — 0.35
(0.0079 — 0.0138)1.0
(0.039)
Second
ring2.0 L0.35 — 0.50
(0.0138 — 0.0197)
1.0
(0.039)
2.5 L0.37 — 0.52
(0.0146 — 0.0204)
Oil ring rail0.20 — 0.50
(0.0079 — 0.0197)1.5
(0.059)
Unit: mm (in)
Standard Limit
Clearance
between pis-
ton ring and
piston ring
grooveTop ring0.040 — 0.080
(0.0016 —
0.0031)0.15 (0.0059)
Second
ring0.030 — 0.070
(0.0012 —
0.0028)0.15 (0.0059)
ME-00177
ME-00178
(A) Thickness gauge
(B) Connecting rod
(A)
(A) (B)
(B)
ME-00179
ME-00180
Page 959 of 2870
ME(H4SO)-88
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
Connecting rod oil clearance:
Standard
0.0158 — 0.0438 mm (0.0006 — 0.0017 in)
Limit
0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
6) Inspect the bushing at connecting rod small end,
and replace if worn or damaged. Also measure the
piston pin clearance at connecting rod small end.
Clearance between piston pin and bushing:
Standard
0 — 0.022 mm (0 — 0.0009 in)
Limit
0.030 mm (0.0012 in)
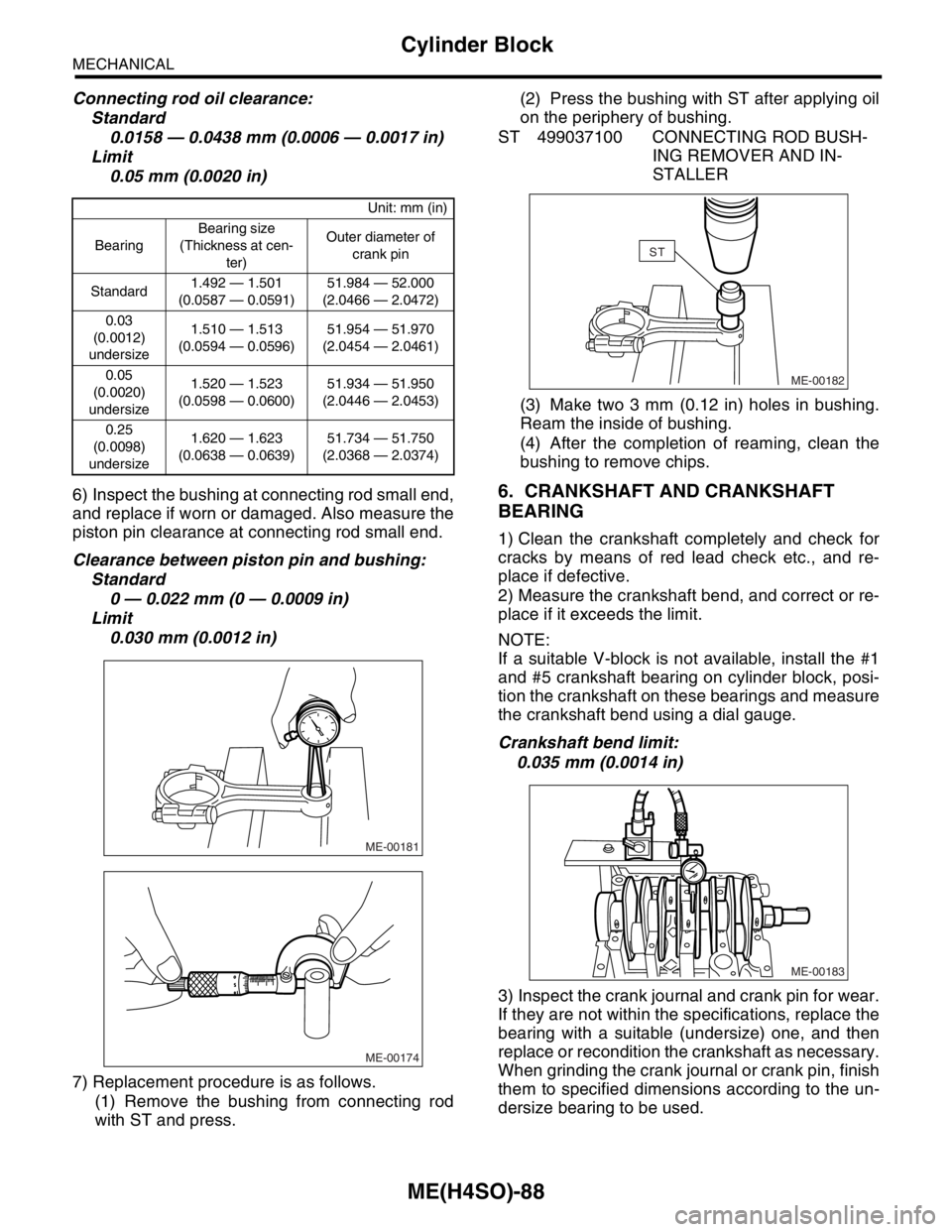
7) Replacement procedure is as follows.
(1) Remove the bushing from connecting rod
with ST and press.(2) Press the bushing with ST after applying oil
on the periphery of bushing.
ST 499037100 CONNECTING ROD BUSH-
ING REMOVER AND IN-
STALLER
(3) Make two 3 mm (0.12 in) holes in bushing.
Ream the inside of bushing.
(4) After the completion of reaming, clean the
bushing to remove chips.
6. CRANKSHAFT AND CRANKSHAFT
BEARING
1) Clean the crankshaft completely and check for
cracks by means of red lead check etc., and re-
place if defective.
2) Measure the crankshaft bend, and correct or re-
place if it exceeds the limit.
NOTE:
If a suitable V-block is not available, install the #1
and #5 crankshaft bearing on cylinder block, posi-
tion the crankshaft on these bearings and measure
the crankshaft bend using a dial gauge.
Crankshaft bend limit:
0.035 mm (0.0014 in)
3) Inspect the crank journal and crank pin for wear.
If they are not within the specifications, replace the
bearing with a suitable (undersize) one, and then
replace or recondition the crankshaft as necessary.
When grinding the crank journal or crank pin, finish
them to specified dimensions according to the un-
dersize bearing to be used.
Unit: mm (in)
BearingBearing size
(Thickness at cen-
ter)Outer diameter of
crank pin
Standard1.492 — 1.501
(0.0587 — 0.0591)51.984 — 52.000
(2.0466 — 2.0472)
0.03
(0.0012)
undersize1.510 — 1.513
(0.0594 — 0.0596)51.954 — 51.970
(2.0454 — 2.0461)
0.05
(0.0020)
undersize1.520 — 1.523
(0.0598 — 0.0600)51.934 — 51.950
(2.0446 — 2.0453)
0.25
(0.0098)
undersize1.620 — 1.623
(0.0638 — 0.0639)51.734 — 51.750
(2.0368 — 2.0374)
ME-00181
ME-00174
ME-00182
ST
ME-00183
Page 960 of 2870

ME(H4SO)-89
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
Crank pin and crank journal:
Out-of-roundness
0.020 mm (0.0008 in) or less
Taper limit
0.07 mm (0.0028 in)
Grinding limit
0.250 mm (0.0098 in)
ME-00184