ASTON MARTIN DB7 1997 Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: ASTON MARTIN, Model Year: 1997, Model line: DB7, Model: ASTON MARTIN DB7 1997Pages: 421, PDF Size: 9.31 MB
Page 381 of 421
The Aston Martin Lagonda Diagnostic System
Users Guide D-^?
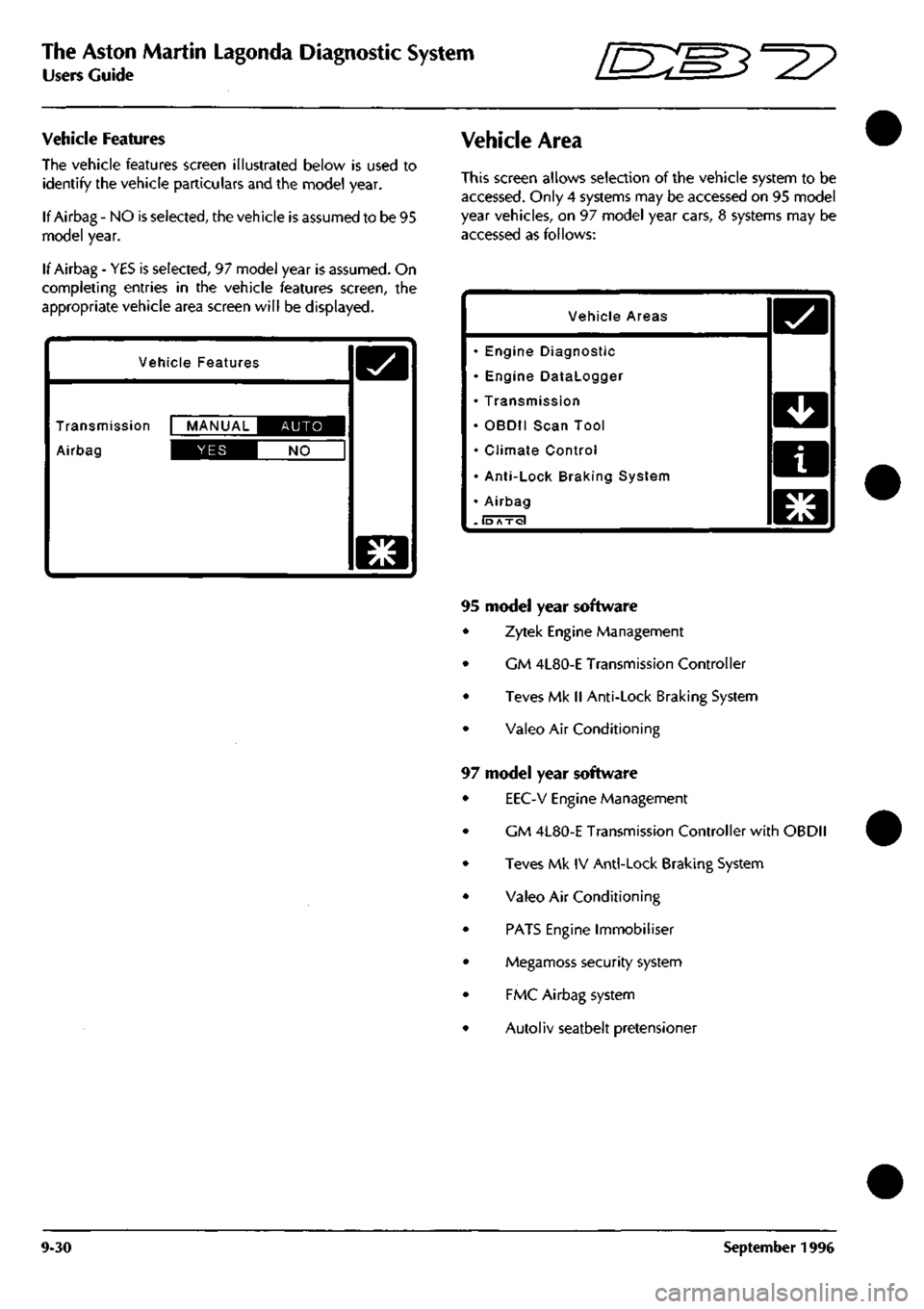
Vehicle Features
The vehicle features screen illustrated below is used to
identify the vehicle particulars and the model year.
If Airbag - NO is selected, the vehicle is assumed to be 95
model year.
If Airbag - YES is selected, 97 model year is assumed. On
completing entries in the vehicle features screen, the
appropriate vehicle area screen will be displayed.
Vehicle Features
Transmission MANUAL IIBIE^^I
Airbag IDS^I NO
D
Vehicle Area
This screen allows selection of the vehicle system to be
accessed.
Only 4 systems may be accessed on 95 model
year vehicles, on 97 model year cars, 8 systems may be
accessed as follows:
Vehicle Areas
• Engine Diagnostic
• Engine Datalogger
• Transmission
• OBDII Scan Tool
• Climate Control
• Anti-Lock Braking System
• Airbag
. lb Axol
o
PI
mLM
n
WLM
El
Ku^
95 model year software
Zytek Engine Management
GM 4L80-E Transmission Controller
Teves Mk II Anti-Lock Braking System
Valeo Air Conditioning
97 model year software
EEC-V Engine Management
CM 4L80-E Transmission Controller with OBDII
Teves Mk IV Anti-Lock Braking System
Valeo Air Conditioning
PATS Engine Immobiliser
Megamoss security system
FMC Airbag system
Autoliv seatbelt pretensioner
9-30 September 1996
Page 382 of 421
^?
The Aston Martin Lagonda Diagnostic System
Users Guide
Cable Setup - 95 MY
On
selectingthe
required
vehiclearea,
the selected
software
will be loaded and then the Cable Setup screen will
appear.
Connections will
be
shown directly
to the selected
control
unit
on
95 nnodel year vehicles
using
the vehicle interface
adaptor (VIA) and appropriate cables from the PDU kit.
Select the specified interface devices and cables from the
PDU kit and connect as shown in the diagram.
Cable Setup - 97 MY
On 97 model year
vehicles,
connections
to the
vehicle are
made via the Aston Martin Multi-Protocol Adaptor and
two diagnostic sockets for most vehicle systems.
Cable Setup
Upper Diagnostic Socket
o
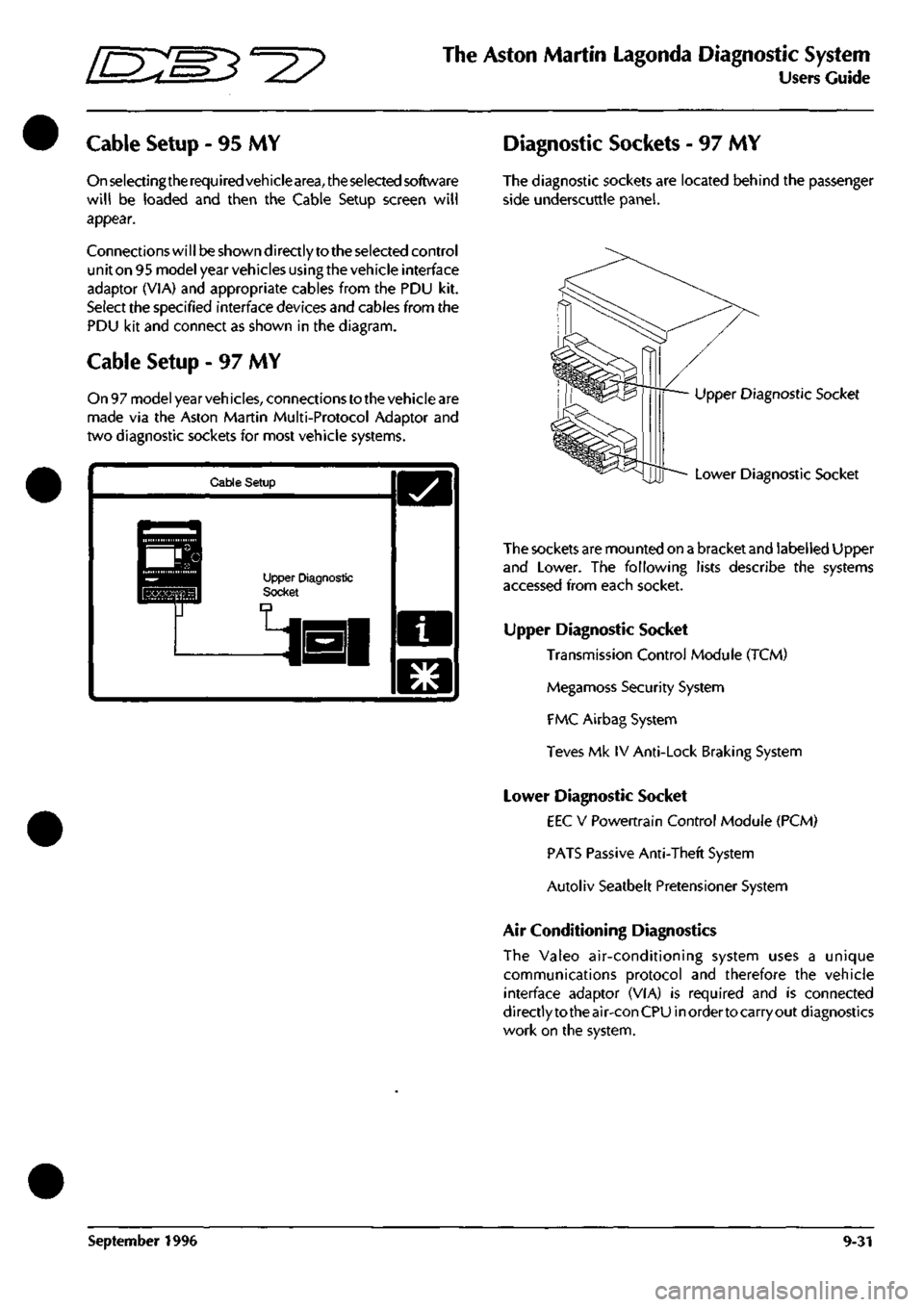
Diagnostic Sockets - 97 MY
The diagnostic sockets are located behind the passenger
side underscuttle panel.
Upper Diagnostic Socket
Lower Diagnostic Socket
The
sockets are
mounted on
a
bracket
and
labelled Upper
and Lower. The following lists describe the systems
accessed from each socket.
Upper Diagnostic Socket
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
Megamoss Security System
FMC Airbag System
Teves Mk IV Anti-Lock Braking System
Lower Diagnostic Socket
EEC V Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
PATS Passive Anti-Theft System
Autoliv Seatbelt Pretensioner System
Air Conditioning Diagnostics
The Valeo air-conditioning system uses a unique
communications protocol and therefore the vehicle
interface adaptor (VIA) is required and is connected
directlytotheair-conCPU inordertocarryout diagnostics
work on the system.
September 1996 9-31
Page 383 of 421

The Aston Martin Lagonda Diagnostic System
Users Guide "^7
Establishing Communications
when cable connections are completed, switch on the
vehicle ignition. The electronic control units will 'wake
up'
and communication between the selected control unit
and the PDU will be established.
As communication
is
established with the selected system,
a system menu similar to that below will be displayed.
System Menu Selections
The options for each vehicle system are described in detai
I
on the following pages but menu entries fall into the
following general areas:
Security
• Datalogger
• Diagnostic Trouble Code and
Alarm History Monitor
• RF Transponder Key Learning
• Exit a
o
Datalogger
The Datalogger function is described in detail using a
worked example at the end of this PDU Users Guide.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes
This application enables the PDU to monitor selected
control module trouble codes and provides the following
functions:
• Decode and display any trouble codes logged by
the control module being monitored.
• When supported by the module, decodeand display
enhanced trouble
codes,
together with any count of
the number of occurrences
• Clear all of the trouble codes and freeze frame data
logged in the control module.
• Monitor other data such as the alarm history in this
example.
Note: The 95model year Zytek engine management
system permits clearing of individual trouble codes
selected by the technician on the PDU.
System Specific Tests
These menu entries cover special tests required to program
ortest system specificfeatures. The following are examples
of tests provided:
Engine KOEO and KOER tests
OBDII Readiness test
Output State Control test
Throttle Potentiometer track test
Ignition Key Learn Menu
Remote Transmitter Key Learn Tests
Special Functions Programming
PATS
Security
Exit
Selecting and then confirming the exit option will return
the PDU to the Main Menu.
PDU Use
In the following
pages,
the use of the PDU on each vehicle
system is described.
Engine Diagnostics
Transmission Diagnostics
Climate Control Diagnostics
Anti-Lock Brakes Diagnostics
Passive Anti-Theft (PATS) Diagnostics
Security System Diagnostics
Airbag Diagnostics
Seat Belt Pretensioner Diagnostics
After these system specific descriptions, the following
general purpose functions are described:
Datalogger
Digital Multi-Meter
Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Printing
Training
OBD II Scan Tool
User Self-Test
9-32 September 1996
Page 384 of 421

^27
The Aston Martin Lagonda Diagnostic System
Users Guide
Engine Diagnostics - 97 MY
Selecting Engine Diagnostics from the Vehicle Area screen
brings up the following Engine Diagnostics Screen.
Engine Diagnostic
• Diagnostic Trouble Codes
• KOEO on Demand Self Test
• KOER on Demand Self Test
• OBDII Readiness Tests
• Output State Control
• Throttle Checks
• Exit
o
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
On selecting DiagnosticTrouble
Codes,
the PCM memory
will be scanned and any recorded DTCs will be decoded
and displayed.
The engine and transmission DTCs are integral to the On
Board Diagnostics (OBDII) system and are ful ly described
in the DB7 OBD II Diagnostics Manual.
Before attempting to clear the logged DTCs, record all
logged DTCs for use in subsequent fault analysis.
All logged DTCs may be cleared by selecting the EEC-V
EMS DTCs
title.
This will bring up the Clear
(C)
icon which
may be selected and confirmed to clear all logged DTCs.
Note that on clearing all logged DTCs you will also clear
the associated timers, counters and fault history files (and
extinguish the engine management warning lightfor North
American vehicles). The OBD II readines test status will
also clear down and a PI 000 (OBD II readiness test
incomplete) trouble code will be set.. A full drive cycle
(see DB7 OBD II Diagnostics Manual) must be completed
to clear the PI 000 code if required. The PI 000 code will
clear automatically after some miles of driving when all
required tests have satisfactorily completed.
Caution: If a transmission code is logged in the PCM, the
TCM DTCs must be cleared first and then clear the PCM
DTCs. If the PCM DTCs are cleared without clearing the
TCM, the TCM code will immediately reset in the PCM
when power is restored.
Key On Engine Off (KOEO) and Key On Engine
Running (KOER) On Demand Self Tests
Before either the KOEO or KOER test will run, the engine
coolant temperature must be in excess of
BO'C.
Select and
confirm either the KOEO or KOER test. If the coolant
temperature is too low, the Pre Test Engine Warm Up
screen will appear. Start the engine and run until coolant
temperature is at 80+°C.
Pre Test Engine Warm Up
Value : 41°C
80 Engine Coolant Temperature {°C)
Waiting for engine to reach
normal operating temperature
o
KOEO Test
As coolant temperature rises through the BO'C level, the
technician will be requested to turn the ignition off and
then on again. The KOEO test will then commence. Static
inputs to the PCM will be checked and any faults detected
will be recorded and displayed as DTCs. If any DTCs other
than PI 000 are logged, go to the OBD II Diagnostics
Manual and resolve the concern(s) using the OBD 11
diagnostic procedures.
KOER Test
If coolant temperature level is below 80°C, the technician
will be prompted to start and run the engine until coolant
temperature rises above 80°C. As the temperature passes
the 80°C
level,
the KOERtest will commence automatically.
If coolant temperature is above the 80°C level, the
technician wi
11
be requested to start the engine. The KOER
test will commence as the engine is started. Dynamic
inputs to the PCM will be checked and any faults detected
will be recorded and displayed as DTCs. If any DTCs other
than PI 000 are logged, go to the OBD 11 Diagnostics
Manual and resolve the problem(s) using the OBD II
diagnostic procedures.
September 1996 9-33
Page 385 of 421

The Aston Martin Lagonda Diagnostic System
Users Guide ^-^z?
OBD
II
Readiness Test Monitor
- 97 MY
SelectingOBD II Readiness
Tests
will bring up the following
screen.
OBDII Readiness Tests
1
of 9
tests completed.
Logged DTCs
: 1
The following tests have been
identified
as
incomplete:
MISFIRE
ir
1 C.C.M.
CAT MON 1IPURGE
MONII SAIR
M"ONn
02 SENS
1l02
HEAT
II EGR
MONTI
@
This software monitors
the
status
of all
significant
components and parameters required
to
control vehicle
emissions. When the tests are satisfactorily completed, the
test boxes wi
11
be empty and the PI 000 status code wi
11
be
removed from
the DTC
list.
If any problem
is
detected,
the tests will be terminated and
the status will be shown as
on
the screen above e.g.:
1 of
9 tests completed. Logged DTCs
: 1
Incomplete test titles will remain
in the
screen boxes.
Completed test titles are deleted from
the
screen boxes.
Details
of any
trouble codes
may be
accessed using
the
Diagnostic Trouble Code function.
The tests incorporated into this routine are as follows:
Misfire Monitoring
Fuel System Monitoring
Comprehensive Component Monitoring
Catalyst Monitoring
Purge System Monitor
Secondary
Air
Injection Monitor
Oxygen Sensor Monitor
Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Monitor
Throttle Position Sensor Track Test
- 97 MY
This test
is
used
to
detect
any
problems with
the
throttle
potentiometer track which could cause faulty throttle
position signals
to
enter
the
PCM. Such signals would
result
in
incorrect calculation
of
engine power demand
and possibly create excessive fuelling and high emissions.
Selecting Throttle Checks from
the
Engine Diagnostics
screen will bring uptheThrottle Position Sensor Track Test
screen:
Throttle
pot
track test
Throttle State: PART
Value
: 1.9V
ov
Throttle
pot
voltage
Depress
The
Throttle Slowly
5V
o
Follow the screen instructions
to
test the throttle position
sensor track. The throttle must be moved slowly from fu
I
ly
closed
to
fully open without hesitation.
Any
pause
in
throttle movement will
be
interpreted
as a
track fault.
If
a
fault
is
detected, repeat
the
test several times
to
elliminate hesitant throttle movement errors from actual
potentiometer faults.
If
a repeatable fault
is
detected,
the
potentiometer must
be
replaced.
9-34 September
1996
Page 386 of 421

^^2?
The Aston Martin Lagonda Diagnostic System
Users Guide
Output State Control - 97 MY
This menu item provides a quick test of the basic electro
mechanical components controlled by the PCM. These
tests should be performed in a key on engine off state.
The selections available are:
• Low Speed Cooling Fans
• High Speed Cooling Fans
• Set Electromechanical Outputs
Low and High Speed Fans
Selecting and confirming either the low or high speed
cooling fans will run the fans at the selected speed for 5
seconds to verify their operation.
Electromechanical Outputs
This selection will cause the following electromechanical
devices to operate for five seconds
Air Pump
Fuel Pumps
Canister Purge Valve
Idle Air Control Valve
Observing each device in turn as the PCM outputs are
turned 'On' will enable the technician to verify correct
operation.
September 1996 9-35
Page 387 of 421

The Aston Martin Lagonda Diagnostic System
Users Guide ffi:S5'=2?
Engine Datalogger
The datalogger software is designed to aid the technician in identifying permanent or intermittent faults in the DB7's
electrical and electronic systems. It can provide a recorded view of selected signals over a chosen time period. This
recording may be captured in a static, rolling road or road test situation. Data recorded during such tests may then be
analysed on completion of the test or printed out for later analysis.
Datalogger operation is described using a fully worked example at the end of this PDU Users Guide.
The full list of datalogger signal names and descriptions is provided in the DB7 OBDII Diagnostic Manual and on the PDU
screen.
The following list is a summary of the PCM signals which may be monitored.
Signal Description
ACCS Air-Con Control Switch - 1 = A/C On
ACP Air-Con Pressure Sensor - 1 = A/C pressure high
ACT MAX Maximum Intake Air Temperature signal during normal running
Adap Fuel 1 Current Adaptive Fuel Correction - (% of range)
Adap Fuel 2 Current Adaptive Fuel Correction - (% of range)
ADPT1F Adaptive Fuel - Table 1 failure mode
ADPT2F Adaptive Fuel - Table 2 failure mode
AIR Air Pump On/Off - 1 = Pump On
AIRM Air Pump Monitor -1 =
high,
pump on
B+ Battery Positive - Volts
BARO Barometric Pressure
CID Cylinder Identification - Cam sensor status
CMP STAT Cam Position Sensor -1 = CID mis, not currently reliable
DRVCNT Number of OBDll Drive Cycles Completed
DSDRPM Desired engine speed (RPM)
DTCCNT Diagnostic Trouiale Codes Count (Fault codes + pending codes. MIL and non-MIL)
ECT MAX Maximum Engine Coolant Temperature signal during normal running
ECT STAT Engine Coolant Temperature - in or out of range
ECT-C Engine Coolant Temperature - "C or raw counts
ECT-V Engine Coolant Temperature - Volts or raw counts
EGR STAT EVP EGR sensor failure
ENGLOAD Engine Load (Ratio of air charge over standard)
ENGRPM Engine Speed - RPM
EPT DPFE Sensor feedback
EVAP DC Cannister Purge Duty Cycle (% on)
EVAPCVA Vapour Management Valve (VMV) fault detected
Evts HI Cumulative cylinder events total carried over from previous background logic executions
Evts LO Cumulative cylinder events total carried over from previous background logic executions
FPM Fuel Pump Monitor - 0 = pump off, 1 = pump on
FPUMP DC Desired Fuel Pump Duty Cycle - 0% or 100%
H02S12 Sensor Output - Volts
H02S21 Sensor Output - Volts
H02S22 Sensor Output - Volts
H02S1I Sensor Output - Volts
HFC High Speed Fan Status
Htrl
1
ret Highest number of retries seen on the H02S 11 heater
Htrl 2 ret Highest number of retries seen on the H02S 12 heater
Htr21 ret Highest number of retries seen on the H02S 21 heater
Htr22 ret Highest number of retries seen on the H02S 22 heater
HTRCM11 H02S n heater current
HTRCM12 H02S 12 heater current
HTRCM21 H02S 21 heater current
HTRCM22 H02S 22 heater current
9-36 September 1996
Page 388 of 421

^
The Aston Martin Lagonda Diagnostic System
Users Guide
Signal Description
lACDTCY Idle Air Control Duty Cycle (% open)
lAT Intake Air Temperature - °C or raw input counts
lAT STAT Air Temperature - Temperature sensor failure
lAT-V Intake Air Temperature - Volts or raw counts
IGN Desired Ignition Timing - ° BTDC
INDS Input from manual lever position sensor (counts)
IPWA Injector Pulse Width in mS- Bank A (Cylinders
1
-3)
IPWB Injector Pulse Width in mS- Bank B (Cylinders 4-6)
LAMSE1 Current Short Term Fuel Trim 1, adjustment from stoich - (% of range)
LAMSE2 Current Short Term Fuel Trim 2, adjustment from stoich - (% of range)
LFC Low Speed Fan Status
LOOP Fuel Control -1 = Open Loop, 0 = Closed Loop
MAF MAX Maximum Mass Air Flow signal during normal running
MAF Raw MAF sensor output (A/D counts)
MAF STAT Mass Air Flow Meter - MAF sensor failure
MIL Mali Indicator Lamp Status -1 = Lamp On
Mis HI Cumulative misfires detected by misfire test (Hi bit).
Mis LO Cumulative misfires detected by misfire test (Lo bit).
Mis nc HI Cumulative misfires detected by a misfire test (Hi bit).
Mis nc LO Cumulative misfires detected by a misfire test.
Misi HI Cumulative misfires detected by cylinder
1
misfire test (Hi bit).
Misi LO Cumulative misfires detected by cylinder
1
misfire test (Lo bit).
Mis2 HI Cumulative misfires detected by cylinder 2 misfire test (Hi bit).
Mis2 LO Cumulative misfires detected by cylinder 2 misfire test (Lo bit).
Mis3 HI Cumulative misfires detected by cylinder 3 misfire test (Hi bit).
Mis3 LO Cumulative misfires detected by cylinder 3 misfire test (Lo bit).
Mis4 HI Cumulative misfires detected by cylinder 4 misfire test (Hi bit).
Mis4 LO Cumulative misfires detected by cylinder 4 misfire test (Lo bit).
Mis5 HI Cumulative misfires detected by cylinder 5 misfire test (Hi bit).
Mis5 LO Cumulative misfires detected by cylinder 5 misfire test (Lo bit).
Mis6 HI Cumulative misfires detected by cylinder 6 misfire test (Hi bit).
Mis6 LO Cumulative misfires detected by cylinder 6 misfire test (Lo bit).
MISF Misfire Monitor - 1 = Currently misfiring
ODCODES Total number of on-demand codes currently stored.
PGM CVS DC Purge Management Duty Cycle (% on)
PIP Profile ignition Pick-Up - PIP input level
PNP Park Neutral Position Switch
R-BIAS1 Rear bias trim (Bank 1, cylinders
1
-3)
R-BIAS2 Rear bias trim (Bank 2, cylinders 4-6)
RATCH Lowest TP reading during driving
TP MAX Maximum Throttle Potentiometer signal during normal running
TP STAT Throttle Position Sensor - TP sensor failure
TP Throttle Potentiometer - Volts or counts
TPR-V Raw counts from sensor
TQ-NET Net torque into the torque convertor
TRIP OBDII Drive Cycle Complete (except cat monitor) - 1 = Trip completed
TRIPCNT Number of Completed OBDII Trips
VS MAX Maximum Vehicle Speed signal during normal running
VS STAT Vehicle Speed Sensor mode flag
VS Vehicle Speed - MPH
WAC Wide Open Throttle A/C Cut-Off -1 = High (WOT Relay)
September 1996 9-37
Page 389 of 421
The Aston Martin Lagonda Diagnostic System
Users Guide ^?
Engine Setup
- 95 MY
Two adjustments
may
beset with the aid of the PDU
on 95
MY vehicles.
• Throttle Potentiometer
• Idle Fuelling Trim
From
the 95 MY
Main Menu, make
and
confirm
the
following sequence
of
selections:
Diagnostics
/
Manual
or
Auto Transmission
/
Engine
/
Engine Setup
/
The following connection diagram will then be displayed.
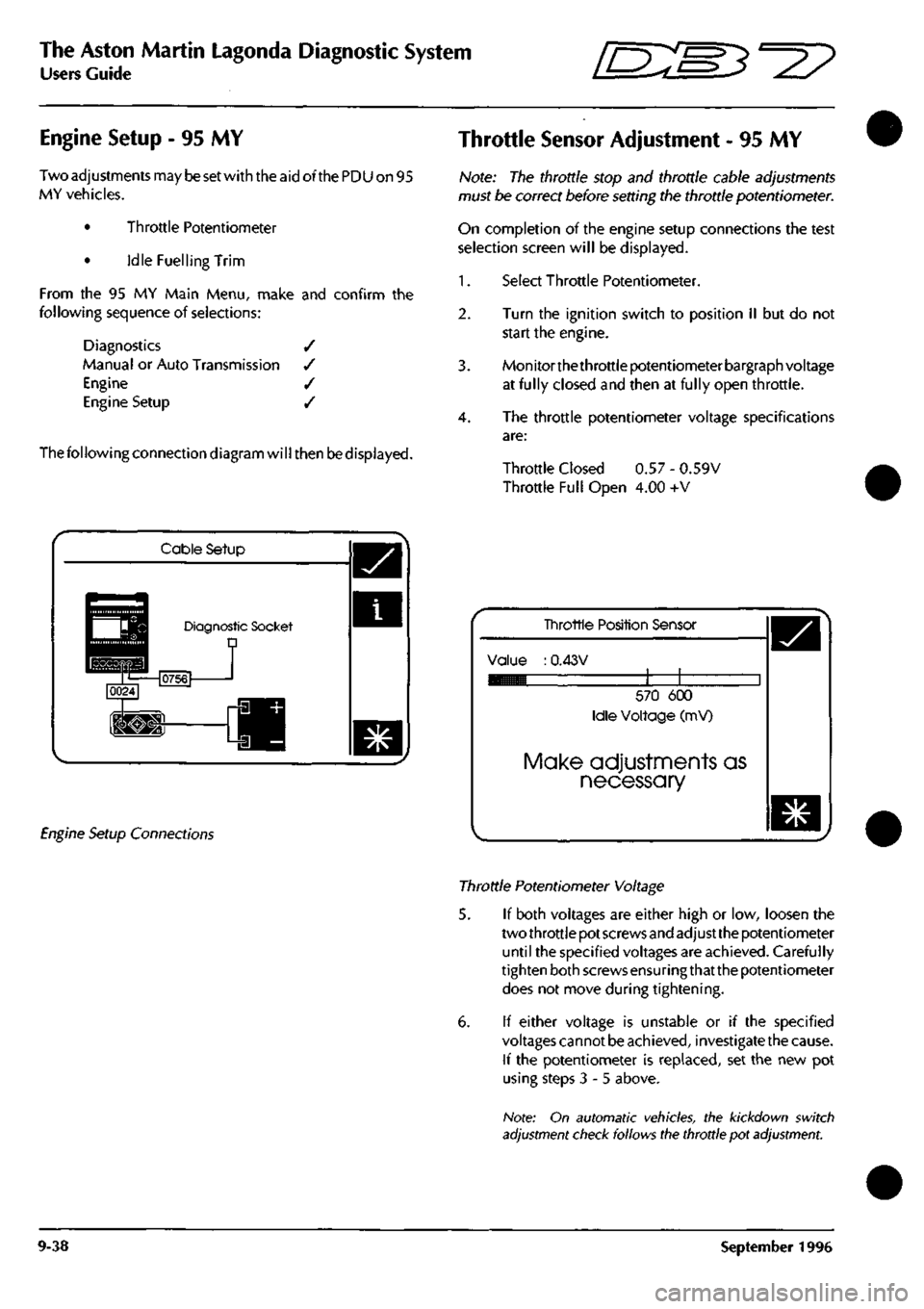
Throttle Sensor Adjustment
- 95 MY
Note:
The
throttle stop
and
throttle cable adjustments
must
be
correct before setting
the
throttle potentiometer.
On completion
of the
engine setup connections
the
test
selection screen will
be
displayed.
1.
Select Throttle Potentiometer.
2.
Turn
the
ignition switch
to
position
II but do not
start
the
engine.
3. Monitorthethrottle potentiometer bargraph voltage
at fully closed
and
then
at
fully open throttle.
4.
The
throttle potentiometer voltage specifications
are:
Throttle Closed
0.57 -
0.59V
Throttle Full Open
4.00 +V
Cable Setup
Diagnostic Socket D
Engine Setup Connections
Tinrottle Position Sensor
Value
:
0.43V
570
600
Idle Voltage
(mV)
Make adjustments as
necessary
Throttle Potentiometer Voltage
5.
If
both voltages
are
either high
or low,
loosen
the
two throttle pot screws and adjust the potentiometer
until
the
specified voltages
are
achieved. Carefully
tighten both screws ensuringthat the potentiometer
does
not
move during tightening.
6.
If
either voltage
is
unstable
or if the
specified
voltages cannot
be
achieved, investigate the cause.
If
the
potentiometer
is
replaced,
set the new pot
using steps
3-5
above.
Note:
On
automatic vehicles,
the
kickdown switch
adjustment check follows the throttle
pot
adjustment.
9-38 September
1996
Page 390 of 421

ffi:
The Aston Martin Lagonda Diagnostic System
Users Guide
Idle Fuelling Trim - 95 MY
This program is used to check and if necessary reset the
fuelling level at idle to ensure that the specified idle speed
and emission levels are attainable. The throttle
potentiometer adjustment sequence must be completed
before the fuel trim sequence can be run.
Note: The throttle setup must be completed before
attempting to set the Idle Fuelling Trim. An error in
throttle
stop,
throttle cable or throttle pot
adjustments can
cause serious
difficulties in setting the Idle Fuelling.
Select Idle Fuelling Trim from the Engine Setup
Menu.
(The PDU connections are
as
fortheThrottle
Potentiometer Adjustment.)
1.
3.
StarttheDB7engineand allow itto warm to normal
operating temperature.
Followthescreeninstructionstorunthe idle fuelling
trim procedure.
Observe the bargraphs for oxygen sensors A and B.
The bargraph indications should oscillate evenly
about the 0% position on the bargraph.
BANK
-100%
BANK
-100%
Idle
Fuel
Trim
Closed Loop Control Data
Q Idle
trim:
8%
9^B 1 1
Oxygen Sensor Fuel Trim 100%
B Idle
trim:
5% —1 1 1
«^
1 1 Oxygen Sensor Fuel
Trim
100%
Idle Fuelling Trim Display
5. Ifthebargraphindicationsarenotoscillatingevenly
about the 0% position, select the A (cylinders 1, 2
and 3) or the B (cylinders 4, 5 and 5) sensor. The
Increase/Decrease buttons will appear.
6. Adjust the fuel trim as required to achieve even
oscillation about the 0% mark for both sensors.
When the adjustment is correct, select the 4 icon
and confirm that the idle fuelling trim is correct. On
confirmation of the adjustment, the PDU will exit
from the idle fuelling program.
7. On completion of the procedure, select Exit from
the Engine Diagnostics Software.
September 1996 9-39