MAZDA PROTEGE 1992 Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 1992, Model line: PROTEGE, Model: MAZDA PROTEGE 1992Pages: 1164, PDF Size: 81.9 MB
Page 1061 of 1164

Reading Wiring Diagrams Z-GI-5
System name
SYSTEM l FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM f
B-lc py,p -
Current flows in the direction of the arrow.
L
::::y...:::..: ::::;IF::::::I::::.:I:I~-. I :I::- .::
F
~~-;..~~~-~-~~~-~-~-~-~-~~~~~-:~-. t /
*Indicates shielded wire.
*Shielded wire:
Prevents signal disturbances due to
electrical interference.
Wire is covered by a metal meshing for
grounding.
*Two-color wires are indicated by a Two-letter
symbol. The first letter indicates the base color of
the wire and the second indicates the color of the
stripe.
For example
W/R is a white wire with a red strip
BR/Y is a brown wire with a yellow strip
Symbol
(Example) solid color wire
Striped wire
Red&ripe)
l
The harness symbol is given in the (
the wire color (Refer to GI-7.). ) following The number (e.g. 6), indicates the
circuit continues to the related system
diagram.
0 Male and female connectors are represented as follows in
the circuit and connector diagrams.
C3r3r;$,diagram
l Like connectors are linked by broken lines between the
connector symbols.
oconnector diagrams always show connectors on the
harness side. The arrow Indicates the view from the
harness side.
(Example)
View horn harness ride
@Colors for connectors other than those that are off white
are given in dia rams.
0 Unused termrn d s are
indicated by $ .
Page 1062 of 1164

z-GI-6 Reading Wiring Diagrams
Routing diagram
l This shows where electrical components are located on the system circuit diagram by lead and connector
symbols.
l Specified values are listed beside the routing diagram or on the following page.
Shows the system that uses the
connector.
Shows the names of components in routing diagrams.
(Example)
I Connector 1 Symbol 1
Joint box JB-04
Common connectors lXi?U
System connectors I-03 Shows the ground in system diagrams.
JOINT Shows values for determining
whether an electrkal component
is good.
Z-6
Page 1063 of 1164

Reading Wiring Diagrams Z-GI-7
HARNESS SYMBOLS
DESCRIPTION OF HARNESS
FRONT HARNESS
ENGINE HARNESS
INSTRUMENT PANEL HARNESS
REAR HARNESS
REAR NO.2 HARNE COLOR SYMBOL DESCRIPTION OF HARNESS SYMBOL
(F) INTERIOR LAMP HARNESS (IN)
(El FLOOR HARNESS
FW
(1) DOOR NO.1 HARNESS Ml)
DOOR NO.2 HARNESS
WW
EMISSION HARNESS AIR CONDITIONER HARNESS
INSTRUMENT PANEL HARNESS
FRONT HARNESS [a ,&<\I INJECTION HARNESS [INJ]
EMISSION’ HARNESS (EM)
I ENGINE HARNESS [E]
/
EMISSION HARNESS (EM)
INTERlOq IAMP HARNESS [IN]
- INTERlO? LAMP HARNESS [IN]
SUNRGOF GESS [SU]
REAR HklNESS [R]
323 HATCHBACK
IARNESS (R3)
FL00F4 HAdNEss(FR1 -,A HARNESS (Rl DOOR NO.3 HARNESS [DRS]
PROTE&
Page 1064 of 1164

Z-Gl-8 Reading Wiring Diagrams
Svmbols I
Symbol Meaning Symbol Meaning
Battery (I, Generates electricity through Resistance l A resistor with a constant value
chemical reaction l Mainly used to protect electrical
l Supplies direct current to circuits components in circuits by maintaining
rated voltage
l Reading resistance values
Ground (1)
l Connecting point to vehicle body or No.1 Cobr band
-A- other ground wire where current flows -No.2 Cobr band
from positive to negative terminal of -No.3 Cobr band
battery No.4 Cobr band
1
l Ground (1) indicates a ground point to Flnt color. Rerkrancs
body through wire harness
Ground (2) l Gound (2) indicates point where
component is grounded directly to body
Remark
oCurrent wilt not flow through a circuit if
ground is faulty
Fuse (1)
(box)
Fuse (2)
l Melts when current flow exceeds that
specified for circuit, stopping current
flow
Precautions
o Do not replace with fuses exceeding
specified capacity
(Cartridge)
vlain fuse/Fusible
l Electrical switching component
a Turns on when voltage is applied to Motor
0 Converts electrical energy into
mechanical energy
Transistor (2)
coiibmr (Cl
l Reading code l Pulls in and expels gases and liquids
Lamp
Number of terminals O:Low- frequency NPN
l Emits light and generates heat when
Cigarette lighter
current flows through filament a Electrical coil that generates heat
Page 1065 of 1164

Reading Wiring Diagrams Z-GI-9
Symbol ‘ Meaning Symbol Meaning
Horn l Generates sound when current flows. Switch (1) l Allows or breaks current flow by
opening and closing circuits.
Speaker
w
Heater l Generates heat when current flows. Normally open (NO)
Switch (2)
Normally closed (NC)
Harness l Unconnected intersecting harness.
Speed sensor l Movement of magnet in speedometer
set turns contact within sensor on and
Off. (Not connected)
l Connected intersecting harness.
Ignition switch @Turning ignition key operates switch
contacts to complete various circuits.
(Connected)
rlormally open (NO)
Relay (1) l Current flowing through coil produces electromagnetic force causing contact to open or close.
____- .~.~~
Open Closed
--.--.-m.---------,
Relay (2) Normally open relay (NO)
- Ri i No flow ’ ni 1 Closed
Normally closed relay (NC) Flow
ormally closed (NC)
Sensor (variable) l Resistor whose resistance changes Diode
l Known as a semiconductor rectifier.
--3p6G- with operation of other components. diode allows current flow in one
direction only
--T- IA
IY Calhode(K)+- Anode(A)
* Flow of electric current
K-1 KD, he>:
-
ensor (thermistor)
l Resistor whose resistance changes Light emitting diode 0 Diode that lights when current flows
with temperature.
(LED)
l Unlike ordinary light bulbs, diode does
not generate heat when lit
Capacitor
l Component that temporarily stores “2, Cathode(K) --&---Anode(A)
I7
Cathode(K)
electrical charge.
c Anode(A)
----il---- .
Flow of electric current
Solenoid
l Current flowing through co11 generates Reference(zener) l Allows current to flow In one dlrectlon
electromagnetic force to operate diode up to a certain voltage. allows current
plungers, etc. cd to flow In other dIrectron once that
J-
voltage IS exceeded.
z-9
Page 1066 of 1164
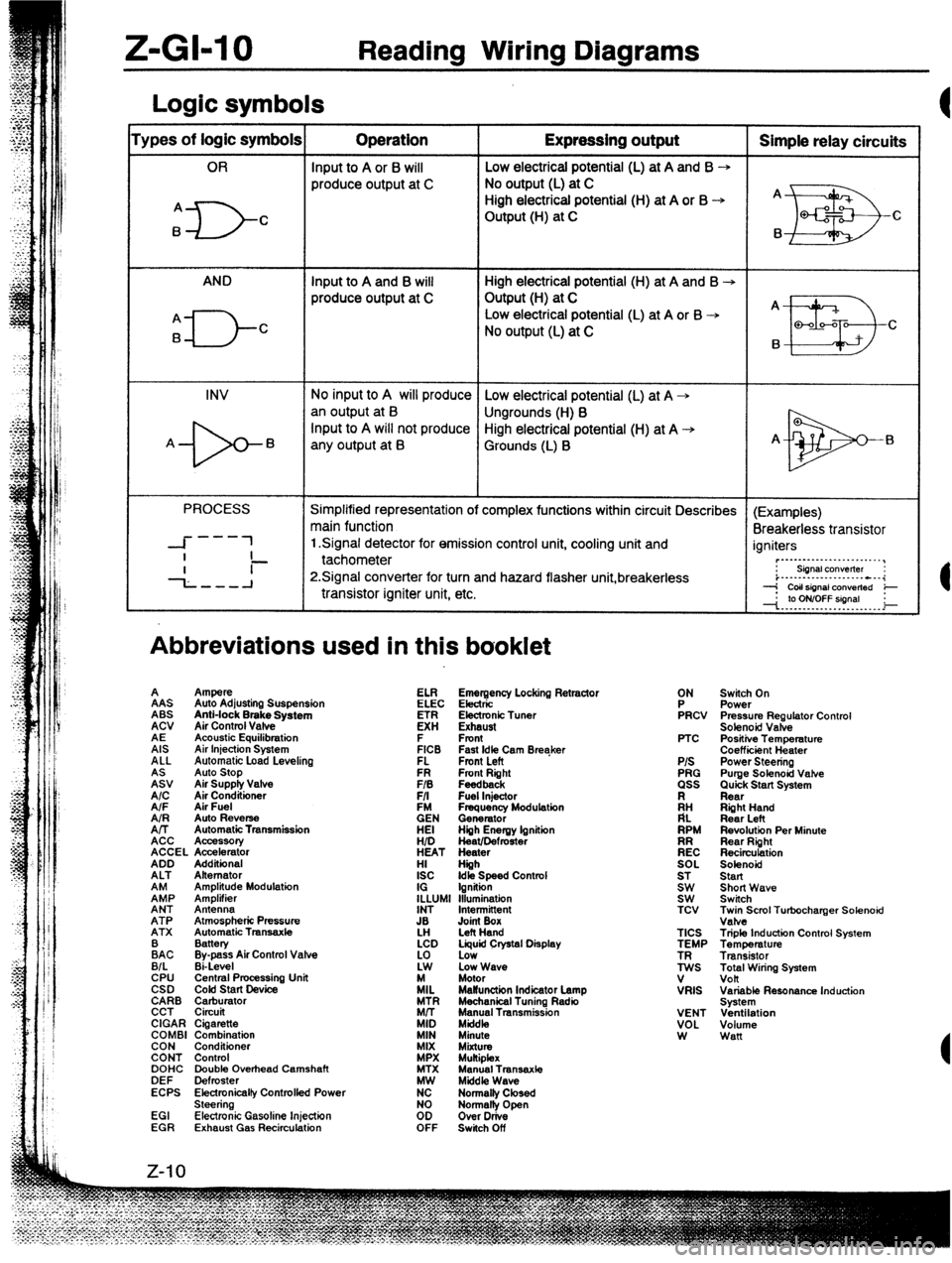
Z-GI-10 Reading Wiring Diagrams
Logic symbols
‘ypes of logic symbols Operation Expressing output Simple relay circuits
OR Input to A or 6 will Low electrical potential (L) at A and B --,
produce output at C No output (L) at C
High electrical potential (H) at A or B -+ A
A
ID- C Output (H) at C
EB Q-f2 c
B B
AND Input to A and B will High electrical potential (H) at A and B -+
produce output at C Output (H) at C
A _
A
El-- Low electrical potential (L) at A or B -+
B C
No output (L) at C
B
II!I3 Q-00-Q
C
INV No input to A will produce Low electrical potential (L) at A +
an output at B
Ungrounds (H) B
-b- Input to A will not produce High electrical potential (H) at A +
A B
any output at B Grounds (L) B A-
El
PROCESS Simplified representation of complex functions within circuit Describes (Examples)
main function
Breakerless transistor
---
-I- 1 1 Signal detector for emission control unit, cooling unit and
I igniters
- ~._..._...._._..._._..__,
--L--A tachometer
P.Signal converter for turn and hazard flasher unit,breakerless : siinalcon”elter :
i..-.--...-.........---i
transistor igniter unit, etc. --j CoIlsignal ConVerted e
--I. .‘p. Y?YT?!!9’. . _ i
Abbreviations used in this booklet
A
%J Ampere
Auto Stop
Air Supply Valve
A/C AAS
Air Conditioner Auto Adjusting Suspension
A/F Air Fuel ABS
AIR Anti-lock Brake System
Auto Reverse
A/T ACV
Automatic Transmission
ACC Air Control Vafve
Acc%K4tIory
ACCEL Accelerator
ADD AE
Additional Acoustic Equilibration
ALT Alternator
EP AIS
Amplitude Modulation Air Injection System
Amplifier ALL
ANT Antenna Automatic Load Levelino
ATP Atmospheric Pressure
ATX Automatic Tmnsaxle FR Fmnt Right ELI?
FIB Feedback
F/I Fuel Injector Emergency Locking Retractor
EN ELEC Electric
Frequency Modulation
Generator
HEI Electronic Tuner
Hiih Energy lgnitiin
HID K!
Heat/Defmster
HEAT Heater Exhaust
HI Hiih F
ISC Front
Idk Speed Contml
IG Ignition
ILLUMI Illumination FICB
INT Intermittent FL Fast Idle Cam Breaker
Fmnt Left
JB
LH Joint Box
Left Hand
:AC Battery
Bypass Air Control Valve
B/L Ei-Level
CPU Central Pmcessing Unit
CSD COM start Device
CARB Carburator
CCT Circuit
CIGAR Cigarette
COMBI Combination
CON Conditioner
CONT Control
DOHC Double Overhead Camshaft
DEF Defroster
ECPS Electronicalfy Controlfed Power
Steering
EGI Electronic Gasoline Injection
EGR Exhaust Gas Recirculation LCD Liquid Crystal Display
:i Low
Low Wave
/IL Motor
MaWunction Indicator Lamp
MTR Mechanical Tuning Radio
Mrr Manual Transmission
MID Mkfdk,
MIN Minute
MIX
MiXtUt MPX Mukiplex
MTX Manual Transaxte
K Middle Wave
Normalty Closed
too Normally Open
Over Drive
OFF Switch Off ON
FRCV
PTC
P/S
PRG
ass
ii:
RPM
EC
SOL
ST
Et TCV
TICS
TEMP
ES
V
VRIS
VENT
VOL
W Switch On
Power
Pressure Regulator Control
Solenoid Valve
Positiie Temperature
Coefficiint Heater
Power Steering
Purge Solenoid Vahe
Quick Start System
Rear
Riiht Hand
Rear Left
Revolution Per Minute
Rear Right
Recirculation
Solenoid
Start
Short Wave
Switch
~;eScml Turbocharger Solenoid
Triple Induction Control System
Temperature
Transistor
Total Wiring System
volt
Variable Resonance Induction
System
Ventilation
Volume
Wan
Page 1067 of 1164

Troubleshootina Z-GM 1
Precautions when servicing electrical system
l Note the following items when servicing the electrical system.
l Do not alter the wiring or electrical equipment in any way as this may damage the vehicle or cause a fire
due to shorting or overcapacity of a circuit.
l Always disconnect the negative (- ) battery cable first and 0 Replace blown fuses with ones having the same designated
reconnect It last when disconnecting the battery. capacity.
1OA
15A
Zaution
l Be sure that the ignition and other switches are OFF
before disconnecting or connecting the battery
terminals.
Failure to do so may damage the semi-conductor
components. Caution l Replacing a fuse with one of a larger capacity than
designated may damage components or cause an electrical
fire.
l Secure harnesses with a clamp when provided to take Up l Tape areas of the
a Be sure that the harness
any slack. harness that may rub or
is not caught or damaged
bump against sharp
when mounting
edges to protect it from
components.
damage.
Caution
l Clamp all harnesses near vibrating components(e.g.
the engine) to remove any slack and prevent Contact
due to vibration.
l Do not handle roughly or drop electrical components.
l Disconnect heat sensitive
parts (e.g. relays, ECU)
when performing
maintenance where
temperatures may exceed l Make sure that the
connectors are securely
connected when
installed.
80°C (176°F) (i.e.welding).
oid
Page 1068 of 1164

Z-GI-12 Troubleshooting
Handling connectors
Caution
l Be sure to grasp the connectors, not the wires, when disconnecting them.
1 .Open the rear cover.
2.Lift the tab with a
small screwdriver
and remove the
improperly engaged
connectors will cause
poor terminal contact. A loose terminal will
cause poor terminal
Lift the tab with a
remove the terminal.
1 .Open the cover.
2.Lift the terminal to
Using a matching male
is no looseness in the
female terminal. Verify that terminals are
connector when engaged. 3.Verify that the
terminal IS securely
mounted in the
connector when
3.Lift the tab with a
small screwdriver
and remove the
Lightly pull each wire to
verify that the terminal
does not pull out of the
Page 1069 of 1164
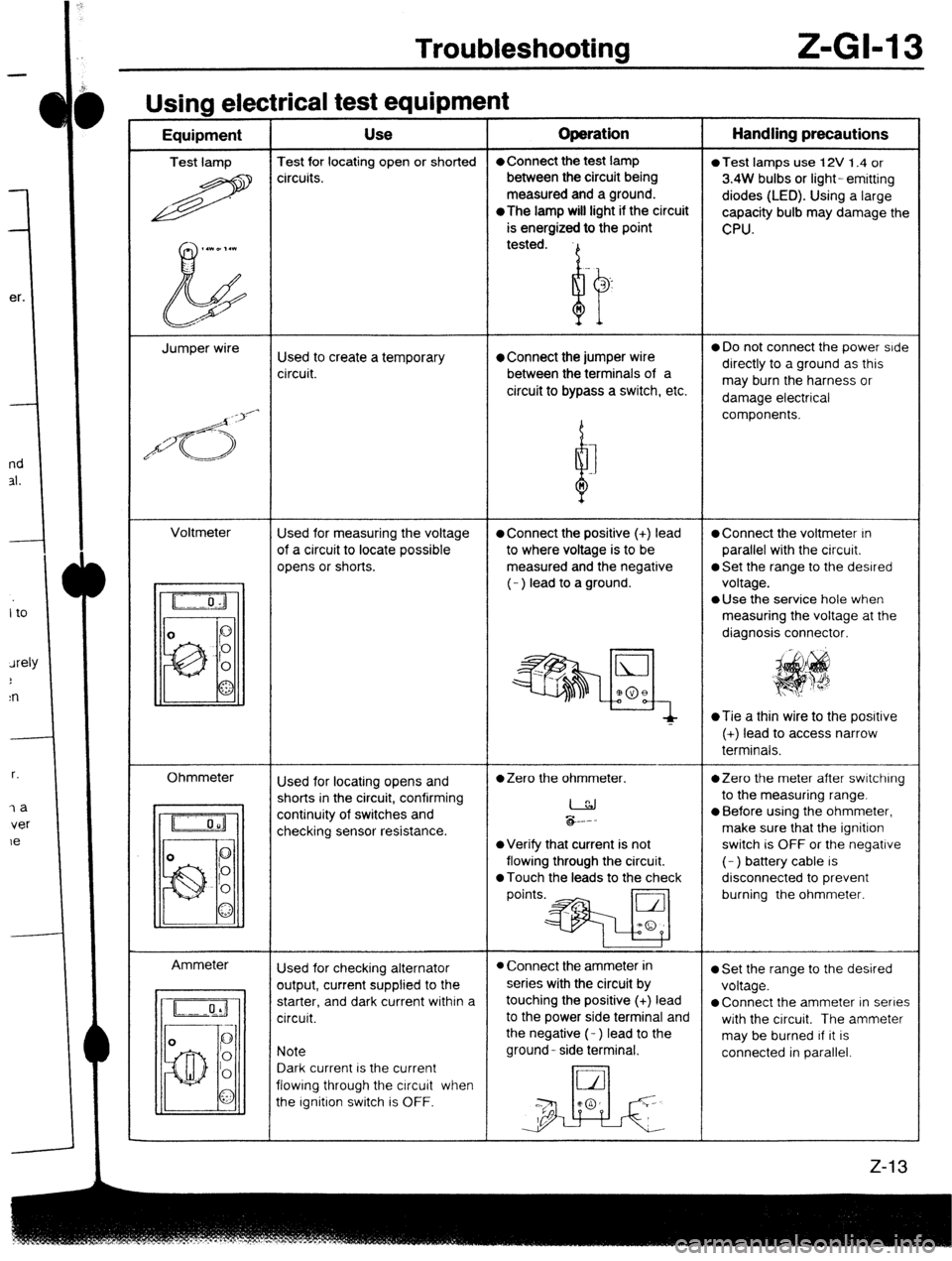
Troubleshooting Z-Gl-13
el
-
Ill
31
-
I1
Jl
:n
r.
7a
ver
le
Usina electrical test eaubment -----w - I - Equipment Use Operation Handling precautions
Test lamp Test for locating open or shorted l Connect the test lamp
0 Test lamps use 12V 1.4 or
R circuits. between the circuit being
3.4W bulbs or light- emitting
measured and a ground.
diodes (LED). Using a large
*The
lamp will light if the circuit
capacity bulb may damage the
is energized to the point
CPU.
,.WD,.l
b tested.
Jumper wire
Used to create a temporary l Connect the jumper wire 0 Do not connect the power side
circuit. between the terminals of a directly to a ground as this
circuit to bypass a switch, etc. may burn the harness or
damage electrical
/d<;>‘-
d components.
I
n
Voltmeter
Used for measuring the voltage
l Connect the positive (+) lead l Connect the voltmeter In
of a circuit to locate possible to where voltage is to be parallel with the circuit.
opens or shorts. measured and the negative
0 Set the range to the desired
(- ) lead to a ground. voltage.
l Use the service hole when
measuring the voltage at the
diagnosis connector.
~Tie a thin wire to the posrtive
(+) lead to access narrow
terminals.
Ohmmeter
Ammeter Used for locating opens and
l Zero the ohmmeter. *Zero the meter after switching
shorts in the circuit, confirming
I to the measuring range.
continuity of switches and
checking sensor resistance. &.--
l Before using the ohmmeter,
make sure that the ignition
l Verify that current is not switch is OFF or the negative
flowing through the circuit. (- ) battery cable is
0 Touch the leads to the check disconnected to prevent
points.* burning the ohmmeter.
Used for checking alternator
l Connect the ammeter in l Set the range to the desired
output, current supplied to the series with the circuit by
voltage.
starter, and dark current within a touching the positive (+) lead
l Connect the ammeter in series
circuit. to the power side terminal and
with the circuit. The ammeter
the negative (- ) lead to the
may be burned If it is
Note ground- side terminal.
connected in parallel.
Dark current is the current
flowing through the circuit when
the Ignition switch is OFF.
Page 1070 of 1164

Z-GM 4 Troubleshooting
Measuring voltage
, ’
Battery
(positive te;minal) lgnitipn switch
Voltmeter
Fuse
Motor Therm0
switch
+ r-
Ground 2 Ground 1
I
!I4 aD
0 0
Test lamp
or
f
“J-
1. Use a Voltmeter or &St lamp to ascertain voltage at the
measuring points.
Circuit operation
Measur-
ing points Ignitio&Gtch: Ignition switch:ON
Thermo switch: Thermo switch:
OFF ON
@ ov x 12v ‘6 12v
‘6
a ov x 12v ~6 ov
X
c ov x ov x ov X
B: 12v ‘6 12v ‘6 12v ~‘. 0
cc ov x ov X 12v .’ 0
@ ov x ov x ov X
‘b’ : Test lamp ON
x : Test lamp OFF
neasuring voltage of connectors Poor contact
A voltmeter lead may momentarily connect a terminal when
inserted into the connector and give an erroneous reading
when checking for rmproperly engaged connectors, poor
terminal contacts, or loose terminals.
Voltmeter lead
Measuring voltage of ground unit
Touch the voltmeter lead to the ground wire when checking
the ground circuit.
Poor contact