ignition OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 9 of 6000
PAGE BACK PAGE NEXT
THIS MALUAL INCLUDES THE FOLLOWING SECTIONS:
6VD1 / 6VE1
SECTION No. CONTRNTS
6A ENGINE MECHANICAL
6B ENGINE COOLING
6C ENGINE FUEL
6D1 ENGINE ELECTRICAL
6D2 IGNITION SYSTEM
6D3 STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
6E ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
6F ENGINE EXHAUST
6G ENGINE LUBRICATION
6H ENGINE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
6J INDUCTION
HOME
6A
6B
6C
6D1
6D2
6D3
6E
6F
6G
6H
6J
Page 217 of 6000

Ignition swich
"ON"
Time
Blower voltage to turn
on the cooling
7 SEC maximum3 SEC
100%
(MAX HI)
33.5%
(LO)5.32%/S
C06RY00001
33.5%
(LO)
2.63%/S
Mode
DEF
Auto
Mode
100%
(MAX HI)
Ignition
switch "ON"
Thermo Unit 58
C(Gasoline)
52C(Diesel) Time
840RY00009
Page 544 of 6000

4B1–11 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (SHIFT ON THE FLY)
Functions of Indicator Lamp
Indication of vehicle condition : Indicator lamp is
controlled by 4WD control unit and shows vehicle
conditions as below.
Indicator
Vehicle condition4WD switchTransfer position
switchFront axle switch
Off2WDOff (Close)2WD (Open)2WD (Open)
On4WDOn (Open)4WD (Close)4WD (Close)
Blink (2Hz)OperatingOn (Open)4WD (Close)2WD (Open)
Off (Close)2WD (Open)4WD (Close)
Blink (4Hz)Stop operatingOn (Open)2WD (Open)2WD (Open)
Off (Close)4WD (Close)4WD (Close)
Bulb check :To check the bulb of indicator lamp, the
indicator lamp comes on when ignition key is turned on,
and goes off when the engine is started.
Retrials from 2WD to 4WD :In cold weather or under
high speed condition, the gear shifting (engagement)sometimes does not complete by 3 trials. In such case,
the indicator lamp inform driver of this incident as
aforementioned chart (shown at Retrial in Outline of shift
on the fly system).
Diagnosis
Before Judging That Troubles Occur
(Unfaulty mode)
When Switching from 2WD to 4WD
1.In case that blinking frequency of the 4WD
indicator changes from 2Hz to 4Hz.
When heavy synchronization load is needed, the
motor actuator tries the shifting transfer gear three
times including the activation shifting. While the
motor actuator tries shifting, the indicator blinks by
2Hz. If the third shifting fails, the indicator’s blinking
changes from 2Hz to 4Hz at the same time that the
motor actuator shifted back to 2WD.
Heavy synchronization load occurs by:
extremely lower temperature.
higher speed, rotation difference of wheels during
cornering.
Solution 1: Operate again after stop the vehicle or
slow down.
2.In case that the 4WD indicator continues blinking
by 2Hz for more than 11.5 seconds.
When there is rotation difference of wheels or there
is phase difference between front wheels and axles,
it is difficult to connect front wheels to front axles. The
blinking by 2Hz shows that shifting the transfer gear
or connecting the front wheels is in the middle of
operating. In above case, the indicator’s blinking by
2Hz shows that connecting the front wheels is not
completed (because the indicator’s blinking changes
to 4Hz when the shifting transfer gear is impossible.).
And removal of rotation or phase difference make
connecting the front wheels possible.
Solution 2: When vehicle is running, drive
straight ahead while accelerating and
decelerating. When vehicle is at a stop, move the
vehicle forward and backward from 2 to 3 meters.When switching from 4WD to 2WD
1.In case that the 4WD indicator continues blinking
by 2Hz .
The 4WD indicator continues blinking by 2Hz until
both shifting the transfer gear and disconnecting the
front wheels are completed when switching 4WD to
2WD. When driveline is loaded with torsional torque,
the shifting transfer gear and disconnecting front
wheels are impossible. In this case, removal of
torsional torque on driveline make the shifting
transfer gear and disconnecting front wheels
possible.
Solution 3: When vehicle is running, drive
straight ahead while accelerating and
decelerating. When vehicle is at a stop, move the
vehicle forward and backward from 2 to 3 meters.
2.In case that the 4WD indicator’s blinking changes
from 2Hz to 4Hz.
Check the position of transfer lever. Is it at “4L”
position? In view of the shifting mechanism of
transfer, the gear shifting from 4WD to 2WD at “4L”
condition is impossible.
Solution 4: Push the 4WD switch to 4WD, shift the
transfer lever to “High” position and re–operate
the 4WD switch to 2WD.
Page 558 of 6000

4B1–25 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (SHIFT ON THE FLY)
Diagnosis of the Faults Based on the
Status of 4WD Indicator Lamp, 4WD
Switch and T/F Change Lever
Diagnosis charts are shown on below. If troubles can not
be solved after every chart was traced, troubles may
occur in the 4WD control unit. In this case, replace the
4WD control unit and trace every chart again.
Fault on switching from 2WD to 4WD
1.In case that 4WD indicator’s blinking changes
from 2Hz to 4Hz after Solution 1 is carried out.
Faults occur in the motor actuator or the transfer case
assembly. Remove the motor actuator and check
function. If problem was found and it was repaired, try
Solution 1 again. After that, disassemble the
transfer case assembly for check and repair or
replace. If incident is not improved after above
mentioned actions were taken, replace the 4WD
control unit.
2.In case that 4WD indicator does not blink nor
light, when switching from 2WD to 4WD.
Step
ActionYe sNo
1Is ignition turned on?
Go to Step 2
Turn on the
ignition and trace
this chart from
start.
2
Does the indicator light comes on when the engine is not started?
Go to Step 3
Burning out of
indicator lamp or
disconnection of
harness wire.
Trace this chart
from the start
after repair or
replace.
3Start the engine.
Is the 4WD switch turned from 2WD to 4WD?Short-circuit
(body short) on
harness of the
4WD switch.
Fault of the 4WD
switch (holding
the closed
condition).
Trace this chart
from the start
after repair or
replace.
Push the 4WD
switch to 4WD.
Page 560 of 6000

4B1–27 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (SHIFT ON THE FLY)
Fault on switching from 4WD to 2WD
1.Case that indicator does not blink nor turn out.
Step
ActionYe sNo
1
Does the indicator turn out by ignition off?Go to Step 2
Short circuit of
the indicator
harness.
2
Is the 4WD switch on 2WD position?
Disconnection on
the 4WD switch
harness or
breakdown of the
4WD switch in
open state.
Trace this chart
from the start
after repair or
replace.
Turn the 4WD
switch to 2WD
position. Trace
this chart from
the start.
Page 597 of 6000
DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (TOD) 4B2–26
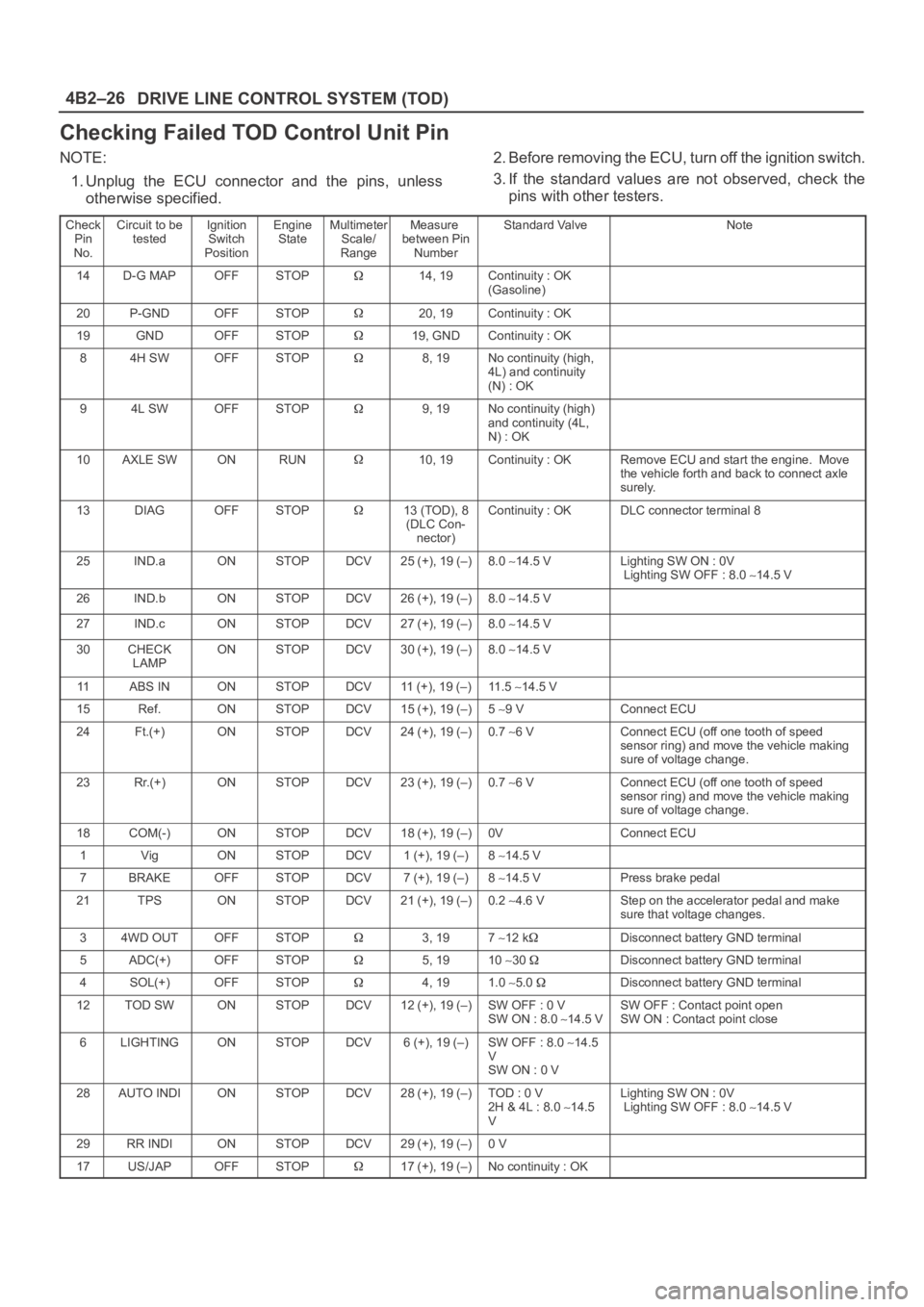
Checking Failed TOD Control Unit Pin
NOTE:
1. Unplug the ECU connector and the pins, unless
otherwise specified.2. Before removing the ECU, turn off the ignition switch.
3. If the standard values are not observed, check the
pins with other testers.
Check
Pin
No.Circuit to be
testedIgnition
Switch
PositionEngine
StateMultimeter
Scale/
RangeMeasure
between Pin
NumberStandard ValveNote
14D-G MAPOFFSTOP14, 19Continuity : OK
(Gasoline)
20P-GNDOFFSTOP20, 19Continuity : OK
19GNDOFFSTOP19, GNDContinuity : OK
84H SWOFFSTOP8, 19No continuity (high,
4L) and continuity
(N) : OK
94L SWOFFSTOP9, 19No continuity (high)
and continuity (4L,
N) : OK
10AXLE SWONRUN10, 19Continuity : OKRemove ECU and start the engine. Move
the vehicle forth and back to connect axle
surely.
13DIAGOFFSTOP13 (TOD), 8
(DLC Con-
nector)Continuity : OKDLC connector terminal 8
25IND.aONSTOPDCV25 (+), 19 (–)8.0 14.5 VLighting SW ON : 0V
Lighting SW OFF : 8.0 14.5 V
26IND.bONSTOPDCV26 (+), 19 (–)8.0 14.5 V
27IND.cONSTOPDCV27 (+), 19 (–)8.0 14.5 V
30CHECK
LAMPONSTOPDCV30 (+), 19 (–)8.0 14.5 V
11ABS INONSTOPDCV11 (+), 19 (–)11 . 5 14.5 V
15Ref.ONSTOPDCV15 (+), 19 (–)5 9 VConnect ECU
24Ft.(+)ONSTOPDCV24 (+), 19 (–)0.7 6 VConnect ECU (off one tooth of speed
sensor ring) and move the vehicle making
sure of voltage change.
23Rr.(+)ONSTOPDCV23 (+), 19 (–)0.7 6 VConnect ECU (off one tooth of speed
sensor ring) and move the vehicle making
sure of voltage change.
18COM(-)ONSTOPDCV18 (+), 19 (–)0VConnect ECU
1VigONSTOPDCV1 (+), 19 (–)8 14.5 V
7BRAKEOFFSTOPDCV7 (+), 19 (–)8 14.5 VPress brake pedal
21TPSONSTOPDCV21 (+), 19 (–)0.2 4.6 VStep on the accelerator pedal and make
sure that voltage changes.
34WD OUTOFFSTOP3, 197 12 kDisconnect battery GND terminal
5ADC(+)OFFSTOP5, 1910 30 Disconnect battery GND terminal
4SOL(+)OFFSTOP4, 191.0 5.0 Disconnect battery GND terminal
12TOD SWONSTOPDCV12 (+), 19 (–)SW OFF : 0 V
SW ON : 8.0 14.5 VSW OFF : Contact point open
SW ON : Contact point close
6LIGHTINGONSTOPDCV6 (+), 19 (–)SW OFF : 8.0 14.5
V
SW ON : 0 V
28AUTO INDIONSTOPDCV28 (+), 19 (–)TOD : 0 V
2H & 4L : 8.0 14.5
VLighting SW ON : 0V
Lighting SW OFF : 8.0 14.5 V
29RR INDIONSTOPDCV29 (+), 19 (–)0 V
17US/JAPOFFSTOP17 (+), 19 (–)No continuity : OK
Page 599 of 6000

DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (TOD) 4B2–28
Getting Started
Before operating the Isuzu PCMCIA card with the
Tech 2, the following steps must be performed:
1. The Isuzu 98 System PCMCIA card (1) inserts into
the Tech 2 (5).
2. Connect the SAE 16/19 adapter (3) to the DLC cable
(4).
3. Connect the DLC cable to the Tech 2 (5)
4. Mark sure the vehicle ignition is off.
5. Connect the Tech 2 SAE 16/19 adapter to the vehicle
ALDL/DLC connector.
810RW308
6. The vehicle ignition turns on.
7. Verify the Tech 2 power up display.
060RW009
NOTE: The RS232 Loop back connector is only to use for
diagnosis of Tech 2 and refer to user guide of the Tech 2.
Operating Procedure
The power up screen is displayed when you power up the
tester with the Isuzu systems PCMCIA card. Follow the
operating procedure below.
060RW014
Page 814 of 6000

5A–4
BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
normal braking when a malfunction has occurred in the
ABS.
The EHCU has a self-diagnosing function which can
indicate faulty circuits during diagnosis.
The EHCU is mounted on the engine compartment front
right side. It consists of a Motor, Plunger Pump, Solenoid
Valves and Check Valve.
On the outside, the relay box containing a motor relay and
a valve relay is installed.
Solenoid Valves: Reduces or holds the caliper fluid
pressure for each front disc brake or both rear disc brakes
according to the signal sent from the EHCU.
Reservoir: Temporarily holds the brake fluid that returns
from the front and rear disc brake caliper so that pressure
of front disc brake caliper can be reduced smoothly.
Plunger Pump: Feeds the brake fluid held in the reservoir
to the master cylinder.
Motor: Drives the pump according to the signal from
EHCU.
Check Valve: Controls the brake fluid flow.
ABS Warning Light
821RW033Vehicles equipped with the Anti-lock Brake System have
an amber “ABS” warning light in the instrument panel.
The “ABS” warning light will illuminate if a malfunction in
the Anti-lock Brake System is detected by the Electronic
Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU). In case of an electronic
malfunction, the EHCU will turn “ON” the “ABS” warning
light and disable the Anti-lock braking function.
The “ABS” light will turn “ON” for approximately three
seconds after the ignition switch is to the “ON” position.
If the “ABS” light stays “ON” after the ignition switch is the
“ON” position, or comes “ON” and stays “ON” while
driving, the Anti-lock Brake System should be inspected
for a malfunction according to the diagnosis procedure.
Wheel Speed Sensor
It consists of a sensor and a rotor. The sensor is attached
to the knuckle on the front wheels and to the axle shaft
bearing holder on the rear wheels.
The rotor is press-fit in the axle shaft.The flux generated from electrodes magnetized by a
magnet in the sensor varies due to rotation of the rotor,
and the electromagnetic induction generates alternating
voltage in the coil. This voltage draws a “sine curve” with
the frequency proportional to rotor speed and it allows
detection of wheel speed.
G-Sensor
The G-sensor installed inside the center console detects
the vehicle deceleration speed and sends a signal to the
EHCU. In 4WD operation, all four wheels may be
decelerated in almost the same phase, since all wheels
are connected mechanically.
This tendency is noticeable particularly on roads with low
friction coefficient, and the ABS control is adversely
affected.
The G-sensor judges whether the friction coefficient of
road surface is low or high, and changes the EHCU’s
operating system to ensure ABS control.
Normal and Anti-lock Braking
Under normal driving conditions, the Anti-lock Brake
System functions the same as a standard power assisted
brake system. However, with the detection of wheel
lock-up, a slight bump or kick-back will be felt in the brake
pedal. This pedal “bump” will be followed by a series of
short pedal pulsations which occurs in rapid succession.
The brake pedal pulsation will continue until there is no
longer a need for the anti-lock function or until the vehicle
is stopped. A slight ticking or popping noise may be heard
during brake applications when the Anti-lock features is
being used.
When the Anti-lock feature is being used, the brake pedal
may rise even as the brakes are being applied. This is
also normal. Maintaining a constant force on the pedal
will provide the shortest stopping distance.
Brake Pedal Travel
Vehicles equipped with the Anti-lock Brake System may
be stopped by applying normal force to the brake pedal.
Although there is no need to push the pedal beyond the
point where it stops or holds the vehicle, by applying more
force the pedal will continue to travel toward the floor.
This extra brake pedal travel is normal.
Acronyms and Abbreviations
Several acronyms and abbreviations are commonly used
throughout this section:
ABS
Anti-lock Brake System
CKT
Circuit
DLC
Data Link Connector
EHCU
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit
FL
Front Left
Page 815 of 6000

5A–5 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
FR
Front Right
GEN
Generator
MV
Millivolts
RL
Rear Left
RR
Rear RightRPS
Revolution per Second
VDC
Vo l t s D C
VA C
Vo l t s A C
W/L
Warning Light
WSS
Wheel Speed Sensor
General Diagnosis
General Information
ABS malfunction can be classified into two types, those
which can be detected by the ABS warning light and those
which can be detected as a vehicle abnormality by the
driver.
In either case, locate the fault in accordance with the
“BASIC DIAGNOSTIC FLOWCHART” and repair.
Please refer to Section 5C for the diagnosis of
mechanical troubles such as brake noise, brake judder
(brake pedal or vehicle vibration felt when braking),
uneven braking, and parking brake trouble.
ABS Service Precautions
Required Tools and Items:
Box Wrench
Brake Fluid
Special Tool
Some diagnosis procedures in this section require the
installation of a special tool.
J-39200 High Impedance Multimeter
When circuit measurements are requested, use a circuit
tester with high impedance.
Computer System Service Precautions
The Anti-lock Brake System interfaces directly with the
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU) which is a
control computer that is similar in some regards to the
Powertrain Control Module. These modules are designed
to withstand normal current draws associated with
vehicle operation. However, care must be taken to avoid
overloading any of the EHCU circuits. In testing for opens
or shorts, do not ground or apply voltage to any of the
circuits unless instructed to do so by the appropriate
diagnostic procedure. These circuits should only be
tested with a high impedance multimeter (J-39200) or
special tools as described in this section. Power should
never be removed or applied to any control module with
the ignition in the “ON” position.
Before removing or connecting battery cables, fuses or
connectors, always turn the ignition switch to the “OFF”
position.
General Service Precautions
The following are general precautions which should be
observed when servicing and diagnosing the Anti-lock
Brake System and/or other vehicle systems. Failure toobserve these precautions may result in Anti-lock Brake
System damage.
If welding work is to be performed on the vehicle using
an electric arc welder, the EHCU and valve block
connectors should be disconnected before the
welding operation begins.
The EHCU and valve block connectors should never
be connected or disconnected with the ignition “ON” .
EHCU of the Anti-lock Brake System are not
separately serviceable and must be replaced as
assemblies. Do not disassemble any component
which is designated as non-serviceable in this
Section.
If only rear wheels are rotated using jacks or drum
tester, the system will diagnose a speed sensor
malfunction and the “ABS” warning light will
illuminate. But actually no trouble exists. After
inspection stop the engine once and re-start it, then
make sure that the “ABS” warning light does not
illuminate.
If the battery has been discharged
The engine may stall if the battery has been completely
discharged and the engine is started via jumper cables.
This is because the Anti-lock Brake System (ABS)
requires a large quantity of electricity. In this case, wait
until the battery is recharged, or set the ABS to a
non-operative state by removing the fuse for the ABS
(40A). After the battery has been recharged, stop the
engine and install the ABS fuse. Start the engine again,
and confirm that the ABS warning light does not light.
Note on Intermittents
As with virtually any electronic system, it is difficult to
identify an intermittent failure. In such a case duplicating
the system malfunction during a test drive or a good
description of vehicle behavior from the customer may be
helpful in locating a “most likely” failed component or
circuit. The symptom diagnosis chart may also be useful
in isolating the failure. Most intermittent problems are
caused by faulty electrical connections or wiring. When
an intermittent failure is encountered, check suspect
circuits for:
Suspected harness damage.
Poor mating of connector halves or terminals not fully
seated in the connector body (backed out).
Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
Page 816 of 6000

5A–6
BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
Test Driving ABS Complaint Vehicles
In case that there has been an malfunction in the lighting
pattern of “ABS” warning light, the fault can be located in
accordance with the “DIAGNOSIS BY “ABS” WARNING
LIGHT ILLUMINATION PATTERN” . In case of such
trouble as can be detected by the driver as a vehicle
symptom, however, it is necessary to give a test drive
following the test procedure mentioned below, thereby
reproducing the symptom for trouble diagnosis on a
symptom basis:
1. Start the engine and make sure that the “ABS” W/L
goes OFF. If the W/L remains ON, it means that the
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored. Therefore,
read the code and locate the fault.
2. Start the vehicle and accelerate to about 30 km/h (19
mph) or more.
3. Slowly brake and stop the vehicle completely.
4. Then restart the vehicle and accelerate to about 40
km/h (25 mph) or more.
5. Brake at a time so as to actuate the ABS and stop the
vehicle.
6. Be cautious of abnormality during the test. If the W/L
is actuated while driving, read the DTC and locate the
fault.
7. If the abnormality is not reproduced by the test, make
best efforts to reproduce the situation reported by the
customer.
8. If the abnormality has been detected, repair in
accordance with the “SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS” .NOTE:Be sure to give a test drive on a wide, even road with
little traffic.
If an abnormality is detected, be sure to suspend the
test and start trouble diagnosis at once.
“ABS” Warning Light
When ABS trouble occurs and actuates when possible
the “ABS” warning light, the trouble code corresponding
to the trouble is stored in the EHCU. Only the ordinary
brake system is available when the ABS is turned off.
When the “ABS” warning light is actuated, if the starter
switch is set ON after setting it OFF once, the EHCU
checks up on the entire system and, if there is no
abnormality, judges ABS to work currently and the
warning light works normally even though the trouble
code is stored.
NOTE: Illumination of the “ABS” warning light indicates
that anti-lock braking is no longer available. Power
assisted braking without anti-lock control is still available.
Normal Operation
“ABS” Warning Light
W h e n t h e i g n i t i o n i s f i r s t m o v e d f r o m “ O F F ” t o “ R U N ” , t h e
amber “ABS” warning light will turn “ON” . The “ABS”
warning light will turn “ON” during engine starting and will
usually stay “ON” for approximately three seconds after
the ignition switch is returned to the “ON” position. The
warning light should remain “OFF” at all other times.
Basic Diagnostic Flow Chart
StepActionYe sNo
11. Customer complaint.
2. Questioning to customer.
3. Basic inspection (Refer to “Basic inspection procedure”)
Using TECH 2?
Go to Step 2Go to Step 4
2Make sure of DTC by mode “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Codes”.
Is EHCU including DTC?
Go to Step 3Go to Step 5
31. Repair of faulty part.
2. Elimination of DTC.
3. Inspection of “ABS” W/L Illumination pattern with ignition SW
“ON”.
4. Test drive.
Does repeat trouble?
Repeat the
diagnosis it the
symptom or DTC
appears again Go
to Step 1
Go to Step 5
4Check if the DTC is stored.
Is EHCU including DTC?
Go to Step 3
Trouble diagnosis
based on
symptom (Refer
to “SYMPTOM
DIAGNOSIS”) Go
to Step 3
51. Reconnect all components and ensure all component are
properly mounted.
2. Clear diagnostic trouble code.
Was this step finished?
FinishedGo to Step 5