PONTIAC FIERO 1988 Service Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: PONTIAC, Model Year: 1988, Model line: FIERO, Model: PONTIAC FIERO 1988Pages: 1825, PDF Size: 99.44 MB
Page 51 of 1825
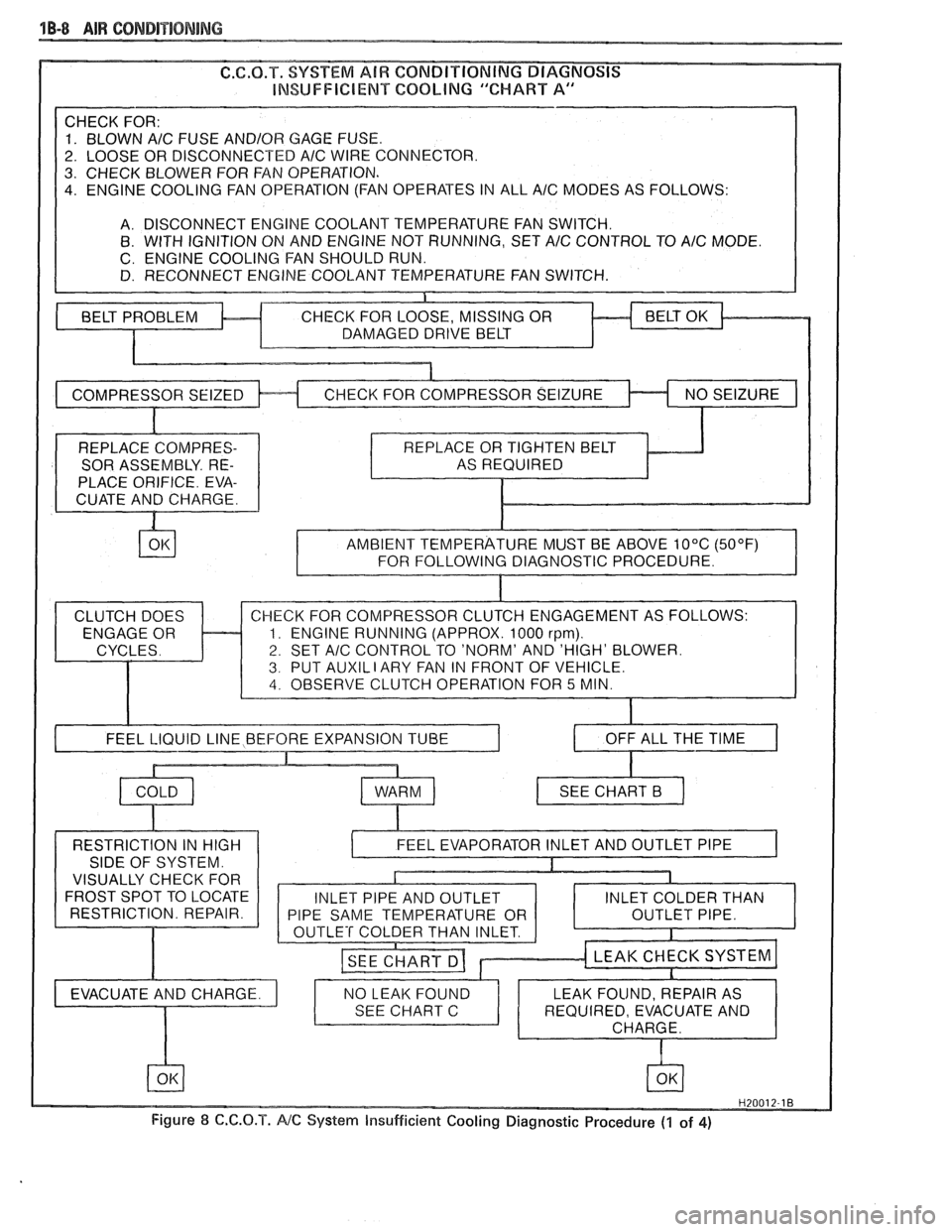
1B-8 AIR CONDITIONING
INSUFFICIENT COQblNG "CHART A
A/C FUSE AND/OR GAGE FUSE.
OR DISCONNECTED
AlC WIRE CONNECTOR.
. CHECK BLOWER FOR FAN OPERATION.
. ENGINE COOLING FAN OPERATION (FAN OPERATES IN ALL A/C MODES AS FOLLOWS:
A. DISCONNECT ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE FAN SWITCH.
8. WITH IGNITION ON AND ENGINE NOT RUNNING, SET A/C CONTROL TO A/C MODE.
C. ENGINE COOLING FAN SHOULD RUN.
D. RECONNECT ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE FAN SWITCH.
REPLACE COMPRES-
SOR ASSEMBLY. RE-
PLACE ORIFICE. EVA-
CUATE AND CHARGE. AS
REQUIRED
AND 'HIGH' BLOWER.
T
AUXIL I ARY FAN IN T OF VEHICLE.
I OFF ALL THE TIME I
RESTRICTION IN HIGH
SIDE OF SYSTEM.
VISUALLY CHECK FOR
FROST SPOT TO LOCATE
RESTRICTION. REPAIR.
Figure
8 C.C.O.T. NC System Insufficient Cooling Diagnostic Procedure (1 of 4)
Page 52 of 1825
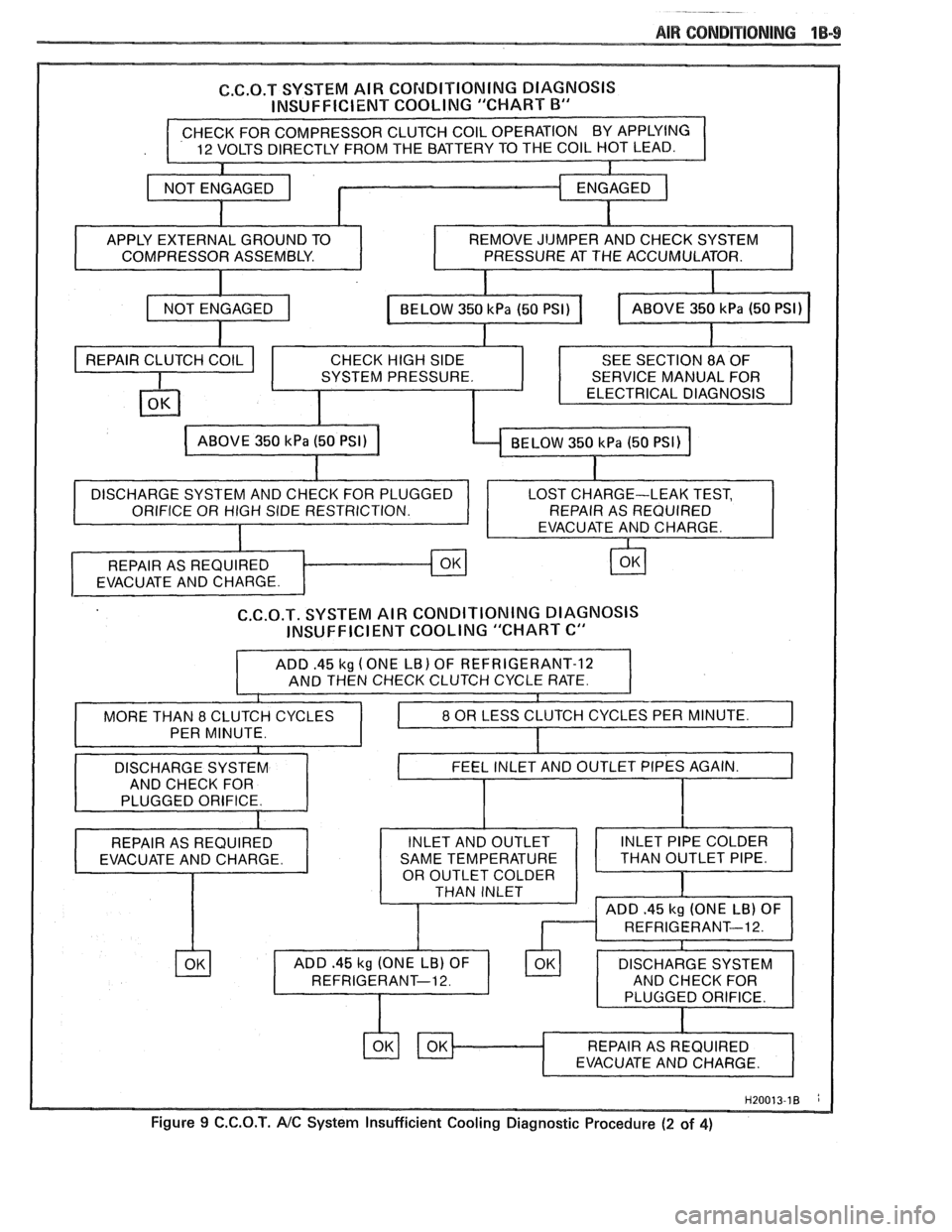
AIR CONBiTlQNlMG 1B-9
C.6.O.T SYSTEM AIR CO~dDITlON1NG DIAGNOSIS
INSUFFICIENT COOLING "CHART
B"
COMPRESSOR ASSEMBLY.
PRESSURE AT THE ACCUMULATOR.
C.C.O.T. SYSTEM AIR CONDITIONING DIAGNOSIS
INSUFFICIENT COOLING "CHART C"
ADD .45 kg (ONE LB) OF REFRIGERANT-12
AND THEN CHECK CLUTCH CYCLE RATE.
THAN INLET
Figure 9 C.C.O.T. AIC System Insufficient Cooling Diagnostic Procedure (2 of 4)
Page 53 of 1825
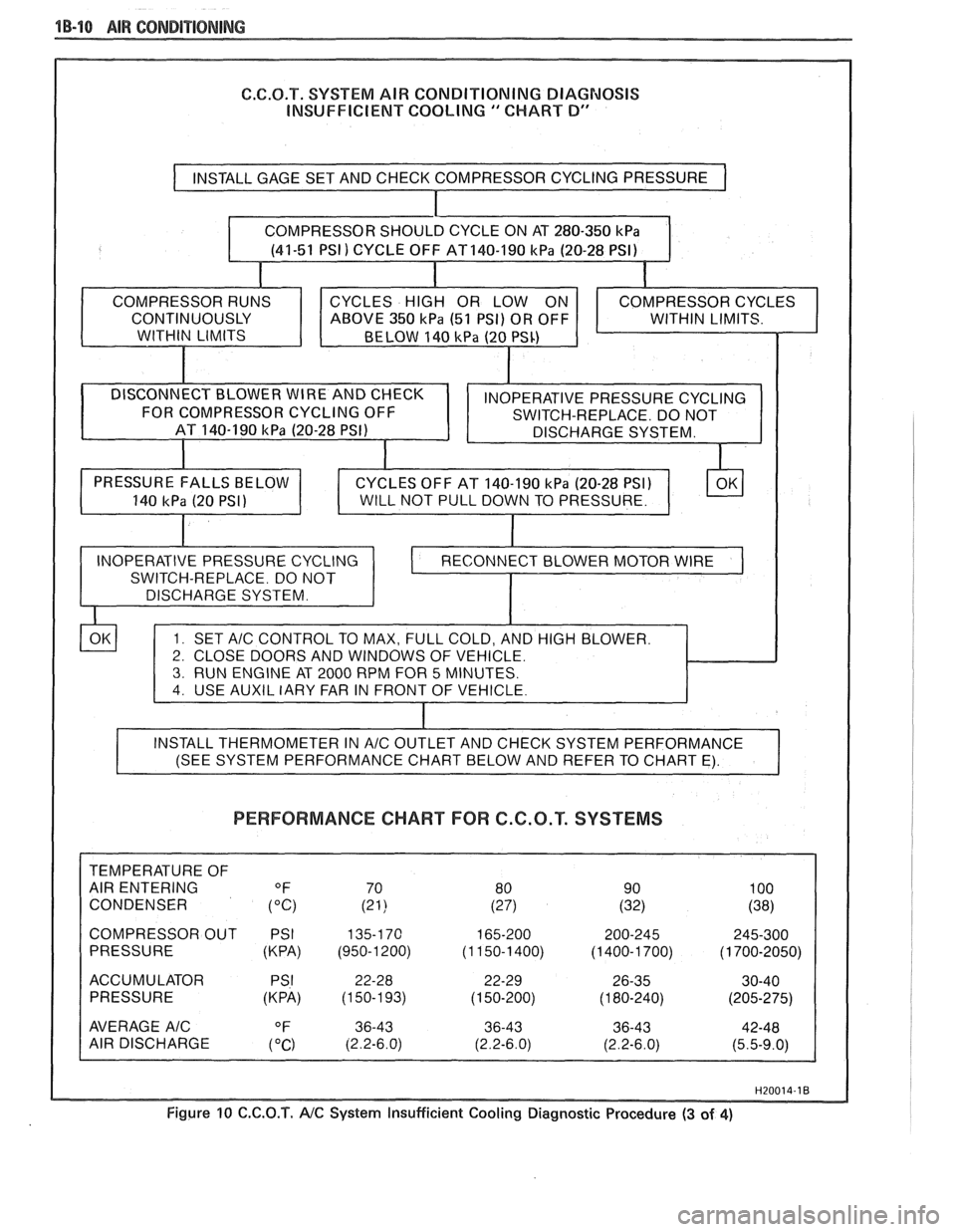
1 B-10 AIR COMDIP"18NING
G.C.O.T. SYSTEM AIR CONDITIONING DIAGNOSIS
INSUFFICIENT COOLING
" CHART D"
PERFORMANCE CHART FOR C.G.O.T. SYSTEMS
CONDENSER
COMPRESSOR OUT PSI
(KPA) (950-1 200)
ACCUMULATOR (KPA) (1 50-1
93)
AVERAGE A/C
AIR DISCHARGE
Page 54 of 1825
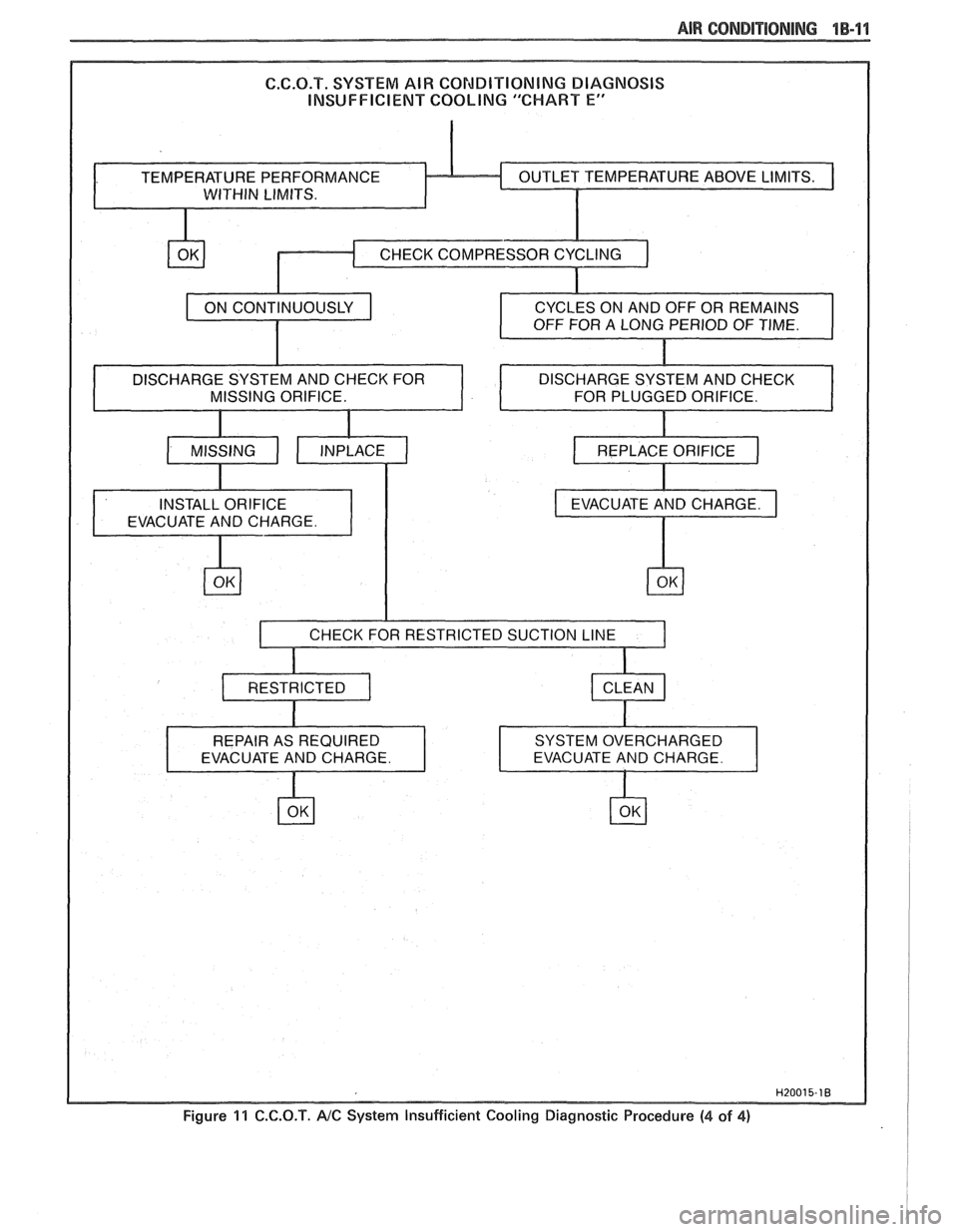
AIR CONBlTiONlNG 1 B-1 1
CHARGE SYSTEM AND CHECK FOR
Figure 11 C.C.Q.T. NC System Insufficient Cooling Diagnostic Procedure (4 of 4) i I
Page 55 of 1825

18-12 AIR CONDITIONING
ELEGTRICAWACUUM SYSTEM
DIAGNOSIS
When diagnosing problems in the electrical sys-
tems of the air conditioning system, consult section
8A.
LEAK TESTING THE REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM
Whenever a refrigerant leak is suspected in the
system or a service operation performed which results
in disturbing lines or connections, it is advisable to
test for leaks.
Liquid Leak Detectors
There are a number of locations (fittings,
valves, etc.) on the air conditioning system where a
liquid leak detector solution may be used to pinpoint
refrigerant leaks.
By applying test solution to the area in question
with the swab that is attached to the bottle cap, bub-
bles will form within seconds if there is a leak.
For restricted access areas, such as sections of
the evaporator and condenser, an electronic leak
detector, such as
5-29547 or equivalent, is more prac-
tical for determining and locating leaks.
3-LOW BATTERY
INDICATOR
2-HI-LOW SWITCH
4-BALANCE CONTROL
Figure 12 Electronic Leak Detector J-29547
ELECTRONIC LEAK TESTERS
(Figure 12)
Electronic leak testers can accurately determine
leaks in areas that are difficult to test with liquid leak
detectors due to poor visibility or inaccessibility.
The H-10 Leak Detector 5-26934 is a 110-volt,
A/C powered tester while the Refrigerant Leak Detec-
tor J-29547 is a portable, battery operated model.
Both models provide visual
and/or audible signals to
indicate leak detection.
The successful use of electronic leak detectors
depends upon carefully following the manufacturer's
instructions regarding calibration, operation and
maintenance. Battery condition is especially impor-
tant to the accuracy of the portable battery powered
model
5-29547 and is monitored by a low battery
indicator.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
Before attempting any service which requires
opening of refrigerant lines or components, the person
doing the work should be thoroughly familiar with the
information under HANDLING REFRIGERANT- 12,
HANDLING REFRIGERANT LINES AND FIT-
TINGS AND MAINTAINING CHEMICAL STA-
BILITY IN THE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM. Very
carefully follow the DISCHARGING, ADDING OIL,
EVACUATING AND CHARGING PROCEDURES
FOR
A/C SYSTEMS instructions given on the fol-
lowing pages for the unit being serviced.
Sealing caps should be removed from sub-
assemblies just prior to making connections for final
assembly. Use a small amount of clean 525 viscosity
refrigerant oil on all tube and hose joints. Always use
new O-rings dipped in the clean 525 viscosity refrig-
erant oil when assembling joints. The oil will aid in
assembly and help provide a leak-proof joint. When
tightening joints, use a second wrench to hold station-
ary part of connection so that
a solid feel can be
attained. This will indicate proper assembly.
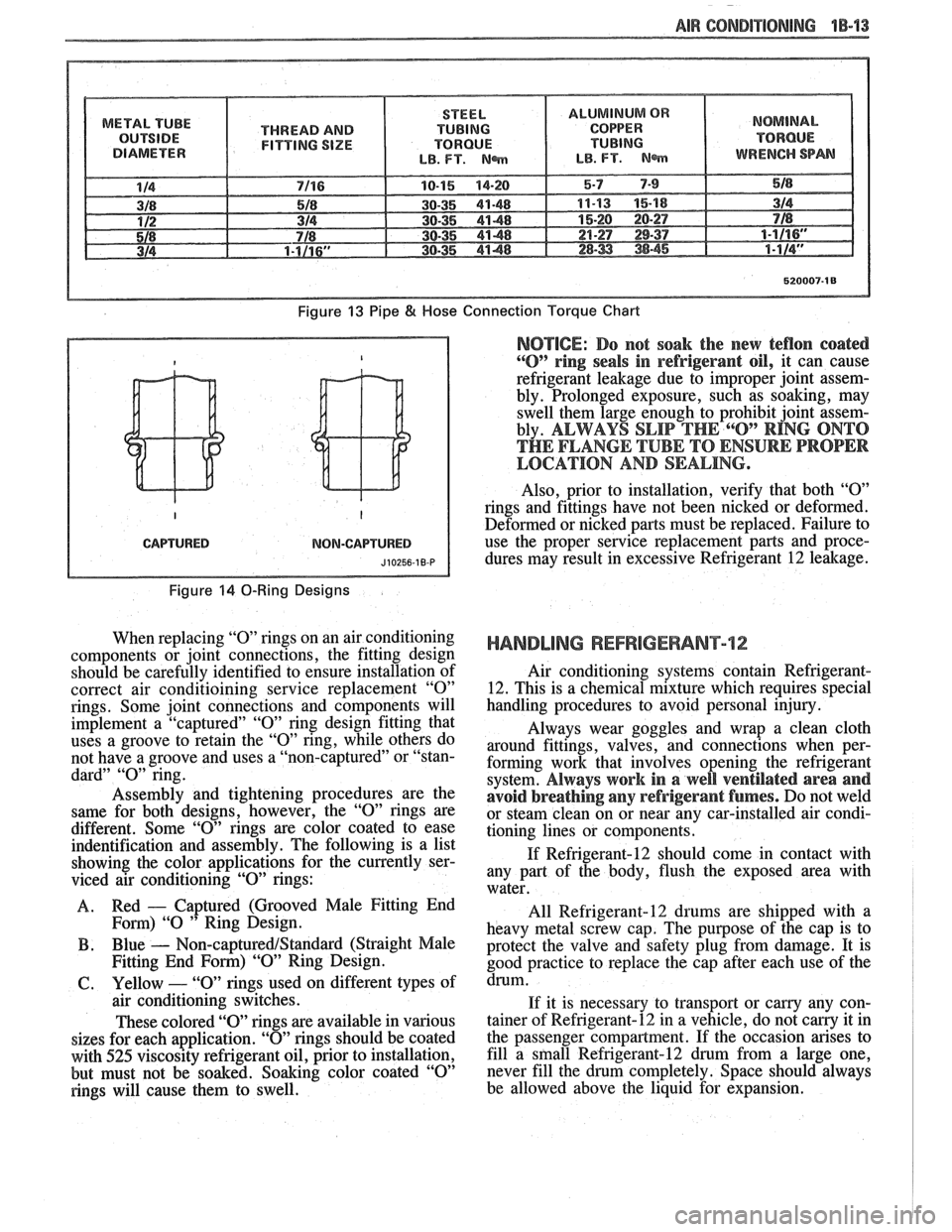
Tighten all tubing connections as shown in
torque chart (Figure
13). Insufficient or excessive
torque when tightening can result in loose joints or
deformed joint parts. Either condition can result in
refrigerant leakage.
O-RING REPWCEMENT
Install new G. M. approved service replacement
air conditioning
"0" rings whenever a joint or fitting
is disassembled, except when provided on new com-
ponents. Even though an
"0" ring may look the same,
it is extremely important that only recommended ser-
vice replacement air conditioning
"0" rings be used or
excessive leakage of Refrigerant 12 may occur.
Page 56 of 1825
-
AIR CONDlTlQNlNG 1B-'13
METAL TUBE
THREAD AND
FITTING SIZE
Figure 13 Pipe 8( Hose
CAPTURED NOM-CAPTURED
Figure 14 0-Ring Designs
When replacing "0" rings on an air conditioning
components or joint connections, the fitting design
should be carefully identified to ensure installation of
correct air conditioining service replacement
"0"
rings. Some joint connections and components will
implement a "captured"
"0" ring design fitting that
uses a groove to retain the
"0" ring, while others do
not have a groove and uses a "non-captured" or "stan-
dard"
"0" ring.
Assembly and tightening procedures are the
same for both designs, however, the
"0" rings are
different. Some
"0" rings are color coated to ease
indentification and assembly. The following is a list
showing the color applications for the currently ser-
viced air conditioning
"0" rings:
A. Red
- Captured
(Grooved Male Fitting End
Fom) "0 " Ring Design.
B . Blue - Non-captured/Standard (Straight Male
Fitting End
Form) "09' Ring Design.
61. Yellow - "0" rings used on different types of
air conditioning switches.
These colored "O" rings are available in various
sizes for each application.
"0" rings should be coated
with
525 viscosity refrigerant oil, prior to installation,
but must not be soaked. Soaking color coated
"0"
rings will cause them to swell.
Connection Torque Chart
NOTICE: Do not soak the new teflon coated
"0" ring seals in refrigerant oil, it can cause
refrigerant leakage due to improper joint assem-
bly. Prolonged exposure, such as soaking, may
swell them large enough to prohibit joint assem-
bly.
ALWAYS SLIP THE 6"O" RING ONTO
THE FLANGE TUBE TO ENSURE PROPER
LOCATION AND SEALING.
Also, prior to installation, verify that both "09'
rings and fittings have not been nicked or deformed.
Deformed or nicked
parts must be replaced. Failure to
use the proper service replacement parts and proce- dures may result in excessive Refrigerant
12 leakage.
HANDLING REFRIGERANT12
Air conditioning systems contain Refrigerant-
12. This is a chemical mixture which requires special
handling procedures to avoid personal injury.
Always wear goggles and wrap a clean cloth
around fittings, valves, and connections when per-
forming work that involves opening the refrigerant
system.
Always work in a well ventilated area and
avoid breathing
any refrigerant fumes. Do not weld
or steam clean on or near any car-installed air condi-
tioning lines or components.
If Refrigerant-12 should come in contact with
any part of the body, flush the exposed area with
water.
All
Refrigerant-12 drums are shipped with a
heavy metal screw cap. The purpose of the cap is to
protect the valve and safety plug from damage. It is
good practice to replace the cap after each use of the
drum.
If it is necessary to transport or carny any con-
tainer of Refrigerant-12 in a vehicle, do not
carry it in
the passenger compartment. If the occasion arises to
fill a
sfnall Refrigerant-12 drum from a large one,
never fill the drum completely. Space should always
be allowed above the liquid for expansion.
Page 57 of 1825

18-14 AIR CONDITIONING
HANDLING OF REFRIGERANT LINES AND
FI-INGS
Tighten all tubing connections as shown in
torque chart (Figure 13). INSUFFICIENT OR
EXCESSIVE TORQUE WHEN TIGHTENING CAN
RESULT IN LOOSE JOINTS OR DEFORMED
JOINT PARTS. Either condition can result in refrig-
erant leakage.
All metal tubing lines should be free of dents or
kinks to prevent loss of system capacity due to line
restriction.
@ The flexible hose lines should never be bent to a
radius of less than four (4) times the diameter of
the hose.
@ The flexible hose lines should never be allowed
to come within a distance of
63.5mm (2-112") of
the exhaust manifold.
@ Flexible hose lines should be inspected regularly
for leaks or brittleness and replaced with new
lines if deterioration or leaking is found.
@ When disconnecting any fitting in the refrigera-
tion system, the system must first be discharged
of all Refrigerant- 12. Proceed very cautiously
regardless of gauge readings. Open very slowly,
keeping face and hands away so that no injury
can occur if there happens to be liquid
Refriger-
ant-12 in the line. If pressure is noticed when
fitting is loosened, allow it to bleed off as
described under DISCHARGING, ADDING
OIL, EVACUATING AND CHARGING PRO-
CEDURES FOR
A/C SYSTEMS.
@ In the event any refrigerant line is opened to the
atmosphere, it should be immediately capped or
taped to prevent entrance of moisture and dirt,
which can cause internal compressor wear or
plugged lines, in the condenser and evaporator
core and expansion (orifice) tubes or compressor
inlet screens.
@ The use of the proper wrenches when making
connections on O-ring fittings is important. The
opposing fitting should always be backed up
with a wrench to prevent distortion of connecting
lines or components. When connecting the flexi-
ble hose connections, it is important that the
swaged fitting and the flare nut, as well as the
coupling to which it is attached, be held at the
same time using three
(3) different wrenches to
prevent turning the fitting and damaging the
ground seat.
@ O-rings and seats must be in perfect condition. A
burr or piece of dirt may cause a refrigerant leak.
When replacing the O-ring, first dip it in clean
525 viscosity refrigeration oil.
MAINTAINING CHEMICAL STABILITY IN
THE
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
The efficient operation and life of the air condi-
tioning system is dependent upon the chemical stabil-
ity of the refrigeration system. When foreign materials, such as
dirt, air, or moisture, contaminate
the refrigeration system, they will change the stability
of the Refrigerant-12 and 525 viscosity compressor
oil. They will also affect pressure-temperature rela-
tionship, reduce efficient operation and possibly cause
interior corrosion and abnormal wear of moving parts.
The following general practices should be
observed to insure chemical stability in the system:
1. Before disconnecting a refrigerant connection,
wipe away any dirt or oil at and near the connec-
tion to reduce the possibility of dirt entering the
system. Both sides of the connection should be
capped, plugged or taped as soon as possible to
prevent the entry of dirt, foreign material and
moisture.
2. Keep tools clean and dry. This includes the
manifold gauge set and replacement parts.
3. When adding 525 viscosity refrigerant oil (see
ADDING OIL in the DISCHARGING,
ADDING OIL, EVACUATING AND
CHARGING PROCEDURES FOR
AIC SYS-
TEMS, the transfer device and container should
be clean and dry to assure that refrigeration oil
remains as moisture-free as possible.
4. When it is necessary to "open" an
AIC system,
have everything needed ready and handy so that
as little time as possible will be required to per-
form the operation. Do not leave the
AIC system
open any longer than is necessary.
5. Any time the
A/C system has been "opened," it
should be properly evacuated before recharging
with Refrigerant- 12 according to the DIS-
CHARGING, ADDING OIL, EVACUATING
& CHARGING PROCEDURES FOR AIC
SYSTEMS.
All service parts are dehydrated and sealed
prior to shipping. They should remain sealed until just
prior to making connections. All parts should be at
room temperature before uncapping. (This prevents
condensation of moisture from the air entering the
system.) If, for any reason, caps are removed but the
connections are not made, parts should be resealed as
soon as possible.
DISCHARGING, ADDING OIL,
EVACUATING AND CHARGING
PROCEDURES FOR NC SYSTEMS
The refrigerant system may be discharged,
evacuated and charged using air conditioning service
charging station J-23500-01 or equivalent, or the
manifold and gauge set
5-23575-01 and 420ml (14
oz.) disposable cans of Refrigerant-12 (Figure 16).
Charging lines from the charging station or
manifold and gauge set require the use of gauge
adapters to connect to the system service fitting.
A
straight gauge adapter 5-5420 and a 90" angle gauge
adapter
5-9459 are available (see A/C Special Tools).
Always wear goggles and wrap a clean cloth
around fittings and connections when doing work that
Page 58 of 1825

AIR GONDlTlONlNG 1B-15
involves opening the refrigeration system. Always
work in a well ventilated area and avoid breathing any
refrigerant fumes. If liquid refrigerant comes into con-
tact with the eyes, injury may result.
@ Before removing and replacing any of the air
conditioning refrigeration lines or components,
the system must be completely discharged of
Refrigerant- 12.
@ Always use service valve and pressure gauge
sets during evacuation and charging procedures.
@ Always discharge system at low-side service fit-
ting and perform the entire evacuate and charg-
ing procedure through the low-side service
fitting.
@ Do not connect high-pressure line or any line to
the high-side
service fitting during discharging
and charging procedures.
CAUTION: Never remove a gauge line
from its adapter when line is connected
to
AIC system. Always remove the line
adapter from the service
fining to dis-
connect a line. Do not remove charging
hose at gauge set while
anached to ser-
vice low-side
fining. This will result in
complete discharge of system due to
the depressed Schrader valve in
service
low-side fining and may cause personal
injury due to escaping Refrigerant-12.
Discharging the NG System
In replacing any of the air conditioning refriger-
ation components, the system must be completely dis-
charged of Refrigerant- 12.
ALWAYS DISCHARGE SYSTEM AT
LOW-SIDE SERVICE FITTING.
1. With ignition turned "OFF," remove protective
cap from LOW-SIDE service fitting (on most
models) on Accumulator and connect charging
station
J-23500-01 or equivalent gauge set. If
charging station J-23500-01 or equivalent is not
being used, discharge system by slowly con-
necting a gauge hose to low-side
sewice fitting
on accumulator and discharging into oil bottle
(Figure 15). As hose is slowly tightened down
onto Schrader valve, Refrigerant-12 will begin
to discharge from the system into the container.
If no discharge occurs, check for missing or
defective Schrader depressor in hose fitting.
2. With the low-side of system fully discharged,
check high-side system fitting (on liquid line or
muffler) for remaining pressure.
3. If pressure is found, attempt to discharge high-
side using same procedure as used for low-side.
(This condition indicates a restriction on the
high-side and the cause must be diagnosed and
corrected before evacuating and charging the
system.)
4. When the system is completely discharged (no
vapor escaping with hose fully tightened down), measure, record
amount, and discard the col-
lected refrigerant oil. If the measured quantity is
15ml (112 fl. 02.) or more, this amount of new
525 viscosity refrigerant oil must be added to system, plus any quantity in removed parts
before system evacuation and charging with
Refrigerant-12 (see REFRIGERANT OIL DIS-
TRIBUTION for specific quantity of oil nor-
mally retained in removed parts).
Adding Oil to the Air Conditioning
Refrigerant System
ADDING OIL TO THE A/C SYSTEM should
take place AFTER discharge and BEFORE evacua-
tion procedures by removing the refrigeration suction
hose at the accumulator outlet pipe connection, pour-
ing the correct quantity of new refrigerant oil into the
hose or pipe and then properly reconnecting hose to
pipe (see REFRIGERANT OIL DISTRIBUTION for
specific quantity instructions).
1-USING J 5420 4-REFRIGERANT OIL BOTTLE UNCAPPED
TO ALLOW GAS
TO ESCAPE
2-GAGE HOSE 5-ACCUMULATOR
Figure 15 Discharging the A/C System Without
Charging Station
Refrigerant Oil Distribution
New 525 viscosity refrigerant oil must be added
to the system when components are replaced, as
follows:
A. All Compressors
@ If less than 30 ml(1 fl. oz.) is drained -
add 60 ml (2 fl. oz.).
@ If more than 30 ml(1 fl. oz.) is drained --
add same amount.
Page 59 of 1825

"18-16 AIR CONDITIONING
B . Accumulator dehydrator
@ Add 105 ml (3.5 fl. 02.) to new
accumulator
C. Evaporator
@ Add 90 ml (3 fl. oz.) oil
D. Condenser
@ Add 30 ml (1 fl. 02.) oil
Refrigerant oil loss due to a large leak
If the refrigerant charge is aburptly lost due to a
large refrigerant leak, approximately 90
ml (3 fl. oz.)
of refrigerant oil will be
carried out of the system sus-
pended in the refrigerant. Any failure that caused an
abrupt refrigerant discharge will experience this oil
loss. Failures that allow the refrigerant to seep or
bleed off over time do not experience this oil loss.
Upon replacement of a component which
caused a large refrigerant leak, add 90 ml(3
fl. oz.) of
new 525 viscosity refrigerant oil plus the required
amount of oil for the particular component (as out-
lined above).
Add the oil directly to the replaced component if
possible. If the oil cannot easily be added to the
replaced part, add the oil to the accumulator.
Evacuating and Charging the A/C System
If the system has been opened for any repair, or
the Refrigerant-12 charge lost, the system must be
evacuated prior to charging.
Evacuating and charging is a combined proce-
dure, and all gauge lines must be purged with R-12
prior to charging.
There are three evacuate and charge procedures.
1.
J 23500-01 Charging Station Method
2. Disposable Can Method 3. Drum Method
NOTICE: Under no circumstances should alco-
hol be used in the system in an attempt to remove
moisture. Damage to the system components
could occur.
Gauge Calibration
Prior to evacuation, check the low-pressure
gauge for proper calibration and determine if vacuum
system is operating properly.
With the gauge disconnected from the refrigera-
tion system, be sure that the pointer indicates to the
center of
"0". Lightly tap gauge a few times to be sure
pointer is not sticking. If necessary, calibrate as
follows:
1. Remove cover from gauge.
2. Holding gauge pointer adjusting screw firmly
with one hand, carefully force pointer in the
proper direction to position pointer at the
"0"
position. Tap gauge a few times to be sure
pointer is not sticking. Replace gauge cover.
Vacuum System Check
Before connecting vacuum pump to the A/C
system, run pump connected to the low-pressure
gauge to determine the vacuum pump capability. If
the vacuum system is unable to reach
7 1 1.2-736.6mm
(28"-29") or more vacuum, the system should be
checked for leaks. If no leaks are found, the vacuum
pump may require repair.
5-23580-81 OR EQUIVALENT CHARGING
STATION METHOD.
Follow charging instructions provided with the
5-23500-01 Charging Station or equivalent in use with
the following exceptions:
1. Do
not connect the high-pressure line to the air
conditioning system.
2. Keep the high-pressure valve on the charging
station closed at all times.
3.
Perform the entire evacuate and charge proce-
dure through the accumulator low-side pressure service fitting.
4. Following these procedures will prevent acci-
dental high-side vehicle system pressure being
subjected to the charging station in the event an
error is made in valve sequence during compres-
sor operation to pull in the Refrigerant-12
charge.
DISPOSABLE CAN OR REFRIGERANT
DRUM METHOD.
If the Refrigerant-12 drum is used, place it on a
scale and note the total weight before charging. Watch
the scale during charging to determine the amount of
R-12 used.
If disposable
420ml (14 ounce) R-12 cans are
used, close the tapping valve and then attach
can(s)
following instructions included with the tapping valve
or tapping manifold adapter.
1. Connect manifold gauge set 5-23575-01 as fol-
lows. Also see Figure 16.
a. Eow-pressure gauge to accumulator fit-
ting.
b. Gauge set center hosk to Refrigerant-12
source.
c. High-pressure gauge to vacuum pump.
2. To begin evacuation of the
A/C system with
manifold gauge set and vacuum pump as illus-
trated in Figure 16, slowly open
high- and low-
side gauge valves and begin vacuum pump oper-
ation. Pump the system until the low-side gauge
reaches 7 1
1.2-736.6mm (28"-29") vacuum.
Note that in all evacuation procedures, the spec-
ification of 7 1
1.2-736.6mm (28"-29") vacuum is
used. This specification can only be reached at
or near sea level. For each
304.8m (1,000 feet)
above sea level, specification should be lowered
by one inch vacuum. At
1524m (5,000 feet)
elevation, only
584.2-609.6mm (23"-24") of
vacuum is required.
Page 60 of 1825
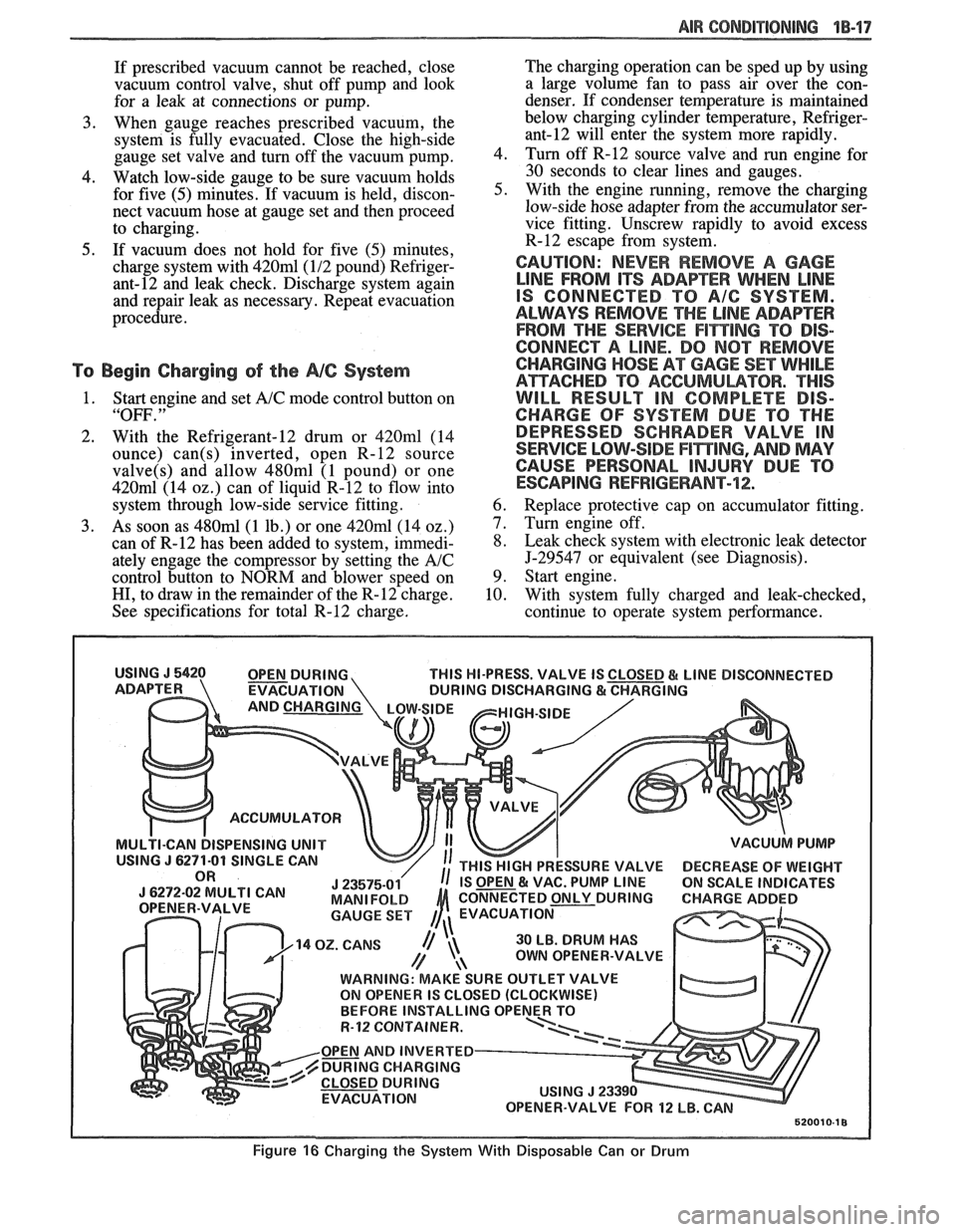
AIR CONDITIONING 1B-17
If prescribed vacuum cannot be reached, close
vacuum control valve, shut off pump and look
for a leak at connections or pump.
3. When gauge reaches prescribed vacuum, the
system is fully evacuated. Close the high-side
gauge set valve and turn off the vacuum pump.
4. Watch low-side gauge to be sure vacuum holds
for five (5) minutes. If vacuum is held, discon-
nect vacuum hose at gauge set and then proceed
to charging.
5. If vacuum does not hold for five (5) minutes,
charge system with
420ml(1/2 pound) Refriger-
ant-12 and leak check. Discharge system again
and repair leak as necessary. Repeat evacuation
procedure.
To Begin Charging of the NC System
1. Start engine and set A/C mode control button on
"OFF. "
2. With the Refrigerant-12 drum or 420ml (14
ounce)
can(s) inverted, open R-12 source
valve(s) and allow 480ml (1 pound) or one
420m1 (14 02.) can of liquid R-12 to flow into
system through low-side service fitting.
3. As soon as 480ml (1 lb.) or one 420ml (14 oz.)
can of R-12 has been added to system, immedi-
ately engage the compressor by setting the
A/C
control button to NORM and blower speed on
HI, to draw in the remainder of the R-12 charge.
See specifications for total R-12 charge. The
charging operation can be sped up by using
a large volume fan to pass air over the con-
denser. If condenser temperature is maintained
below charging cylinder temperature,
Refriger-
ant-12 will enter the system more rapidly.
4. Turn off
R-12 source valve and run engine for
30 seconds to clear lines and gauges.
5. With the engine running, remove the charging
low-side hose adapter from the accumulator ser-
vice fitting. Unscrew rapidly to avoid excess
R-12 escape from system.
CAUTION: NEVER REMOVE A GAGE
LINE FROM ITS ADAPEER WHEN LINE
IS CONNECTED TO A/G SYSTEM.
ALWAYS REMOVE
THE LINE ADAPTER
FROM THE
SERVICE F1miNG TO DIS-
CONNECT A LINE. DO
NOT REMOVE
CHARGING
HOSE AT GAGE SET WHILE
ATTACHED TO ACGUMULBTOR. "THIS
WILL RESULT IN COMPLETE DIS-
CHARGE OF SYSTEM DUE TO THE
DEPRESSED SCHRADER VALVE IN
SERVICE LOW-SIDE
F17$TING, AND MAY
CAUSE PERSONAL
INJURY DUE TO
ESCAPING REFRIGERANT-72;.
6. Replace protective cap on accumulator fitting.
7. Turn engine off.
8. Leak check system with electronic leak detector
5-29547 or equivalent (see Diagnosis).
9. Start engine.
10. With system fully charged and leak-checked,
continue to operate system performance.
THIS HI-PRESS. VALVE IS
EVACUATION
ACCUMULATOR
ISPENSING UNIT
30 LB. DRUM HAS
OWN OPENER-VALVE
WARNING: MAKE SURE OUTLET VALVE
ON OPENER IS CLOSED (CLOCKWISE)
R-12 CQNTAINER.
OPEN AND INVERTED
DURING CHARGING
EVACUATION
Figure 16 Charging the System With Disposable Can or Drum