SUBARU FORESTER 2004 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: SUBARU, Model Year: 2004, Model line: FORESTER, Model: SUBARU FORESTER 2004Pages: 2870, PDF Size: 38.67 MB
Page 1571 of 2870

ME(H4DOTC)-111
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
7) Replacement procedure is as follows:
(1) Remove the bushing from connecting rod
with ST and press.
(2) Press the bushing with ST after applying oil
on the periphery of bushing.
ST 499037100 CONNECTING ROD BUSH-
ING REMOVER AND IN-
STALLER
(3) Make two 3 mm (0.12 in) holes in bushing.
Ream the inside of bushing.
(4) After the completion of reaming, clean the
bushing to remove chips.
6. CRANKSHAFT AND CRANKSHAFT
BEARING
1) Clean the crankshaft completely and check for
cracks by means of red lead check etc., and re-
place if defective.
2) Measure the crankshaft bend, and correct or re-
place if it exceeds the limit.
NOTE:
If a suitable V-block is not available, install the #1
and #5 crankshaft bearing on cylinder block, posi-
tion the crankshaft on these bearings and measure
the crankshaft bend using a dial gauge.
Crankshaft bend limit:
0.035 mm (0.0014 in)
3) Inspect the crank journal and crank pin for wear.
If they are not within the specifications, replace the
bearing with a suitable (undersize) one, and then
replace or recondition the crankshaft as necessary.
When grinding the crank journal or crank pin, finishthem to specified dimensions according to the un-
dersize bearing to be used.
Crank pin and crank journal:
Out-of-roundness
0.005 mm (0.0002 in) or less
Taper limit
0.07 mm (0.0028 in)
Grinding limit
0.250 mm (0.0098 in)
ME-00182
ST
ME-00183
ME-00184
Page 1572 of 2870
ME(H4DOTC)-112
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
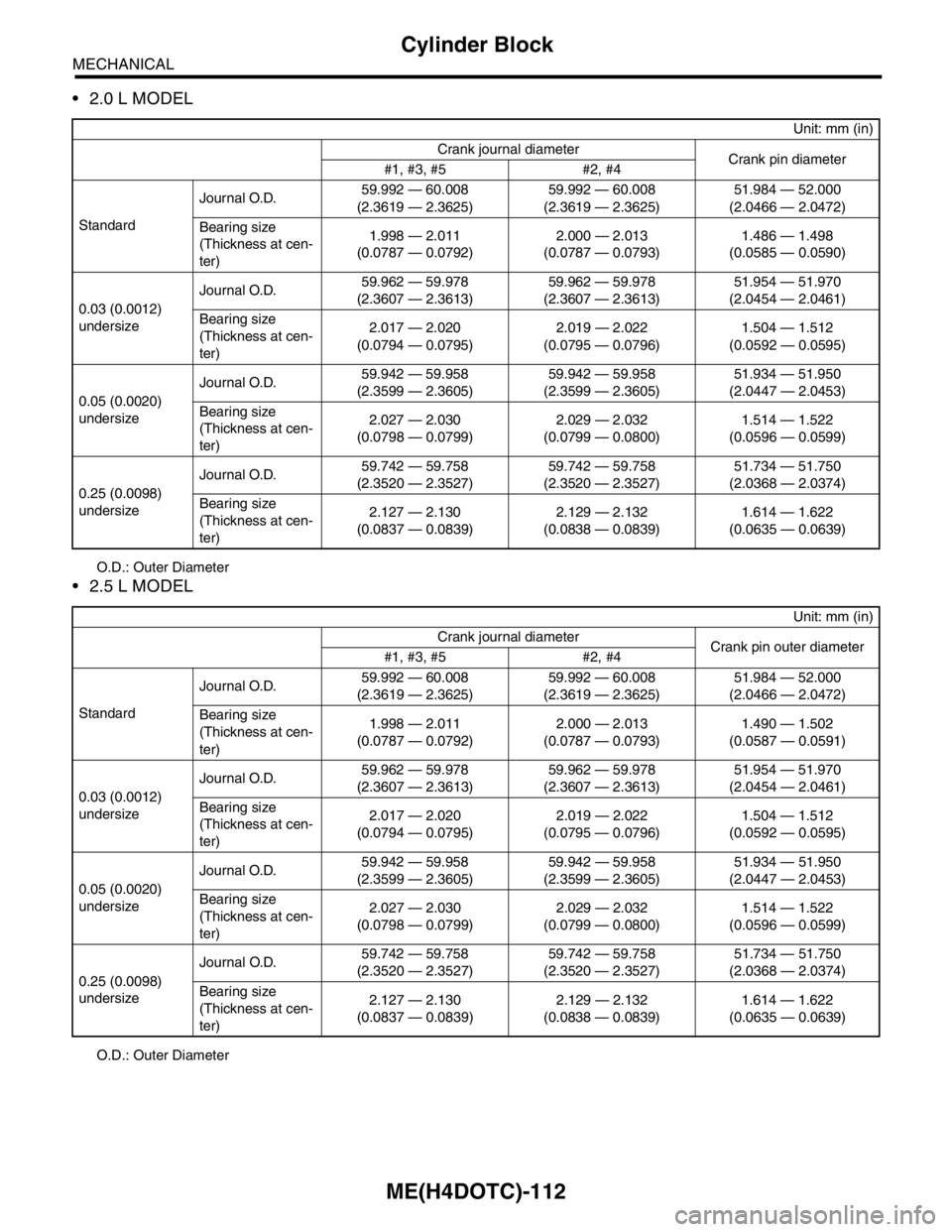
2.0 L MODEL
O.D.: Outer Diameter
2.5 L MODEL
O.D.: Outer DiameterUnit: mm (in)
Crank journal diameter
Crank pin diameter
#1, #3, #5 #2, #4
StandardJournal O.D.59.992 — 60.008
(2.3619 — 2.3625)59.992 — 60.008
(2.3619 — 2.3625)51.984 — 52.000
(2.0466 — 2.0472)
Bearing size
(Thickness at cen-
ter)1.998 — 2.011
(0.0787 — 0.0792)2.000 — 2.013
(0.0787 — 0.0793)1.486 — 1.498
(0.0585 — 0.0590)
0.03 (0.0012)
undersizeJournal O.D.59.962 — 59.978
(2.3607 — 2.3613)59.962 — 59.978
(2.3607 — 2.3613)51.954 — 51.970
(2.0454 — 2.0461)
Bearing size
(Thickness at cen-
ter)2.017 — 2.020
(0.0794 — 0.0795)2.019 — 2.022
(0.0795 — 0.0796)1.504 — 1.512
(0.0592 — 0.0595)
0.05 (0.0020)
undersizeJournal O.D.59.942 — 59.958
(2.3599 — 2.3605)59.942 — 59.958
(2.3599 — 2.3605)51.934 — 51.950
(2.0447 — 2.0453)
Bearing size
(Thickness at cen-
ter)2.027 — 2.030
(0.0798 — 0.0799)2.029 — 2.032
(0.0799 — 0.0800)1.514 — 1.522
(0.0596 — 0.0599)
0.25 (0.0098)
undersizeJournal O.D.59.742 — 59.758
(2.3520 — 2.3527)59.742 — 59.758
(2.3520 — 2.3527)51.734 — 51.750
(2.0368 — 2.0374)
Bearing size
(Thickness at cen-
ter)2.127 — 2.130
(0.0837 — 0.0839)2.129 — 2.132
(0.0838 — 0.0839)1.614 — 1.622
(0.0635 — 0.0639)
Unit: mm (in)
Crank journal diameter
Crank pin outer diameter
#1, #3, #5 #2, #4
StandardJournal O.D.59.992 — 60.008
(2.3619 — 2.3625)59.992 — 60.008
(2.3619 — 2.3625)51.984 — 52.000
(2.0466 — 2.0472)
Bearing size
(Thickness at cen-
ter)1.998 — 2.011
(0.0787 — 0.0792)2.000 — 2.013
(0.0787 — 0.0793)1.490 — 1.502
(0.0587 — 0.0591)
0.03 (0.0012)
undersizeJournal O.D.59.962 — 59.978
(2.3607 — 2.3613)59.962 — 59.978
(2.3607 — 2.3613)51.954 — 51.970
(2.0454 — 2.0461)
Bearing size
(Thickness at cen-
ter)2.017 — 2.020
(0.0794 — 0.0795)2.019 — 2.022
(0.0795 — 0.0796)1.504 — 1.512
(0.0592 — 0.0595)
0.05 (0.0020)
undersizeJournal O.D.59.942 — 59.958
(2.3599 — 2.3605)59.942 — 59.958
(2.3599 — 2.3605)51.934 — 51.950
(2.0447 — 2.0453)
Bearing size
(Thickness at cen-
ter)2.027 — 2.030
(0.0798 — 0.0799)2.029 — 2.032
(0.0799 — 0.0800)1.514 — 1.522
(0.0596 — 0.0599)
0.25 (0.0098)
undersizeJournal O.D.59.742 — 59.758
(2.3520 — 2.3527)59.742 — 59.758
(2.3520 — 2.3527)51.734 — 51.750
(2.0368 — 2.0374)
Bearing size
(Thickness at cen-
ter)2.127 — 2.130
(0.0837 — 0.0839)2.129 — 2.132
(0.0838 — 0.0839)1.614 — 1.622
(0.0635 — 0.0639)
Page 1573 of 2870

ME(H4DOTC)-113
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
4) Measure the thrust clearance of crankshaft at
center bearing. If the clearance exceeds the limit,
replace the bearing.
Crankshaft thrust clearance:
Standard
0.030 — 0.115 mm (0.0012 — 0.0045 in)
Limit
0.25 mm (0.0098 in)
5) Inspect individual crankshaft bearings for signs
of flaking, seizure, melting and wear.6) Measure the oil clearance on each crankshaft
bearing by means of plastigage. If the measure-
ment is not within the specification, replace the de-
fective bearing with an undersize one, and replace
or recondition the crankshaft as necessary.
Crankshaft oil clearance:
Standard
0.010 — 0.030 mm (0.0004 — 0.0012 in)
Limit
0.040 mm (0.0016 in)
ME-00313
Page 1574 of 2870

ME(H4DOTC)-114
MECHANICAL
Intake and Exhaust Valve
21.Intake and Exhaust Valve
A: REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
For operations related to intake and exhaust valve,
refer to “19. Cylinder Head.”
sembly.>
Page 1575 of 2870

ME(H4DOTC)-115
MECHANICAL
Piston
22.Piston
A: REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
For operations related to piston, refer to “20. Cylin-
der Block.”
Page 1576 of 2870

ME(H4DOTC)-116
MECHANICAL
Connecting Rod
23.Connecting Rod
A: REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
For operations related to connecting rod, refer to
“20. Cylinder Block.”
Block.>
Page 1577 of 2870

ME(H4DOTC)-117
MECHANICAL
Crankshaft
24.Crankshaft
A: REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
For operations related to crankshaft, refer to “20.
Cylinder Block.”
Page 1578 of 2870
ME(H4DOTC)-118
MECHANICAL
Engine Trouble in General
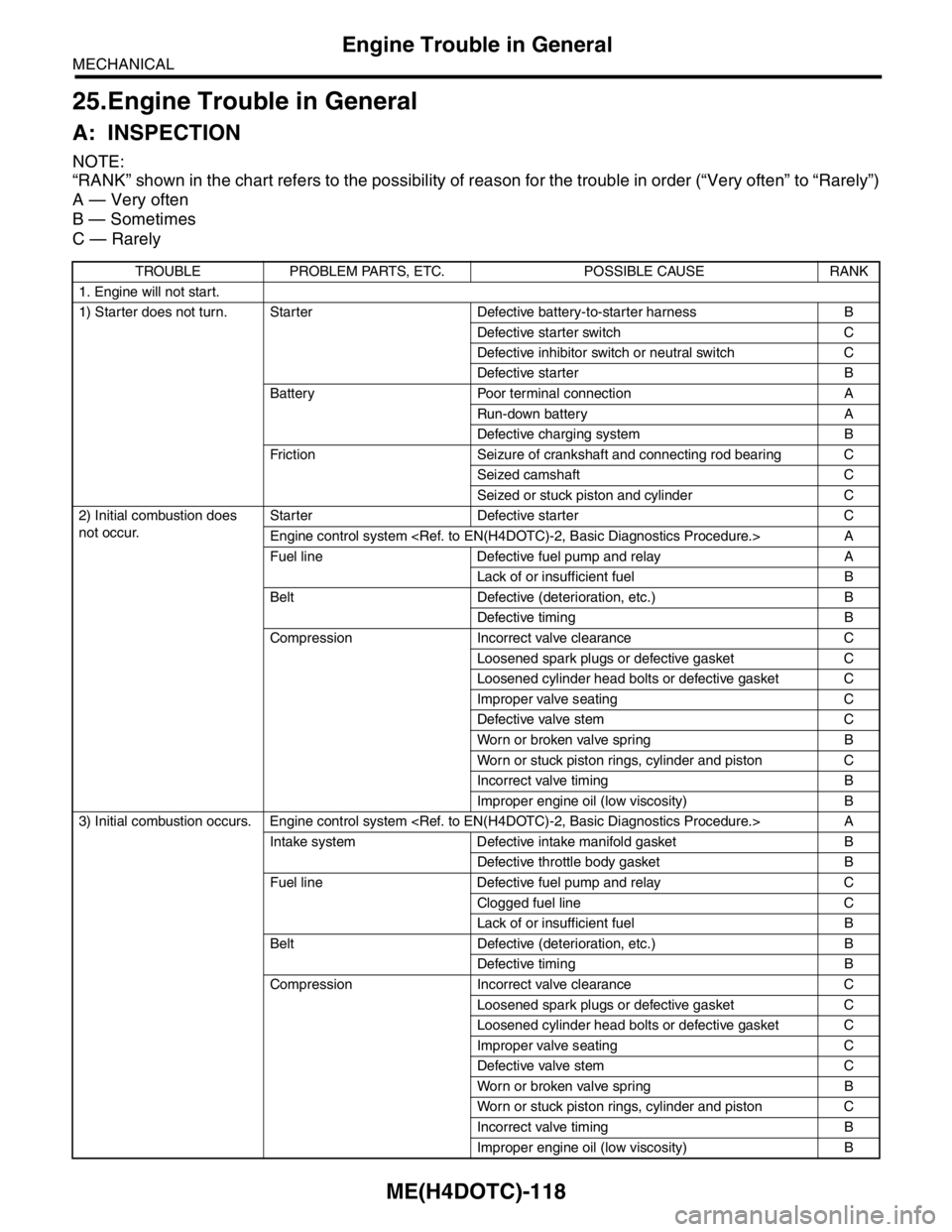
25.Engine Trouble in General
A: INSPECTION
NOTE:
“RANK” shown in the chart refers to the possibility of reason for the trouble in order (“Very often” to “Rarely”)
A — Very often
B — Sometimes
C — Rarely
TROUBLE PROBLEM PARTS, ETC. POSSIBLE CAUSE RANK
1. Engine will not start.
1) Starter does not turn. Starter Defective battery-to-starter harness B
Defective starter switch C
Defective inhibitor switch or neutral switch C
Defective starter B
Battery Poor terminal connection A
Run-down battery A
Defective charging system B
Friction Seizure of crankshaft and connecting rod bearing C
Seized camshaft C
Seized or stuck piston and cylinder C
2) Initial combustion does
not occur. Starter Defective starter C
Engine control system
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay A
Lack of or insufficient fuel B
Belt Defective (deterioration, etc.) B
Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance C
Loosened spark plugs or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolts or defective gasket C
Improper valve seating C
Defective valve stem C
Worn or broken valve spring B
Worn or stuck piston rings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing B
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
3) Initial combustion occurs. Engine control system
Intake system Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay C
Clogged fuel line C
Lack of or insufficient fuel B
Belt Defective (deterioration, etc.) B
Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance C
Loosened spark plugs or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolts or defective gasket C
Improper valve seating C
Defective valve stem C
Worn or broken valve spring B
Worn or stuck piston rings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing B
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Page 1579 of 2870
ME(H4DOTC)-119
MECHANICAL
Engine Trouble in General
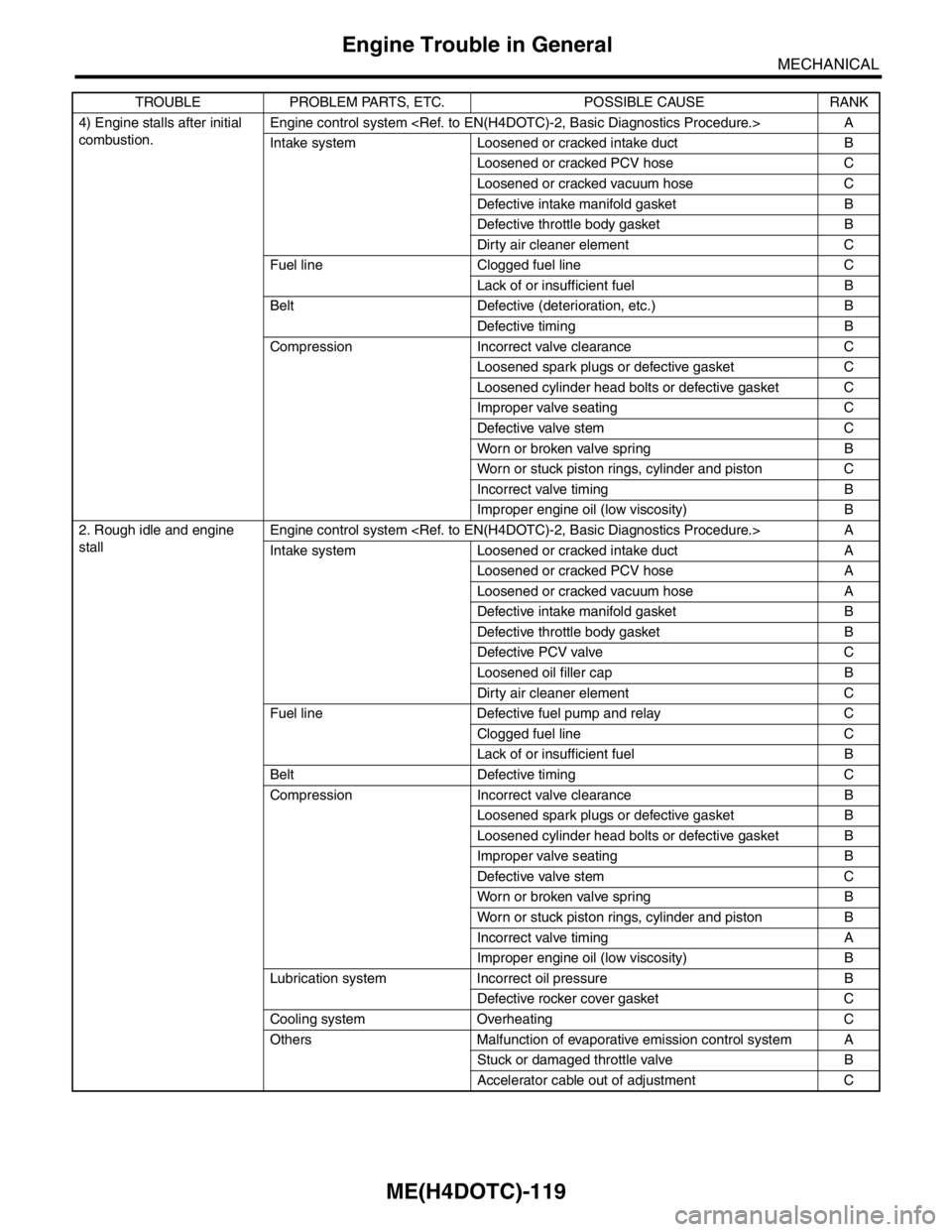
4) Engine stalls after initial
combustion. Engine control system
Intake system Loosened or cracked intake duct B
Loosened or cracked PCV hose C
Loosened or cracked vacuum hose C
Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Dirty air cleaner element C
Fuel line Clogged fuel line C
Lack of or insufficient fuel B
Belt Defective (deterioration, etc.) B
Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance C
Loosened spark plugs or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolts or defective gasket C
Improper valve seating C
Defective valve stem C
Worn or broken valve spring B
Worn or stuck piston rings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing B
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
2. Rough idle and engine
stallEngine control system
Intake system Loosened or cracked intake duct A
Loosened or cracked PCV hose A
Loosened or cracked vacuum hose A
Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Defective PCV valve C
Loosened oil filler cap B
Dirty air cleaner element C
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay C
Clogged fuel line C
Lack of or insufficient fuel B
Belt Defective timing C
Compression Incorrect valve clearance B
Loosened spark plugs or defective gasket B
Loosened cylinder head bolts or defective gasket B
Improper valve seating B
Defective valve stem C
Worn or broken valve spring B
Worn or stuck piston rings, cylinder and piston B
Incorrect valve timing A
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Lubrication system Incorrect oil pressure B
Defective rocker cover gasket C
Cooling system Overheating C
Others Malfunction of evaporative emission control system A
Stuck or damaged throttle valve B
Accelerator cable out of adjustment C TROUBLE PROBLEM PARTS, ETC. POSSIBLE CAUSE RANK
Page 1580 of 2870
ME(H4DOTC)-120
MECHANICAL
Engine Trouble in General
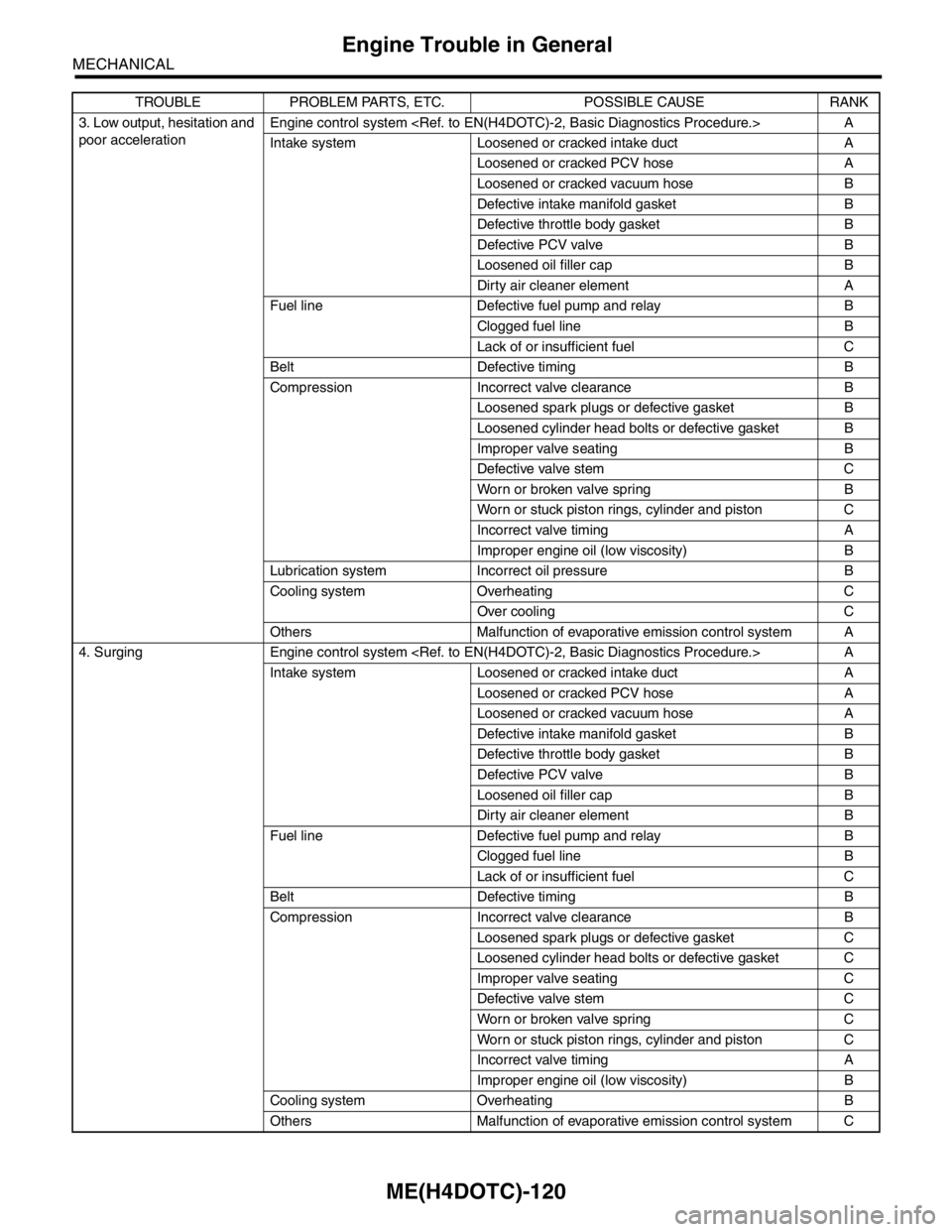
3. Low output, hesitation and
poor accelerationEngine control system
Intake system Loosened or cracked intake duct A
Loosened or cracked PCV hose A
Loosened or cracked vacuum hose B
Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Defective PCV valve B
Loosened oil filler cap B
Dirty air cleaner element A
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay B
Clogged fuel line B
Lack of or insufficient fuel C
Belt Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance B
Loosened spark plugs or defective gasket B
Loosened cylinder head bolts or defective gasket B
Improper valve seating B
Defective valve stem C
Worn or broken valve spring B
Worn or stuck piston rings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing A
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Lubrication system Incorrect oil pressure B
Cooling system Overheating C
Over cooling C
Others Malfunction of evaporative emission control system A
4. Surging Engine control system
Intake system Loosened or cracked intake duct A
Loosened or cracked PCV hose A
Loosened or cracked vacuum hose A
Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Defective PCV valve B
Loosened oil filler cap B
Dirty air cleaner element B
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay B
Clogged fuel line B
Lack of or insufficient fuel C
Belt Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance B
Loosened spark plugs or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolts or defective gasket C
Improper valve seating C
Defective valve stem C
Worn or broken valve spring C
Worn or stuck piston rings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing A
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Cooling system Overheating B
Others Malfunction of evaporative emission control system C TROUBLE PROBLEM PARTS, ETC. POSSIBLE CAUSE RANK