lock SUBARU FORESTER 2004 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUBARU, Model Year: 2004, Model line: FORESTER, Model: SUBARU FORESTER 2004Pages: 2870, PDF Size: 38.67 MB
Page 1057 of 2870
SP(H4SO)-4
SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
Accelerator Pedal
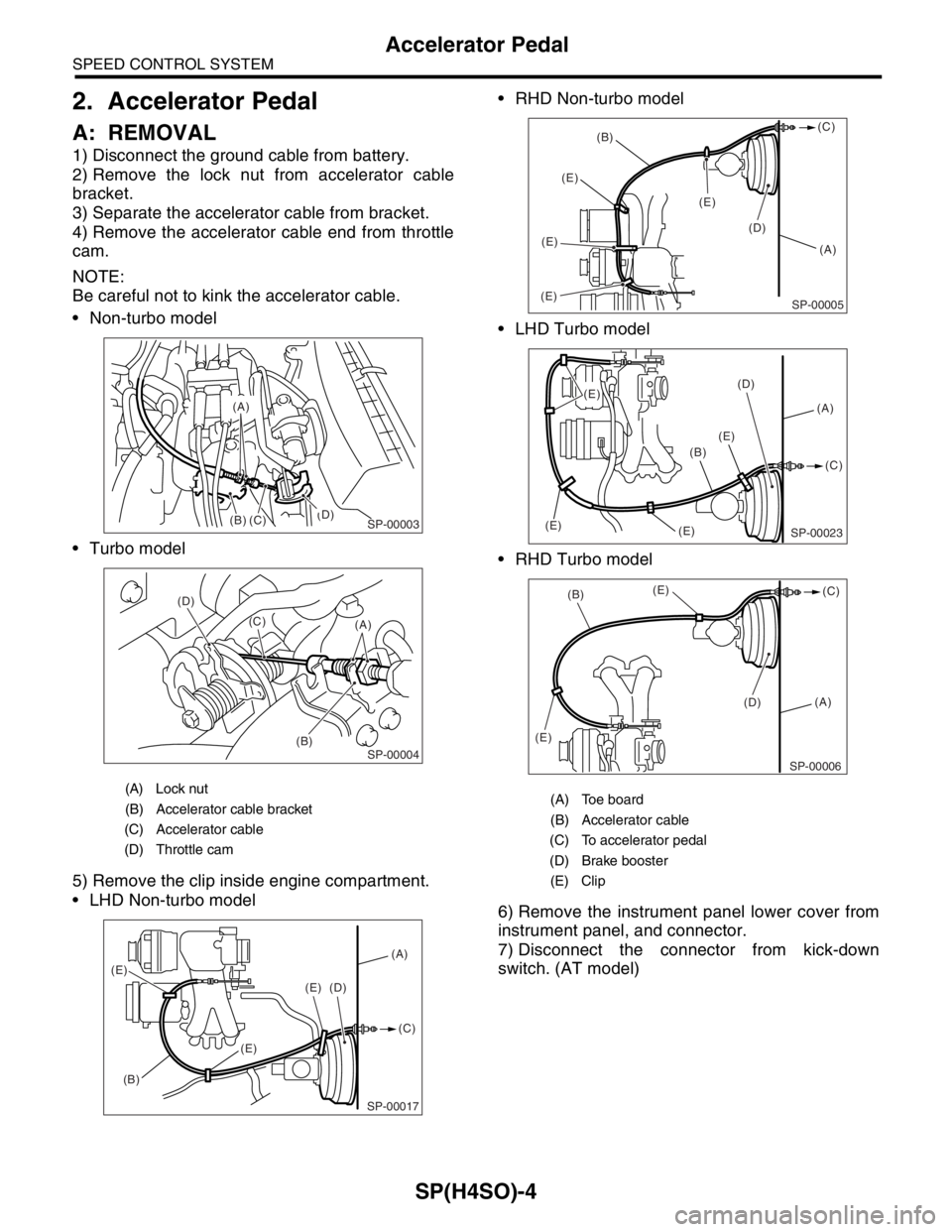
2. Accelerator Pedal
A: REMOVAL
1) Disconnect the ground cable from battery.
2) Remove the lock nut from accelerator cable
bracket.
3) Separate the accelerator cable from bracket.
4) Remove the accelerator cable end from throttle
cam.
NOTE:
Be careful not to kink the accelerator cable.
Non-turbo model
Turbo model
5) Remove the clip inside engine compartment.
LHD Non-turbo model RHD Non-turbo model
LHD Turbo model
RHD Turbo model
6) Remove the instrument panel lower cover from
instrument panel, and connector.
7) Disconnect the connector from kick-down
switch. (AT model)
(A) Lock nut
(B) Accelerator cable bracket
(C) Accelerator cable
(D) Throttle cam
(B)(D)
(C)
(A)
SP-00003
(B) (D)
(C)
(A)SP-00004
SP-00017
(A)
(B)(C) (D)
(E)
(E)
(E)
(A) Toe board
(B) Accelerator cable
(C) To accelerator pedal
(D) Brake booster
(E) Clip
(A) (B)(C)
(E)(E)(E)
(E)
(D)
SP-00005
(A) (D)
(E)
(E) (E)(C)
(B)
(E)
SP-00023
(A)
(D) (E)
(E)(B)(C)
SP-00006
Page 1060 of 2870
SP(H4SO)-7
SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
Accelerator Pedal
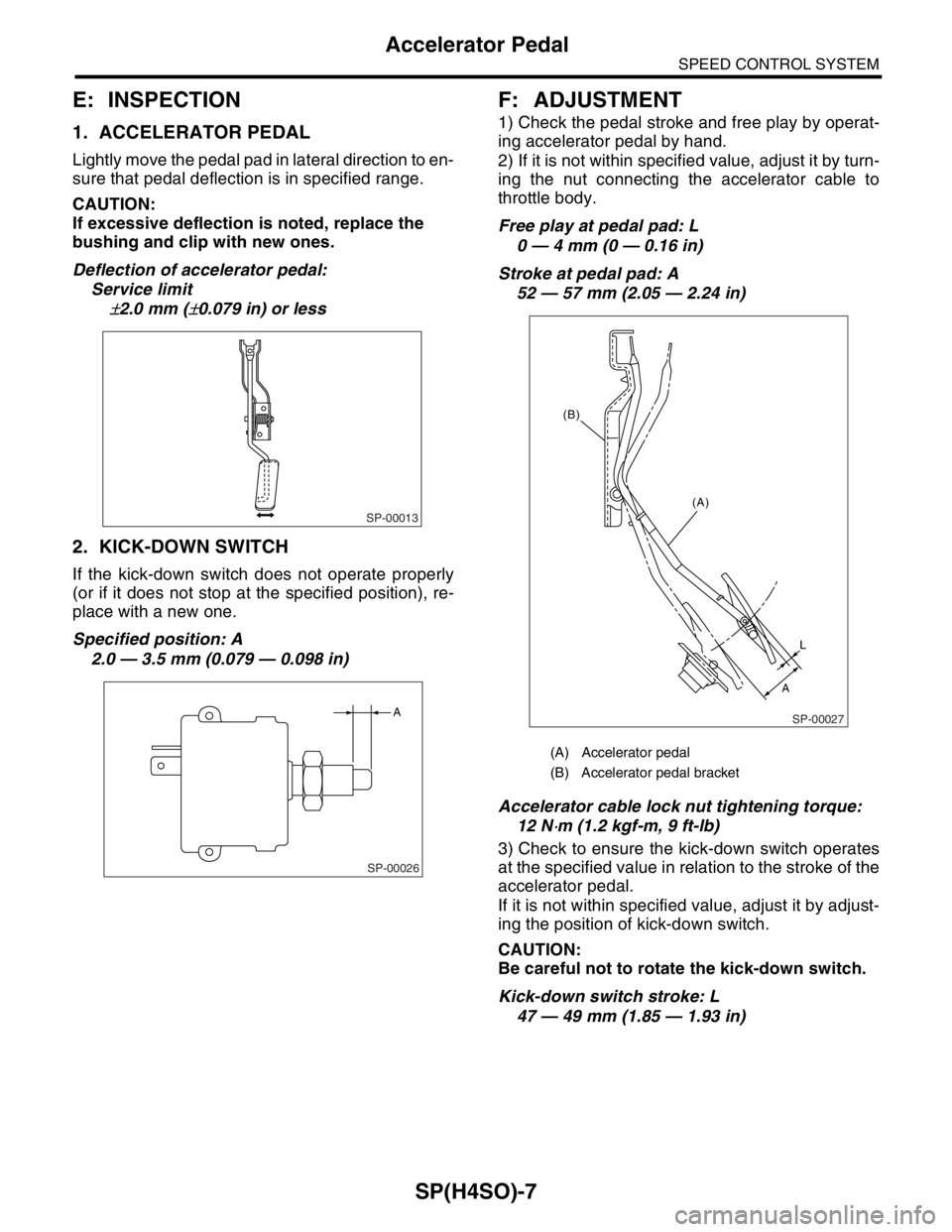
E: INSPECTION
1. ACCELERATOR PEDAL
Lightly move the pedal pad in lateral direction to en-
sure that pedal deflection is in specified range.
CAUTION:
If excessive deflection is noted, replace the
bushing and clip with new ones.
Deflection of accelerator pedal:
Service limit
±2.0 mm (±0.079 in) or less
2. KICK-DOWN SWITCH
If the kick-down switch does not operate properly
(or if it does not stop at the specified position), re-
place with a new one.
Specified position: A
2.0 — 3.5 mm (0.079 — 0.098 in)
F: ADJUSTMENT
1) Check the pedal stroke and free play by operat-
ing accelerator pedal by hand.
2) If it is not within specified value, adjust it by turn-
ing the nut connecting the accelerator cable to
throttle body.
Free play at pedal pad: L
0 — 4 mm (0 — 0.16 in)
Stroke at pedal pad: A
52 — 57 mm (2.05 — 2.24 in)
Accelerator cable lock nut tightening torque:
12 N
⋅m (1.2 kgf-m, 9 ft-lb)
3) Check to ensure the kick-down switch operates
at the specified value in relation to the stroke of the
accelerator pedal.
If it is not within specified value, adjust it by adjust-
ing the position of kick-down switch.
CAUTION:
Be careful not to rotate the kick-down switch.
Kick-down switch stroke: L
47 — 49 mm (1.85 — 1.93 in)
SP-00013
SP-00026
A
(A) Accelerator pedal
(B) Accelerator pedal bracket
SP-00027
(A)
L
A (B)
Page 1077 of 2870
SC(H4SO)-2
STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEM
General Description
1. General Description
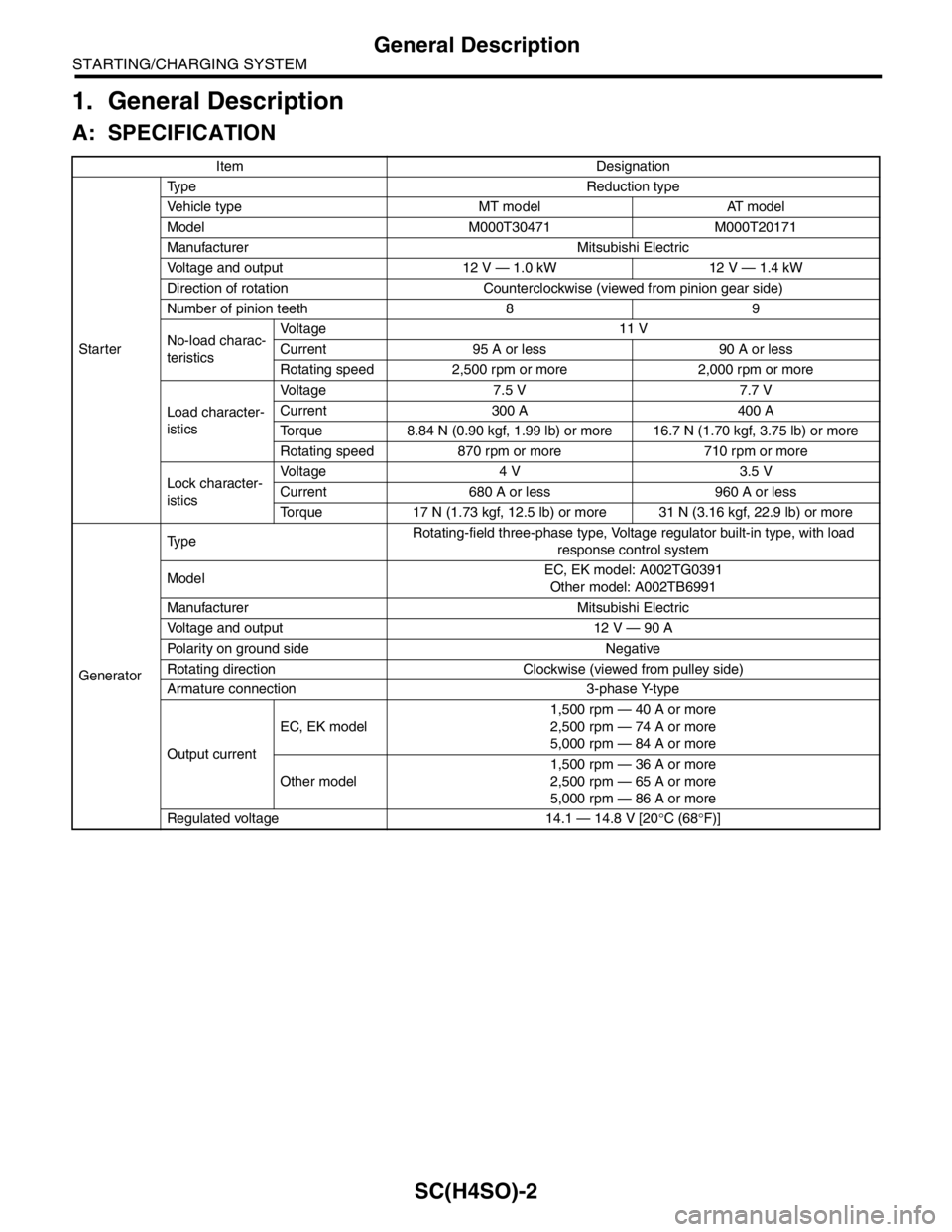
A: SPECIFICATION
Item Designation
StarterType Reduction type
Vehicle type MT model AT model
Model M000T30471 M000T20171
Manufacturer Mitsubishi Electric
Voltage and output 12 V — 1.0 kW 12 V — 1.4 kW
Direction of rotation Counterclockwise (viewed from pinion gear side)
Number of pinion teeth 8 9
No-load charac-
teristicsVo l t a g e 1 1 V
Current 95 A or less 90 A or less
Rotating speed 2,500 rpm or more 2,000 rpm or more
Load character-
isticsVoltage 7.5 V 7.7 V
Current 300 A 400 A
Torque 8.84 N (0.90 kgf, 1.99 lb) or more 16.7 N (1.70 kgf, 3.75 lb) or more
Rotating speed 870 rpm or more 710 rpm or more
Lock character-
isticsVo l t a g e 4 V 3 . 5 V
Current 680 A or less 960 A or less
Torque 17 N (1.73 kgf, 12.5 lb) or more 31 N (3.16 kgf, 22.9 lb) or more
GeneratorTy p eRotating-field three-phase type, Voltage regulator built-in type, with load
response control system
ModelEC, EK model: A002TG0391
Other model: A002TB6991
Manufacturer Mitsubishi Electric
Voltage and output 12 V — 90 A
Polarity on ground side Negative
Rotating direction Clockwise (viewed from pulley side)
Armature connection 3-phase Y-type
Output currentEC, EK model1,500 rpm — 40 A or more
2,500 rpm — 74 A or more
5,000 rpm — 84 A or more
Other model1,500 rpm — 36 A or more
2,500 rpm — 65 A or more
5,000 rpm — 86 A or more
Regulated voltage 14.1 — 14.8 V [20°C (68°F)]
Page 1086 of 2870
SC(H4SO)-11
STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEM
Starter
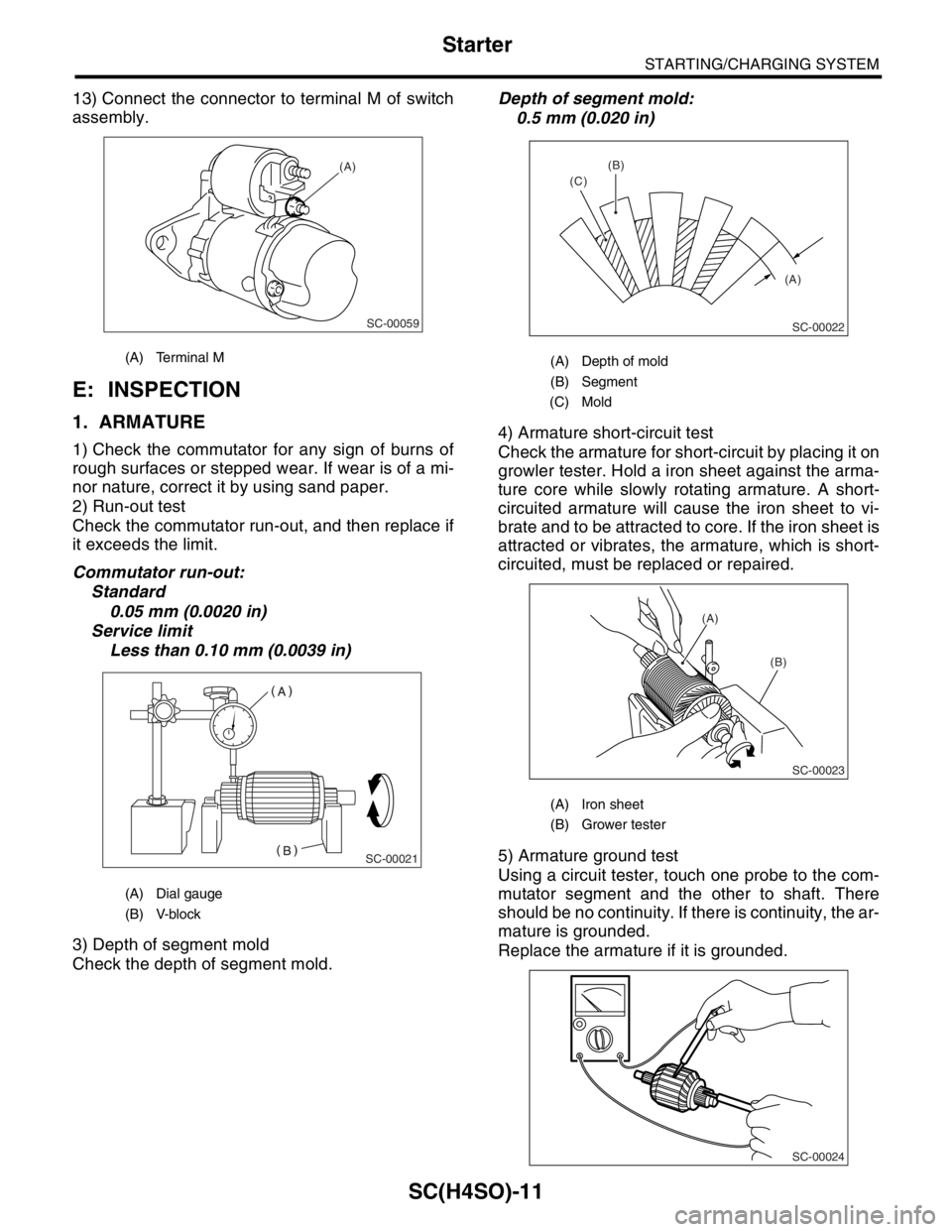
13) Connect the connector to terminal M of switch
assembly.
E: INSPECTION
1. ARMATURE
1) Check the commutator for any sign of burns of
rough surfaces or stepped wear. If wear is of a mi-
nor nature, correct it by using sand paper.
2) Run-out test
Check the commutator run-out, and then replace if
it exceeds the limit.
Commutator run-out:
Standard
0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
Service limit
Less than 0.10 mm (0.0039 in)
3) Depth of segment mold
Check the depth of segment mold.Depth of segment mold:
0.5 mm (0.020 in)
4) Armature short-circuit test
Check the armature for short-circuit by placing it on
growler tester. Hold a iron sheet against the arma-
ture core while slowly rotating armature. A short-
circuited armature will cause the iron sheet to vi-
brate and to be attracted to core. If the iron sheet is
attracted or vibrates, the armature, which is short-
circuited, must be replaced or repaired.
5) Armature ground test
Using a circuit tester, touch one probe to the com-
mutator segment and the other to shaft. There
should be no continuity. If there is continuity, the ar-
mature is grounded.
Replace the armature if it is grounded.
(A) Terminal M
(A) Dial gauge
(B) V-block
SC-00059
(A)
SC-00021
(A) Depth of mold
(B) Segment
(C) Mold
(A) Iron sheet
(B) Grower tester
(A) (B)
(C)
SC-00022
(A)
(B)
SC-00023
SC-00024
Page 1087 of 2870
SC(H4SO)-12
STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEM
Starter
2. YOKE
Make sure the pole is set in position.
3. OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
Inspect the teeth of pinion for wear and damage.
Replace if it is damaged. Rotate the pinion in direc-
tion of rotation (counterclockwise). It should rotate
smoothly. But in opposite direction, it should be
locked.
CAUTION:
Do not clean the overrunning clutch with oil to
prevent grease from flowing out.
4. BRUSH AND BRUSH HOLDER
1) Brush length
Measure the brush length, and then replace if it ex-
ceeds the service limit.
Replace if abnormal wear or cracks are noticed.
Brush length:
Standard
12.3 mm (0.484 in)
Service limit
7.0 mm (0.276 in)
2) Brush movement
Be sure the brush moves smoothly inside brush
holder.
3) Brush spring force
Measure the brush spring force with a spring scale.
If it is less than the service limit, replace the brush
holder.
Brush spring force:
Standard
15.9 — 19.5 N (1.62 — 1.99 kgf, 3.57 — 4.38
lb) (when new)
Service limit
2.5 N (0.25 kgf, 0.56 lb)
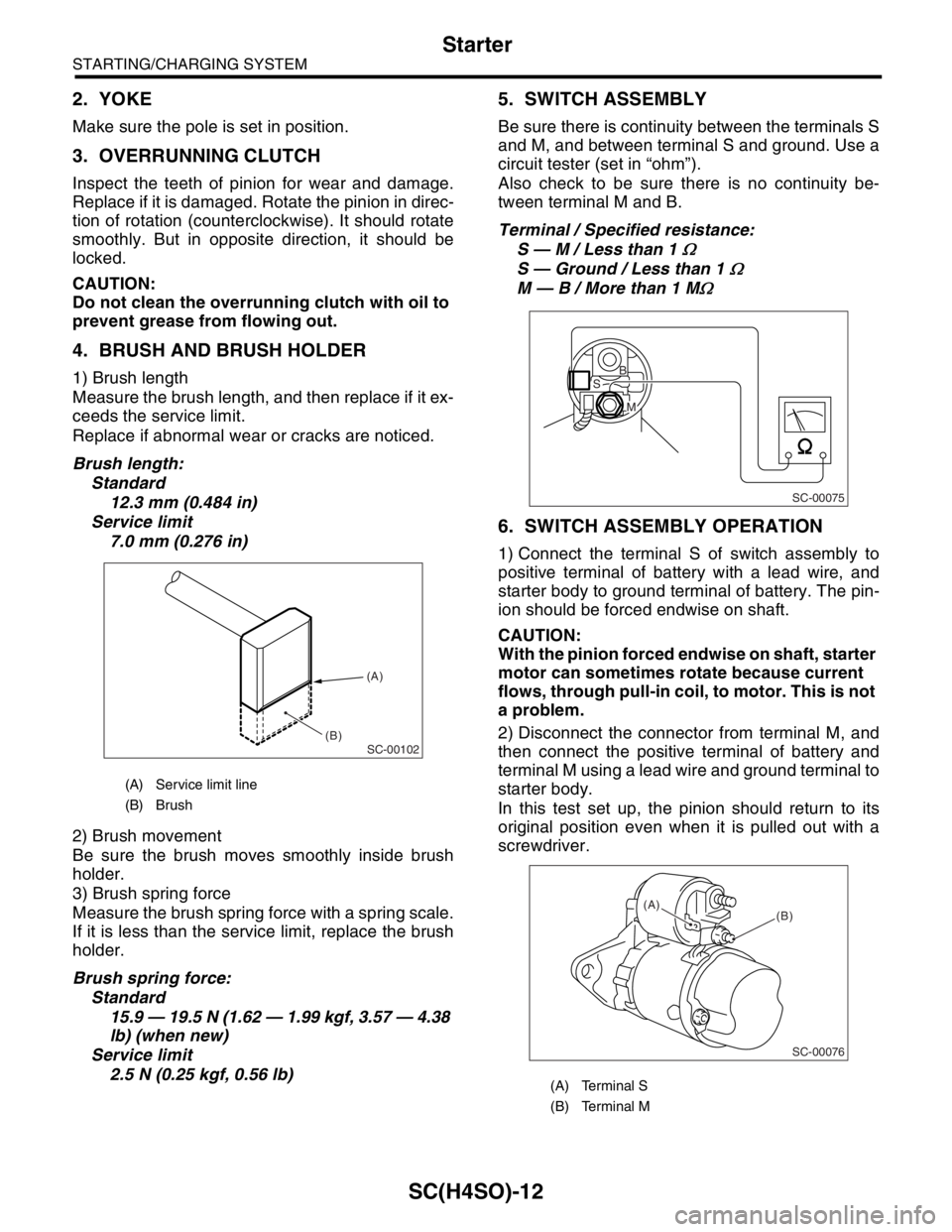
5. SWITCH ASSEMBLY
Be sure there is continuity between the terminals S
and M, and between terminal S and ground. Use a
circuit tester (set in “ohm”).
Also check to be sure there is no continuity be-
tween terminal M and B.
Terminal / Specified resistance:
S — M / Less than 1
Ω
S — Ground / Less than 1 Ω
M — B / More than 1 MΩ
6. SWITCH ASSEMBLY OPERATION
1) Connect the terminal S of switch assembly to
positive terminal of battery with a lead wire, and
starter body to ground terminal of battery. The pin-
ion should be forced endwise on shaft.
CAUTION:
With the pinion forced endwise on shaft, starter
motor can sometimes rotate because current
flows, through pull-in coil, to motor. This is not
a problem.
2) Disconnect the connector from terminal M, and
then connect the positive terminal of battery and
terminal M using a lead wire and ground terminal to
starter body.
In this test set up, the pinion should return to its
original position even when it is pulled out with a
screwdriver.
(A) Service limit line
(B) Brush
SC-00102
(A)
(B)
(A) Terminal S
(B) Terminal M
SC-00075
B
M
S
SC-00076
(B) (A)
Page 1088 of 2870
SC(H4SO)-13
STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEM
Starter
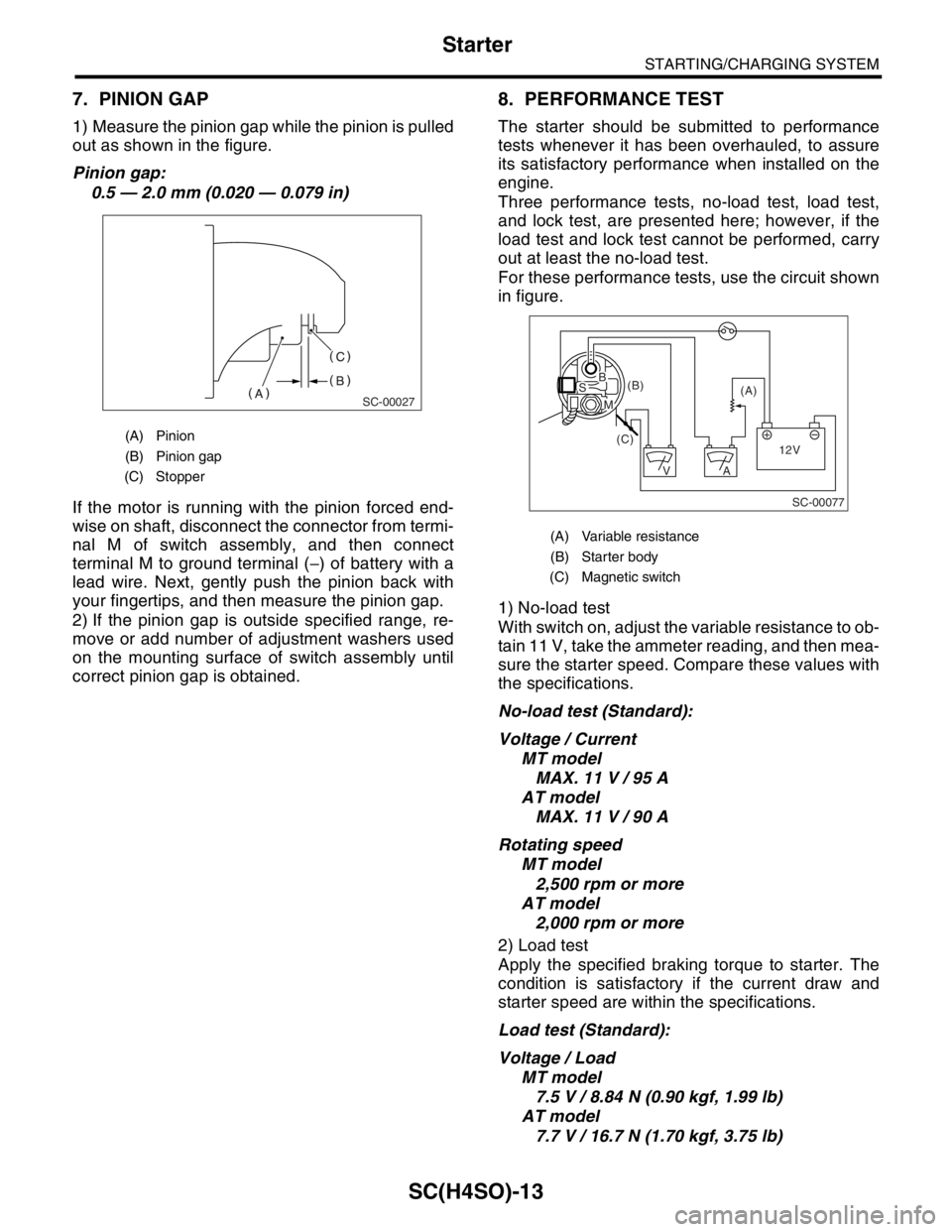
7. PINION GAP
1) Measure the pinion gap while the pinion is pulled
out as shown in the figure.
Pinion gap:
0.5 — 2.0 mm (0.020 — 0.079 in)
If the motor is running with the pinion forced end-
wise on shaft, disconnect the connector from termi-
nal M of switch assembly, and then connect
terminal M to ground terminal (−) of battery with a
lead wire. Next, gently push the pinion back with
your fingertips, and then measure the pinion gap.
2) If the pinion gap is outside specified range, re-
move or add number of adjustment washers used
on the mounting surface of switch assembly until
correct pinion gap is obtained.
8. PERFORMANCE TEST
The starter should be submitted to performance
tests whenever it has been overhauled, to assure
its satisfactory performance when installed on the
engine.
Three performance tests, no-load test, load test,
and lock test, are presented here; however, if the
load test and lock test cannot be performed, carry
out at least the no-load test.
For these performance tests, use the circuit shown
in figure.
1) No-load test
With switch on, adjust the variable resistance to ob-
tain 11 V, take the ammeter reading, and then mea-
sure the starter speed. Compare these values with
the specifications.
No-load test (Standard):
Voltage / Current
MT model
MAX. 11 V / 95 A
AT model
MAX. 11 V / 90 A
Rotating speed
MT model
2,500 rpm or more
AT model
2,000 rpm or more
2) Load test
Apply the specified braking torque to starter. The
condition is satisfactory if the current draw and
starter speed are within the specifications.
Load test (Standard):
Voltage / Load
MT model
7.5 V / 8.84 N (0.90 kgf, 1.99 lb)
AT model
7.7 V / 16.7 N (1.70 kgf, 3.75 lb)
(A) Pinion
(B) Pinion gap
(C) Stopper
SC-00027
(A) Variable resistance
(B) Starter body
(C) Magnetic switch
SC-00077
(A) (B)
(C)
12V +
AV
BS
M
Page 1089 of 2870

SC(H4SO)-14
STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEM
Starter
Current / Speed
MT model
300 A / 870 rpm or more
AT model
400 A / 710 rpm or more
3) Lock test
With the starter stalled, or not rotating, measure the
torque developed and current draw when the volt-
age is adjusted to the specified voltage.
Lock test (Standard):
Voltage / Current
MT model
4 V / 680 A or less
AT model
3.5 V / 960 A or less
Torque
MT model
17.0 N (1.73 kgf, 3.82 lb) or more
AT model
31.0 N (3.16 kgf, 6.97 lb) or more
Page 1106 of 2870
EN(H4SO)-8
ENGINE (DIAGNOSTIC)
General Description
The OBD-II diagnostics procedure is different
from the usual diagnosis procedure. When trouble-
shooting the OBD-II models, connect Subaru Se-
lect Monitor or the OBD-II general scan tool to the
vehicle.
2. ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYS-
TEM
MFI system is a system that supplies the opti-
mum air-fuel mixture to the engine for all the vari-
ous operating conditions through the use of the
latest electronic technology.
With this system fuel, which is pressurized at a con-
stant pressure, is injected into the intake air pas-
sage of the cylinder head. The injection quantity of
fuel is controlled by an intermittent injection system
where the electro-magnetic injection valve (fuel in-
jector) opens only for a short period of time, de-
pending on the quantity of air required for one cycle
of operation. In actual operation, the injection quan-
tity is determined by the duration of an electric sig-
nal applied to the fuel injector and this permits
simple, yet highly precise metering of the fuel.
Further, all the operating conditions of the engine
are converted into electric signals, and this results
in additional features of the system, such as large
improved adaptability, easier addition of compen-
sating element, etc.The MFI system also has the following features:
Reduced emission of harmful exhaust gases.
Reduced in fuel consumption.
Increased engine output.
Superior acceleration and deceleration.
Excellent engine start and warm-up perfor-
mance by the correction of engine coolant tem-
perature and intake air temperature.3. AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION AND
ELECTRONIC-HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYS-
TEM
The electronic-hydraulic control system consists of
various sensors and switches, TCM and the hy-
draulic controller including solenoid valves. The
system controls the transmission body including
shift control, lock-up control, overrunning clutch
control, line pressure control and shift timing con-
trol. It also controls the AWD transfer clutch. In oth-
er words, the system detects various operating
conditions from various input signals and sends
output signals to shift solenoids 1, 2 and low clutch
timing solenoid and 2-4 brake timing solenoid, line
pressure duty solenoid, lock-up duty solenoid,
transfer duty solenoid and 2-4 brake duty solenoid
(a total of eight solenoids).
D: PREPARATION TOOL
ILLUSTRATION TOOL NUMBER DESCRIPTION REMARKS
24082AA230
(Newly adopted tool)CARTRIDGE Troubleshooting for electrical system.
22771AA030 SUBARU SELECT
MONITOR KITTroubleshooting for electrical system.
English: 22771AA030 (Without printer)
German: 22771AA070 (Without printer)
French: 22771AA080 (Without printer)
Spanish: 22771AA090 (Without printer)
ST24082AA230
ST22771AA030
Page 1118 of 2870
EN(H4SO)-20
ENGINE (DIAGNOSTIC)
Electrical Component Location
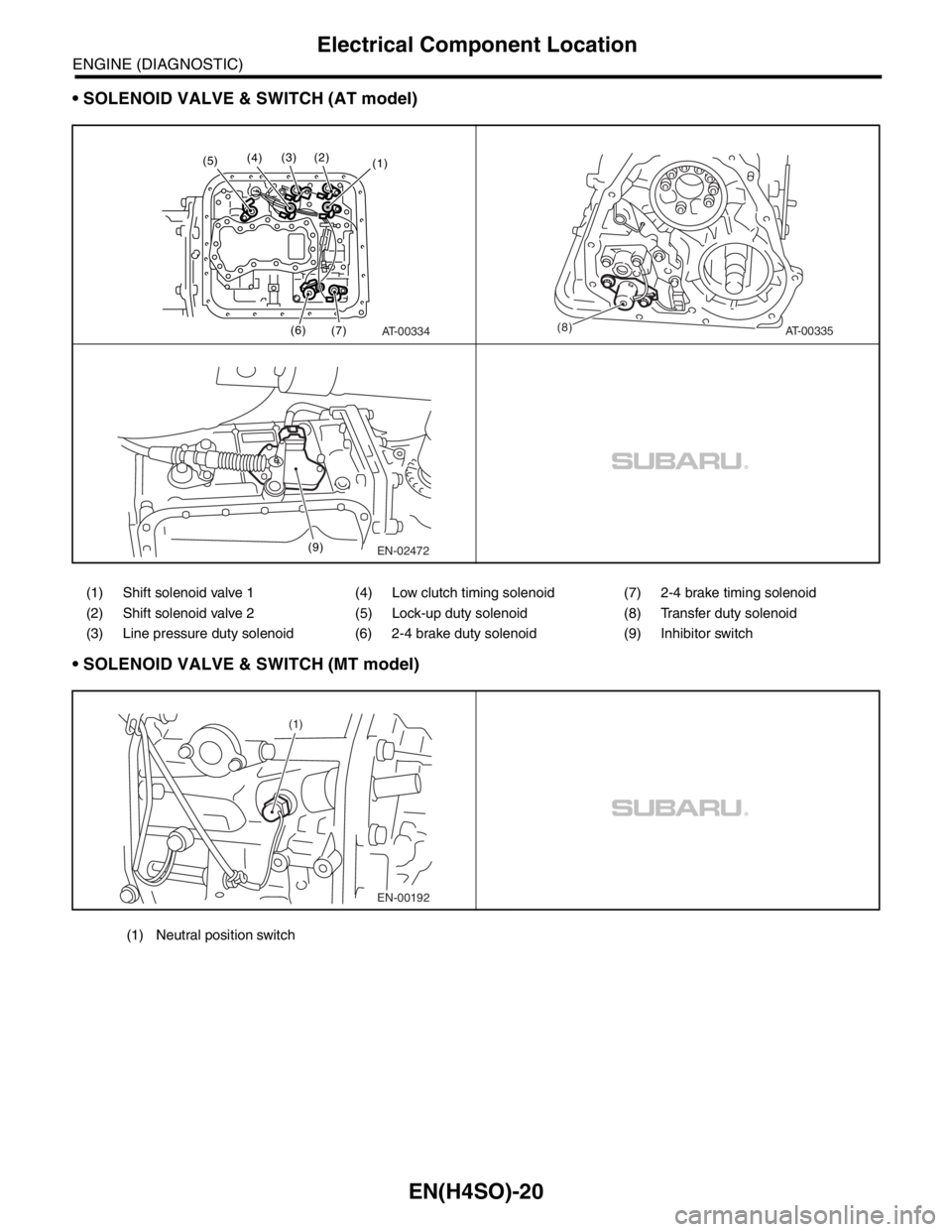
SOLENOID VALVE & SWITCH (AT model)
SOLENOID VALVE & SWITCH (MT model)
(1) Shift solenoid valve 1 (4) Low clutch timing solenoid (7) 2-4 brake timing solenoid
(2) Shift solenoid valve 2 (5) Lock-up duty solenoid (8) Transfer duty solenoid
(3) Line pressure duty solenoid (6) 2-4 brake duty solenoid (9) Inhibitor switch
AT-00334
(1)
(6)
(7) (2)(3)(4)(5)
AT-00335(8)
EN-02472 (9)
EN-00192 (1)
(1) Neutral position switch
Page 1133 of 2870
![SUBARU FORESTER 2004 Service Repair Manual EN(H4SO)-35
ENGINE (DIAGNOSTIC)
Subaru Select Monitor
8. READ CURRENT DATA FOR AT
1) On the «Main Menu» display screen, select the {Each System Check} and press the [YES] key.
2) On the «System Sel SUBARU FORESTER 2004 Service Repair Manual EN(H4SO)-35
ENGINE (DIAGNOSTIC)
Subaru Select Monitor
8. READ CURRENT DATA FOR AT
1) On the «Main Menu» display screen, select the {Each System Check} and press the [YES] key.
2) On the «System Sel](/img/17/57426/w960_57426-1132.png)
EN(H4SO)-35
ENGINE (DIAGNOSTIC)
Subaru Select Monitor
8. READ CURRENT DATA FOR AT
1) On the «Main Menu» display screen, select the {Each System Check} and press the [YES] key.
2) On the «System Selection Menu» display screen, select the {Transmission} and press the [YES] key.
3) Press the [YES] key after the information of transmission type is displayed.
4) On the «Transmission Diagnosis» display screen, select the {Current Data Display & Save} and press the
[YES] key.
5) On the «Transmission Diagnosis» display screen, select the {Data Display} and press the [YES] key.
6) Using the scroll key, scroll the display screen up or down until the desired data is shown.
A list of the support data is shown in the following table.
Description Display Unit of measure
Battery voltage Battery Voltage V
Rear vehicle speed sensor signal Rear Wheel Speed km/h or MPH
Front vehicle speed sensor signal Front Wheel Speed km/h or MPH
Engine speed signal Engine speed rpm
ATF temperature signal ATF Temp.°C or °F
Throttle position sensor Throttle Sensor Voltage V
Gear Position Gear position —
Line pressure control duty ratio Line pressure duty %
Lock up clutch control duty ratio L/U Duty %
Transfer clutch control duty ratio AWD duty %
Throttle position sensor power supply Throttle sensor power supply V
Turbine revolution signal Turbine Revolution Speed rpm
2-4 Brake timing pressure control duty ratio 2-4 B Pressure Duty %
Intake manifold pressure sensor voltage Mani. Relative Voltage V
FWD switch signal FWD SW ON or OFF
Kick down switch signal Kick Down Switch ON or OFF
Stop light switch signal Stop Light SW ON or OFF
Anti lock brake system signal ABS signal ON or OFF
Cruise control system signal Cruise Control Signal ON or OFF
Neutral/Parking range signal N/P range ON or OFF
Reverse range signal R Range ON or OFF
Drive range signal D Range ON or OFF
3rd range signal 3rd Range Signal ON or OFF
2nd range signal 2nd Range Signal ON or OFF
1st range signal 1st Range Signal ON or OFF
Shift control solenoid A Shift Solenoid #1 ON or OFF
Shift control solenoid B Shift Solenoid #2 ON or OFF
Torque control output signal #1 Torque control output signal 1 ON or OFF
Torque control output signal #2 Torque control output signal 2 ON or OFF
Torque control cut signal Torque Control Cut Sig ON or OFF
2-4 brake timing control solenoid valve 2-4B Timing Solenoid ON or OFF
Low clutch timing control solenoid valve L/C timing solenoid ON or OFF
Automatic transmission diagnosis light output signal Diagnosis Lamp ON or OFF