DODGE NEON 1999 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 221 of 1200

²Fuel pump fuse (20 Amp)
²Interior lamps fuse (10 Amp)
(6) If there is any reading with fuses removed
there is a current draw or short circuit in the wiring.
Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams. If OK go to
Step 7.
(7) Install interior lamp fuse. After installing fuse,
the current can reach 250 milliamperes. After time-out the reading should not exceed 8 milliamperes. If
NOT OK go to Step 8. If OK go to Step 9.
²Ignition key lamp system
²Radio
²Remote keyless entry module, if equipped
(8) Disconnect radio and ignition switch key lamp
one component at time, to see if any component is at
fault. If the high reading is not eliminated there is a
short circuit in the wiring. Refer to Group 8W, Wir-
ing Diagrams.
CAUTION: Always disconnect the meter before
opening a door.
(9) Remove interior lamps fuse and install the fuel
pump fuse. The reading should be between 1-3 milli-
amperes. If reading is higher than 3 milliamperes:
(a) Disconnect Powertrain Control Module.
(b) If reading drops to zero, replace Powertrain
Control Module.
(c) If reading remains the same there is a cur-
rent draw or short circuit in the A14 circuit. Refer
to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
BATTERY DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
STEPS POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
VISUAL INSPECTION
Check for possible damage to
battery and clean battery.(1) Loose battery post, Cracked
battery cover or case, Leaks or Any
other physical
(2) Battery OK.(1) Replace Battery
(2) Check state of charge. Refer to
Test Indicator.
TEST INDICATOR
Check Charge Eye Color(1) GREEN
(2) BLACK
(3) CLEAR(1) Battery is charged. Perform
Battery 0pen Circuit Voltage Test
(2) Perform Battery Charging
procedure.
(3) Replace Battery.
BATTERY OPEN CIRCUIT
VOLTAGE TEST(1) Battery is above 12.40 Volts
(2) Battery is below 12.40 Volts.(1) Perform the Battery Load Test.
(2) Perform Battery Charging
procedure.
BATTERY CHARGING (1) Battery accepted Charge.
(2) Battery will not accept charge(1) Ensure that the indicator eye is
GREEN and perform Battery 0pen
Circuit Voltage Test
(2) Perform Charging a Completely
Discharged Battery.
BATTERY LOAD TEST (1) Acceptable minimum voltage.
(2) Unacceptable minimum voltage(1) Battery is OK to put in use,
perform Battery Ignition Off Draw
Test.
(2) Replace Battery and perform
Battery Ignition Off Draw Test.
CHARGING A COMPLETELY
DISCHARGED BATTERY(1) Battery accepted charge.
(2) Battery will not accept charge.(1) Ensure that the indicator eye is
GREEN and perform Battery 0pen
Circuit Voltage Test.
(2) Replace Battery.
IGNITION OFF DRAW TEST (1) IOD is 5-25 Milliamperes.
(2) IOD Exceeds 25 Milliamperes.(1) Vehicle is normal.
(2) Eliminate excess IOD draw.
Fig. 4 Disconnect Battery Negative Cable
8A - 4 BATTERYPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 222 of 1200
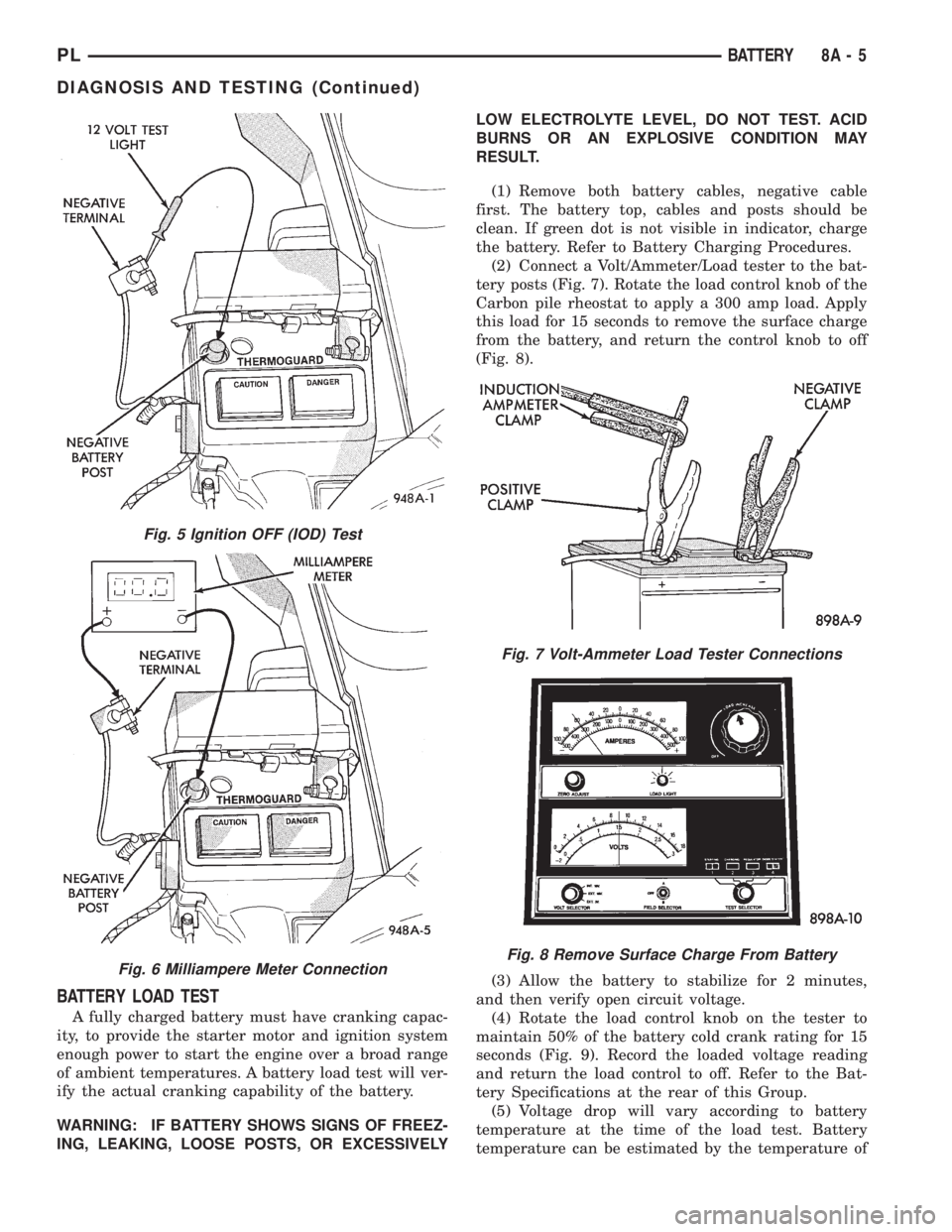
BATTERY LOAD TEST
A fully charged battery must have cranking capac-
ity, to provide the starter motor and ignition system
enough power to start the engine over a broad range
of ambient temperatures. A battery load test will ver-
ify the actual cranking capability of the battery.
WARNING: IF BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF FREEZ-
ING, LEAKING, LOOSE POSTS, OR EXCESSIVELYLOW ELECTROLYTE LEVEL, DO NOT TEST. ACID
BURNS OR AN EXPLOSIVE CONDITION MAY
RESULT.
(1) Remove both battery cables, negative cable
first. The battery top, cables and posts should be
clean. If green dot is not visible in indicator, charge
the battery. Refer to Battery Charging Procedures.
(2) Connect a Volt/Ammeter/Load tester to the bat-
tery posts (Fig. 7). Rotate the load control knob of the
Carbon pile rheostat to apply a 300 amp load. Apply
this load for 15 seconds to remove the surface charge
from the battery, and return the control knob to off
(Fig. 8).
(3) Allow the battery to stabilize for 2 minutes,
and then verify open circuit voltage.
(4) Rotate the load control knob on the tester to
maintain 50% of the battery cold crank rating for 15
seconds (Fig. 9). Record the loaded voltage reading
and return the load control to off. Refer to the Bat-
tery Specifications at the rear of this Group.
(5) Voltage drop will vary according to battery
temperature at the time of the load test. Battery
temperature can be estimated by the temperature of
Fig. 5 Ignition OFF (IOD) Test
Fig. 6 Milliampere Meter Connection
Fig. 7 Volt-Ammeter Load Tester Connections
Fig. 8 Remove Surface Charge From Battery
PLBATTERY 8A - 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 223 of 1200

exposure over the preceding several hours. If the bat-
tery has been charged or boosted a few minutes prior
to the test, the battery would be slightly warmer.
Refer to Battery Load Test Temperatures Table for
proper voltage/temperature reading:
(6) If battery passes load test, it is in good condi-
tion and further tests are not necessary. If it fails
load test, it should be replaced.
BATTERY OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TEST
An open circuit voltage no load test shows the
state of charge of a battery and whether it is ready
for a load test at 50 percent of the battery's cold
crank rating. Refer to Battery Load Test. If a battery
has open circuit voltage reading of 12.4 volts or
greater, and will not pass the load test, replace the
battery because it is defective. To test open circuit
voltage, perform the following operation.
(1) Remove both battery cables, negative cable
first. Battery top, cables and posts should be clean. If
green dot is not visible in indicator, charge the bat-
tery. Refer to Battery Charging Procedures.
(2) Connect a Volt/Ammeter/Load tester to the bat-
tery posts (Fig. 7). Rotate the load control knob of theCarbon pile rheostat to apply a 300 amp load. Apply
this load for 15 seconds to remove the surface charge
from the battery, and return the control knob to off
(Fig. 8).
(3) Allow the battery to stabilize for 2 minutes,
and then verify the open circuit voltage (Fig. 10).
(4) This voltage reading will approximate the state
of charge of the battery. It will not reveal battery
cranking capacity. Refer to Battery Open Circuit
Voltage Table.
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
For Battery Temperature Sensor refer to Group 8C
Generator.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
BATTERY CHARGING
A battery is considered fully charged when it will
meet all the following requirements.
²It has an open circuit voltage charge of at least
12.4 volts.
²It passes the 15 second load test. Refer to Bat-
tery Load Test.
²The built in test indicator dot is GREEN (Fig.
1).
NOTE: The battery cannot be refilled with water, it
must be replaced.
Fig. 9 Load 50% Cold Crank Rating
BATTERY LOAD TEST TEMPERATURES
Minimum
VoltageTemperature
ÉF ÉC
9.6 volts 70É and above 21É and above
9.5 volts 60É 16É
9.4 volts 50É 10É
9.3 volts 40É 4É
9.1 volts 30É -1É
8.9 volts 20É -7É
8.7 volts 10É -12É
8.5 volts 0É -18É
Fig. 10 Testing Open Circuit Voltage
BATTERY OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE
Open Circuit Volts Charge Percentage
11.7 volts or less 0%
12.0 volts 25%
12.2 volts 50%
12.4 volts 75%
12.6 volts or more 100%
8A - 6 BATTERYPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 224 of 1200

WARNING: DO NOT CHARGE A BATTERY THAT
HAS EXCESSIVELY LOW ELECTROLYTE LEVEL.
BATTERY MAY SPARK INTERNALLY AND
EXPLODE. EXPLOSIVE GASES FORM OVER THE
BATTERY. DO NOT SMOKE, USE FLAME, OR CRE-
ATE SPARKS NEAR BATTERY. DO NOT ASSIST
BOOST OR CHARGE A FROZEN BATTERY. BAT-
TERY CASING MAY FRACTURE. BATTERY ACID IS
POISON, AND MAY CAUSE SEVERE BURNS. BAT-
TERIES CONTAIN SULFURIC ACID. AVOID CON-
TACT WITH SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING. IN THE
EVENT OF CONTACT, FLUSH WITH WATER AND
CALL PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. KEEP OUT OF
REACH OF CHILDREN.
CAUTION: Disconnect the battery NEGATIVE cable
first, before charging battery to avoid damage to
electrical systems. Lift the red battery boot cover
from the positive cable clamp. Do not exceed 16.0
volts while charging battery. Refer to the instruc-
tions supplied with charging equipment
Battery electrolyte may bubble inside of battery
case while being charged properly. If the electrolyte
boils violently, or is discharged from the vent holes
while charging, immediately reduce charging rate or
turn off charger. Evaluate battery condition. Battery
damage may occur if charging is excessive.
Some battery chargers are equipped with polarity
sensing devices to protect the charger or battery from
being damaged if improperly connected. If the bat-
tery state of charge is too low for the polarity sensor
to detect, the sensor must be bypassed for charger to
operate. Refer to operating instructions provided
with battery charger being used.
CAUTION: Charge battery until test indicator
appears green. Do not overcharge.
It may be necessary to jiggle the battery or vehicle
to bring the green dot in the test indicator into view.
After the battery has been charged to 12.4 volts or
greater, perform a load test to determine cranking
capacity. Refer to Battery Load Test in this Group. If
the battery passes the load test, the battery is OK to
use. If battery will not pass the load test, it must be
replaced. Properly clean and inspect battery hold
downs, tray, terminals, cables, posts, and top before
completing service.
CHARGING COMPLETELY DISCHARGED BATTERY
The following procedure should be used to recharge
a completely discharged battery. Unless procedure is
properly followed, a good battery may be needlessly
replaced. Refer to Battery Charging Rate Table for
proper charging time.(1) Measure the voltage at battery posts with a
voltmeter accurate to 1/10 volt (Fig. 11). If below 10
volts, charge current will be low, and it could take
some time before it accepts a current in excess of a
few milliamperes. Such low current may not be
detectable on amp meters built into many chargers.
(2) Connect charger leads. Some chargers feature
polarity protection circuitry that prevents operation
unless charger is connected to battery posts correctly.
A completely discharged battery may not have
enough voltage to activate this circuitry. This may
happen even though the leads are connected properly.
(3) Battery chargers vary in the amount of voltage
and current they provide. For the time required for
the battery to accept measurable charger current at
various voltages, refer to the Battery Charging Rate
table. If charge current is still not measurable after
charging times, the battery should be replaced. If
charge current is measurable during charging time,
the battery may be good, and charging should be
completed in the normal manner.
VISUAL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not allow baking soda solution to
enter vent holes, as damage to battery can result.
(1) Clean top of battery with a solution of warm
water and baking soda.
(2) Apply soda solution with a bristle brush and
allow to soak until acid deposits loosen (Fig. 12).
BATTERY CHARGING RATE
Voltage Hours
16.0 volts maximum up to 4 hours
14.0 to 15.9 volts up to 8 hours
13.9 volts or less up to 16 hours
Fig. 11 Voltmeter Accurate to 1/10 Volt (Connected)
PLBATTERY 8A - 7
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 225 of 1200
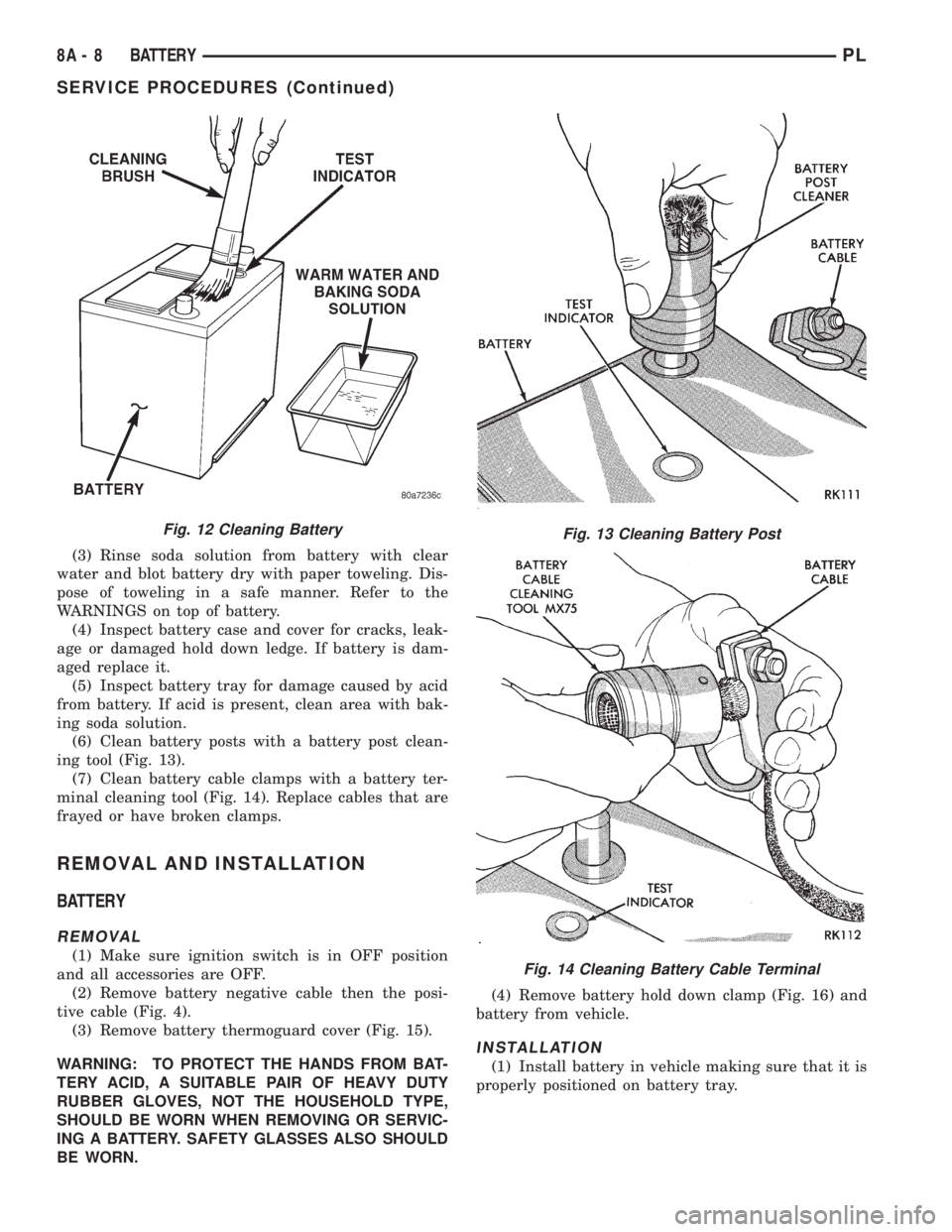
(3) Rinse soda solution from battery with clear
water and blot battery dry with paper toweling. Dis-
pose of toweling in a safe manner. Refer to the
WARNINGS on top of battery.
(4) Inspect battery case and cover for cracks, leak-
age or damaged hold down ledge. If battery is dam-
aged replace it.
(5) Inspect battery tray for damage caused by acid
from battery. If acid is present, clean area with bak-
ing soda solution.
(6) Clean battery posts with a battery post clean-
ing tool (Fig. 13).
(7) Clean battery cable clamps with a battery ter-
minal cleaning tool (Fig. 14). Replace cables that are
frayed or have broken clamps.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
BATTERY
REMOVAL
(1) Make sure ignition switch is in OFF position
and all accessories are OFF.
(2) Remove battery negative cable then the posi-
tive cable (Fig. 4).
(3) Remove battery thermoguard cover (Fig. 15).
WARNING: TO PROTECT THE HANDS FROM BAT-
TERY ACID, A SUITABLE PAIR OF HEAVY DUTY
RUBBER GLOVES, NOT THE HOUSEHOLD TYPE,
SHOULD BE WORN WHEN REMOVING OR SERVIC-
ING A BATTERY. SAFETY GLASSES ALSO SHOULD
BE WORN.(4) Remove battery hold down clamp (Fig. 16) and
battery from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install battery in vehicle making sure that it is
properly positioned on battery tray.
Fig. 12 Cleaning BatteryFig. 13 Cleaning Battery Post
Fig. 14 Cleaning Battery Cable Terminal
8A - 8 BATTERYPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 226 of 1200
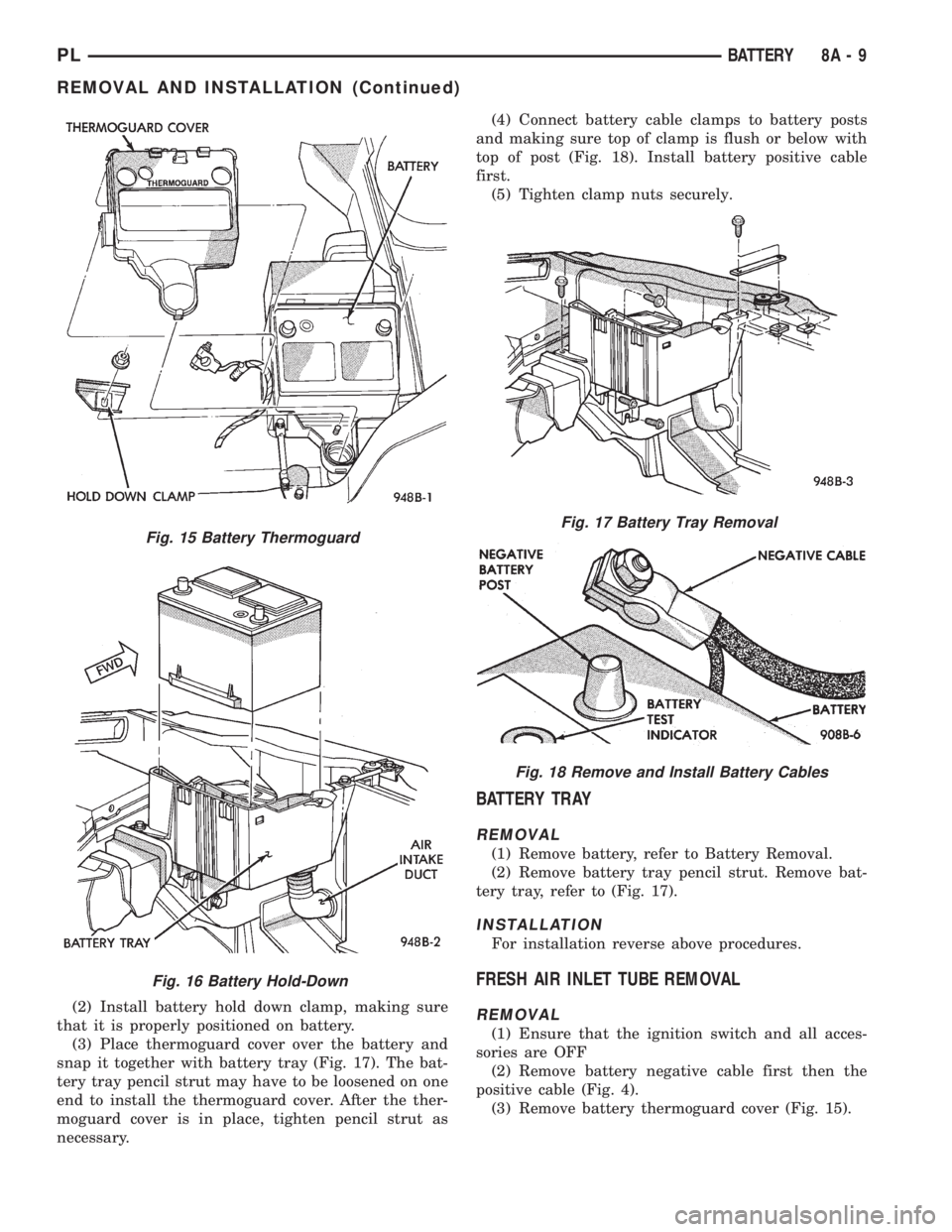
(2) Install battery hold down clamp, making sure
that it is properly positioned on battery.
(3) Place thermoguard cover over the battery and
snap it together with battery tray (Fig. 17). The bat-
tery tray pencil strut may have to be loosened on one
end to install the thermoguard cover. After the ther-
moguard cover is in place, tighten pencil strut as
necessary.(4) Connect battery cable clamps to battery posts
and making sure top of clamp is flush or below with
top of post (Fig. 18). Install battery positive cable
first.
(5) Tighten clamp nuts securely.
BATTERY TRAY
REMOVAL
(1) Remove battery, refer to Battery Removal.
(2) Remove battery tray pencil strut. Remove bat-
tery tray, refer to (Fig. 17).
INSTALLATION
For installation reverse above procedures.
FRESH AIR INLET TUBE REMOVAL
REMOVAL
(1) Ensure that the ignition switch and all acces-
sories are OFF
(2) Remove battery negative cable first then the
positive cable (Fig. 4).
(3) Remove battery thermoguard cover (Fig. 15).
Fig. 15 Battery Thermoguard
Fig. 16 Battery Hold-Down
Fig. 17 Battery Tray Removal
Fig. 18 Remove and Install Battery Cables
PLBATTERY 8A - 9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 227 of 1200

WARNING: TO PROTECT THE HANDS FROM BAT-
TERY ACID, A SUITABLE PAIR OF HEAVY DUTY
RUBBER GLOVES, NOT THE HOUSEHOLD TYPE,
SHOULD BE WORN WHEN REMOVING OR SERVIC-
ING A BATTERY. SAFETY GLASSES ALSO SHOULD
BE WORN.
(4) Squeeze the sides of the tube at the pull strap
lock tabs and push down through the hole in the bat-
tery tray (Fig. 19). DO NOT push directly down on
the pull strap itself.
(5) Remove the tube from the radiator closure
panel by squeezing the lock tabs and pushing from
the front side (Fig. 16).INSTALLATION
For installation reverse above procedures. Ensure
that the lock tabs are properly seated in the radiator
panel and to the bottom of battery tray (Fig. 19).
Ensure that the tube opening is properly aligned
with hole before pulling on strap.
SPECIFICATIONS
BATTERY SPECIFICATIONS
COLD CRANK RATING
The current battery can deliver for 30 seconds and
maintain a terminal voltage of 7.2 volts or greater at
±18É C (0É F).
RESERVE CAPACITY RATING
The length of time a battery can deliver 25 amps
and maintain a minimum terminal voltage of 10.5
volts at 27ÉC (80ÉF).
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Battery Hold Down Bolt
Clamp Bolt.................9N´m(75in.lbs.)
Fig. 19 Air Inlet Tube Pull Strap
Load Test Cold
CrankingReserve
(Amps) Rating @
-18ÉC (0ÉF)Capacity
225 Amp 450 Amp 85 Minutes
8A - 10 BATTERYPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 228 of 1200
STARTING
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
BOSCH STARTER........................ 1
INTRODUCTION......................... 1
SUPPLY CIRCUIT AND CONTROL CIRCUIT.... 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
FEED CIRCUIT RESISTANCE TEST........... 2
FEED CIRCUIT TEST...................... 2
STARTER CONTROL CIRCUIT.............. 1STARTING SYSTEM TEST................. 4
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SAFETY SWITCHES...................... 6
STARTER RELAY........................ 7
STARTER .............................. 6
SPECIFICATIONS
STARTER .............................. 7
TORQUE............................... 7
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
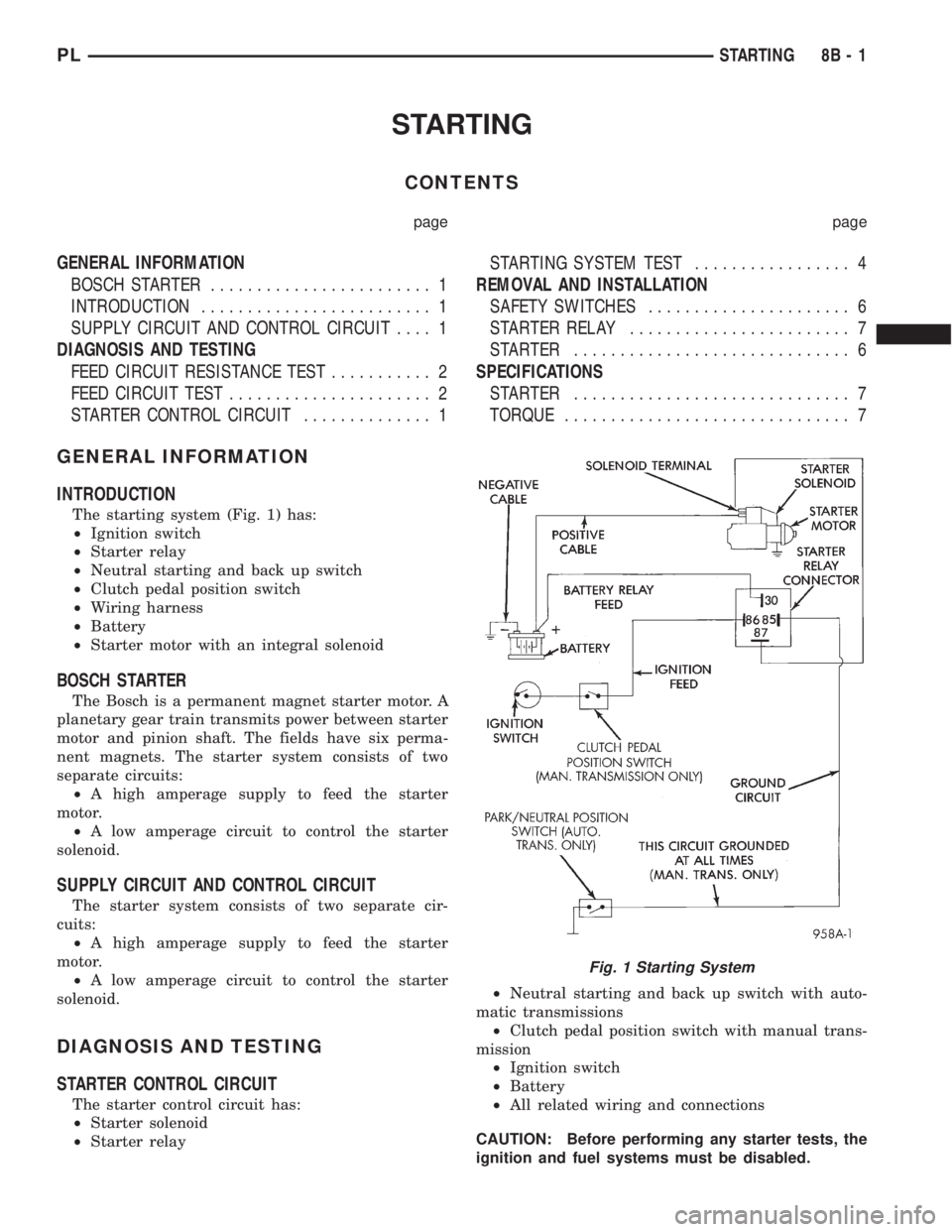
The starting system (Fig. 1) has:
²Ignition switch
²Starter relay
²Neutral starting and back up switch
²Clutch pedal position switch
²Wiring harness
²Battery
²Starter motor with an integral solenoid
BOSCH STARTER
The Bosch is a permanent magnet starter motor. A
planetary gear train transmits power between starter
motor and pinion shaft. The fields have six perma-
nent magnets. The starter system consists of two
separate circuits:
²A high amperage supply to feed the starter
motor.
²A low amperage circuit to control the starter
solenoid.
SUPPLY CIRCUIT AND CONTROL CIRCUIT
The starter system consists of two separate cir-
cuits:
²A high amperage supply to feed the starter
motor.
²A low amperage circuit to control the starter
solenoid.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
STARTER CONTROL CIRCUIT
The starter control circuit has:
²Starter solenoid
²Starter relay²Neutral starting and back up switch with auto-
matic transmissions
²Clutch pedal position switch with manual trans-
mission
²Ignition switch
²Battery
²All related wiring and connections
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition and fuel systems must be disabled.
Fig. 1 Starting System
PLSTARTING 8B - 1
Page 229 of 1200

To disable the ignition and fuel systems, disconnect
the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The ASD relay
is located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay location.
FEED CIRCUIT RESISTANCE TEST
Before proceeding with this operation, review Diag-
nostic Preparation and Starter Feed Circuit Tests.
The following operation will require a voltmeter,
accurate to 1/10 of a volt.
CAUTION: Ignition system also must be disabled
to prevent engine start while performing the follow-
ing tests.
(1) To disable the ignition and fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location.
(2) With all wiring harnesses and components
properly connected, perform the following:
(a) Connect the negative lead of the voltmeter to
the battery negative post, and positive lead to the
battery negative cable clamp (Fig. 2). Rotate and
hold the ignition switch in the START position.
Observe the voltmeter. If voltage is detected, cor-
rect poor contact between cable clamp and post.
(b) Connect positive lead of the voltmeter to the
battery positive post, and negative lead to the bat-
tery positive cable clamp (Fig. 2). Rotate and hold
the ignition switch key in the START position.
Observe the voltmeter. If voltage is detected, cor-
rect poor contact between the cable clamp and
post.
(c) Connect negative lead of voltmeter to battery
negative terminal, and positive lead to engine
block near the battery cable attaching point (Fig.
3). Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the
START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt,
correct poor contact at ground cable attaching
point. If voltage reading is still above 0.2 volt after
correcting poor contacts, replace ground cable.
(3) Connect positive voltmeter lead to the starter
motor housing and the negative lead to the battery
negative terminal (Fig. 4). Hold the ignition switch
key in the START position. If voltage reads above 0.2
volt, correct poor starter to engine ground.
(a) Connect the positive voltmeter lead to the
battery positive terminal, and negative lead to bat-
tery cable terminal on starter solenoid (Fig. 5).
Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the START
position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct
poor contact at battery cable to solenoid connec-
tion. If reading is still above 0.2 volt after correct-
ing poor contacts, replace battery positive cable.(b) If resistance tests do not detect feed circuit
failures, replace the starter motor.
FEED CIRCUIT TEST
The following procedure will require a suitable
volt-ampere tester (Fig. 6).
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition and fuel systems must be disabled.
Fig. 2 Test Battery Connection Resistance
Fig. 3 Test Ground Circuit Resistance
8B - 2 STARTINGPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 230 of 1200

(1) Connect a volt-ampere tester to the battery ter-
minals (Fig. 7). Refer to the operating instructions
provided with the tester being used.
(2) To disable the ignition and fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location. The 2.5L Diesel Engine, to disable the
engine from starting, disconnect wire connector from
the Fuel Solenoid.
(3) Verify that all lights and accessories are OFF,
and the transmission shift selector is in the PARKposition or with the clutch pedal depressed and SET
parking brake.
CAUTION: Do not overheat the starter motor or
draw the battery voltage below 9.6 volts during
cranking operations.
(4) Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the
START position. Observe the volt-ampere tester (Fig.
6).
²If voltage reads above 9.6 volts, and amperage
draw reads above 280 amps or the Diesel engine
above 450 amps, check for engine seizing or faulty
starter.
²If voltage reads 12.4 volts or greater and amper-
age reads 0 to 10 amps, check for corroded cables
and/or bad connections.
²Voltage below 9.6 volts and amperage draw
above 300 amps or Diesel engine above 500 amps,
the problem is the starter. Replace the starter refer
to starter removal.
(5) After the starting system problems have been
corrected, verify the battery state-of-charge and
Fig. 6 Volt Ampere Tester
Fig. 7 Volt-Ampere Tester Connections
Fig. 4 Test Starter Motor Ground
Fig. 5 Test Battery Positive Cable Resistance
PLSTARTING 8B - 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)