LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 151 of 1672

ENGINE - TD5
12-1-12 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Description
General
The Td5 diesel engine is a 2.5 litre, 5 cylinder, in-line direct injection unit having 2 valves per cylinder, operated by a
single overhead camshaft. The engine emissions, on pre EU3 models, comply with ECD2 (European Commission
Directive) and on EU3 models, comply with ECD3 legislative requirements. Both models employ electronic engine
management control, positive crankcase ventilation and exhaust gas recirculation to limit the emission of pollutants.
The unit is water cooled and turbo-charged and is controlled by an electronic engine management system.
The engine is a monobloc cast iron construction with an aluminium stiffening plate fitted to the bottom of the cylinder
block to improve lower structure rigidity. The cylinder head and sump are cast aluminium. An acoustic cover is fitted
over the upper engine to reduce engine generated noise.
The engine utilises the following features:
lElectronic Unit Injectors (EUI's) controlled by an Engine Management System for precise fuel delivery under
all prevailing operating conditions.
lTurbocharging which delivers compressed air to the combustion chambers via an intercooler for improved
power output.
lFuel Cooler
lOil Cooler
lCentrifuge Oil Filter
lHydraulic Lash Adjusters with independent finger followers
Cylinder block components
The cylinder block components are described below:
Cylinder Block
The cylinders and crankcase are contained in a single cast iron construction. The cylinders are direct bored and
plateau honed with lubrication oil supplied via lubrication jets for piston and gudgeon pin lubrication and cooling. It is
not possible to rebore the cylinder block if the cylinders become worn or damaged. Three metal core plugs are fitted
to the three centre cylinders on the right hand side of the cylinder block.
Lubrication oil is distributed throughout the block via the main oil gallery to critical moving parts through channels
bored in the block which divert oil to the main and big-end bearings via oil holes machined into the crankshaft. Oil is
also supplied from the cylinder block main gallery to the five lubrication jets which cool and lubricate the piston and
gudgeon pins. Plugs are used to seal both ends of the main oil gallery at front and rear of the engine block. An oil
cooler is fitted to the LH side of the engine block; ports in the oil cooler assembly mate with ports in the cylinder block
to facilitate coolant flow. Oil is diverted through the oil cooler, centrifuge filter and full-flow filter before supplying the
main oil gallery. A tapping in the oil filter housing provides a lubrication source for the turbocharger bearings and an
oil pressure switch is included in a tapping in the oil cooler housing which determines whether sufficient oil pressure
is available to provide engine lubrication and cooling.
Cylinder cooling is achieved by water circulating through chambers in the engine block casting. A threaded coolant
jacket plug is located at the front RH side of the cylinder block.
Cast mounting brackets are bolted to both sides of the engine block for mounting the engine to the chassis on the LH
and RH hydramount studs.
The gearbox bolts directly to the engine block; a gearbox shim plate is located between the adjoining faces of the
gearbox and the flywheel side of the engine block and is fixed to the rear of the engine block by two bolts. Two hollow
metal dowels locate the rear of the cylinder block to the gearbox shim plate. The gearbox casing provides the
mounting for the starter motor.
A port is included at the rear left hand side of the cylinder block which connects to the turbocharger oil drain pipe to
return lubrication oil to the sump.
A plug sealing the lubrication cross-drilling gallery is located at the front right hand side of the cylinder block and plugs
for the main lubrication gallery is included at the front and rear of the cylinder block.
Page 152 of 1672
ENGINE - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 12-1-13
Two plastic dowels are used to locate the cylinder head to the cylinder block and must be replaced every time the
cylinder head is removed from the cylinder block.
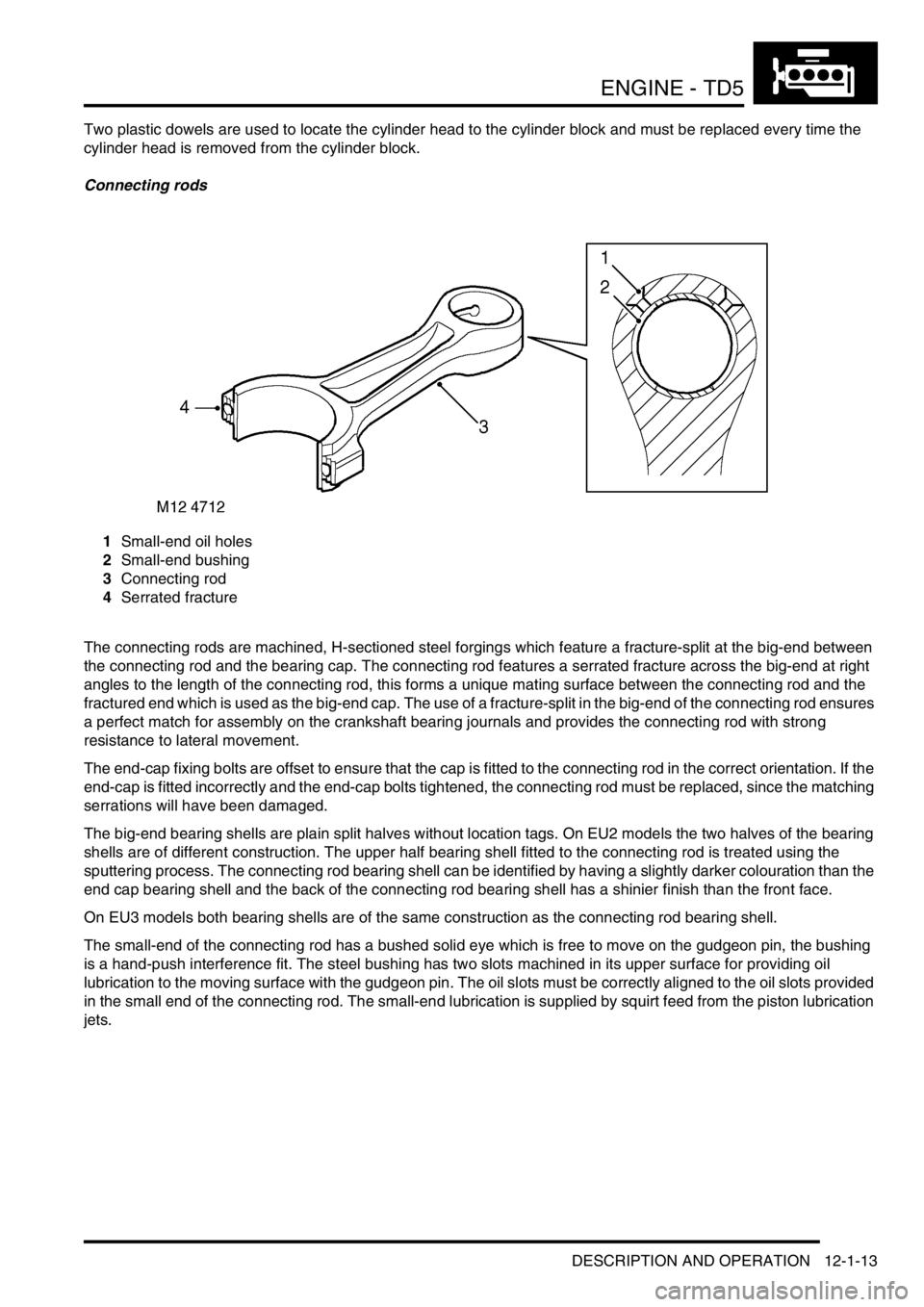
Connecting rods
1Small-end oil holes
2Small-end bushing
3Connecting rod
4Serrated fracture
The connecting rods are machined, H-sectioned steel forgings which feature a fracture-split at the big-end between
the connecting rod and the bearing cap. The connecting rod features a serrated fracture across the big-end at right
angles to the length of the connecting rod, this forms a unique mating surface between the connecting rod and the
fractured end which is used as the big-end cap. The use of a fracture-split in the big-end of the connecting rod ensures
a perfect match for assembly on the crankshaft bearing journals and provides the connecting rod with strong
resistance to lateral movement.
The end-cap fixing bolts are offset to ensure that the cap is fitted to the connecting rod in the correct orientation. If the
end-cap is fitted incorrectly and the end-cap bolts tightened, the connecting rod must be replaced, since the matching
serrations will have been damaged.
The big-end bearing shells are plain split halves without location tags. On EU2 models the two halves of the bearing
shells are of different construction. The upper half bearing shell fitted to the connecting rod is treated using the
sputtering process. The connecting rod bearing shell can be identified by having a slightly darker colouration than the
end cap bearing shell and the back of the connecting rod bearing shell has a shinier finish than the front face.
On EU3 models both bearing shells are of the same construction as the connecting rod bearing shell.
The small-end of the connecting rod has a bushed solid eye which is free to move on the gudgeon pin, the bushing
is a hand-push interference fit. The steel bushing has two slots machined in its upper surface for providing oil
lubrication to the moving surface with the gudgeon pin. The oil slots must be correctly aligned to the oil slots provided
in the small end of the connecting rod. The small-end lubrication is supplied by squirt feed from the piston lubrication
jets.
Page 153 of 1672
ENGINE - TD5
12-1-14 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
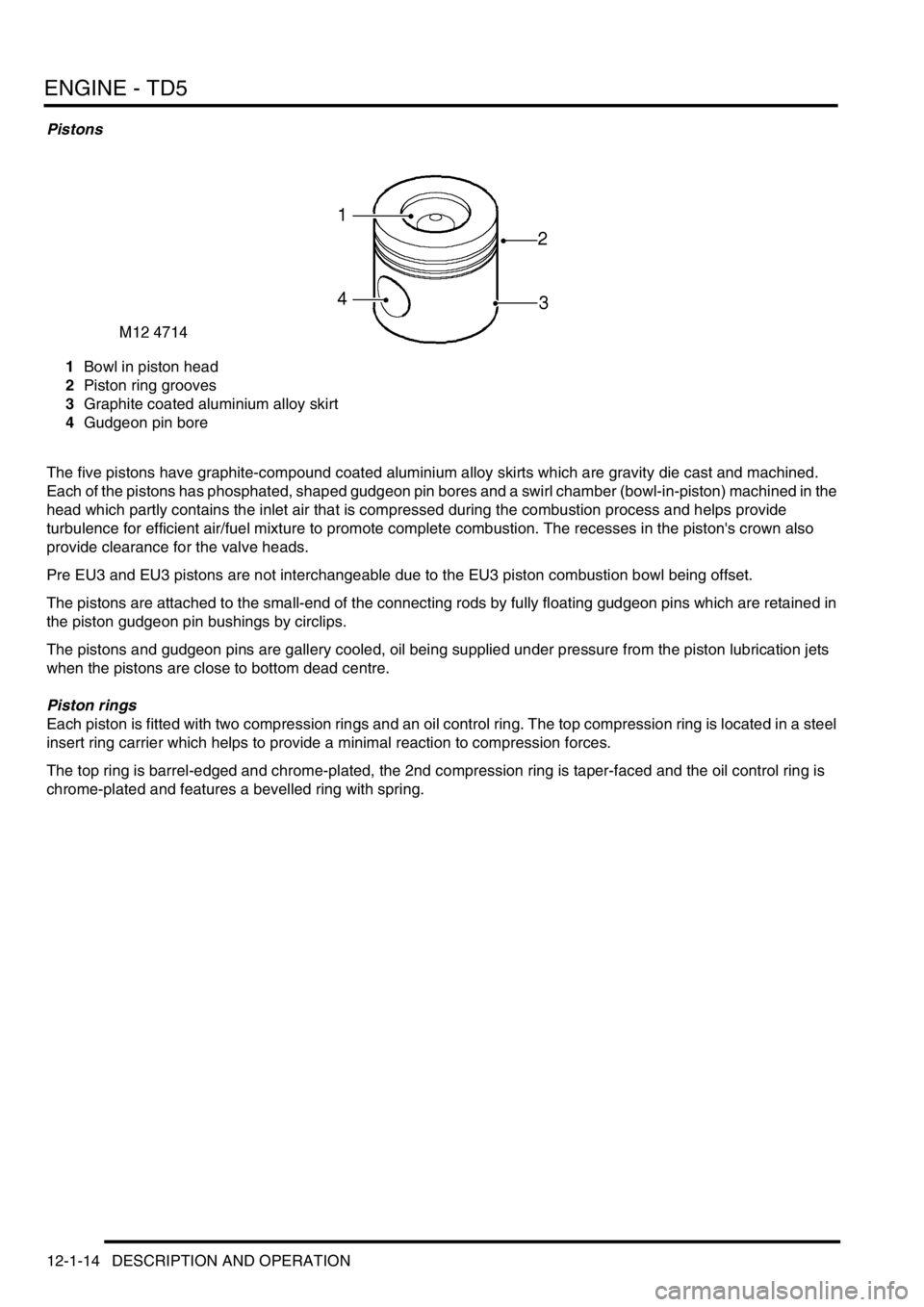
Pistons
1Bowl in piston head
2Piston ring grooves
3Graphite coated aluminium alloy skirt
4Gudgeon pin bore
The five pistons have graphite-compound coated aluminium alloy skirts which are gravity die cast and machined.
Each of the pistons has phosphated, shaped gudgeon pin bores and a swirl chamber (bowl-in-piston) machined in the
head which partly contains the inlet air that is compressed during the combustion process and helps provide
turbulence for efficient air/fuel mixture to promote complete combustion. The recesses in the piston's crown also
provide clearance for the valve heads.
Pre EU3 and EU3 pistons are not interchangeable due to the EU3 piston combustion bowl being offset.
The pistons are attached to the small-end of the connecting rods by fully floating gudgeon pins which are retained in
the piston gudgeon pin bushings by circlips.
The pistons and gudgeon pins are gallery cooled, oil being supplied under pressure from the piston lubrication jets
when the pistons are close to bottom dead centre.
Piston rings
Each piston is fitted with two compression rings and an oil control ring. The top compression ring is located in a steel
insert ring carrier which helps to provide a minimal reaction to compression forces.
The top ring is barrel-edged and chrome-plated, the 2nd compression ring is taper-faced and the oil control ring is
chrome-plated and features a bevelled ring with spring.
Page 154 of 1672
ENGINE - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 12-1-15
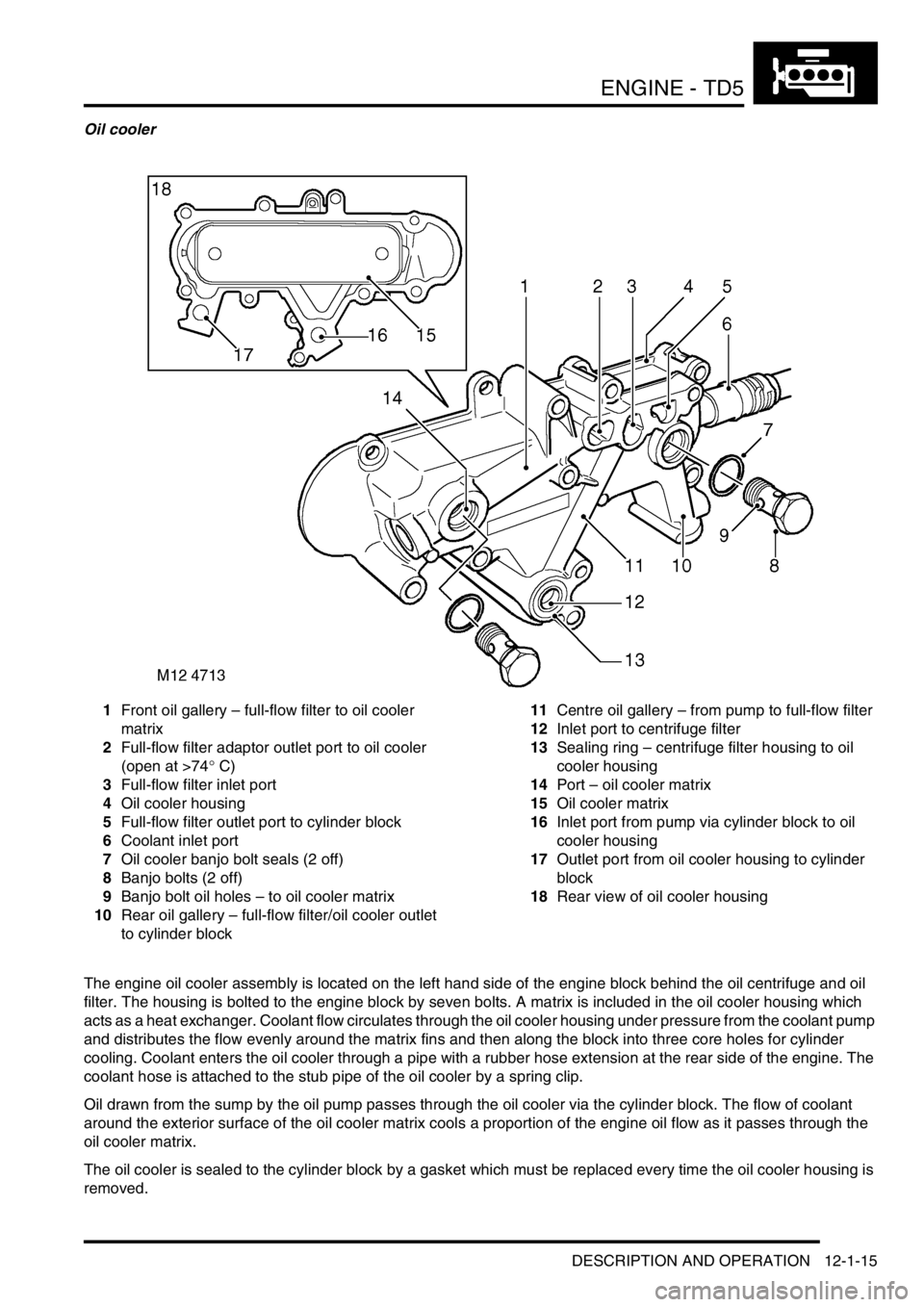
Oil cooler
1Front oil gallery – full-flow filter to oil cooler
matrix
2Full-flow filter adaptor outlet port to oil cooler
(open at >74
° C)
3Full-flow filter inlet port
4Oil cooler housing
5Full-flow filter outlet port to cylinder block
6Coolant inlet port
7Oil cooler banjo bolt seals (2 off)
8Banjo bolts (2 off)
9Banjo bolt oil holes – to oil cooler matrix
10Rear oil gallery – full-flow filter/oil cooler outlet
to cylinder block11Centre oil gallery – from pump to full-flow filter
12Inlet port to centrifuge filter
13Sealing ring – centrifuge filter housing to oil
cooler housing
14Port – oil cooler matrix
15Oil cooler matrix
16Inlet port from pump via cylinder block to oil
cooler housing
17Outlet port from oil cooler housing to cylinder
block
18Rear view of oil cooler housing
The engine oil cooler assembly is located on the left hand side of the engine block behind the oil centrifuge and oil
filter. The housing is bolted to the engine block by seven bolts. A matrix is included in the oil cooler housing which
acts as a heat exchanger. Coolant flow circulates through the oil cooler housing under pressure from the coolant pump
and distributes the flow evenly around the matrix fins and then along the block into three core holes for cylinder
cooling. Coolant enters the oil cooler through a pipe with a rubber hose extension at the rear side of the engine. The
coolant hose is attached to the stub pipe of the oil cooler by a spring clip.
Oil drawn from the sump by the oil pump passes through the oil cooler via the cylinder block. The flow of coolant
around the exterior surface of the oil cooler matrix cools a proportion of the engine oil flow as it passes through the
oil cooler matrix.
The oil cooler is sealed to the cylinder block by a gasket which must be replaced every time the oil cooler housing is
removed.
Page 155 of 1672
ENGINE - TD5
12-1-16 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
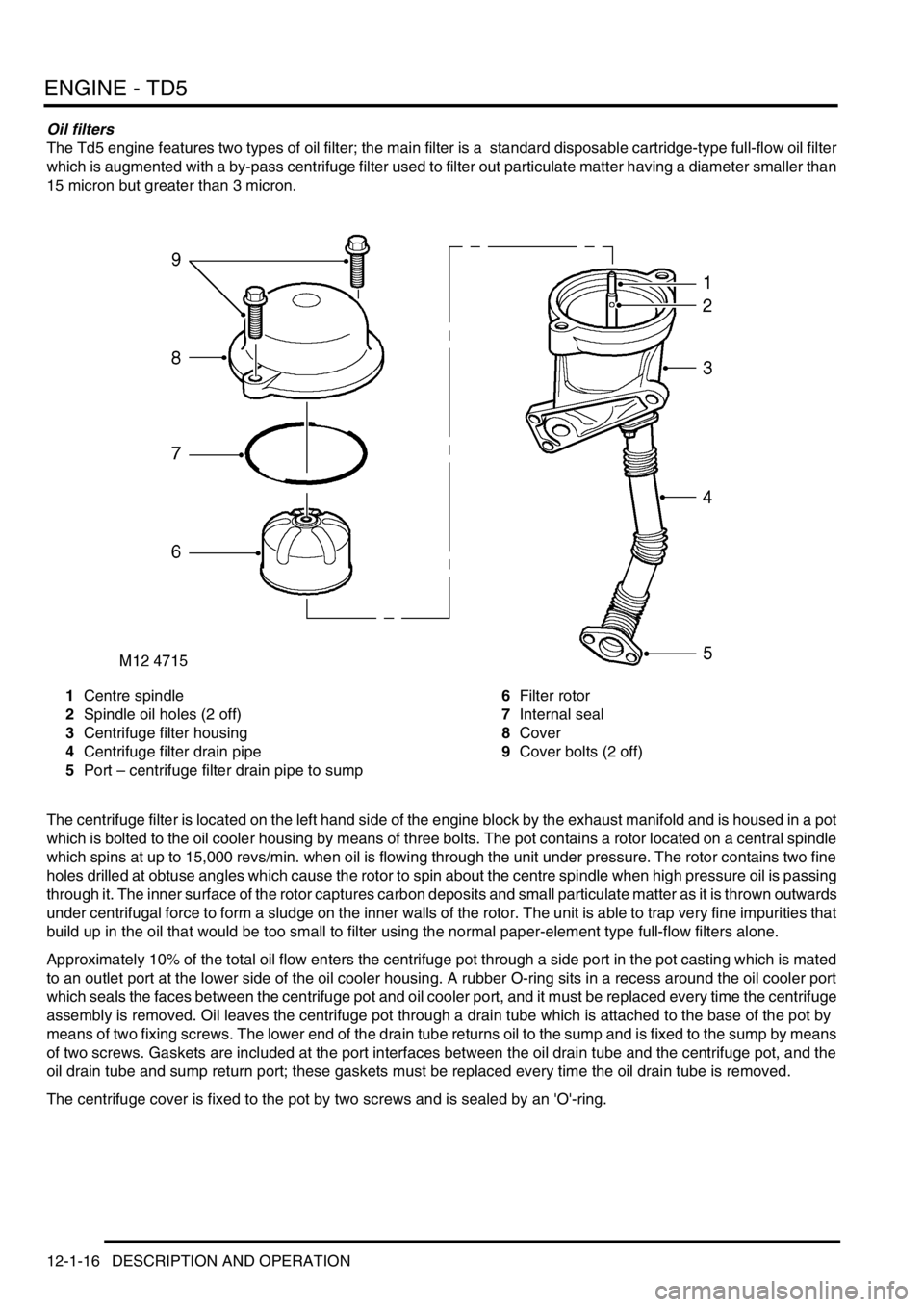
Oil filters
The Td5 engine features two types of oil filter; the main filter is a standard disposable cartridge-type full-flow oil filter
which is augmented with a by-pass centrifuge filter used to filter out particulate matter having a diameter smaller than
15 micron but greater than 3 micron.
1Centre spindle
2Spindle oil holes (2 off)
3Centrifuge filter housing
4Centrifuge filter drain pipe
5Port – centrifuge filter drain pipe to sump6Filter rotor
7Internal seal
8Cover
9Cover bolts (2 off)
The centrifuge filter is located on the left hand side of the engine block by the exhaust manifold and is housed in a pot
which is bolted to the oil cooler housing by means of three bolts. The pot contains a rotor located on a central spindle
which spins at up to 15,000 revs/min. when oil is flowing through the unit under pressure. The rotor contains two fine
holes drilled at obtuse angles which cause the rotor to spin about the centre spindle when high pressure oil is passing
through it. The inner surface of the rotor captures carbon deposits and small particulate matter as it is thrown outwards
under centrifugal force to form a sludge on the inner walls of the rotor. The unit is able to trap very fine impurities that
build up in the oil that would be too small to filter using the normal paper-element type full-flow filters alone.
Approximately 10% of the total oil flow enters the centrifuge pot through a side port in the pot casting which is mated
to an outlet port at the lower side of the oil cooler housing. A rubber O-ring sits in a recess around the oil cooler port
which seals the faces between the centrifuge pot and oil cooler port, and it must be replaced every time the centrifuge
assembly is removed. Oil leaves the centrifuge pot through a drain tube which is attached to the base of the pot by
means of two fixing screws. The lower end of the drain tube returns oil to the sump and is fixed to the sump by means
of two screws. Gaskets are included at the port interfaces between the oil drain tube and the centrifuge pot, and the
oil drain tube and sump return port; these gaskets must be replaced every time the oil drain tube is removed.
The centrifuge cover is fixed to the pot by two screws and is sealed by an 'O'-ring.
Page 156 of 1672

ENGINE - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 12-1-17
1Full-flow filter housing
2Thermostat
3Roll-pin
4Port – feed line to turbocharger
5Outlet port from full-flow filter (> 74
° C)
6Inlet port to full-flow filter
7Outlet port from full-flow filter (< 74
° C)
The main filter is a conventional full-flow cartridge-type filter containing a paper element able to trap particles greater
than 15 micron (0.015 mm) in diameter.
The cartridge is screwed to an adaptor casting by way of a hollow brass threaded insert which connects the filter outlet
port to the adaptor casting. A sealing ring seals the union between the oil filter cartridge and the adaptor casting.
Page 157 of 1672
ENGINE - TD5
12-1-18 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
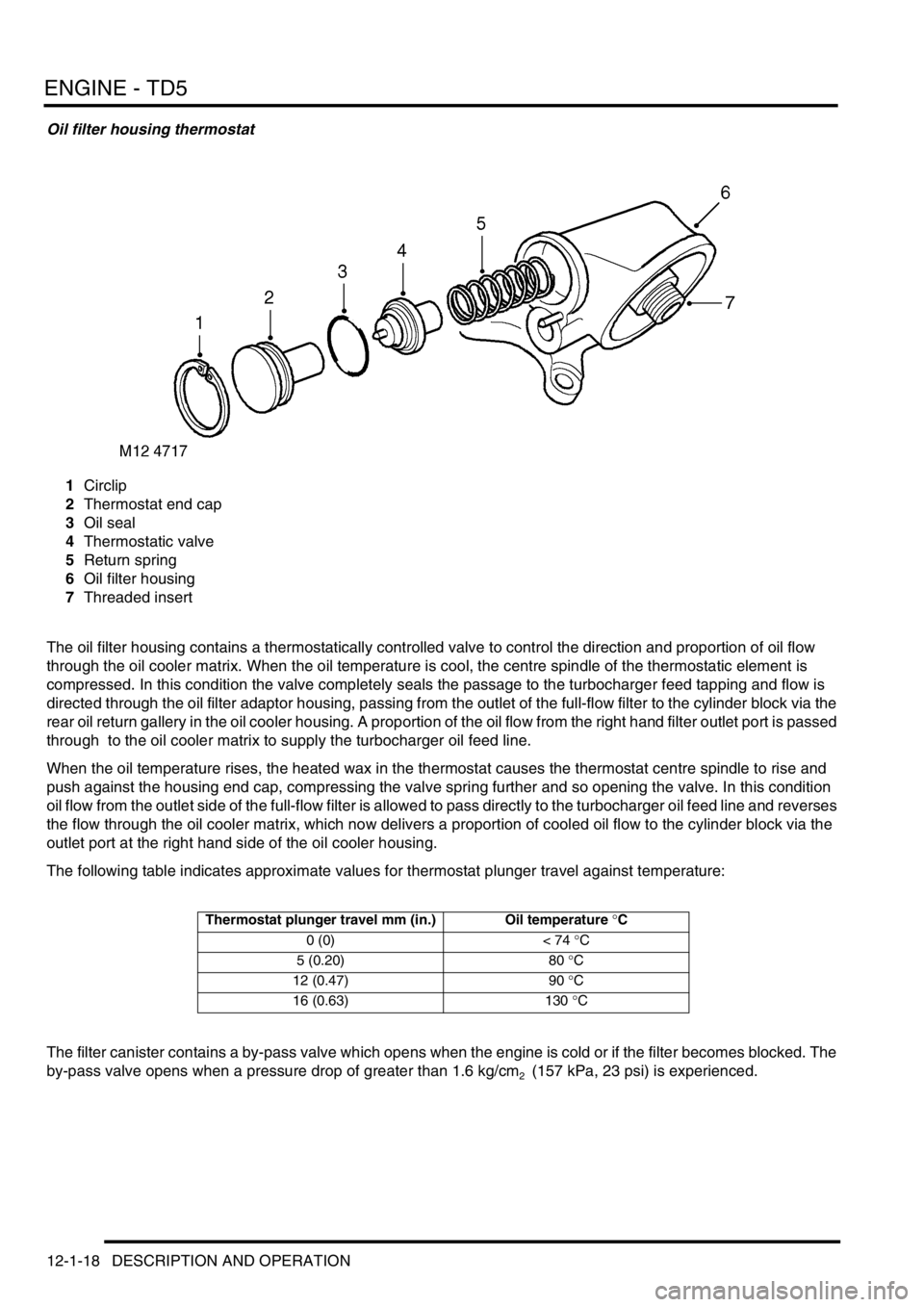
Oil filter housing thermostat
1Circlip
2Thermostat end cap
3Oil seal
4Thermostatic valve
5Return spring
6Oil filter housing
7Threaded insert
The oil filter housing contains a thermostatically controlled valve to control the direction and proportion of oil flow
through the oil cooler matrix. When the oil temperature is cool, the centre spindle of the thermostatic element is
compressed. In this condition the valve completely seals the passage to the turbocharger feed tapping and flow is
directed through the oil filter adaptor housing, passing from the outlet of the full-flow filter to the cylinder block via the
rear oil return gallery in the oil cooler housing. A proportion of the oil flow from the right hand filter outlet port is passed
through to the oil cooler matrix to supply the turbocharger oil feed line.
When the oil temperature rises, the heated wax in the thermostat causes the thermostat centre spindle to rise and
push against the housing end cap, compressing the valve spring further and so opening the valve. In this condition
oil flow from the outlet side of the full-flow filter is allowed to pass directly to the turbocharger oil feed line and reverses
the flow through the oil cooler matrix, which now delivers a proportion of cooled oil flow to the cylinder block via the
outlet port at the right hand side of the oil cooler housing.
The following table indicates approximate values for thermostat plunger travel against temperature:
The filter canister contains a by-pass valve which opens when the engine is cold or if the filter becomes blocked. The
by-pass valve opens when a pressure drop of greater than 1.6 kg/cm
2 (157 kPa, 23 psi) is experienced.
Thermostat plunger travel mm (in.) Oil temperature °C
0 (0) < 74 °C
5 (0.20) 80 °C
12 (0.47) 90 °C
16 (0.63) 130 °C
Page 158 of 1672
ENGINE - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 12-1-19
Oil Pressure switch
The oil pressure switch is located in a port on the outlet side of the oil cooler housing. It detects when a safe operating
pressure has been reached during engine starting and initiates the illumination of a warning light in the instrument
pack if the pressure drops below a given value.
Crankshaft, sump and oil pump components
The crankshaft, sump and oil pump components are described below:
Sump
The sump is a wet-type, of aluminium construction and is sealed to the engine block by means of a rubber gasket and
twenty fixing bolts. The four bolts at the gearbox end of the sump are longer than the other sixteen bolts.
The sump gasket incorporates compression limiters (integrated metal sleeves) at the bolt holes, which are included
to prevent distortion of the gasket when the sump to cylinder block bolts are being tightened.
The oil drain plug is fitted at the bottom of the oil sump reservoir. An oil return drain pipe is also attached to the oil
sump which returns oil from the centrifugal filter.
Stiffener Plate
The stiffener plate assembly provides lower engine block rigidity and utilises dowels to align it to the bottom of the
cylinder block. A rotary oil pump is integral with the stiffener plate and an oil pick-up and strainer assembly is fitted
to the underside of the stiffener plate. The stiffener and oil pump assembly is secured to the cylinder block by 22 bolts.
Page 159 of 1672

ENGINE - TD5
12-1-20 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Oil pump
1Stiffener plate
2Ring dowel
3Outlet port
4Outer rotor
5Inner rotor6Spring dowel
7Oil pressure relief valve cap
8Oil pressure relief valve spring
9Oil pressure relief valve plunger
10Inlet port
The eccentric rotor oil pump is integrated with the stiffener plate and contains no serviceable parts except for the
pressure relief valve spring. The oil pump drive sprocket is attached to the front of the stiffener plate and is driven
through a chain and sprocket system.
A pressure relief valve is included at the outlet side of the oil pump to restrict oil pressure at high engine speeds by
recirculating oil through the relief valve back around the pump to the inlet. The relief valve and spring is a plunger type.
When oil pressure is great enough to lift the plunger, oil is allowed to escape past the plunger to relieve pressure and
prevent further rise.
Oil is delivered to the pump from the pick-up through a channel in the stiffener plate. The outlet side of the oil pump
delivers pressurised oil flow to the engine block main oil delivery gallery through a port in the stiffener plate.
Piston lubrication jets
Piston lubrication jets are fitted to the cylinder block to provide lubrication to the cylinder walls, and to the piston
underskirt for cooling the pistons and lubricating the gudgeon pins. The input port to each lubrication jet mates with a
port provided in each mounting position tapped at the underside of the cylinder block from the main oil delivery gallery.
When oil pressure is sufficient to supply flow through the jets, oil is squirted to the inside of the cylinder walls to provide
piston to wall lubrication and cooling and to the underside of the piston skirt at the bottom of the piston stroke (gallery
cooled piston). The squirt jets also provide splash feed lubrication supply to the small end bearings of the connecting
rods.
Each lubrication jet is fixed to a mounting position on the underside of the engine block by a single Torx screw.
Chain lubrication jet
A chain lubrication jet is located on the front face of the cylinder block, behind the front engine timing chain cover. The
inlet port to the lubrication jet mates with an oil supply port from the cylinder block main oil delivery gallery. The
lubrication jet is fixed to the front of the engine block by a single screw. Additional chain lubrication is provided by oil
supply through a small aperture tapped from the cylinder head oil delivery gallery.
Page 160 of 1672
ENGINE - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 12-1-21
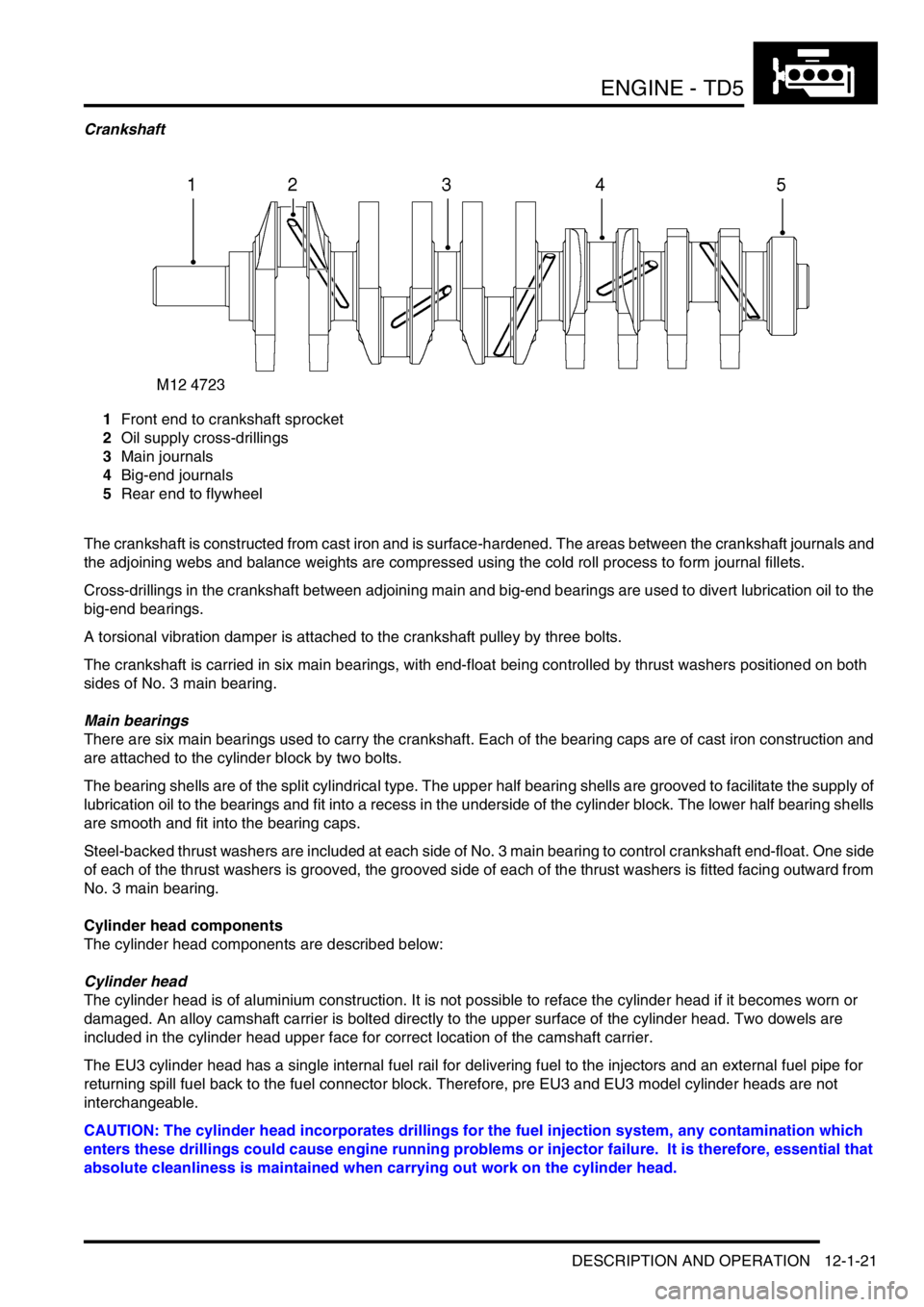
Crankshaft
1Front end to crankshaft sprocket
2Oil supply cross-drillings
3Main journals
4Big-end journals
5Rear end to flywheel
The crankshaft is constructed from cast iron and is surface-hardened. The areas between the crankshaft journals and
the adjoining webs and balance weights are compressed using the cold roll process to form journal fillets.
Cross-drillings in the crankshaft between adjoining main and big-end bearings are used to divert lubrication oil to the
big-end bearings.
A torsional vibration damper is attached to the crankshaft pulley by three bolts.
The crankshaft is carried in six main bearings, with end-float being controlled by thrust washers positioned on both
sides of No. 3 main bearing.
Main bearings
There are six main bearings used to carry the crankshaft. Each of the bearing caps are of cast iron construction and
are attached to the cylinder block by two bolts.
The bearing shells are of the split cylindrical type. The upper half bearing shells are grooved to facilitate the supply of
lubrication oil to the bearings and fit into a recess in the underside of the cylinder block. The lower half bearing shells
are smooth and fit into the bearing caps.
Steel-backed thrust washers are included at each side of No. 3 main bearing to control crankshaft end-float. One side
of each of the thrust washers is grooved, the grooved side of each of the thrust washers is fitted facing outward from
No. 3 main bearing.
Cylinder head components
The cylinder head components are described below:
Cylinder head
The cylinder head is of aluminium construction. It is not possible to reface the cylinder head if it becomes worn or
damaged. An alloy camshaft carrier is bolted directly to the upper surface of the cylinder head. Two dowels are
included in the cylinder head upper face for correct location of the camshaft carrier.
The EU3 cylinder head has a single internal fuel rail for delivering fuel to the injectors and an external fuel pipe for
returning spill fuel back to the fuel connector block. Therefore, pre EU3 and EU3 model cylinder heads are not
interchangeable.
CAUTION: The cylinder head incorporates drillings for the fuel injection system, any contamination which
enters these drillings could cause engine running problems or injector failure. It is therefore, essential that
absolute cleanliness is maintained when carrying out work on the cylinder head.