MAZDA 6 2002 Workshop Manual Suplement
Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 2002, Model line: 6, Model: MAZDA 6 2002Pages: 909, PDF Size: 17.16 MB
Page 491 of 909

K2–76
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
D Range Test
Note
•The NORMAL mode and SLOPE mode are automatically selected by the TCM in D range. The TCM shifts
to SLOPE mode when the upgrade is approx. 5 % or more, and shifts to NORMAL mode when the
upgrade is approx. 3 % or less.
1. Perform road test preparation. (See K2–75 Road Test Preparation.)
2. Shift the selector lever to D range.
3. Accelerate the vehicle with half and WOT, then verify that 1→2, 2→3, 3→4, and 4→5 upshifts and downshifts
are obtained. The shift points must be as shown in the table below.
•If not as specified, inspect the TCM and ATX. (See K2–183 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SYMPTOM
TROUBLESHOOTING.)
4. Drive the vehicle in 5GR, 4GR, 3GR, and 2GR and verify that kickdown occurs for 5→4, 4→3, 3→2, and 2→1
downshifts, and that the shift points are as shown in the table below.
•If not as specified, inspect the TCM and ATX. (See K2–183 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SYMPTOM
TROUBLESHOOTING.)
5. Decelerate the vehicle and verify that engine braking effect is felt in 5GR.
•If not as specified, inspect the TCM and ATX. (See K2–183 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SYMPTOM
TROUBLESHOOTING.)
6. Drive the vehicle and verify that TCC operation is obtained. The operation points must be as shown in the table
below.
•If not as specified, inspect the TCM and ATX. (See K2–183 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SYMPTOM
TROUBLESHOOTING.)
Note
•The shift solenoid electrical ON-OFF pattern is this chart describes the stabilized condition before and
after shift control. The pattern may oscillate between ON and OFF momentarily while shifting-up or down.
This is normal.
Vehicle speed at shift point table
Range ModeThrottle
conditionShiftVehicle speed
(km/h {mph})Turbine speed
(rpm)
DNORMALWide open
throttleD
1→D250—56 {31—34} 5,800—6,450
D
2→D389—97 {56—60} 5,800—6,250
D
3→D4139—149 {87—92} 5,800—6,150
TCC ON (D
4)
127—137 {79—84} 3,650—3,850
D
4→D5195—205 {121—127} 5,550—5,800
TCC ON (D
5)
195—205 {121—127} 4,100—4,250
Half throttleD
1→D225—34 {16—21} 2,850—3,950
D
2→D345—62 {28—38} 2,900—4,000
D
3→D472—99 {45—61} 3,000—4,100
TCC ON (D
4)
93—121 {58—75} 2,650—3,450
D
4→D5124—149 {77—92} 3,550—4,200
TCC ON (D
5)
124—149 {77—92} 2,600—3,100
Closed throttle
positionD
5→D455—61 {35—37} 1,1500—1,250
D
4→D323—29 {15—17} 700—800
D
3→D17—13 {5—8} 300—500
KickdownD
5→D4185—195 {115—120} 3,850—4,050
D
4→D3127—137 {79—84} 3,650—3,850
D
3→D277—85 {48—52} 3,200—3,500
D
2→D137—43 {23—26} 2,400—2,750
Page 492 of 909

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–77
K2
M Range Test
1. Perform road test preparation. (See K2–75 Road Test Preparation.)
2. Shift the selector lever to M range.
3. Verify that 1→2, 2→3, 3→4, and 4→5 upshifts and 5→4, 4→3, 3→2, and 2→1 downshifts are obtained by
manual shifting of the selector lever forward and back. The shift points must be as shown in the table below.
•If not as specified, inspect the TCM and ATX. (See K2–183 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SYMPTOM
TROUBLESHOOTING.)
4. Decelerate the vehicle and verify that 5→4, 4→3, 3→1, and 2→1 downshifts are obtained. The shift points
must be as shown in the table below.
•If not as specified, inspect the TCM and ATX.(See K2–183 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SYMPTOM
TROUBLESHOOTING.)
5. Decelerate the vehicle and verify that engine braking effect is felt in all gears.
•If not as specified, inspect the TCM and ATX. (See K2–183 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SYMPTOM
TROUBLESHOOTING.)
6. Drive the vehicle and verify that TCC operation is obtained in 5GR. The operation points must be as shown in
the table below.
•If not as specified, inspect the TCM and ATX. (See K2–183 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SYMPTOM
TROUBLESHOOTING.)
Vehicle speed at shift point table
Noise and Vibration Test
1. Drive the vehicle and listen closely for any noise or vibration. The torque converter, drive shaft, and differential
can be sources of noise and vibration if they are not functioning properly. Inspect these when searching for
sources of noise and vibration.
P Position Test
1. Shift into P position on a gentle slope. Release the brake, and verify that the vehicle does not roll.
•If the vehicle rolls, inspect the ATX. (See K2–183 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SYMPTOM
TROUBLESHOOTING.)
Range ModeThrottle
conditionShiftVehicle speed
(km/h {mph})Turbine speed
(rpm)
MManualHalf throttleTCC ON (M
5)
106—129 {66—79} 2,200—2,600
All roundM
5→M430—36 {19—22} 650—700
M
4→M323—29 {15—17} 650—800
M
2→M14—10 {3—6} 300—600
M
3→M14—10 {3—6} 200—400
Page 493 of 909

K2–78
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
Evaluation
End Of SieAUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID (ATF) INSPECTIONA6E571419001201Automatic Transaxle Fluid (ATF) Condition Inspection
1. One way of determining whether the transaxle should be replaced is by noting:
•If the ATF is muddy or varnished.
•If the ATF smells strange or unusual.
ATF Condition
Condition Possible Cause
No 1-2 up- or downshiftStuck shift solenoid C
Stuck shift valve C
Wore 2-4 brake
Trouble intermediate sensor
No 2-3 up- or downshiftStuck shift solenoid A
Stuck shift valve A
Wore high clutch
No 3-4 up- or downshiftStuck shift solenoid B
Stuck shift valve B
Wore 2-4 brake
No 4-5 up- or downshiftStuck shift solenoid A
Stuck shift valve A
Wore direct clutch
Trouble TFT
TCC non operation shiftStuck TCC solenoid valve
Stuck TCC valve
Incorrect shift pointTrouble VSS output signal
Trouble TR switch
Trouble TP signal and engine torque signal
Excessive shift shock slippageStuck pressure control solenoid
Stuck pressure regulator valve
Stuck pressure modifier valve
Stuck accumulator valve A, B, or C
Stuck 2-4 brake solenoid valve
Stuck high clutch solenoid valve
Stuck low clutch accumulator
Stuck 2-4 brake accumlator
Stuck high clutch accumlator
Stuck direct clutch accumlator
Stuck reduction accumlator
Trouble VSS
No Engine braking effect Wore reduction brake band
Stuck reduction reducing valve
Stuck reduction timing valve
Stuck reduction timing solenoid valve
Condition Possible cause
Clear dark red Normal—
Light red (pink) Contaminated with water•Broken oil cooler inside of radiator
•Poor filler tube installation:
Problem could be occurring to parts inside the
transaxle by water contamination. If necessary,
exchange transaxle.
Reddish
brownHas burnt smell and metal
specs are foundDeteriorated ATFDefect powertrain components inside of transaxle:
Specks cause wide range of problems by plugging up
in oil pipe, control valve body and oil cooler in radiator.
•When large amount of metal specks are found.
Exchange transaxle if necessary.
•Implement flushing operation as there is a
possibility to have specks plugging up oil pipe and/
or oil cooler inside of radiator.
Has no burnt smell Normal•Discoloration by oxidation
Page 494 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–79
K2
Automatic Transaxle Fluid (ATF) Level Inspection
Caution
•The ATF amount varies according to ATF's temperature. Therefore, when checking the ATF level or
replacing the ATF, use a thermometer to measure the temperature then adjust the ATF amount to
the specified level according to the specified temperature.
1. Park the vehicle on level ground.
2. Apply the parking brake and position wheel chocks securely to prevent the vehicle from rolling.
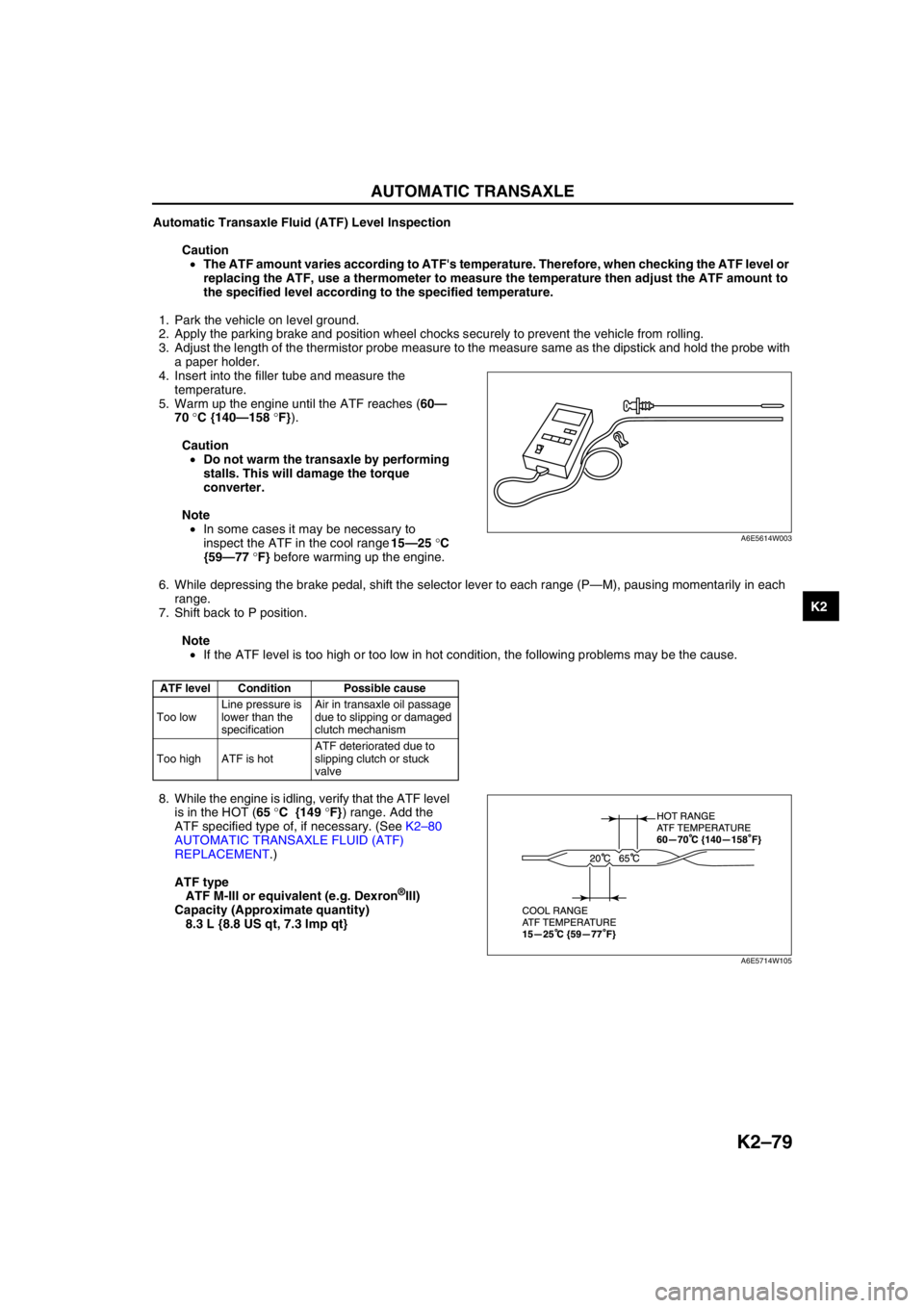
3. Adjust the length of the thermistor probe measure to the measure same as the dipstick and hold the probe with
a paper holder.
4. Insert into the filler tube and measure the
temperature.
5. Warm up the engine until the ATF reaches (60—
70 °C {140—158 °F}).
Caution
•Do not warm the transaxle by performing
stalls. This will damage the torque
converter.
Note
•In some cases it may be necessary to
inspect the ATF in the cool range 15—25 °C
{59—77 °F} before warming up the engine.
6. While depressing the brake pedal, shift the selector lever to each range (P—M), pausing momentarily in each
range.
7. Shift back to P position.
Note
•If the ATF level is too high or too low in hot condition, the following problems may be the cause.
8. While the engine is idling, verify that the ATF level
is in the HOT (65 °C {149 °F}) range. Add the
ATF specified type of, if necessary. (See K2–80
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID (ATF)
REPLACEMENT.)
ATF type
ATF M-III or equivalent (e.g. Dexron
®III)
Capacity (Approximate quantity)
8.3 L {8.8 US qt, 7.3 Imp qt}
End Of Sie
ATF level Condition Possible cause
Too lowLine pressure is
lower than the
specificationAir in transaxle oil passage
due to slipping or damaged
clutch mechanism
Too high ATF is hotATF deteriorated due to
slipping clutch or stuck
valve
A6E5614W003
A6E5714W105
Page 495 of 909
K2–80
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID (ATF) REPLACEMENTA6E571419001202
Warning
•When the transaxle and ATF are hot, they can badly burn you. Turn off the engine and wait until
they are cool before changing the ATF.
1. Remove the oil dipstick.
2. Remove the oil drain plug and washer.
3. Drain the ATF into a container.
4. Install a new washer and the drain plug.
Tightening torque
39—54 N·m {3.9—5.6 kgf·m, 29—40 ft·lbf}
5. Add the specified type of ATF through the oil filler
tube, until ATF level reaches lower notch of
dipstick.
ATF type
ATF M-III or equivalent (e.g. Dexron
®III)
Capacity (Approximate quantity)
8.3 L {8.8 US qt, 7.3 Imp qt}
6. Verify that the ATF level is in the HOT (65 °C {149 °F}) range.
•Add ATF to the specified level as necessary.
End Of Sie
TRANSAXLE RANGE (TR) SWITCH INSPECTIONA6E571419440201
Note
•Input signals of the TR switch can be inspected with a WDS or equivalent. (See K2–90 TCM
INSPECTION.)
Inspection of Operation
1. Verify that the starter operates only with the ignition switch at the START position and the selector lever in P
and N positions.
•If not as specified, inspect for continuity at the TR switch. (See K2–80 Inspection of Continuity.)
2. Verify that the back-up lights illuminate when shifted to R position with the ignition switch at the ON position.
•If not as specified, inspect for continuity at the TR switch.
Inspection of Continuity
1. Disconnect the TR switch connector.
2. Inspect for continuity at the TR switch.
•If not as specified, adjust the TR switch, then
reinspect the TR switch. (See K2–83
TRANSAXLE RANGE (TR) SWITCH
ADJUSTMENT.)
A6E5714W106
TR SWITCHTR SWITCH
CONNECTOR
A6E5714W107
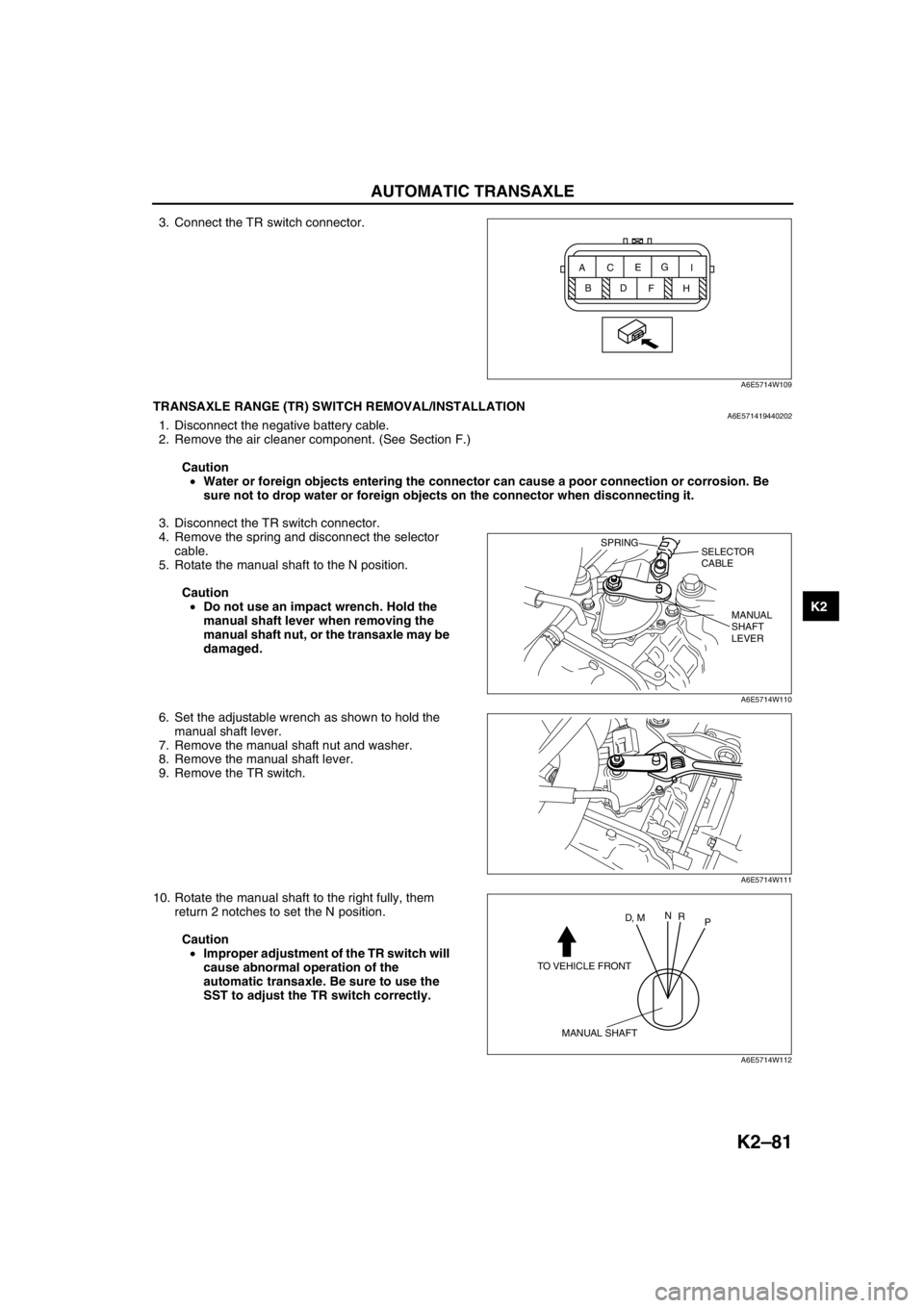
Position/
Range
H
P
R
N
DBCAEDGI FConnector terminal: Continuity
A6E5714W108
Page 496 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–81
K2
3. Connect the TR switch connector.
End Of SieTRANSAXLE RANGE (TR) SWITCH REMOVAL/INSTALLATIONA6E5714194402021. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the air cleaner component. (See Section F.)
Caution
•Water or foreign objects entering the connector can cause a poor connection or corrosion. Be
sure not to drop water or foreign objects on the connector when disconnecting it.
3. Disconnect the TR switch connector.
4. Remove the spring and disconnect the selector
cable.
5. Rotate the manual shaft to the N position.
Caution
•Do not use an impact wrench. Hold the
manual shaft lever when removing the
manual shaft nut, or the transaxle may be
damaged.
6. Set the adjustable wrench as shown to hold the
manual shaft lever.
7. Remove the manual shaft nut and washer.
8. Remove the manual shaft lever.
9. Remove the TR switch.
10. Rotate the manual shaft to the right fully, them
return 2 notches to set the N position.
Caution
•Improper adjustment of the TR switch will
cause abnormal operation of the
automatic transaxle. Be sure to use the
SST to adjust the TR switch correctly.
BC AE
DG
I
FH
A6E5714W109
SPRING
SELECTOR
CABLE
MANUAL
SHAFT
LEVER
A6E5714W110
A6E5714W111
TO VEHICLE FRONT
MANUAL SHAFT
D, MN
R
P
A6E5714W112
Page 497 of 909
K2–82
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
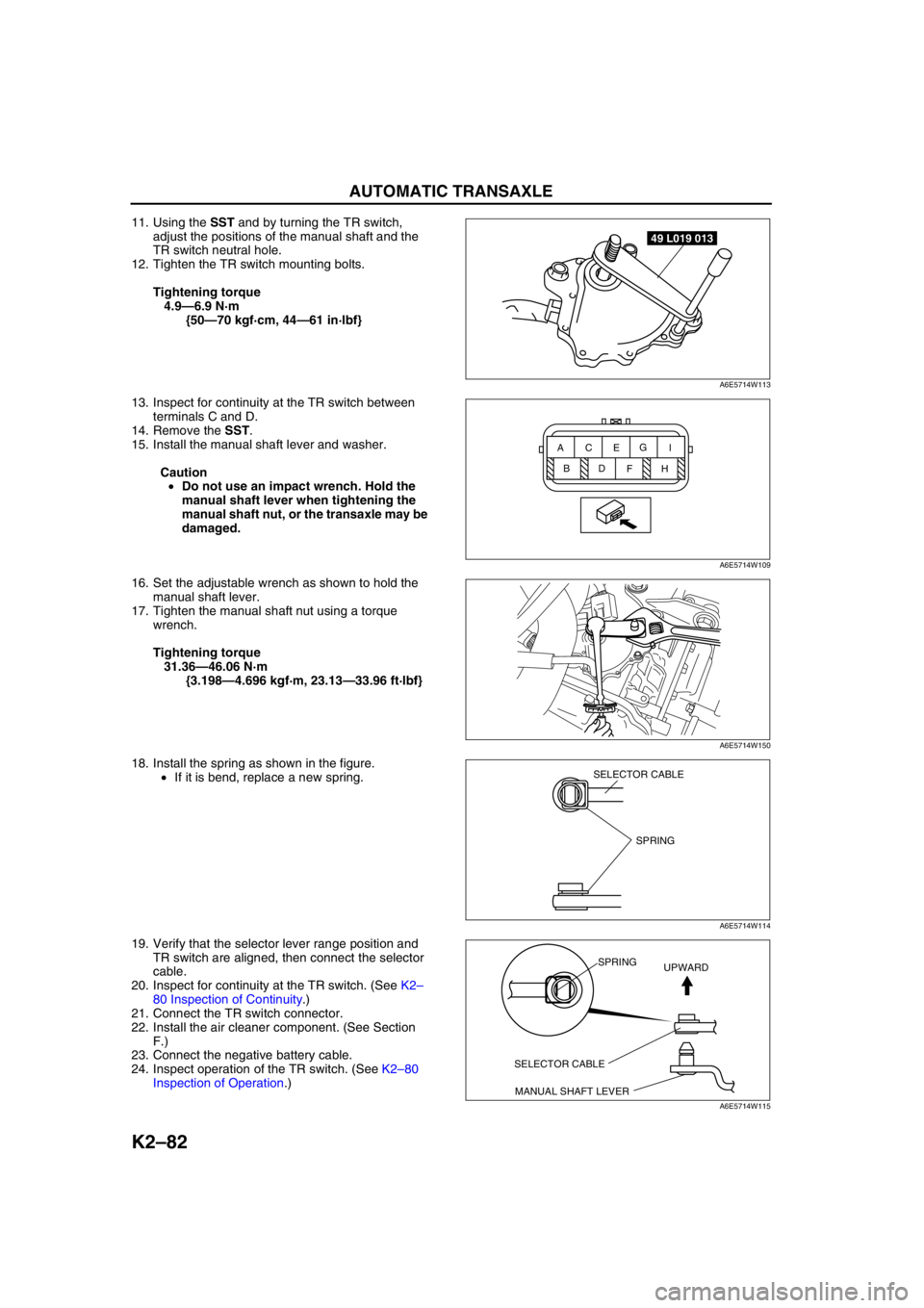
11. Using the SST and by turning the TR switch,
adjust the positions of the manual shaft and the
TR switch neutral hole.
12. Tighten the TR switch mounting bolts.
Tightening torque
4.9—6.9 N·m
{50—70 kgf·cm, 44—61 in·lbf}
13. Inspect for continuity at the TR switch between
terminals C and D.
14. Remove the SST.
15. Install the manual shaft lever and washer.
Caution
•Do not use an impact wrench. Hold the
manual shaft lever when tightening the
manual shaft nut, or the transaxle may be
damaged.
16. Set the adjustable wrench as shown to hold the
manual shaft lever.
17. Tighten the manual shaft nut using a torque
wrench.
Tightening torque
31.36—46.06 N·m
{3.198—4.696 kgf·m, 23.13—33.96 ft·lbf}
18. Install the spring as shown in the figure.
•If it is bend, replace a new spring.
19. Verify that the selector lever range position and
TR switch are aligned, then connect the selector
cable.
20. Inspect for continuity at the TR switch. (See K2–
80 Inspection of Continuity.)
21. Connect the TR switch connector.
22. Install the air cleaner component. (See Section
F.)
23. Connect the negative battery cable.
24. Inspect operation of the TR switch. (See K2–80
Inspection of Operation.)
49 L019 013
A6E5714W113
BC AE
DG
I
FH
A6E5714W109
A6E5714W150
SPRING
SELECTOR CABLE
A6E5714W114
SELECTOR CABLE
MANUAL SHAFT LEVERSPRING
UPWARD
A6E5714W115
Page 498 of 909
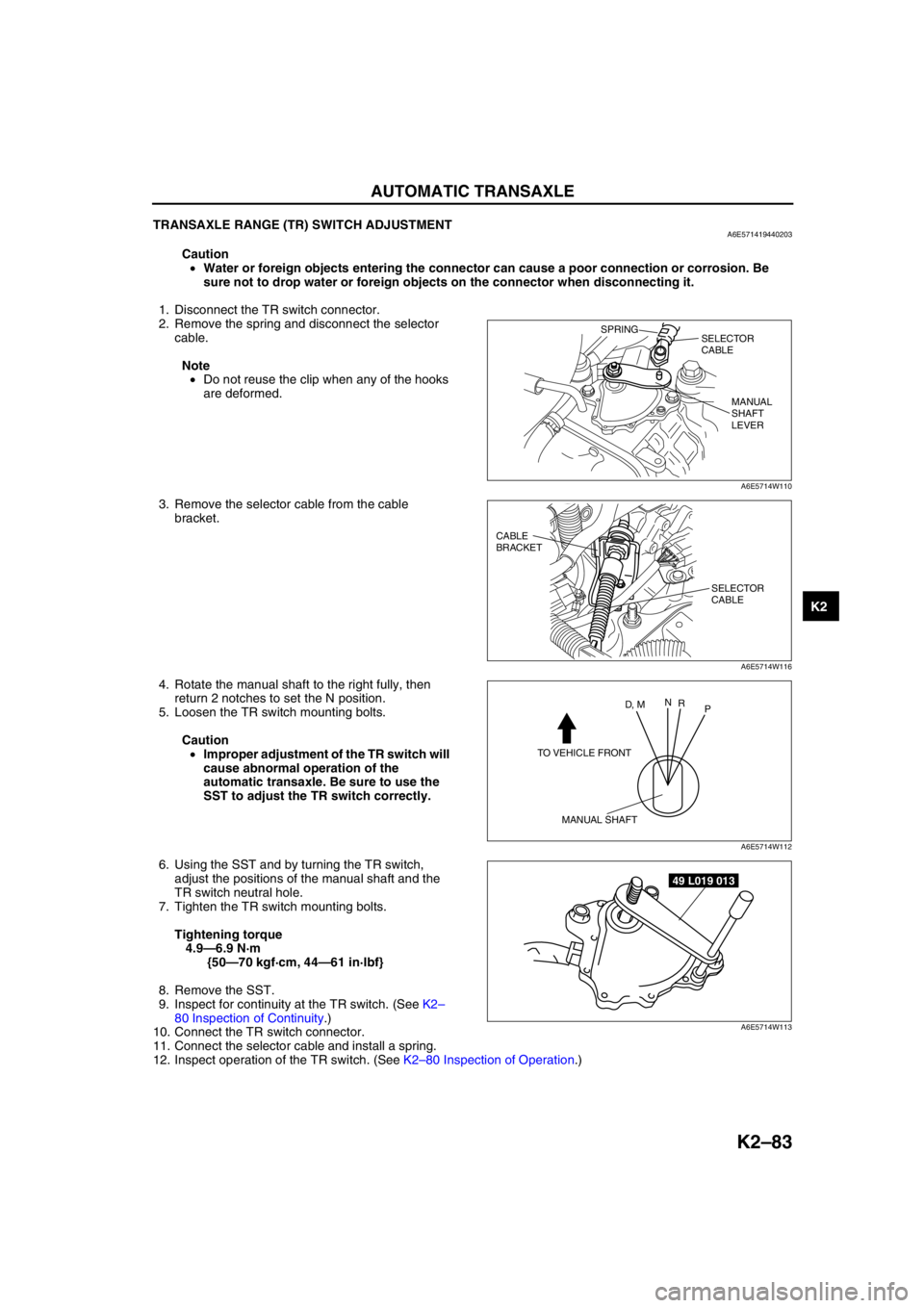
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–83
K2
End Of SieTRANSAXLE RANGE (TR) SWITCH ADJUSTMENTA6E571419440203
Caution
•Water or foreign objects entering the connector can cause a poor connection or corrosion. Be
sure not to drop water or foreign objects on the connector when disconnecting it.
1. Disconnect the TR switch connector.
2. Remove the spring and disconnect the selector
cable.
Note
•Do not reuse the clip when any of the hooks
are deformed.
3. Remove the selector cable from the cable
bracket.
4. Rotate the manual shaft to the right fully, then
return 2 notches to set the N position.
5. Loosen the TR switch mounting bolts.
Caution
•Improper adjustment of the TR switch will
cause abnormal operation of the
automatic transaxle. Be sure to use the
SST to adjust the TR switch correctly.
6. Using the SST and by turning the TR switch,
adjust the positions of the manual shaft and the
TR switch neutral hole.
7. Tighten the TR switch mounting bolts.
Tightening torque
4.9—6.9 N·m
{50—70 kgf·cm, 44—61 in·lbf}
8. Remove the SST.
9. Inspect for continuity at the TR switch. (See K2–
80 Inspection of Continuity.)
10. Connect the TR switch connector.
11. Connect the selector cable and install a spring.
12. Inspect operation of the TR switch. (See K2–80 Inspection of Operation.)
End Of Sie
SPRING
SELECTOR
CABLE
MANUAL
SHAFT
LEVER
A6E5714W110
CABLE
BRACKET
SELECTOR
CABLE
A6E5714W116
TO VEHICLE FRONT
MANUAL SHAFT
D, MN
R
P
A6E5714W112
49 L019 013
A6E5714W113
Page 499 of 909
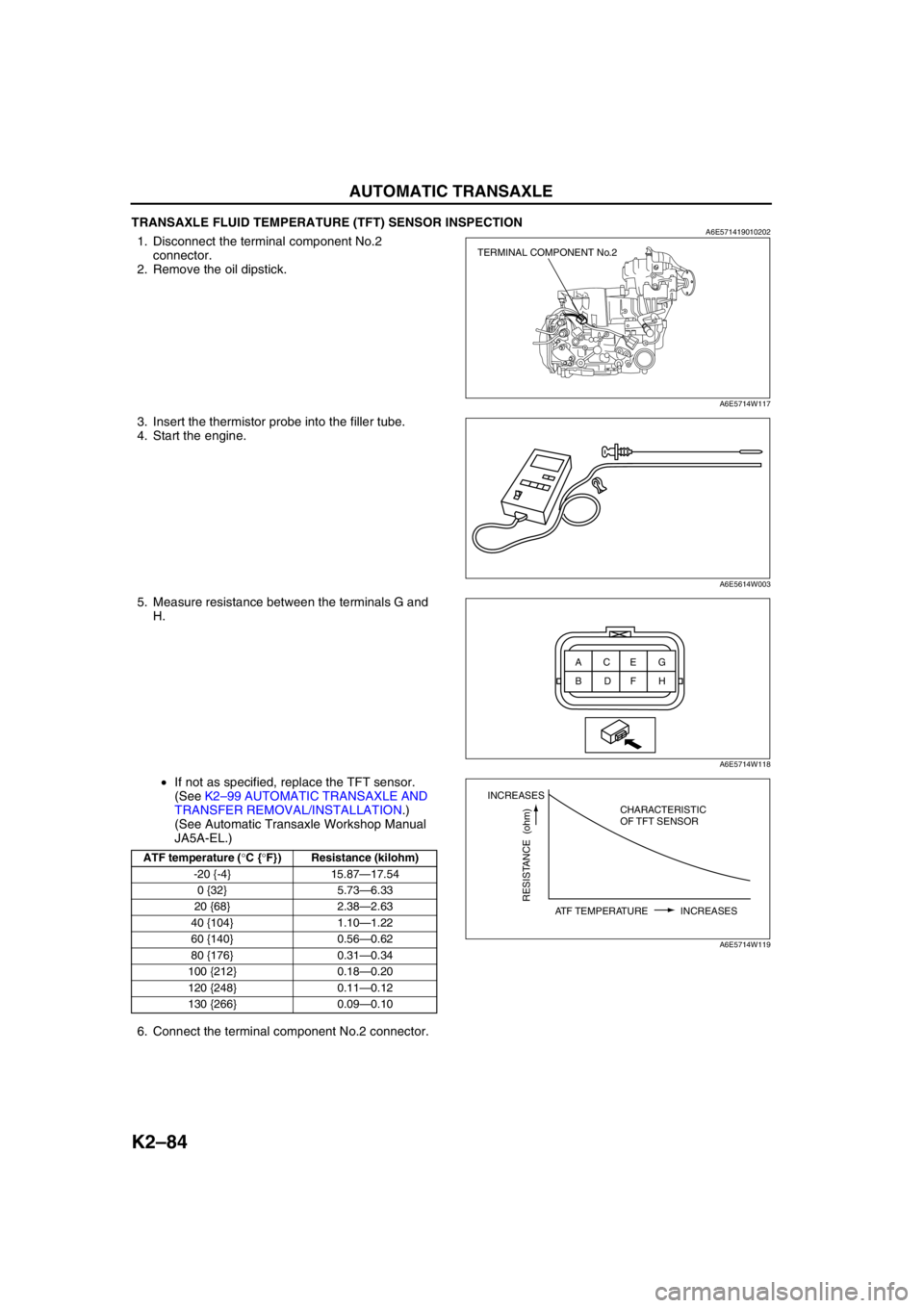
K2–84
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
TRANSAXLE FLUID TEMPERATURE (TFT) SENSOR INSPECTIONA6E5714190102021. Disconnect the terminal component No.2
connector.
2. Remove the oil dipstick.
3. Insert the thermistor probe into the filler tube.
4. Start the engine.
5. Measure resistance between the terminals G and
H.
•If not as specified, replace the TFT sensor.
(See K2–99 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE AND
TRANSFER REMOVAL/INSTALLATION.)
(See Automatic Transaxle Workshop Manual
JA5A-EL.)
6. Connect the terminal component No.2 connector.
End Of Sie
ATF temperature (°C {°F}) Resistance (kilohm)
-20 {-4} 15.87—17.54
0 {32} 5.73—6.33
20 {68} 2.38—2.63
40 {104} 1.10—1.22
60 {140} 0.56—0.62
80 {176} 0.31—0.34
100 {212} 0.18—0.20
120 {248} 0.11—0.12
130 {266} 0.09—0.10
TERMINAL COMPONENT No.2
A6E5714W117
A6E5614W003
ACEG
BDFH
A6E5714W118
INCREASES
RESISTANCE (ohm)
ATF TEMPERATURE INCREASESCHARACTERISTIC
OF TFT SENSOR
A6E5714W119
Page 500 of 909
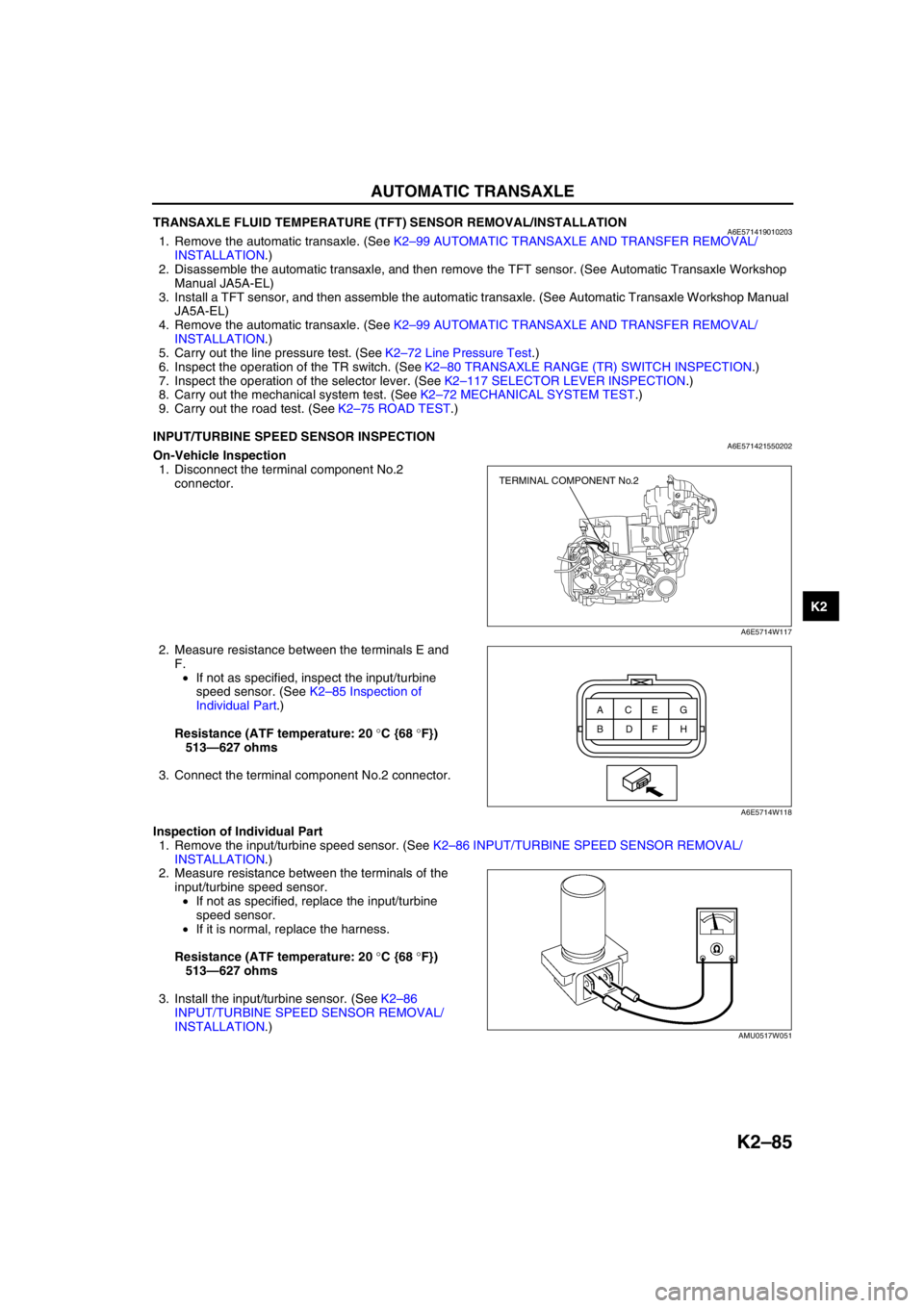
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–85
K2
TRANSAXLE FLUID TEMPERATURE (TFT) SENSOR REMOVAL/INSTALLATIONA6E5714190102031. Remove the automatic transaxle. (See K2–99 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE AND TRANSFER REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION.)
2. Disassemble the automatic transaxle, and then remove the TFT sensor. (See Automatic Transaxle Workshop
Manual JA5A-EL)
3. Install a TFT sensor, and then assemble the automatic transaxle. (See Automatic Transaxle Workshop Manual
JA5A-EL)
4. Remove the automatic transaxle. (See K2–99 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE AND TRANSFER REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION.)
5. Carry out the line pressure test. (See K2–72 Line Pressure Test.)
6. Inspect the operation of the TR switch. (See K2–80 TRANSAXLE RANGE (TR) SWITCH INSPECTION.)
7. Inspect the operation of the selector lever. (See K2–117 SELECTOR LEVER INSPECTION.)
8. Carry out the mechanical system test. (See K2–72 MECHANICAL SYSTEM TEST.)
9. Carry out the road test. (See K2–75 ROAD TEST.)
End Of Sie
INPUT/TURBINE SPEED SENSOR INSPECTIONA6E571421550202On-Vehicle Inspection
1. Disconnect the terminal component No.2
connector.
2. Measure resistance between the terminals E and
F.
•If not as specified, inspect the input/turbine
speed sensor. (See K2–85 Inspection of
Individual Part.)
Resistance (ATF temperature: 20 °C {68 °F})
513—627 ohms
3. Connect the terminal component No.2 connector.
Inspection of Individual Part
1. Remove the input/turbine speed sensor. (See K2–86 INPUT/TURBINE SPEED SENSOR REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION.)
2. Measure resistance between the terminals of the
input/turbine speed sensor.
•If not as specified, replace the input/turbine
speed sensor.
•If it is normal, replace the harness.
Resistance (ATF temperature: 20 °C {68 °F})
513—627 ohms
3. Install the input/turbine sensor. (See K2–86
INPUT/TURBINE SPEED SENSOR REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION.)
End Of Sie
TERMINAL COMPONENT No.2
A6E5714W117
ACEG
BDFH
A6E5714W118
AMU0517W051