MAZDA 626 1987 Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 1987, Model line: 626, Model: MAZDA 626 1987Pages: 1865, PDF Size: 94.35 MB
Page 501 of 1865
IDLE-UP SYSTEM 4B
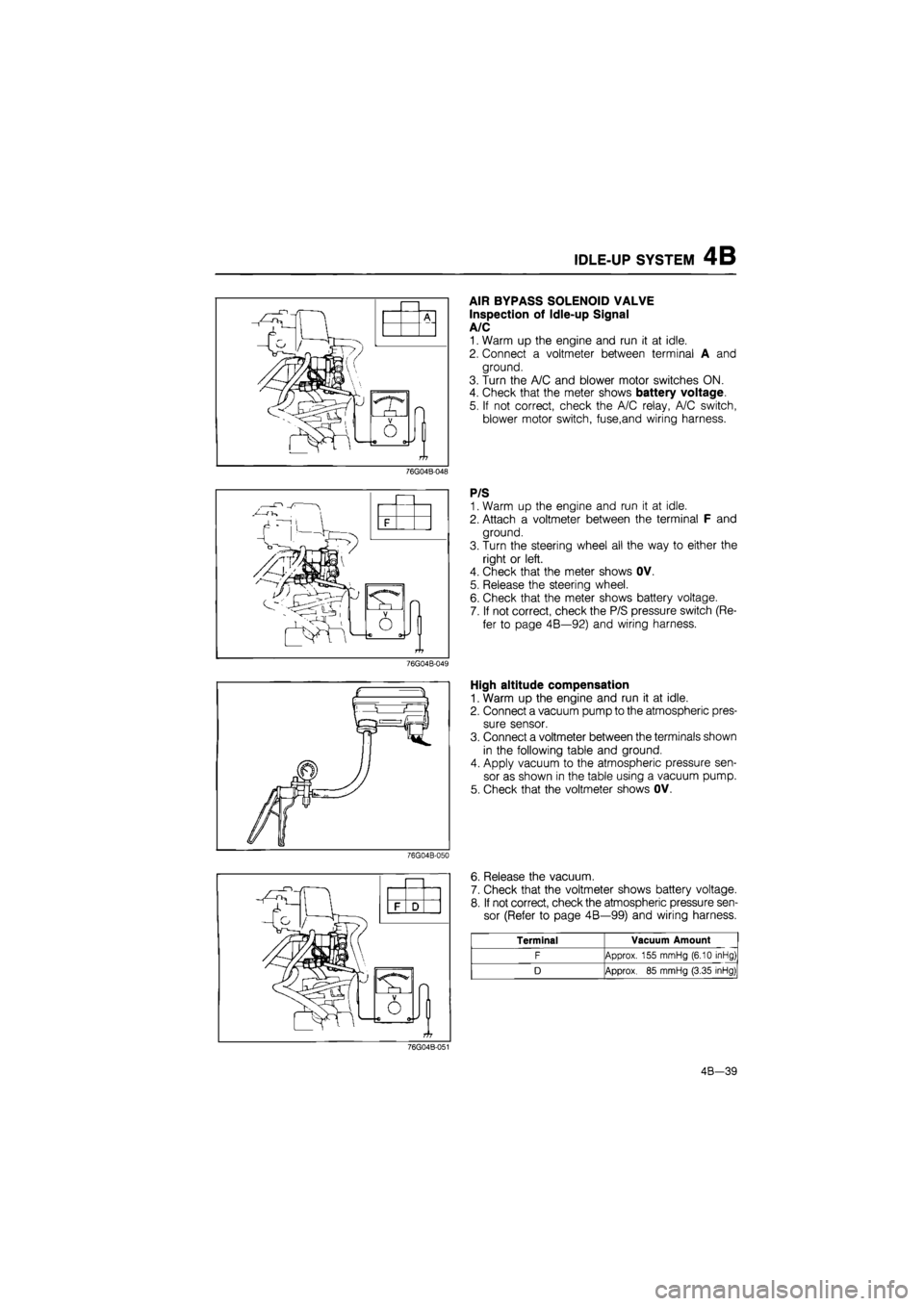
AIR BYPASS SOLENOID VALVE
Inspection of Idle-up Signal
A/C
1. Warm up the engine and run it at idle.
2. Connect a voltmeter between terminal A and
ground.
3. Turn the A/C and blower motor switches ON.
4. Check that the meter shows battery voltage.
5. If not correct, check the A/C relay, A/C switch,
blower motor switch, fuse,and wiring harness.
76G04B-048
P/S
1. Warm up the engine and run it at idle.
2. Attach a voltmeter between the terminal F and
ground.
3. Turn the steering wheel all the way to either the
right or left.
4. Check that the meter shows OV.
5. Release the steering wheel.
6. Check that the meter shows battery voltage.
7. If not correct, check the P/S pressure switch (Re-
fer to page 4B—92) and wiring harness.
76G04B-049
High altitude compensation
1. Warm up the engine and run it at idle.
2. Connect a vacuum pump to the atmospheric pres-
sure sensor.
3. Connect a voltmeter between the terminals shown
in the following table and ground.
4. Apply vacuum to the atmospheric pressure sen-
sor as shown in the table using a vacuum pump.
5. Check that the voltmeter shows OV.
76G04B-050
J
O
6. Release the vacuum.
7. Check that the voltmeter shows battery voltage.
8. If not correct, check the atmospheric pressure sen-
sor (Refer to page 4B—99) and wiring harness.
Terminal Vacuum Amount
F Approx. 155 mmHg (6.10 inHg)
D Approx.
85
mmHg (3.35 inHg)
76G04B-051
4B-39
Page 502 of 1865
4B IDLE-UP SYSTEM
76G04B-052
76G04B-053
76G04B-054
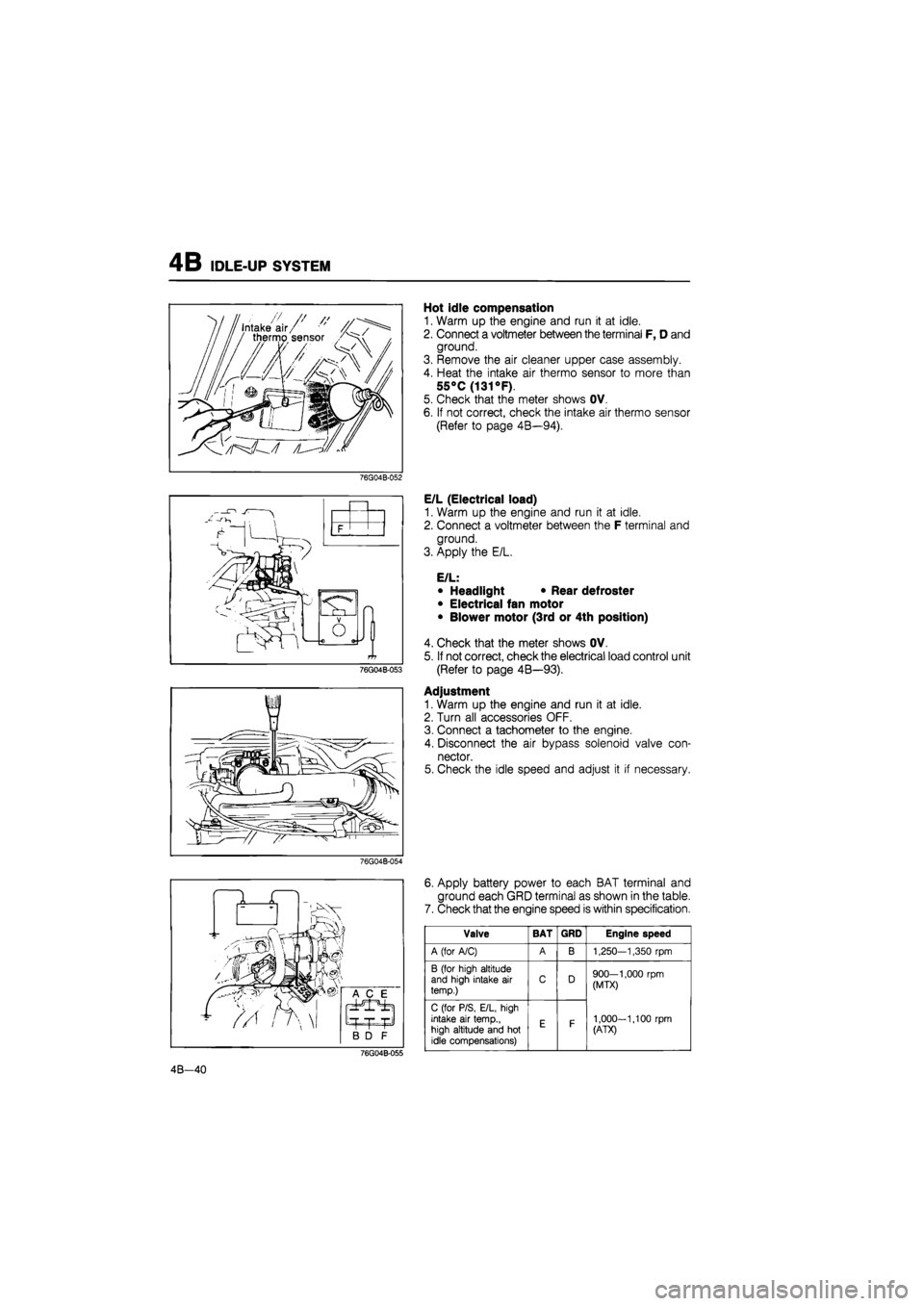
Hot idle compensation
1. Warm up the engine and run it at idle.
2. Connect a voltmeter between the terminal F, D and
ground.
3. Remove the air cleaner upper case assembly.
4. Heat the intake air thermo sensor to more than
55°C
(131
°F).
5. Check that the meter shows OV.
6. If not correct, check the intake air thermo sensor
(Refer to page 4B—94).
E/L (Electrical load)
1. Warm up the engine and run it at idle.
2. Connect a voltmeter between the F terminal and
ground.
3. Apply the E/L.
E/L:
• Headlight • Rear defroster
• Electrical fan motor
• Blower motor (3rd or 4th position)
4. Check that the meter shows OV.
5. If not correct, check the electrical load control unit
(Refer to page 4B—93).
Adjustment
1. Warm up the engine and run it at idle.
2. Turn all accessories OFF.
3. Connect a tachometer to the engine.
4. Disconnect the air bypass solenoid valve con-
nector.
5. Check the idle speed and adjust it if necessary.
6. Apply battery power to each BAT terminal and
ground each GRD terminal as shown in the table.
7. Check that the engine speed is within specification.
76G04B-055
Valve BAT GRD Engine speed
A (for A/C) A B 1,250—1,350
rpm
B (for high altitude and high intake
air
temp.) C D 900—1,000
rpm
(MTX)
1,000-1,100
rpm
(ATX)
C (for P/S, E/L, high intake
air
temp., high altitude and
hot
idle compensations)
E F
900—1,000
rpm
(MTX)
1,000-1,100
rpm
(ATX)
4B—40
Page 503 of 1865

IDLE-UP SYSTEM 4B
8. If not correct, adjust by adjusting the respective
adjusting screw.
9. If there is no idle-up, replace the air bypass sole-
noid valve.
10. Reconnect the connector to the valves.
76G04B-056
4B—41
Page 504 of 1865
4B FUEL SYSTEM
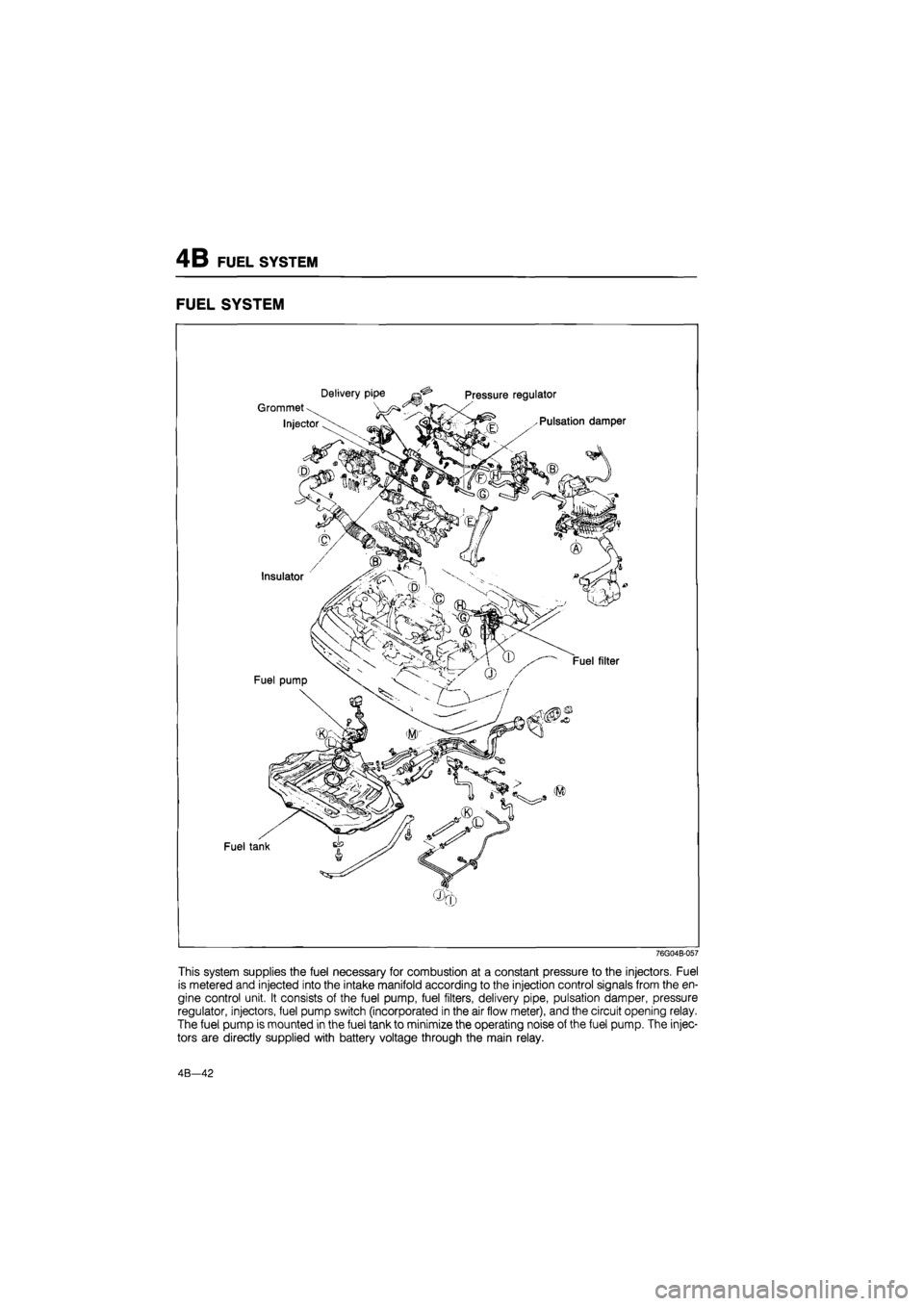
FUEL SYSTEM
76G04B-057
This system supplies the fuel necessary for combustion at a constant pressure to the injectors. Fuel
is metered and injected into the intake manifold according to the injection control signals from the en-
gine control unit. It consists of the fuel pump, fuel filters, delivery pipe, pulsation damper, pressure
regulator, injectors, fuel pump switch (incorporated in the air flow meter), and the circuit opening relay.
The fuel pump is mounted in the fuel tank to minimize the operating noise of the fuel pump. The injec-
tors are directly supplied with battery voltage through the main relay.
4B—42
Page 505 of 1865
FUEL SYSTEM 4B
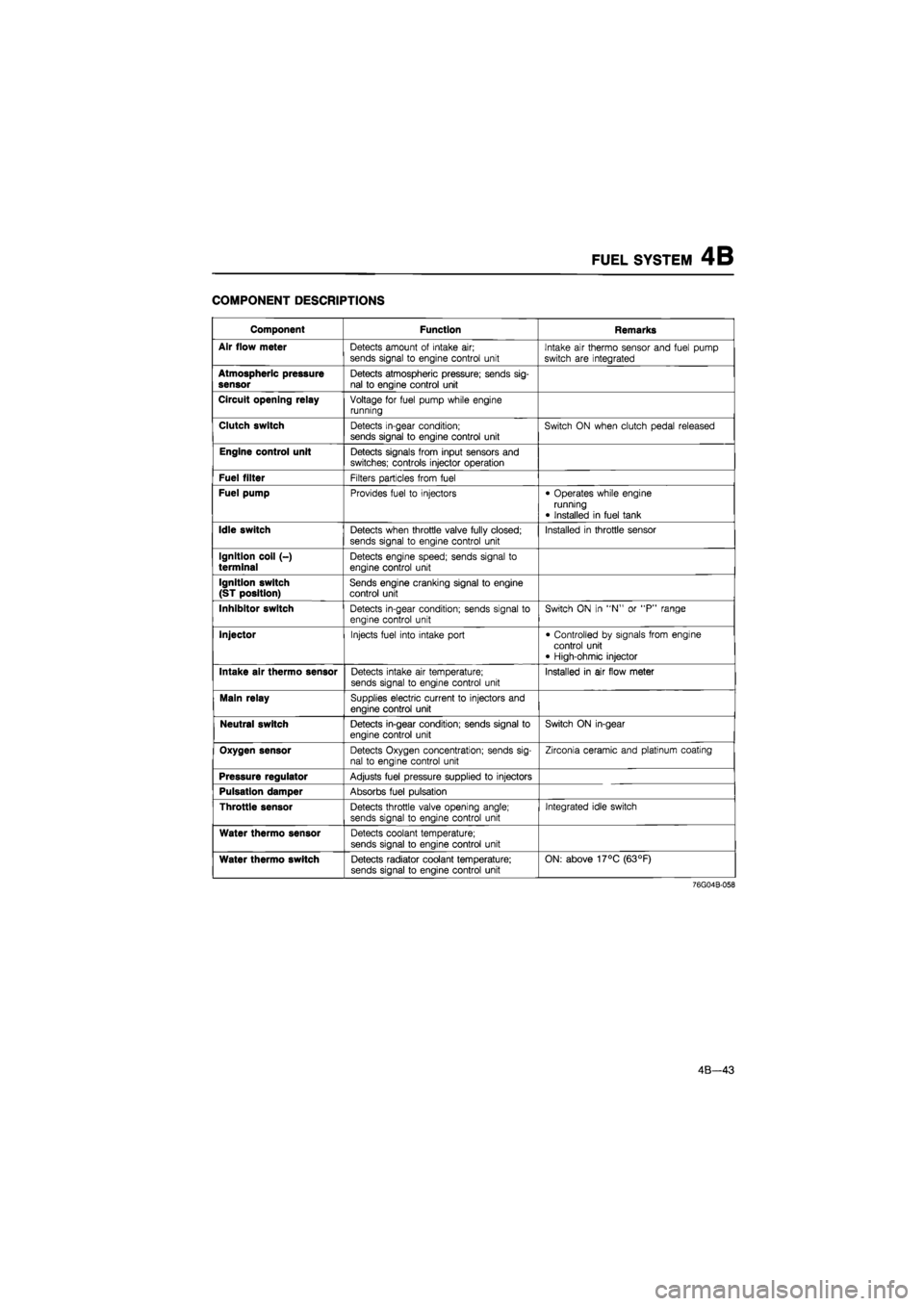
COMPONENT DESCRIPTIONS
Component Function Remarks
Air flow meter
Detects amount
of
intake
air;
sends signal
to
engine control unit Intake
air
thermo sensor and fuel pump
switch
are
integrated
Atmospheric pressure sensor
Detects atmospheric pressure; sends sig-nal
to
engine control unit
Circuit opening relay
Voltage
for
fuel pump while engine running
Clutch switch
Detects in-gear condition; sends signal
to
engine control unit Switch
ON
when clutch pedal released
Engine control unit
Detects signals from input sensors and switches; controls injector operation
Fuel filter
Filters particles from fuel
Fuel pump
Provides fuel
to
injectors • Operates while engine running
• Installed
in
fuel tank
Idle switch
Detects when throttle valve fully closed;
sends signal
to
engine control unit
Installed
in
throttle sensor
Ignition coil (-) terminal
Detects engine speed; sends signal
to
engine control unit
Ignition switch (ST position)
Sends engine cranking signal
to
engine control unit
Inhibitor switch
Detects in-gear condition; sends signal
to
engine control unit
Switch
ON in "N" or "P"
range
Injector
Injects fuel into intake port • Controlled
by
signals from engine control unit • High-ohmic injector
Intake air thermo sensor
Detects intake
air
temperature;
sends signal
to
engine control unit Installed
in air
flow meter
Main relay
Supplies electric current
to
injectors and engine control unit
Neutral switch
Detects in-gear condition; sends signal
to
engine control unit
Switch
ON
in-gear
Oxygen sensor
Detects Oxygen concentration; sends sig-nal
to
engine control unit
Zirconia ceramic and platinum coating
Pressure regulator
Adjusts fuel pressure supplied
to
injectors
Pulsation damper
Absorbs fuel pulsation
Throttle sensor
Detects throttle valve opening angle; sends signal
to
engine control unit
Integrated idle switch
Water thermo sensor
Detects coolant temperature;
sends signal
to
engine control unit
Water thermo switch
Detects radiator coolant temperature; sends signal
to
engine control unit ON: above 17°C (63°F)
76G04B-058
4B—43
Page 506 of 1865

4B FUEL SYSTEM
TROUBLESHOOTING
Check
the
condition
of
the wiring harness and connectors before checking
the
sensors
or
switches.
Possible
cause
Page
V
S E
i
o
o V)
0
e
~
0)
Ju
»
•E
<»
CL
01
3
0
<0
1
£
Oxygen
sensor
s c V
in
V
P
o E k_
•E **
l_
h
O
v
w
Water
thermo
switch
Q.
E
3 Q.
u
Injector
£ 3 3 o d
aj
Engine
con-
trol unit terminal
< £
8
<
Q. Oxygen
sensor
£ t->
0)
>
M Water
thermo
switch
3
u.
Injector
3
u. 3C
3E
3B
Symptom 4B-94 4B-99 4B—98 4B-95 48—97 4B-97 4B-49 4B-S1 4B-48 4B-90 4B-90
Hard start
or
won't start (Cranks
OK)
5 4 1 3 2
Engine While warming
up
4 3 2 1 5
stalls After warming
up
1 3 2 4
Rough Idle While warming
up
4 3 2 1
Rough Idle After warming
up
1 2 4 3
Poor acceleration, hesitation,
or
lack
of
power
1 3 4 2
Runs rough
on
deceleration
1 2
Afterburn
in
exhaust system
1 2
Poor fuel consumption
5 6 4 3 2 1
Falls emission test
1 2
Engine stalls
or
rough after
hot
starting
1 3 2
76G04B-059
4B—44
Page 507 of 1865
FUEL SYSTEM 4B
86U04A-068
FUEL PRESSURE RELEASE AND SERVICING
FUEL SYSTEM
Fuel in the fuel system remains under high pressure
even when the engine is not running.
a) Before disconnecting any fuel line, release the fuel
pressure from the fuel system to reduce the pos-
sibility of injury or fire.
1. Start the engine.
2. Disconnect the circuit opening relay.
3. After the engine stalls, turn OFF the ignition
switch.
4. Reconnect the circuit opening relay.
b) Use a rag as protection from fuel spray when dis-
connecting the hoses.
Plug the hoses after removal.
c) When inspecting the fuel system, use the SST.
86U04A-069
4B—45
Page 508 of 1865
4B FUEL SYSTEM
MULTI-PRESSURE TESTER (49 9200 750A)
HII11I PHS3SUBE lESTtj
as
49 9200 750A
69G04A-099
The MULTI-PRESSURE TESTER (49 9200 750A) has been developed to check the fuel pressure
and intake manifold vacuum. These can easily be inspected by setting the buttons on the tester.
4B—46
Page 509 of 1865

FUEL SYSTEM 4B
Pressure .
regulator ^^ \ To multi-pressure tester
How to Connect Multi-Pressure Tester
Warning
Before connecting the SST, release the fuel
pressure from the fuel system to reduce the
possibility of injury or fire. (Refer to page
4B—45.)
1. Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
2. Disconnect the fuel main hose from the fuel filter.
3. Connect the SST between the fuel main hose and
fuel pump with the adapter.
Caution
Do not reverse the adapter connection.
4. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the pressure
regulator control solenoid valve. Connect the SST
vacuum hose with a three-way joint.
5. Connect the negative battery terminal.
6. Connect the SST to the battery.
86U04A-071
v *
- i\zLTest connector (Yellow)
7. Connect the terminals of the test connector (Yel-
low) with a jumper wire. Turn the ignition switch
ON to operate the fuel pump.
8. Check for fuel leaks.
Caution
After checking for fuel leakage, turn the igni-
tion switch OFF and disconnect the jumper
wire from the test connector.
86U04A-072
4B—47
Page 510 of 1865
4B FUEL SYSTEM
76G04B-061
I i. i { 1 t' i 1 I • i i 1 1 "1 —r
1 . . • , 1 ,
EDO 250
86U04A-074
w Test connector
(Yellow)
86U04A-075
Lever
To fuel pump To pulsation damper
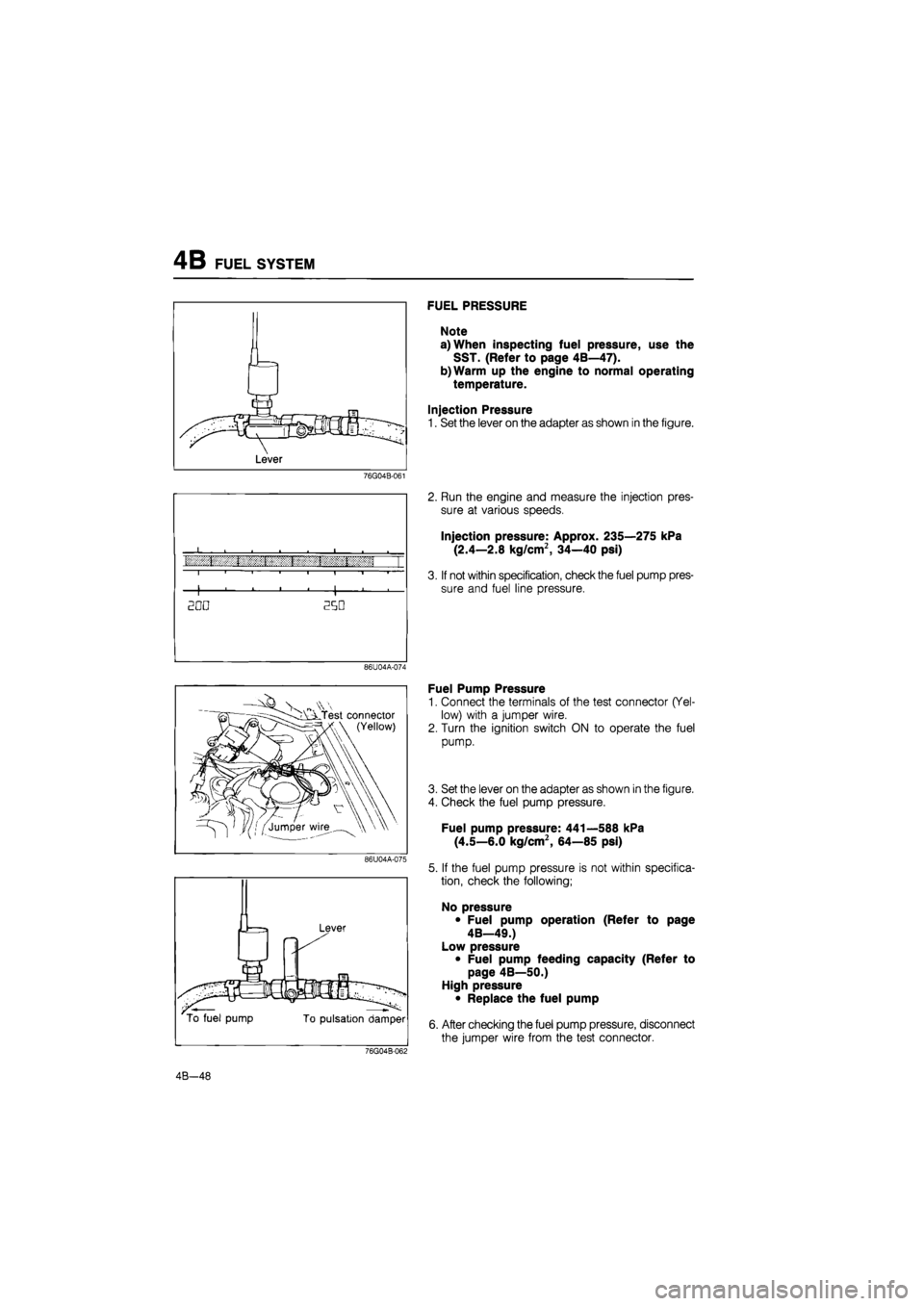
FUEL PRESSURE
Note
a) When inspecting fuel pressure, use the
SST. (Refer to page 4B—47).
b)Warm up the engine to normal operating
temperature.
Injection Pressure
1. Set the lever on the adapter as shown in the figure.
2. Run the engine and measure the injection pres-
sure at various speeds.
Injection pressure: Approx. 235—275 kPa
(2.4—2.8 kg/cm2, 34—40 psi)
3. If not within specification, check the fuel pump pres-
sure and fuel line pressure.
Fuel Pump Pressure
1. Connect the terminals of the test connector (Yel-
low) with a jumper wire.
2. Turn the ignition switch ON to operate the fuel
pump.
3. Set the lever on the adapter as shown in the figure.
4. Check the fuel pump pressure.
Fuel pump pressure: 441—588 kPa
(4.5—6.0 kg/cm2, 64—85 psi)
5. If the fuel pump pressure is not within specifica-
tion, check the following;
No pressure
• Fuel pump operation (Refer to page
4B—49.)
Low pressure
• Fuel pump feeding capacity (Refer to
page 4B—50.)
High pressure
• Replace the fuel pump
6. After checking the fuel pump pressure, disconnect
the jumper wire from the test connector.
76G04B-062
4B—48