NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2005, Model line: NAVARA, Model: NISSAN NAVARA 2005Pages: 3171, PDF Size: 49.59 MB
Page 2471 of 3171
MTC-84
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
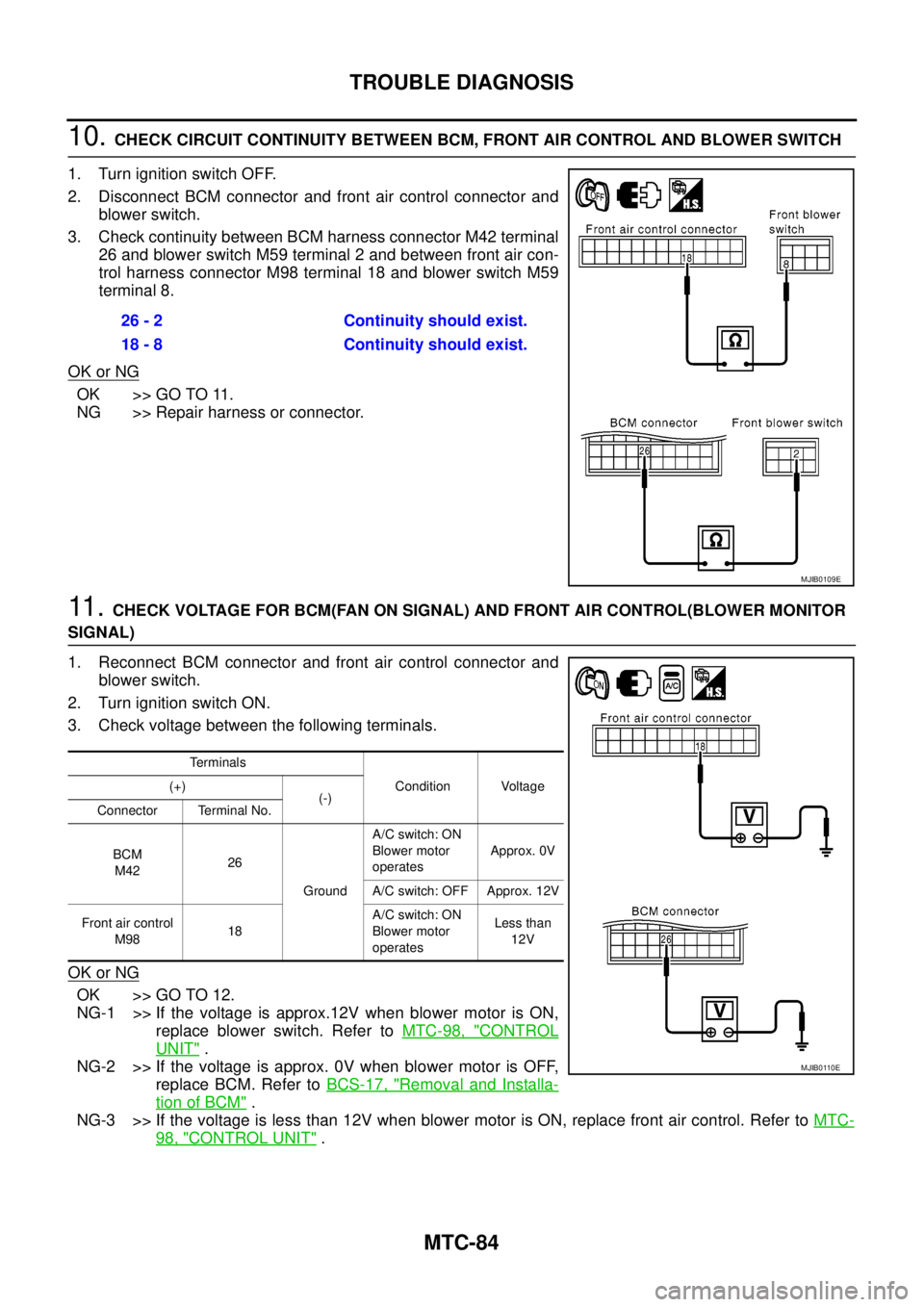
10.CHECK CIRCUIT CONTINUITY BETWEEN BCM, FRONT AIR CONTROL AND BLOWER SWITCH
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect BCM connector and front air control connector and
blower switch.
3. Check continuity between BCM harness connector M42 terminal
26 and blower switch M59 terminal 2 and between front air con-
trol harness connector M98 terminal 18 and blower switch M59
terminal 8.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 11.
NG >> Repair harness or connector.
11 .CHECK VOLTAGE FOR BCM(FAN ON SIGNAL) AND FRONT AIR CONTROL(BLOWER MONITOR
SIGNAL)
1. Reconnect BCM connector and front air control connector and
blower switch.
2. Turn ignition switch ON.
3. Check voltage between the following terminals.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 12.
NG-1 >> If the voltage is approx.12V when blower motor is ON,
replace blower switch. Refer toMTC-98, "
CONTROL
UNIT".
NG-2 >> If the voltage is approx. 0V when blower motor is OFF,
replace BCM. Refer toBCS-17, "
Removal and Installa-
tion of BCM".
NG-3 >> If the voltage is less than 12V when blower motor is ON, replace front air control. Refer toMTC-
98, "CONTROL UNIT". 26 - 2 Continuity should exist.
18 - 8 Continuity should exist.
MJIB0109E
Terminals
Condition Voltage (+)
(-)
Connector Terminal No.
BCM
M4226
GroundA/C switch: ON
Blower motor
operatesApprox. 0V
A/C switch: OFF Approx. 12V
Front air control
M9818A/C switch: ON
Blower motor
operatesLess than
12V
MJIB0110E
Page 2472 of 3171

TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
MTC-85
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
MTC
12.CHECK SELF-DIAGNOSTIC RESULT
Perform self-diagnosis. Refer toAT C - 5 5 , "
A/C System Self-diagnosis Function"
OK or NG
OK >> Inspection End.
NG >> Refer toAT C - 5 6 , "
SELF-DIAGNOSIS CODE CHART".
COMPONENT INSPECTION
Refrigerant Pressure Sensor
The refrigerant pressure sensor is attached to the condenser.
MJIB0197E
Page 2473 of 3171

MTC-86
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
Insufficient Cooling
EJS005GM
SYMPTOM: Insufficient cooling
INSPECTION FLOW
*1 .MTC-53, "Operational Check".*2MTC-51, "A/C System Self-diagno-
sis Function".*3MTC-52, "
SELF-DIAGNOSIS CODE
CHART".
*4EC-132, "
Description".*5MTC-4, "Contaminated Refrigerant".*6 .MTC-87, "PERFORMANCE TEST
DIAGNOSES"
*7MTC-89, "Test Reading"*8EM-12, "Checking Drive Belts"
MJIB0244E
Page 2474 of 3171
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
MTC-87
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
MTC
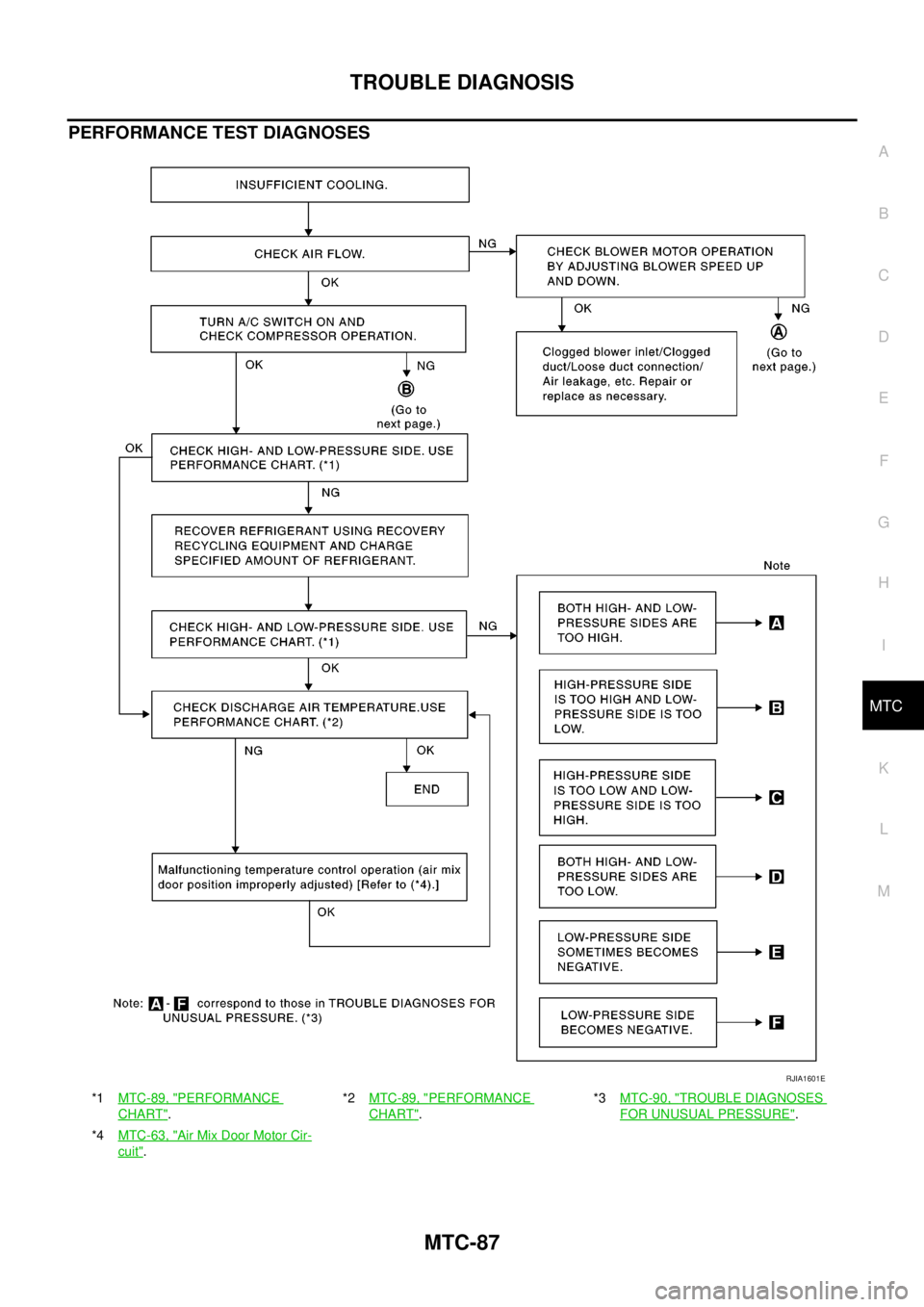
PERFORMANCE TEST DIAGNOSES
*1MTC-89, "PERFORMANCE
CHART".*2MTC-89, "
PERFORMANCE
CHART".*3MTC-90, "
TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
FOR UNUSUAL PRESSURE".
*4MTC-63, "
AirMixDoorMotorCir-
cuit".
RJIA1601E
Page 2475 of 3171
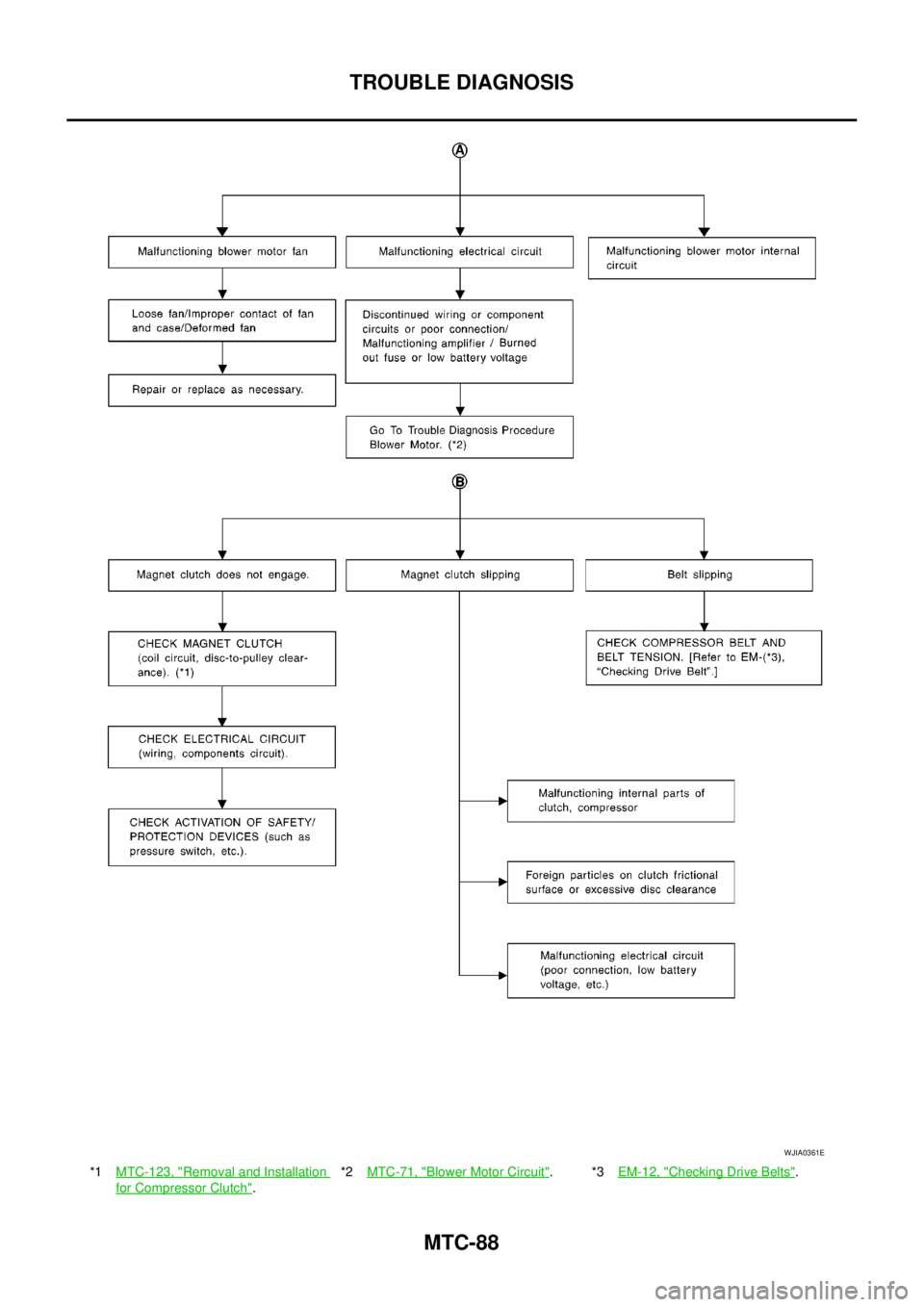
MTC-88
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
*1MTC-123, "Removal and Installation
for Compressor Clutch".*2MTC-71, "
Blower Motor Circuit".*3EM-12, "Checking Drive Belts".
WJIA0361E
Page 2476 of 3171

TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
MTC-89
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
MTC
PERFORMANCE CHART
Test Condition
Testing must be performed as follows:
Test Reading
Recirculating-to-discharge Air Temperature Table
Ambient Air Temperature-to-operating Pressure Table
Vehicle location Indoors or in the shade (in a well-ventilated place)
Doors Closed
Door window Open
Hood Open
TEMP. Max. COLD
Mode switch
(Ventilation) set
Recirculation (REC) switch
(Recirculation) set
Blower speedMax. speed set
Engine speed Idle speed
Operate the air conditioning system for 10 minutes before taking measurements.
Inside air (Recirculating air) at blower assembly inlet
Discharge air temperature at center ventilator
°C(°F) Relative humidity
%Air temperature
°C(°F)
40 - 6020 (68) 4.9 - 6.9 (41 - 44)
25 (77) 8.1 - 10.8 (47- 51)
30 (86) 12.1 - 15.1 (54 - 59)
35 (95) 16.9 - 20.5 (62 - 69)
60 - 8020 (68) 6.9 - 8.8 (44 - 48)
25 (77) 10.6 - 13.1 (51 - 56)
30 (86) 15.1 - 18.2 (59 - 65)
35 (95) 20.5 - 24.0 (69 - 75)
Ambient air
High-pressure (Discharge side)
kPa (kg/cm
2,psi)Low-pressure (Suction side)
kPa (kg/cm2, psi) Relative humidity
%Air temperature
°C(°F)
40 - 6020 (68)920 - 1,020
(9.38 - 10.40, 133.4 - 147.9)190 - 210
(1.94 - 2.14, 27.5 - 30.4)
25 (77)1,250 - 1,390
(12.74 - 14.17, 181.2 - 201.5)240 - 270
(2.45 - 2.75, 34.8 - 39.1)
30 (86)1,590 - 1,770
(16.21 - 18.04, 230.5 - 256.6)300 - 330
(3.06 - 3.36, 43.5 - 47.8)
35 (95)1,900 - 2,110
(19.37 - 21.51, 275.4 - 305.9)360 - 400
(3.67 - 4.08, 52.2 - 58.0)
60 - 8020 (68)1,020 - 1,120
(10.40 - 11.42, 147.9 - 162.3)210 - 230
(2.14 - 2.34, 30.4 - 33.3)
25 (77)1,390 - 1,530
(14.17 - 15.60, 201.5 - 221.8)270 - 300
(2.75 - 3.06, 39.1 - 43.5)
30 (86)1,770 - 1,950
(18.04 - 19.88, 256.6 - 282.7)330 - 360
(3.36 - 3.67, 47.8 - 52.2)
35 (95)2,110 - 2,320
(21.51 - 23.65, 305.9 - 336.3)400 - 440
(4.08 - 4.49, 58.0 - 63.8)
Page 2477 of 3171
MTC-90
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
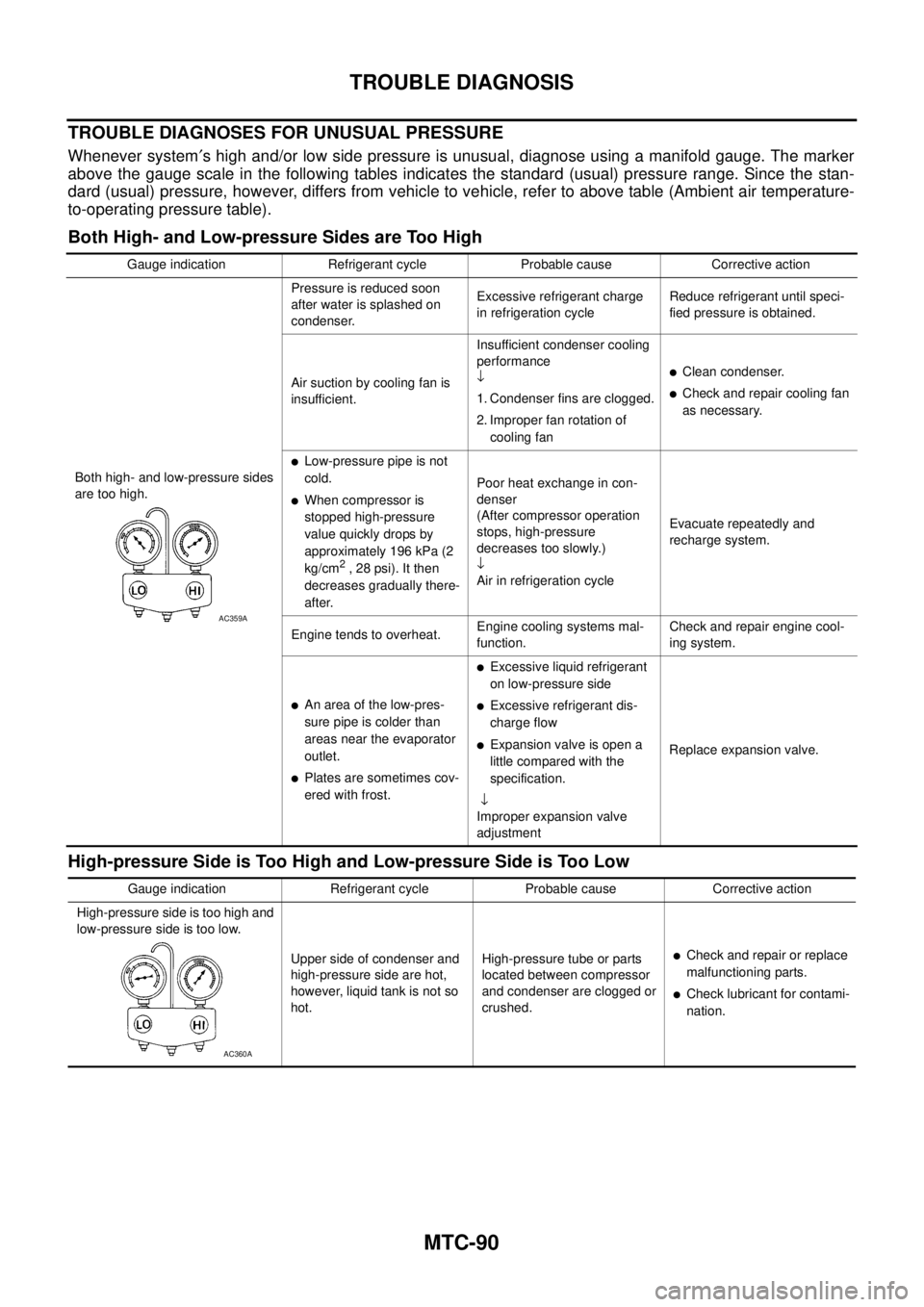
TROUBLE DIAGNOSES FOR UNUSUAL PRESSURE
Whenever system¢s high and/or low side pressure is unusual, diagnose using a manifold gauge. The marker
above the gauge scale in the following tables indicates the standard (usual) pressure range. Since the stan-
dard (usual) pressure, however, differs from vehicle to vehicle, refer to above table (Ambient air temperature-
to-operating pressure table).
Both High- and Low-pressure Sides are Too High
High-pressure Side is Too High and Low-pressure Side is Too Low
Gauge indication Refrigerant cycle Probable cause Corrective action
Both high- and low-pressure sides
are too high.Pressure is reduced soon
after water is splashed on
condenser.Excessive refrigerant charge
in refrigeration cycleReduce refrigerant until speci-
fied pressure is obtained.
Air suction by cooling fan is
insufficient.Insufficient condenser cooling
performance
¯
1. Condenser fins are clogged.
2. Improper fan rotation of
cooling fan
lClean condenser.
lCheck and repair cooling fan
as necessary.
lLow-pressure pipe is not
cold.
lWhen compressor is
stopped high-pressure
value quickly drops by
approximately 196 kPa (2
kg/cm
2,28psi).Itthen
decreases gradually there-
after.Poor heat exchange in con-
denser
(After compressor operation
stops, high-pressure
decreases too slowly.)
¯
Air in refrigeration cycleEvacuate repeatedly and
recharge system.
Engine tends to overheat.Engine cooling systems mal-
function.Check and repair engine cool-
ing system.
lAn area of the low-pres-
sure pipe is colder than
areas near the evaporator
outlet.
lPlates are sometimes cov-
ered with frost.
lExcessive liquid refrigerant
on low-pressure side
lExcessive refrigerant dis-
charge flow
lExpansion valve is open a
littlecomparedwiththe
specification.
¯
Improper expansion valve
adjustmentReplace expansion valve.
AC359A
Gauge indication Refrigerant cycle Probable cause Corrective action
High-pressure side is too high and
low-pressure side is too low.
Upper side of condenser and
high-pressure side are hot,
however, liquid tank is not so
hot.High-pressure tube or parts
located between compressor
and condenser are clogged or
crushed.
lCheck and repair or replace
malfunctioning parts.
lCheck lubricant for contami-
nation.
AC360A
Page 2478 of 3171
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
MTC-91
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
MTC
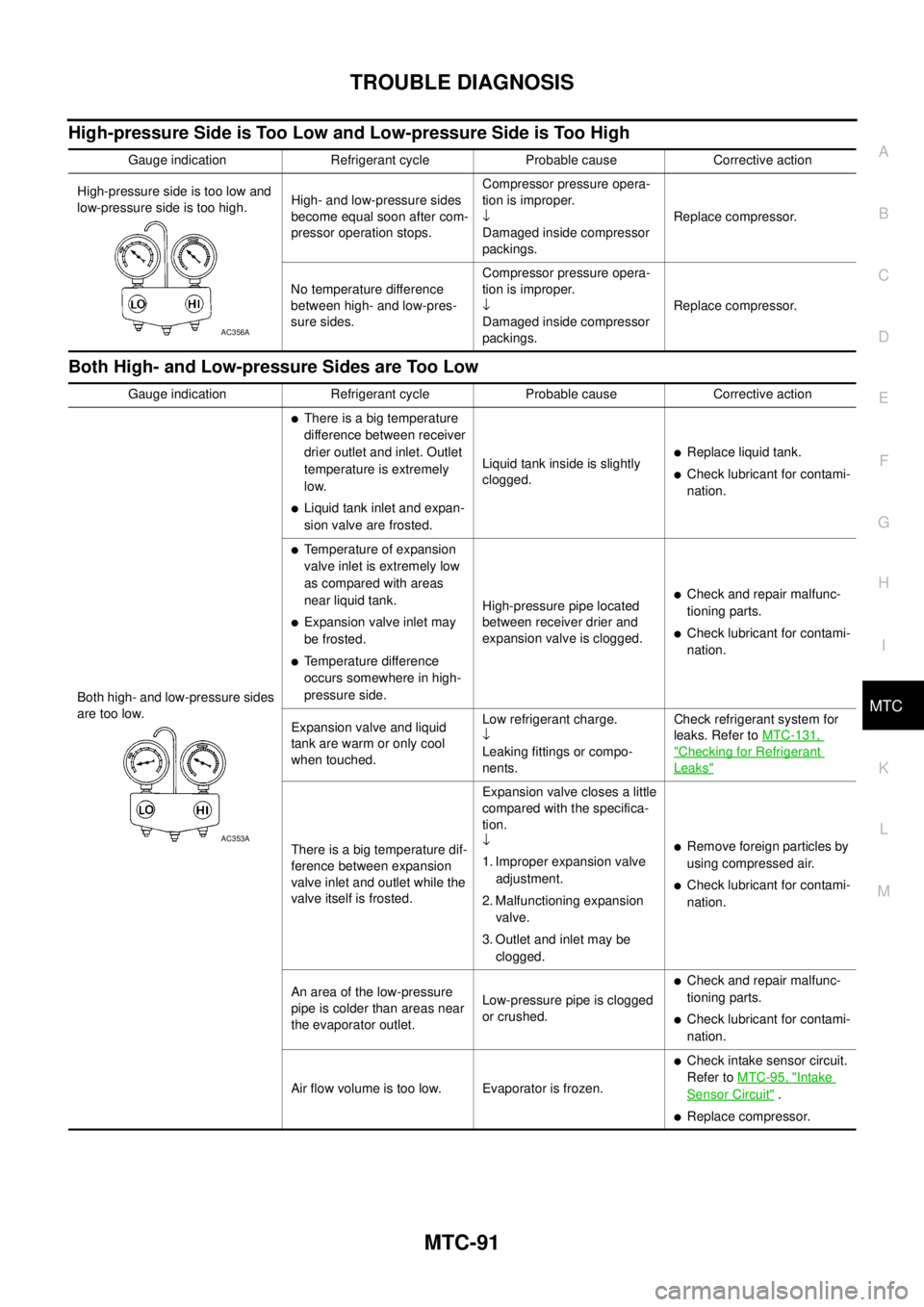
High-pressure Side is Too Low and Low-pressure Side is Too High
Both High- and Low-pressure Sides are Too Low
Gauge indication Refrigerant cycle Probable cause Corrective action
High-pressure side is too low and
low-pressure side is too high.High- and low-pressure sides
become equal soon after com-
pressor operation stops.Compressor pressure opera-
tion is improper.
¯
Damaged inside compressor
packings.Replace compressor.
No temperature difference
between high- and low-pres-
sure sides.Compressor pressure opera-
tion is improper.
¯
Damaged inside compressor
packings.Replace compressor.
AC356A
Gauge indication Refrigerant cycle Probable cause Corrective action
Both high- and low-pressure sides
are too low.
lThere is a big temperature
difference between receiver
drier outlet and inlet. Outlet
temperature is extremely
low.
lLiquid tank inlet and expan-
sion valve are frosted.Liquid tank inside is slightly
clogged.
lReplace liquid tank.
lCheck lubricant for contami-
nation.
lTemperature of expansion
valve inlet is extremely low
as compared with areas
near liquid tank.
lExpansion valve inlet may
be frosted.
lTemperature difference
occurs somewhere in high-
pressure side.High-pressure pipe located
between receiver drier and
expansion valve is clogged.
lCheck and repair malfunc-
tioning parts.
lCheck lubricant for contami-
nation.
Expansion valve and liquid
tank are warm or only cool
when touched.Low refrigerant charge.
¯
Leaking fittings or compo-
nents.Check refrigerant system for
leaks. Refer toMTC-131,
"Checking for Refrigerant
Leaks"
There is a big temperature dif-
ference between expansion
valve inlet and outlet while the
valve itself is frosted.Expansion valve closes a little
compared with the specifica-
tion.
¯
1. Improper expansion valve
adjustment.
2. Malfunctioning expansion
valve.
3. Outlet and inlet may be
clogged.lRemove foreign particles by
using compressed air.
lCheck lubricant for contami-
nation.
An area of the low-pressure
pipe is colder than areas near
the evaporator outlet.Low-pressure pipe is clogged
or crushed.
lCheck and repair malfunc-
tioning parts.
lCheck lubricant for contami-
nation.
Air flow volume is too low. Evaporator is frozen.
lCheck intake sensor circuit.
Refer toMTC-95, "
Intake
Sensor Circuit".
lReplace compressor.
AC353A
Page 2479 of 3171
MTC-92
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
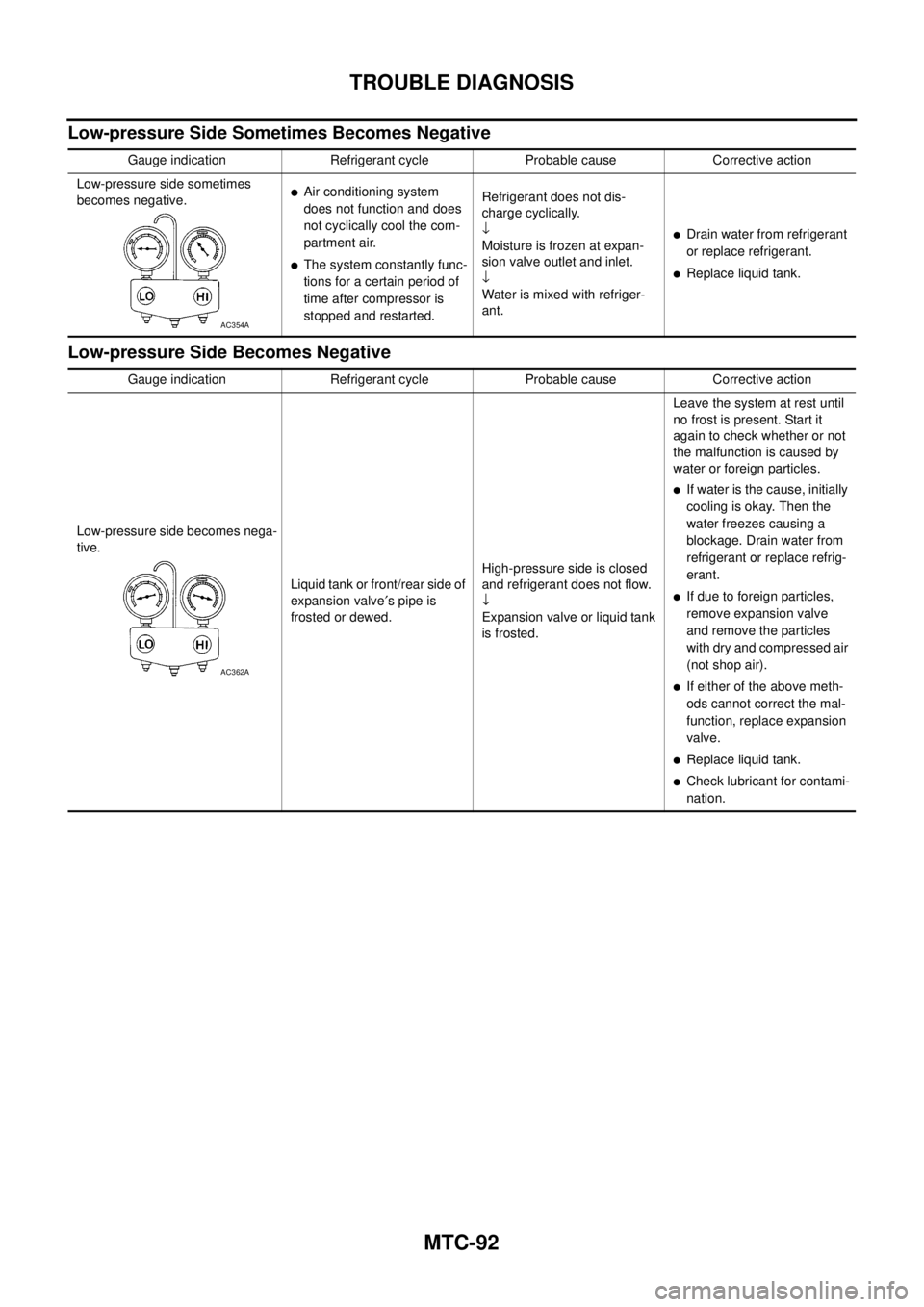
Low-pressure Side Sometimes Becomes Negative
Low-pressure Side Becomes Negative
Gauge indication Refrigerant cycle Probable cause Corrective action
Low-pressure side sometimes
becomes negative.
lAir conditioning system
does not function and does
not cyclically cool the com-
partment air.
lThe system constantly func-
tions for a certain period of
time after compressor is
stopped and restarted.Refrigerant does not dis-
charge cyclically.
¯
Moisture is frozen at expan-
sion valve outlet and inlet.
¯
Water is mixed with refriger-
ant.
lDrain water from refrigerant
or replace refrigerant.
lReplace liquid tank.
AC354A
Gauge indication Refrigerant cycle Probable cause Corrective action
Low-pressure side becomes nega-
tive.
Liquid tank or front/rear side of
expansion valve¢spipeis
frosted or dewed.High-pressure side is closed
and refrigerant does not flow.
¯
Expansion valve or liquid tank
is frosted.Leave the system at rest until
no frost is present. Start it
again to check whether or not
the malfunction is caused by
waterorforeignparticles.
lIf water is the cause, initially
cooling is okay. Then the
water freezes causing a
blockage. Drain water from
refrigerant or replace refrig-
erant.
lIf due to foreign particles,
remove expansion valve
and remove the particles
with dry and compressed air
(not shop air).
lIf either of the above meth-
ods cannot correct the mal-
function, replace expansion
valve.
lReplace liquid tank.
lCheck lubricant for contami-
nation.
AC362A
Page 2480 of 3171
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
MTC-93
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
MTC
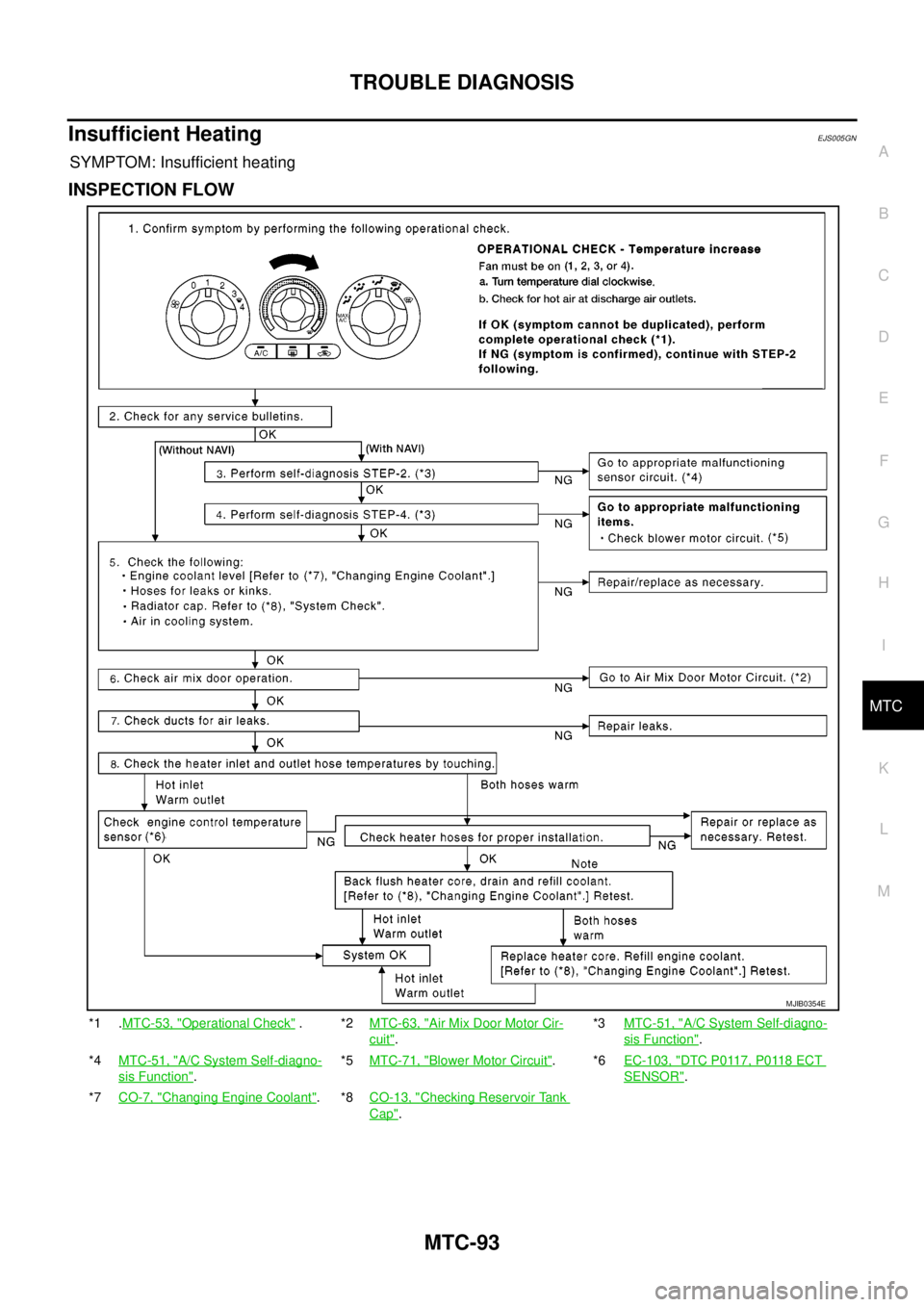
Insufficient HeatingEJS005GN
SYMPTOM: Insufficient heating
INSPECTION FLOW
*1 .MTC-53, "Operational Check".*2MTC-63, "Air Mix Door Motor Cir-
cuit".*3MTC-51, "
A/C System Self-diagno-
sis Function".
*4MTC-51, "
A/C System Self-diagno-
sis Function".*5MTC-71, "
Blower Motor Circuit".*6EC-103, "DTC P0117, P0118 ECT
SENSOR".
*7CO-7, "
Changing Engine Coolant".*8CO-13, "Checking Reservoir Tank
Cap".
MJIB0354E