NISSAN PICK-UP 1998 Repair Manual
Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 1998, Model line: PICK-UP, Model: NISSAN PICK-UP 1998Pages: 1659, PDF Size: 53.39 MB
Page 831 of 1659

Voltage check method
1. Remove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads (i.e. SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid dis-
connected) powered through the fuse.
2. Turn the ignition key to the ON or START position. Verify battery voltage at the B
+side of the fuse ter-
minal (one lead on the B
+terminal side of the fuse block and one lead on a known good ground).
3. With SW1 open and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
4. With SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check
for voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
5. With SW1 closed, relay contacts jumped with fused jumper wire check for voltage.
voltage; short is down the circuit of the relay or between the relay and the disconnected solenoid
(point C).
no voltage; retrace steps and check power to fuse block.
GROUND INSPECTION
Ground connections are very important to the proper operation of electrical and electronic circuits. Ground
connections are often exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corrosion (rust) can
become an unwanted resistance. This unwanted resistance can change the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper grounding. A loose or corroded ground can
drastically affect an electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can easily affect the circuit.
Even when the ground connection looks clean, there can be a thin film of rust on the surface.
When inspecting a ground connection follow these rules:
1. Remove the ground bolt screw or clip.
2. Inspect all mating surfaces for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
3. Clean as required to assure good contact.
4. Reinstall bolt or screw securely.
5. Inspect for ``add-on'' accessories which may be interfering with the ground circuit.
6. If several wires are crimped into one ground eyelet terminal, check for proper crimps. Make sure all of
the wires are clean, securely fastened and providing a good ground path. If multiple wires are cased in
one eyelet make sure no ground wires have excess wire insulation.
SGI853
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS
FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont'd)
GI-27
Page 832 of 1659
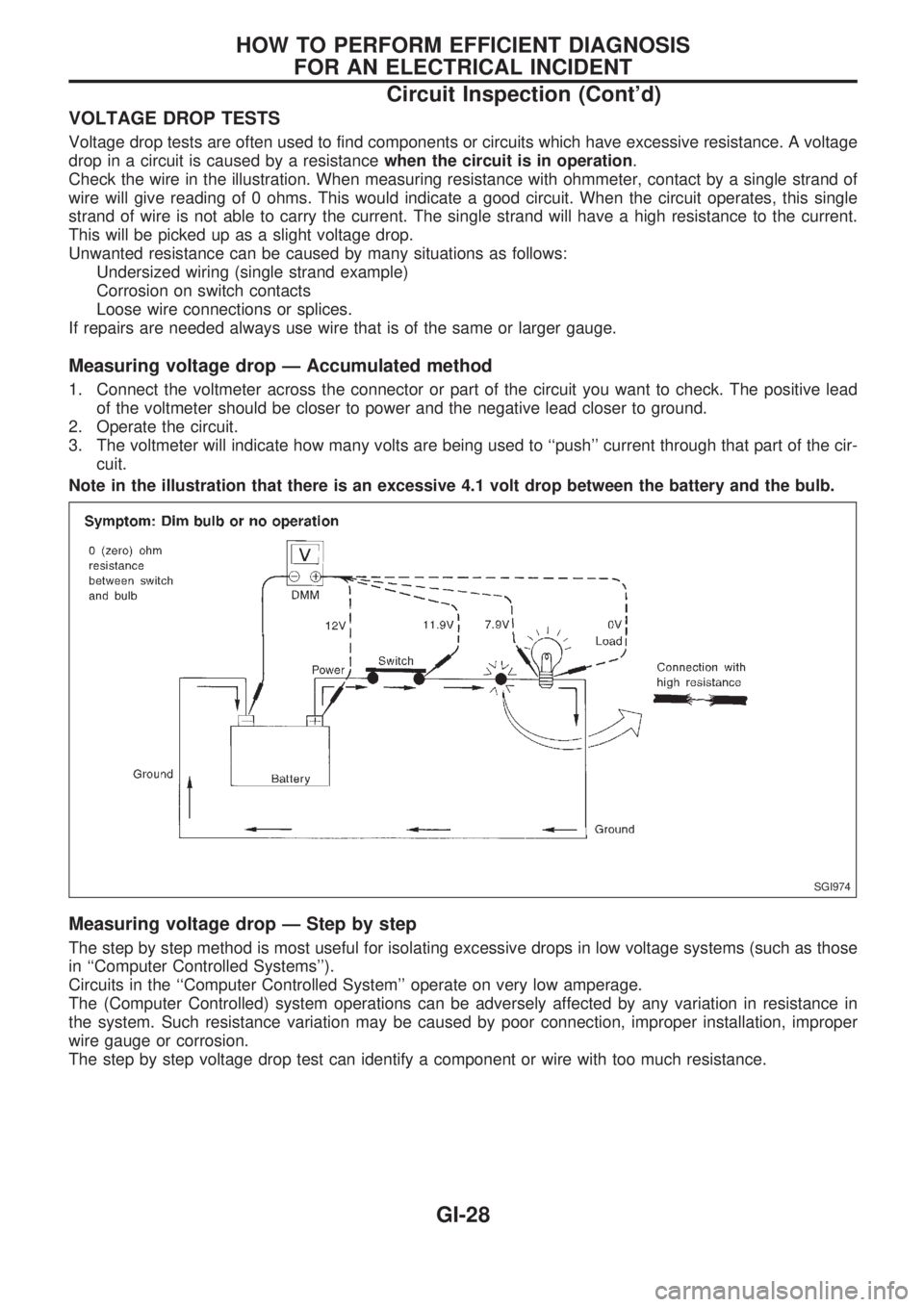
VOLTAGE DROP TESTS
Voltage drop tests are often used to find components or circuits which have excessive resistance. A voltage
drop in a circuit is caused by a resistancewhen the circuit is in operation.
Check the wire in the illustration. When measuring resistance with ohmmeter, contact by a single strand of
wire will give reading of 0 ohms. This would indicate a good circuit. When the circuit operates, this single
strand of wire is not able to carry the current. The single strand will have a high resistance to the current.
This will be picked up as a slight voltage drop.
Unwanted resistance can be caused by many situations as follows:
Undersized wiring (single strand example)
Corrosion on switch contacts
Loose wire connections or splices.
If repairs are needed always use wire that is of the same or larger gauge.
Measuring voltage drop Ð Accumulated method
1. Connect the voltmeter across the connector or part of the circuit you want to check. The positive lead
of the voltmeter should be closer to power and the negative lead closer to ground.
2. Operate the circuit.
3. The voltmeter will indicate how many volts are being used to ``push'' current through that part of the cir-
cuit.
Note in the illustration that there is an excessive 4.1 volt drop between the battery and the bulb.
Measuring voltage drop Ð Step by step
The step by step method is most useful for isolating excessive drops in low voltage systems (such as those
in ``Computer Controlled Systems'').
Circuits in the ``Computer Controlled System'' operate on very low amperage.
The (Computer Controlled) system operations can be adversely affected by any variation in resistance in
the system. Such resistance variation may be caused by poor connection, improper installation, improper
wire gauge or corrosion.
The step by step voltage drop test can identify a component or wire with too much resistance.
SGI974
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS
FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont'd)
GI-28
Page 833 of 1659

SGI854
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS
FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont'd)
GI-29
Page 834 of 1659
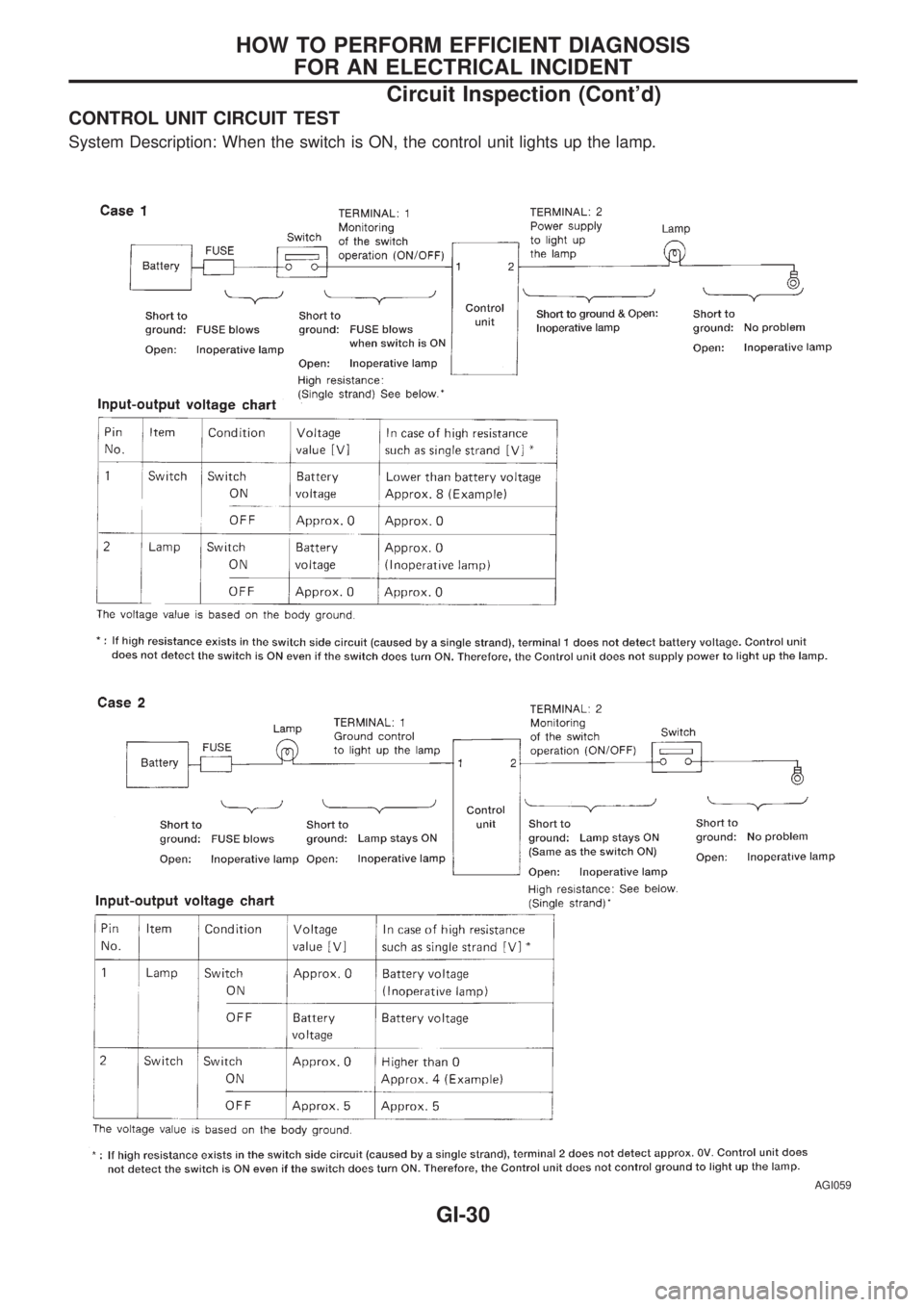
CONTROL UNIT CIRCUIT TEST
System Description: When the switch is ON, the control unit lights up the lamp.
AGI059
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS
FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont'd)
GI-30
Page 835 of 1659
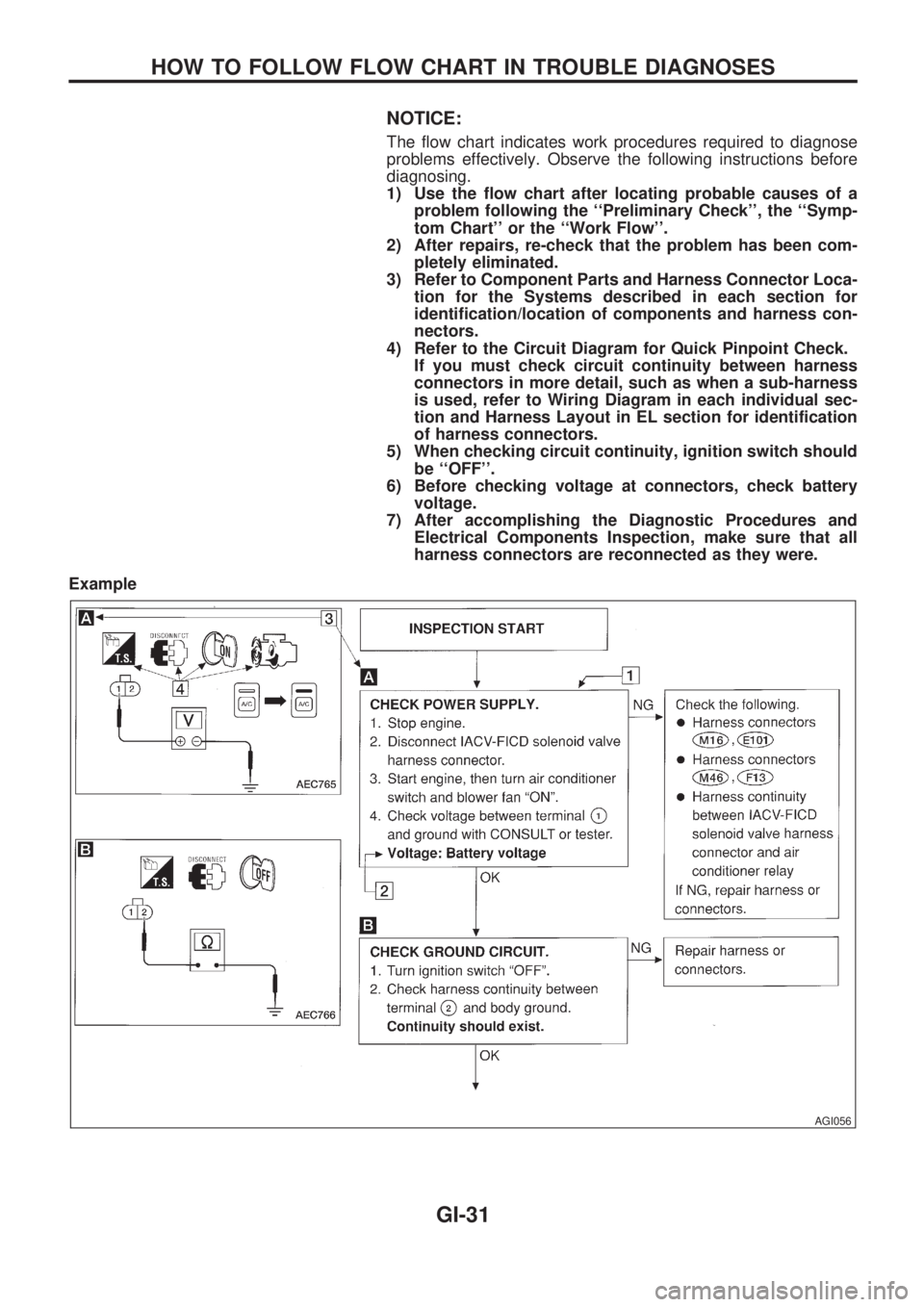
NOTICE:
The flow chart indicates work procedures required to diagnose
problems effectively. Observe the following instructions before
diagnosing.
1) Use the flow chart after locating probable causes of a
problem following the ``Preliminary Check'', the ``Symp-
tom Chart'' or the ``Work Flow''.
2) After repairs, re-check that the problem has been com-
pletely eliminated.
3) Refer to Component Parts and Harness Connector Loca-
tion for the Systems described in each section for
identification/location of components and harness con-
nectors.
4) Refer to the Circuit Diagram for Quick Pinpoint Check.
If you must check circuit continuity between harness
connectors in more detail, such as when a sub-harness
is used, refer to Wiring Diagram in each individual sec-
tion and Harness Layout in EL section for identification
of harness connectors.
5) When checking circuit continuity, ignition switch should
be ``OFF''.
6) Before checking voltage at connectors, check battery
voltage.
7) After accomplishing the Diagnostic Procedures and
Electrical Components Inspection, make sure that all
harness connectors are reconnected as they were.
Example
AGI056
HOW TO FOLLOW FLOW CHART IN TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
GI-31
Page 836 of 1659

How to Follow This Flow Chart
Work and diagnostic procedure
Start to diagnose a problem using procedures indicated in
enclosed blocks, as shown in the following example.
CHECK POWER SUPPLY.
1) Turn ignition switch ``ON''.
2) Check voltage between terminal
V1and ground.
Battery voltage should exist.
bCheck item being performed.
Procedure, steps or
measurement results
Measurement results
Required results are indicated in bold type in the correspond-
ing block, as shown below:
These have the following meanings:
Battery voltage®11 - 14V or approximately 12V
Voltage: Approximately 0V®Less than 1V
Cross reference of work symbols in the text and
illustrations
Illustrations are provided as visual aids for work procedures.
For example, symbol
indicated in the left upper portion of
each illustration corresponds with the symbol in the flow chart
for easy identification. More precisely, the procedure under
the ``CHECK POWER SUPPLY'' outlined previously is indi-
cated by illustration
.
Symbols used in illustrations
Symbols included in illustrations refer to measurements or
procedures. Before diagnosing a problem, familiarize your-
self with each symbol.
DIRECTION MARK
Refer to ``CONNECTOR SYMBOLS'' on GI-13.
HOW TO FOLLOW FLOW CHART IN TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
GI-32
Page 837 of 1659
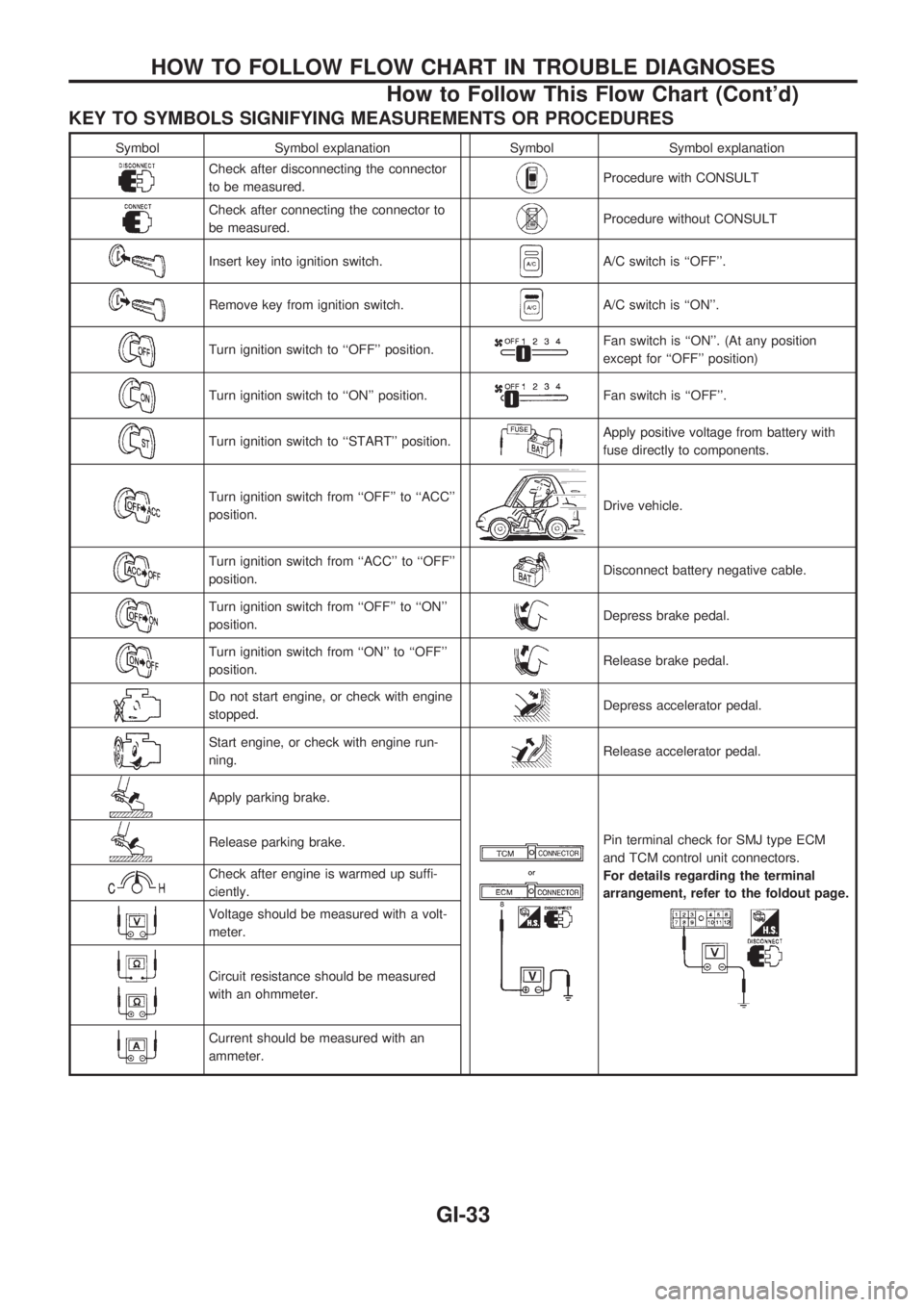
KEY TO SYMBOLS SIGNIFYING MEASUREMENTS OR PROCEDURES
Symbol Symbol explanation Symbol Symbol explanation
Check after disconnecting the connector
to be measured.Procedure with CONSULT
Check after connecting the connector to
be measured.Procedure without CONSULT
Insert key into ignition switch.A/C switch is ``OFF''.
Remove key from ignition switch.A/C switch is ``ON''.
Turn ignition switch to ``OFF'' position.Fan switch is ``ON''. (At any position
except for ``OFF'' position)
Turn ignition switch to ``ON'' position.Fan switch is ``OFF''.
Turn ignition switch to ``START'' position.Apply positive voltage from battery with
fuse directly to components.
Turn ignition switch from ``OFF'' to ``ACC''
position.Drive vehicle.
Turn ignition switch from ``ACC'' to ``OFF''
position.Disconnect battery negative cable.
Turn ignition switch from ``OFF'' to ``ON''
position.Depress brake pedal.
Turn ignition switch from ``ON'' to ``OFF''
position.Release brake pedal.
Do not start engine, or check with engine
stopped.Depress accelerator pedal.
Start engine, or check with engine run-
ning.Release accelerator pedal.
Apply parking brake.
Pin terminal check for SMJ type ECM
and TCM control unit connectors.
For details regarding the terminal
arrangement, refer to the foldout page.Release parking brake.
Check after engine is warmed up suffi-
ciently.
Voltage should be measured with a volt-
meter.
Circuit resistance should be measured
with an ohmmeter.
Current should be measured with an
ammeter.
HOW TO FOLLOW FLOW CHART IN TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
How to Follow This Flow Chart (Cont'd)
GI-33
Page 838 of 1659
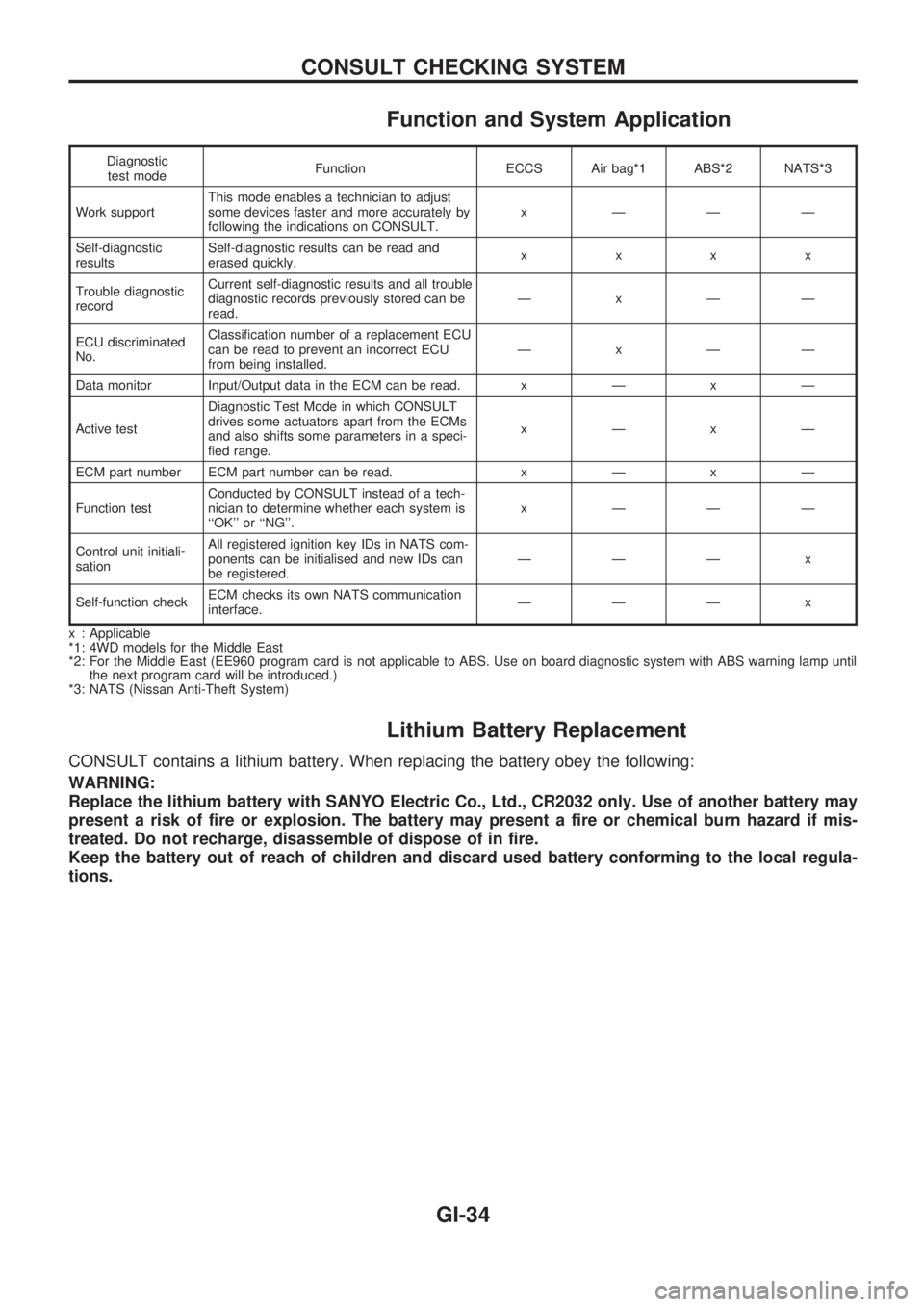
Function and System Application
Diagnostic
test modeFunction ECCS Air bag*1 ABS*2 NATS*3
Work supportThis mode enables a technician to adjust
some devices faster and more accurately by
following the indications on CONSULT.x ÐÐÐ
Self-diagnostic
resultsSelf-diagnostic results can be read and
erased quickly.xxxx
Trouble diagnostic
recordCurrent self-diagnostic results and all trouble
diagnostic records previously stored can be
read.ÐxÐÐ
ECU discriminated
No.Classification number of a replacement ECU
can be read to prevent an incorrect ECU
from being installed.ÐxÐÐ
Data monitor Input/Output data in the ECM can be read.xÐxÐ
Active testDiagnostic Test Mode in which CONSULT
drives some actuators apart from the ECMs
and also shifts some parameters in a speci-
fied range.xÐxÐ
ECM part number ECM part number can be read.xÐxÐ
Function testConducted by CONSULT instead of a tech-
nician to determine whether each system is
``OK'' or ``NG''.x ÐÐÐ
Control unit initiali-
sationAll registered ignition key IDs in NATS com-
ponents can be initialised and new IDs can
be registered.ÐÐÐ x
Self-function checkECM checks its own NATS communication
interface.ÐÐÐ x
x : Applicable
*1: 4WD models for the Middle East
*2: For the Middle East (EE960 program card is not applicable to ABS. Use on board diagnostic system with ABS warning lamp until
the next program card will be introduced.)
*3: NATS (Nissan Anti-Theft System)
Lithium Battery Replacement
CONSULT contains a lithium battery. When replacing the battery obey the following:
WARNING:
Replace the lithium battery with SANYO Electric Co., Ltd., CR2032 only. Use of another battery may
present a risk of fire or explosion. The battery may present a fire or chemical burn hazard if mis-
treated. Do not recharge, disassemble of dispose of in fire.
Keep the battery out of reach of children and discard used battery conforming to the local regula-
tions.
CONSULT CHECKING SYSTEM
GI-34
Page 839 of 1659
Checking Equipment
When ordering the below equipment, contact your NISSAN distributor.
Tool name Description
NISSAN CONSULT
V1CONSULT unit
and accessories
V2Program card
lEE960
lNATS-E940* for NATS
NT004
*: An order for NATS program card must be placed only with NISSAN EUROPE N.V.
CONSULT CHECKING SYSTEM
GI-35
Page 840 of 1659
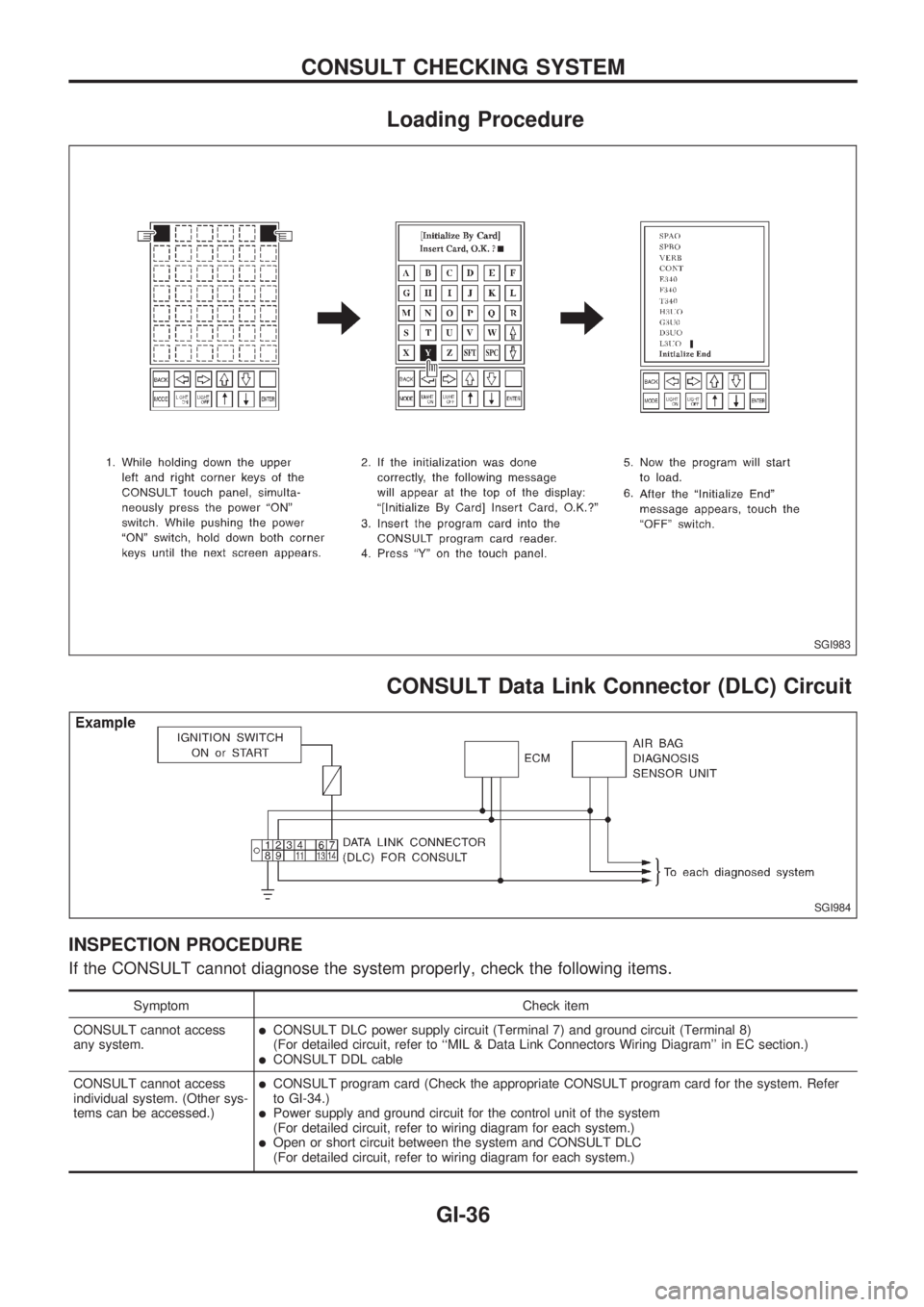
Loading Procedure
CONSULT Data Link Connector (DLC) Circuit
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
If the CONSULT cannot diagnose the system properly, check the following items.
Symptom Check item
CONSULT cannot access
any system.
lCONSULT DLC power supply circuit (Terminal 7) and ground circuit (Terminal 8)
(For detailed circuit, refer to ``MIL & Data Link Connectors Wiring Diagram'' in EC section.)
lCONSULT DDL cable
CONSULT cannot access
individual system. (Other sys-
tems can be accessed.)
lCONSULT program card (Check the appropriate CONSULT program card for the system. Refer
to GI-34.)
lPower supply and ground circuit for the control unit of the system
(For detailed circuit, refer to wiring diagram for each system.)
lOpen or short circuit between the system and CONSULT DLC
(For detailed circuit, refer to wiring diagram for each system.)
SGI983
SGI984
CONSULT CHECKING SYSTEM
GI-36