DATSUN 210 1979 Owners Manual
Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1979, Model line: 210, Model: DATSUN 210 1979Pages: 548, PDF Size: 28.66 MB
Page 91 of 548
Engine
Fuel
S
Idle
compensator
is
ill
good
order
if
a
hissing
sound
is
heard
when
its
temperature
reaches
operating
tern
perature
If
not
replace
idle
compensator
ldlerompensator
l
b
l
r
I
No
1
60
to
700C
140
to
15
Of
No
2
70
to
800C
158
to
1760F
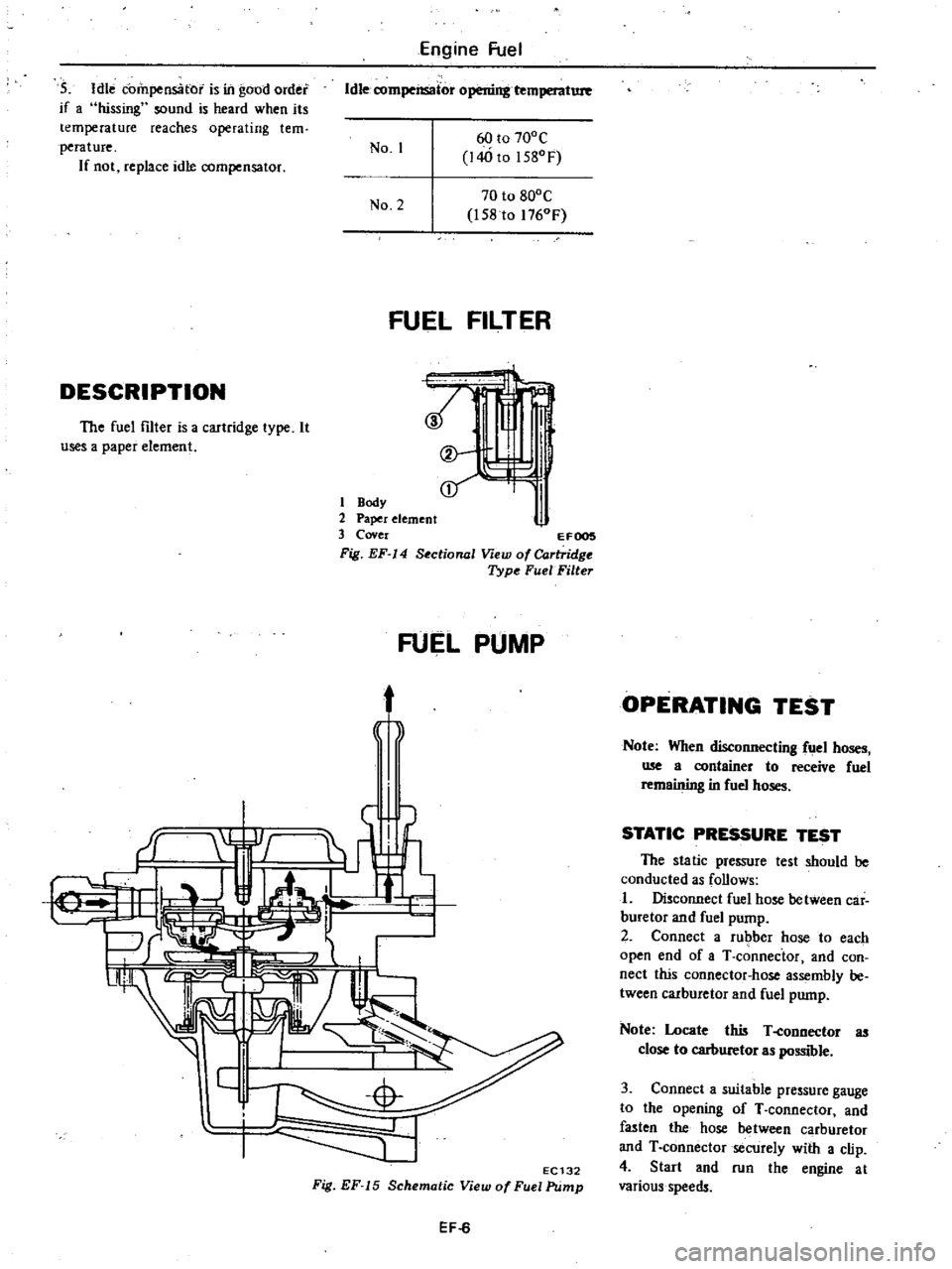
FUEL
FILTER
DESCRIPTION
t
t
I
J
i
l
The
fuel
filter
is
a
cartridge
type
It
useS
a
paper
element
1
Body
2
Paper
element
3
Cover
EFOOS
Fig
EF
14
Sectional
View
of
Cartridge
Type
FuelFilte
FUEL
PUMP
t
j
f
EC132
Fig
EF
15
Schematic
View
of
Fuel
Pump
EF
6
OPERATING
TEST
Note
When
disconnecting
fuel
hoses
me
a
container
to
receive
fuel
remaining
in
fuel
hoses
STATIC
PRESSURE
TEST
The
static
pressure
test
should
be
conducted
as
follows
I
Disconnect
fuel
hose
between
car
buretor
and
fuel
pump
2
Connect
a
rubber
hose
to
each
open
end
of
aT
connector
and
con
nect
this
connector
hose
assembly
be
tween
carburetor
and
fuel
pump
Note
Locate
this
T
eonnector
as
close
to
carburetor
as
possible
3
Connect
a
suitable
pressure
gauge
to
the
opening
of
T
connector
and
fasten
the
hose
between
carburetor
and
T
connector
secUrely
with
a
clip
4
Start
and
run
the
engine
at
various
speeds
Page 92 of 548

5
The
pressure
gauge
indicates
static
fuel
pressure
in
the
line
The
gauge
reading
should
be
within
the
specified
value
Fuel
pump
pressure
0
21
to
0
27
kg
em2
3
0
to
3
8
pli
I
Note
If
the
fuel
in
the
carburetor
float
chamber
has
run
out
and
engine
has
stopped
remove
clip
and
pour
fuel
into
carburetor
Fasten
clip
securely
and
repeat
static
pres
sure
test
If
pressure
is
not
within
the
specifi
ed
limit
remove
pump
as
an
assembly
CAPACITY
TEST
The
capacity
test
is
conducted
only
when
static
pressure
is
within
the
specification
To
conduct
this
test
proceed
as
follows
1
Disconnect
pressure
gauge
from
T
connector
and
in
its
vacant
place
install
a
suitable
container
as
a
fuel
sump
2
Start
engine
and
run
at
1
000
pm
3
Pump
should
deliver
the
specified
amouni
of
fuel
If
little
or
no
fuel
flows
from
open
end
of
pipe
it
is
an
indication
that
fuel
line
is
clogged
or
pump
is
mal
functioning
Fuel
pump
capacity
450
cc
27
46
eu
inl
min
at
1
000
rpm
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
Note
When
disconnecting
fuel
lines
use
a
container
to
receive
fuel
remaining
in
fuel
hoses
I
Disconnect
inlet
and
outlet
fuel
hoses
from
fuel
pump
2
Remove
fuel
pump
3
To
install
reverse
the
order
of
removal
Engine
Fuel
DISASSEMBLY
@@
@@
@
@@
1
Remove
screws
and
detach
upper
and
lower
bodies
2
Remove
screws
and
take
off
cap
and
cap
gasket
from
upper
body
3
Remove
inlet
and
outlet
connee
tors
4
Remove
valve
retainer
screws
and
take
off
valve
retainer
S
To
remove
diaphragm
press
down
its
center
against
spring
force
With
diaphragm
pressed
down
ilt
it
until
end
of
pull
rod
touches
inner
wall
of
body
Then
release
diaphragm
to
unhook
push
rod
Note
Be
careful
not
to
damage
dia
phragm
or
oil
seal
INSPECTION
Check
all
components
for
cracks
EF
7
I
Packing
2
Valve
a5scm
bly
3
Retainer
4
Screw
5
Diaphragm
assembly
6
Diaphragm
spring
7
Retainer
8
Diaphragm
assembly
9
Complete
body
lower
10
Screw
11
Washer
spring
12
Fuel
pump
cap
13
Cap
gasket
14
Connector
inlet
15
Connector
outlet
16
Rocker
arm
spring
17
Nut
18
Washer
spring
19
Washer
pJain
20
Gasket
21
Spacer
22
Rocker
pin
23
Spacer
24
Rocker
arm
EC134
Fig
EF
16
Fuel
Pump
wear
or
any
abnormalities
and
replace
with
new
parts
if
necessary
ASSEMBLY
I
To
assemble
reverse
the
order
of
disassembly
Closely
observe
the
following
instructions
Use
new
gaskets
Lubricate
rocker
arm
rocker
arm
link
and
rocker
arm
pin
before
installation
2
After
assembly
test
the
function
as
follows
a
Position
fuel
pump
assembly
about
I
meter
3
3
ft
above
fuel
level
of
fuel
strainer
and
connect
a
pipe
from
strainer
to
fuel
pump
b
Operate
rocker
arm
by
hand
If
fuel
is
drawn
up
soon
after
rocker
arm
is
released
fuel
pump
is
functioning
properly
Page 93 of 548
DESCRIPTION
The
carburetors
are
of
downdraft
two
barrel
type
designed
to
increase
ppwe
r
a
fu
l
eC
l
Il
Y
t
3
ell
a
to
reduce
exhaust
gas
emissions
These
carburetors
present
several
distinct
features
of
importance
to
car
owner
A
summary
of
features
is
as
fol
lows
1
Secondary
throttle
valve
is
oper
ated
by
throttle
lever
High
power
and
good
acceleration
are
gained
with
com
bination
of
the
auxiliary
valve
2
Accelerating
pump
provide
ex
cellent
acceleration
3
Power
valve
mechanism
is
a
vacuo
urn
actuated
boost
type
and
improves
high
speed
driving
4
The
throttle
opener
control
sys
tem
Except
FU
model
incorporates
a
servo
diaphragm
which
helps
open
the
throttle
valve
at
a
decreasing
speed
so
as
to
reduce
hydrocarbon
emissions
to
a
minimum
5
An
anti
d
eseling
solenoid
valve
is
installed
to
prevent
dieseling
When
ignition
key
is
turned
off
the
fuel
passage
involved
in
the
ow
system
is
closed
and
the
fuel
supply
is
shut
down
completely
The
solenoid
valve
also
serves
as
an
actuator
of
the
fuel
shut
off
system
on
the
FU
model
6
In
the
choke
mechanism
an
elec
trie
automatic
choke
is
used
to
auto
maticaDy
control
chok
valve
opera
tion
during
engin
war
up
7
The
carburetor
comes
equipped
with
dash
pot
which
ensures
smooth
deceleration
without
engine
stall
under
aU
operating
conditions
STRUCTURE
AND
OPERATION
These
carburetors
consist
of
a
main
system
for
normal
running
a
slow
system
for
idling
and
an
accelerating
and
power
mechanisIll
Some
emission
control
devices
are
added
E
ngine
Fuel
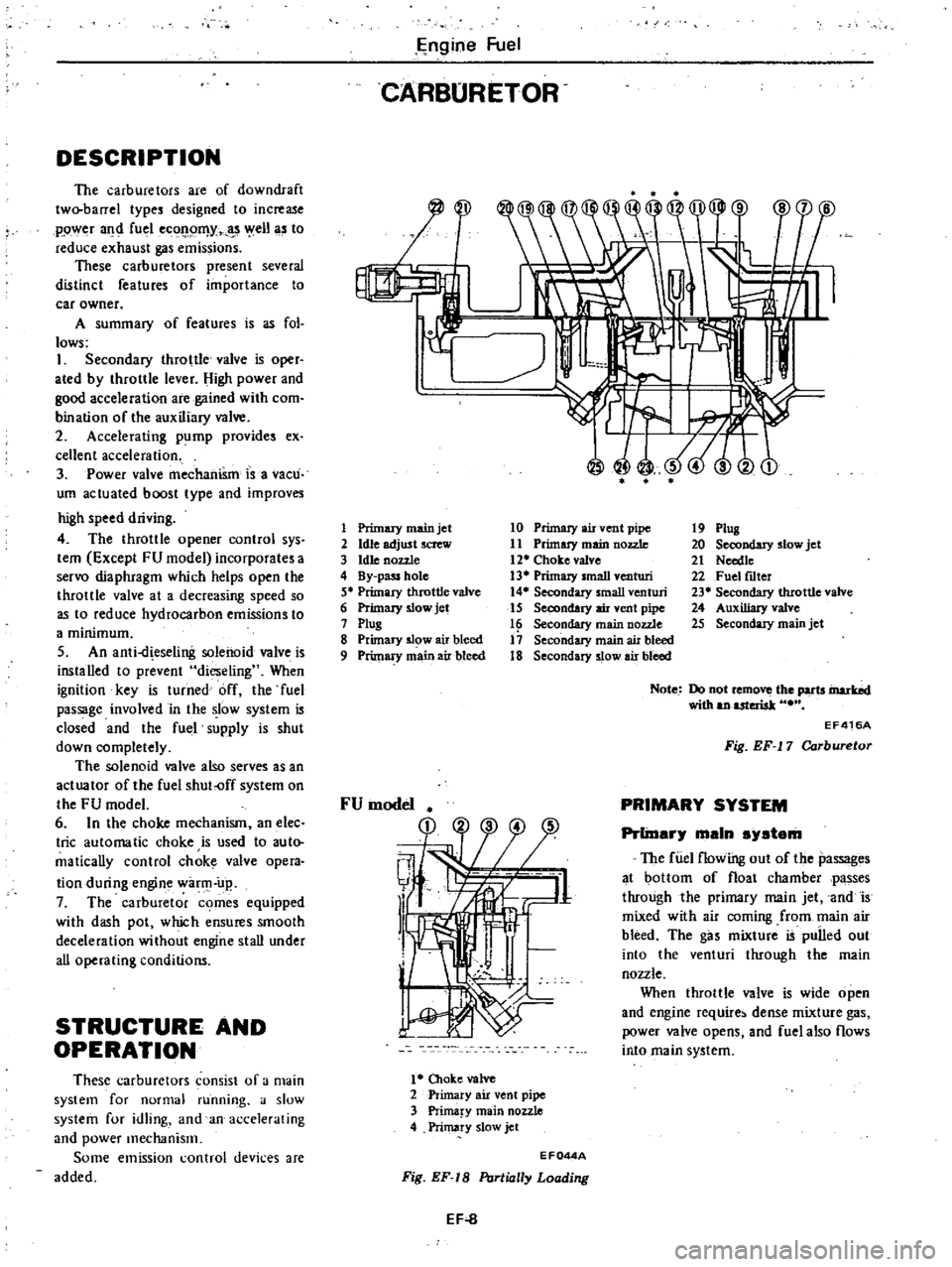
CARBURETOR
I
J
1
Primary
main
jet
2
Idle
adjust
screw
3
hUe
nozzle
4
By
pass
hole
5
Primary
throttle
valve
6
Primary
slow
jet
7
ptug
8
Primary
5l
w
air
bleed
9
Primary
main
air
bleed
10
Primary
air
vent
pipe
11
Primuy
main
nozzle
12
Choke
valve
13
Primary
small
venturi
14
Secondary
small
venturi
15
Secondary
air
vent
pipe
16
Secondary
main
nozzle
17
Secondary
main
air
bleed
18
Secondary
slow
air
bleed
1
Oloke
valve
2
Primary
air
vent
pipe
3
Prima
y
main
nozzle
4
Primary
slow
jet
19
Plug
20
Secondary
slow
jet
21
Needte
22
Fuel
fLlter
23
Secondary
tIuottle
valve
24
Auxiliary
valve
25
Secondary
main
jet
Note
Do
not
remo
the
parts
inarbd
with
anuteriak
EF416A
Fig
EF
17
Carburetor
PRIMARY
SYSTEM
PrlinarJ
main
sJstam
The
fUel
flowing
out
of
the
passages
at
bottom
of
float
chamber
passes
through
the
primary
main
jet
and
is
mixed
with
air
coming
from
main
air
bleed
The
gas
mixture
is
pulled
out
into
the
venturi
through
the
main
nozzle
When
throttle
valve
is
wide
open
and
engine
require
dense
mixture
gas
power
valve
opens
and
fuel
also
flows
into
main
system
EF044A
Fig
EF
18
PtJrlially
Loading
EF
8
Page 94 of 548
t
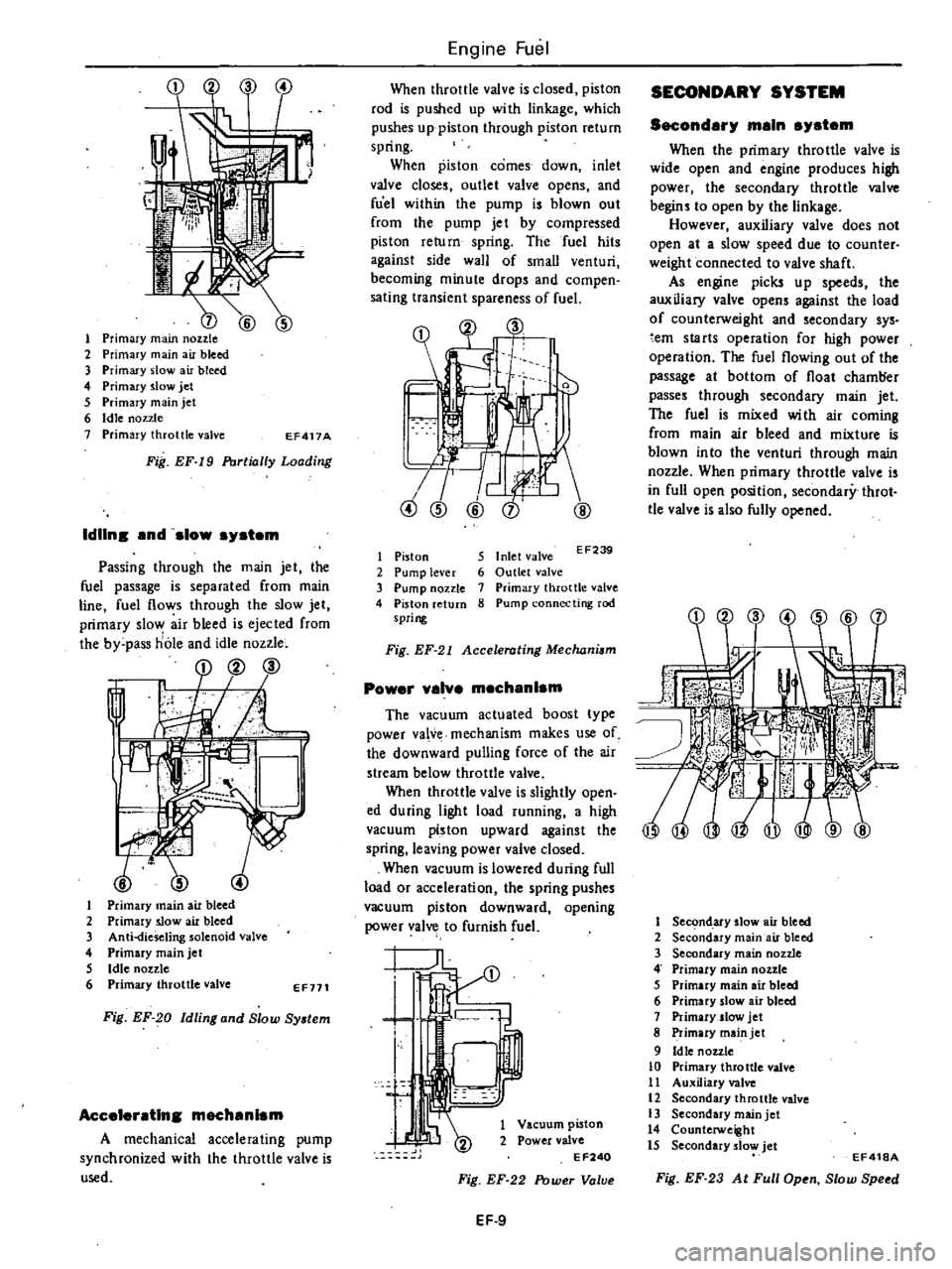
1
Primary
main
nozzle
2
Primary
main
air
bleed
3
Primary
slow
air
bleed
4
Primary
slow
jet
5
Primary
main
jet
6
Idle
nozzle
7
Primary
throttle
valve
EF417A
Fig
EF
I9
Portially
Loading
IdUns
nd
slow
system
Passing
through
the
main
jet
the
fuel
passage
is
separated
from
main
line
fuel
flows
through
the
slow
jet
primary
slow
air
bleed
is
ejected
from
the
by
pass
hole
and
idle
nozzle
cp
v
Ii
l
1
Primary
main
air
bleed
2
Primary
slow
air
bleed
3
Anti
fieseling
solenoid
valve
4
Primary
main
jet
5
Idle
nozzle
6
Primary
throttle
valve
EF711
Fig
EF
20
Idling
and
Slow
System
Aceeler
tlns
meeh
nlsm
A
mechanical
accelerating
pump
synchronized
with
the
throttle
valve
is
used
Engine
Fuel
When
throttle
valve
is
closed
piston
rod
is
pushed
up
wi
th
linkage
which
pushes
up
piston
through
piston
return
spring
When
piston
comes
down
inlet
valve
closes
outlet
valve
opens
and
fuel
within
the
pump
is
blown
out
from
the
pump
je
t
by
compressed
piston
return
spring
The
fuel
hits
against
side
wall
of
small
venturi
becoming
minute
drops
and
compen
sating
transient
spareness
of
fuel
1
r
@
CD
V
1
Piston
2
Pump
lever
3
Pump
nozzle
4
Piston
return
spring
5
Inlet
valve
EF239
6
Outlet
valve
7
Primary
throttle
valve
8
Pump
connecting
rod
Fig
EF
21
Accelerating
Mechani
m
Power
v
lve
meeh
nlsm
The
vacuum
actuated
boost
type
power
va
v
mechanism
makes
use
of
the
downward
pulling
force
of
the
air
stream
below
throttle
valve
When
throttle
valve
is
slightly
open
ed
during
light
load
running
a
high
vacuum
p
ston
upward
against
the
spring
leaving
power
valve
closed
When
vacuum
is
lowered
during
full
load
or
acceleration
the
spring
pushes
vacuum
piston
downward
opening
power
valve
to
furnish
fuel
I
t
f
i
1
Vacuum
piston
2
Power
valve
EF240
Fig
EF
22
Power
Valve
EF
9
SECONDARY
SYSTEM
Second
ry
m
ln
system
When
the
primary
throttle
valve
is
wide
open
and
engine
produces
high
power
the
secondary
throttle
valve
begins
to
open
by
the
linkage
However
auxiliary
valve
does
not
open
at
a
slow
speed
due
to
counter
weight
connected
to
valve
shaft
As
engine
picks
up
speeds
the
auxiliary
valve
opens
against
the
load
of
counterweight
and
secondary
sys
em
starts
operation
for
high
power
operation
The
fuel
flowing
out
of
the
passage
at
bottom
of
float
chamt
er
passes
through
secondary
main
jet
The
fuel
is
mixed
wi
th
air
coming
from
main
air
bleed
and
mixture
is
blown
in
to
the
venturi
through
main
nozzle
When
primary
throttle
valve
is
in
full
open
position
secondary
throt
tle
valve
is
also
fully
opened
I
Secl
ndary
slow
air
bleed
2
Secondary
main
air
bleed
3
Secondary
main
nozzle
4
Primary
main
nozzle
5
Primary
main
air
bleed
6
Primary
slow
air
bleed
7
Primary
slow
jet
8
Primary
main
jet
9
Idle
nozzle
10
Primary
throttle
valve
11
Auxiliary
valve
12
Secondary
throttle
valve
13
Secondary
main
jet
14
Counterweight
15
Secondary
slow
jet
EF418A
Fig
EF
23
At
Full
Open
Stow
Speed
Page 95 of 548
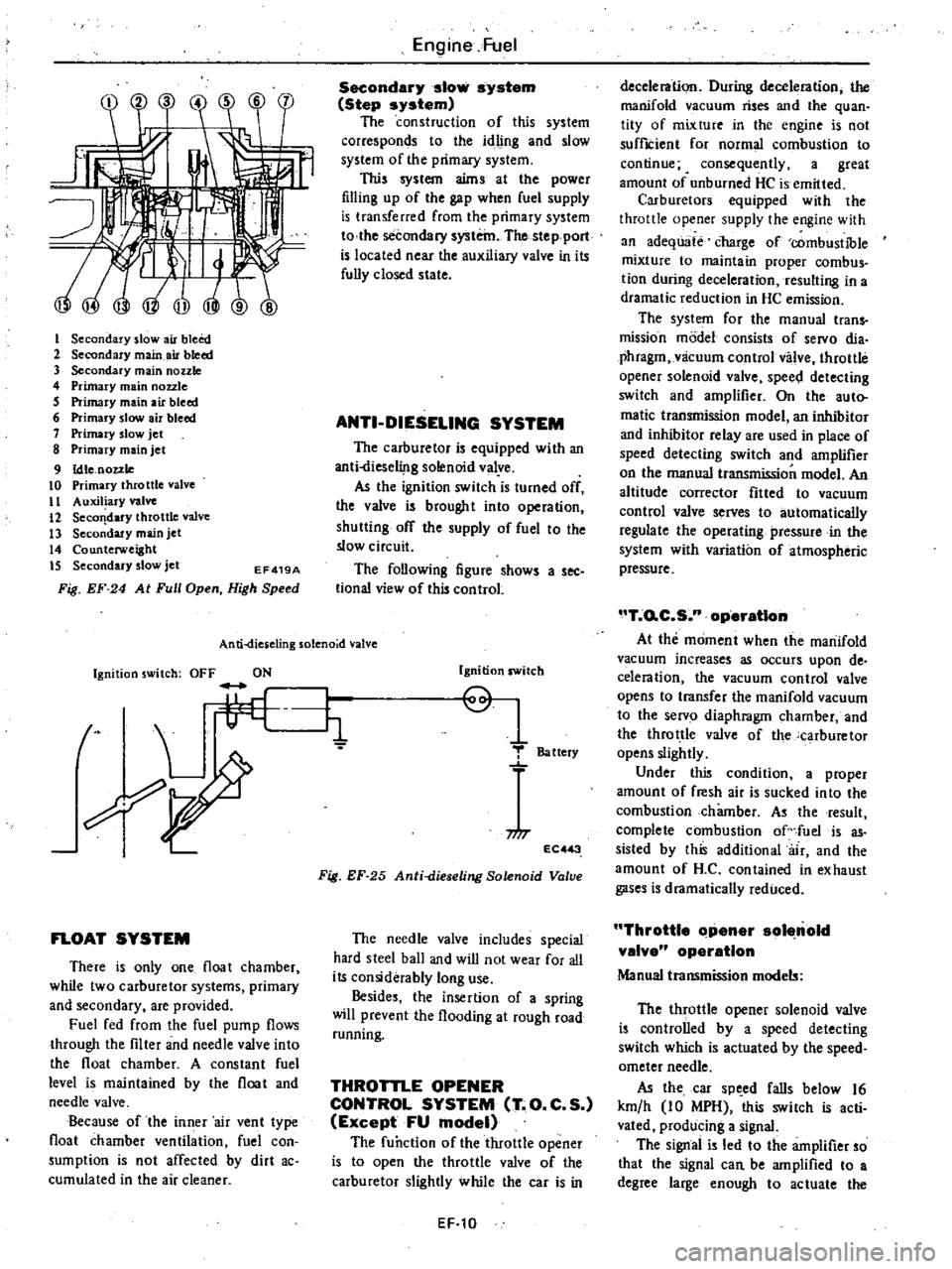
I
Secondary
slow
air
bleed
2
Secondary
main
air
bleed
3
Secondary
main
nozzle
4
Primary
main
nozzle
5
Primary
main
air
bleed
6
Primary
slow
air
bleed
7
Primary
slow
jet
8
Primary
main
jet
9
Idle
nozzle
10
Primary
throttle
valve
II
Auxiliary
valve
12
Seco
dary
throttle
valve
13
Secondary
main
jet
14
Counterweight
IS
Secondary
slow
jet
EF419A
Fig
EF
24
At
Full
Open
High
Speed
Engine
Fuel
Secondary
slow
system
Step
system
The
construction
of
this
system
corresponds
to
the
idling
and
slow
system
of
the
primary
system
This
system
aims
at
the
power
filling
up
of
the
gap
when
fuel
supply
is
transferred
from
the
primary
system
to
the
secondary
system
The
stepport
is
located
near
the
auxiliary
valve
in
its
fully
closed
state
ANTI
DIESELING
SYSTEM
The
carburetor
is
equipped
with
an
anti
liese1i
lg
solenoid
valye
As
the
ignition
switch
is
turned
off
the
valve
is
brought
into
operation
shutting
off
the
supply
of
fuel
to
the
slow
circuit
The
following
figure
shows
a
see
tional
view
of
this
control
An
ti
dies
eling
solenoid
valve
Ignition
switch
OFF
ON
t
L
li
FLOAT
SYSTEM
There
is
only
one
float
chamber
while
two
carburetor
systems
primary
and
secondary
are
provided
Fuel
fed
from
the
fuel
pump
flows
through
the
filter
and
needle
valve
into
the
float
chamber
A
constant
fuel
level
is
maintained
by
the
float
and
needle
valve
Because
of
the
inner
air
vent
type
float
chamber
ventilation
fuel
con
sumption
is
not
affected
by
dirt
ac
cumulated
in
the
air
cleaner
Ignition
switch
Q
1
T
Battery
niT
EC
3
Fig
EF
25
Anti
dieseling
Solenoid
Valve
The
needle
valve
includes
special
hard
steel
ball
and
wiD
not
wear
for
all
its
considerably
long
use
Besides
the
insertion
of
a
spring
will
prevent
the
flooding
at
rough
road
running
THROTTLE
OPENER
CONTROL
SYSTEM
T
O
C
S
Except
FU
model
The
function
of
the
throttle
opener
is
to
open
the
throttle
valve
of
the
carburetor
slightly
while
the
car
is
in
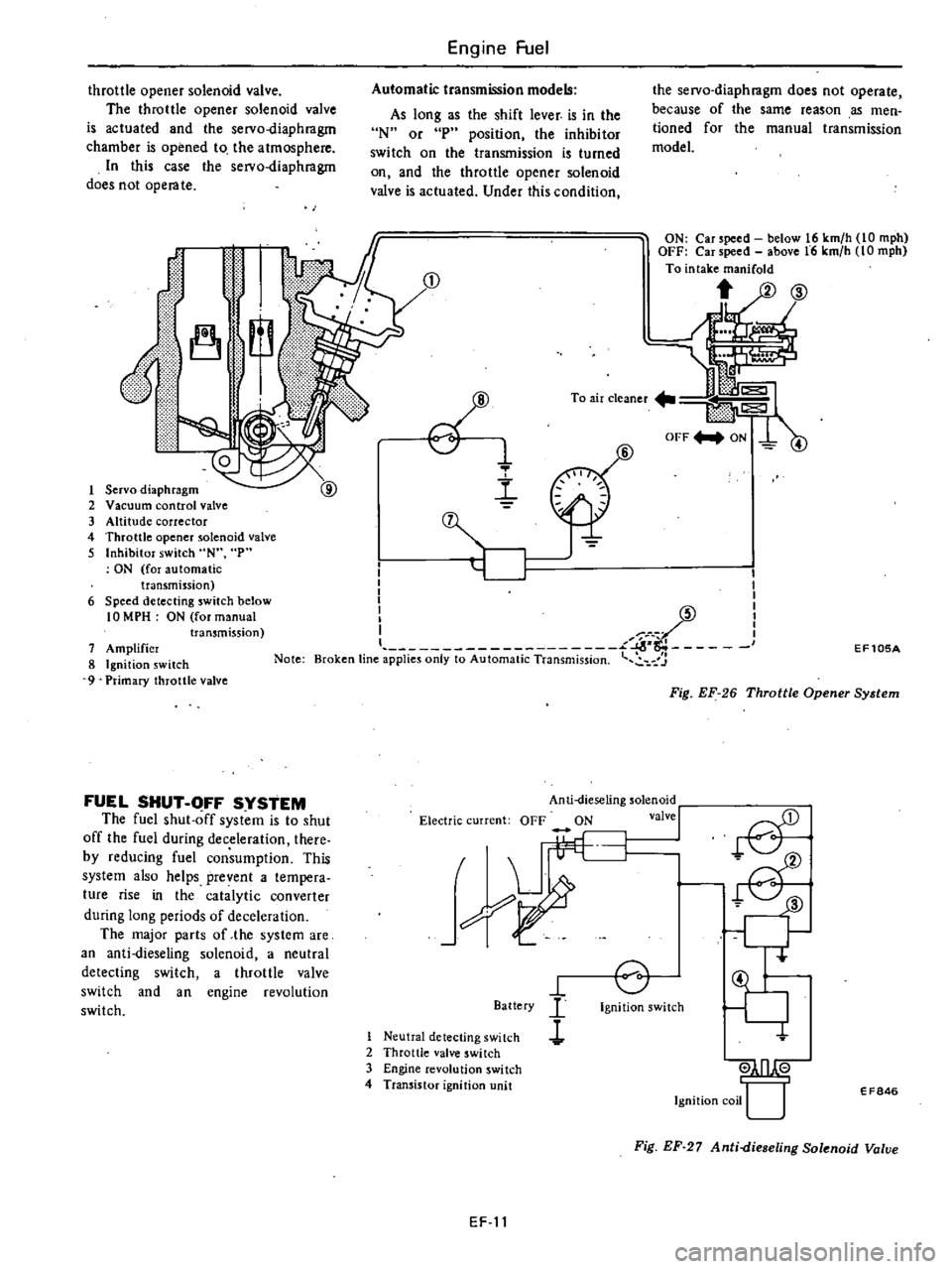
EF
10
deceleration
During
deceleration
the
manifold
vacuum
rises
and
the
quan
tity
of
mixture
in
the
engine
is
not
suffICient
for
normal
combustion
to
continue
4
consequently
a
great
amount
of
unburned
HC
is
emitted
Carburetors
equipped
with
the
throttle
opener
supply
the
engine
with
an
adequate
charge
of
combustible
mixture
to
maintain
proper
combus
tion
during
deceleration
resulting
in
a
dramatic
reduction
in
HC
emission
The
system
for
the
manual
trans
mission
model
consists
of
servo
dia
phragm
vlicuum
control
valve
throttle
opener
solenoid
valve
spee
l
detecting
switch
and
amplifier
On
the
auto
matic
transmission
model
an
inhibitor
and
inhibitor
relay
are
used
in
place
of
speed
detecting
switch
and
amplifier
on
the
manual
transmission
model
An
altitude
corrector
fitted
to
vacuum
control
valve
serves
to
automatically
regulate
the
operating
pressure
in
the
system
with
variation
of
atmospheric
pressure
T
o
C
S
n
operatIon
At
the
moment
when
the
manifold
vacuum
increases
as
occurs
upon
de
celeration
the
vacuum
control
valve
opens
to
transfer
the
manifold
vacuum
to
the
servo
diaphragm
chamber
and
the
throttle
valve
of
the
carburetor
opens
slightly
Under
this
condition
a
proper
amount
of
fresh
air
is
sucked
into
the
combustion
chamber
As
the
result
complete
combustion
of
fuel
is
as
sisted
by
this
additional
air
and
the
amount
of
H
C
contained
in
exhaust
gases
is
dramatically
reduced
Throttle
Clpener
sol
nold
valve
operation
Manual
transmission
models
The
throttle
opener
solenoid
valve
is
controlled
by
a
speed
detecting
switch
which
is
actuated
by
the
speed
ometer
needle
As
the
car
sp
ed
falls
below
16
km
h
10
MPH
this
switch
is
acti
vated
producing
a
signal
The
signal
is
led
to
the
amplifier
so
that
the
signal
can
be
amplified
to
a
degree
large
enough
to
actuate
the
Page 96 of 548
throttle
opener
solenoid
valve
The
throttle
opener
solenoid
valve
is
actuated
and
the
servo
diaphragm
chamber
is
opened
to
the
atmosphere
In
this
case
the
seIVo
diaphragm
does
not
opera
te
Engine
Fuel
Automatic
transmission
models
As
long
as
the
shift
lever
is
in
the
N
or
p
position
the
inhibitor
switch
on
the
transmission
is
turned
on
and
the
throttle
opener
solenoid
valve
is
actuated
Under
this
condition
the
seIVo
diaphragm
does
not
operate
because
of
the
same
reason
as
men
tioned
for
the
manual
transmission
model
ON
Car
peed
betow
t6
km
h
to
mph
OFF
Car
peed
above
16
km
h
to
mph
To
intake
manifold
j
lJl
11
1
ti
i
ljn
L
o
1
Servo
diaphragm
2
Vacuum
control
valve
3
Altitude
corrector
4
Throttle
opener
solenoid
valve
5
Inhibitor
switch
N
p
ON
for
automatic
transmission
6
Speed
detecting
switch
below
10
MPH
ON
for
manual
transmission
7
Amplifier
8
Ignition
switch
9
Primary
throttle
valve
Note
FUEL
SHUT
OFF
SYSTEM
The
fuel
shut
off
system
is
to
shut
off
the
fuel
during
deceleration
there
by
reducing
fuel
consumption
This
system
also
helps
prevent
a
tempera
ture
rise
in
the
catalytic
converter
during
long
periods
of
deceleration
The
major
parts
of
the
system
are
an
anti
dieseling
solenoid
a
neutral
detecting
switch
a
throttle
valve
switch
and
an
engine
revolution
switch
e
1
l
6
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
l
L
I
Broken
tine
applies
only
to
Automatic
Transmission
7
Anti
dieseling
solenoid
Electric
current
OFF
ON
valve
I
I
h
L
Battery
I
Neutral
detecting
switch
l
2
Throttle
valve
switch
3
Engine
revolution
switch
4
Transistor
ignition
unit
o
Ignition
switch
EF105A
Fig
EF
26
Throttle
Opener
System
ill
Ignition
coil
U
EF846
Fig
EF
27
Anti
dieseling
Solenoid
Valve
EF
11
Page 97 of 548
Fuel
shut
oH
s
stein
operation
During
deceleration
when
the
en
gine
speed
is
above
a
certain
level
the
anti
dieseling
solenoid
valve
of
the
carburetor
closes
so
that
the
fuel
is
shut
off
When
engine
speed
falls
below
a
certain
level
the
anti
dieseling
solenoid
vaJv
oP
lS
so
that
the
f
el
flows
However
if
the
engine
speed
is
below
the
designated
level
even
during
deceleration
the
fuel
shut
off
system
does
not
operate
When
the
shift
lever
is
in
neutral
the
fuel
shut
off
system
does
not
operate
The
functions
of
each
part
of
this
system
are
as
follows
I
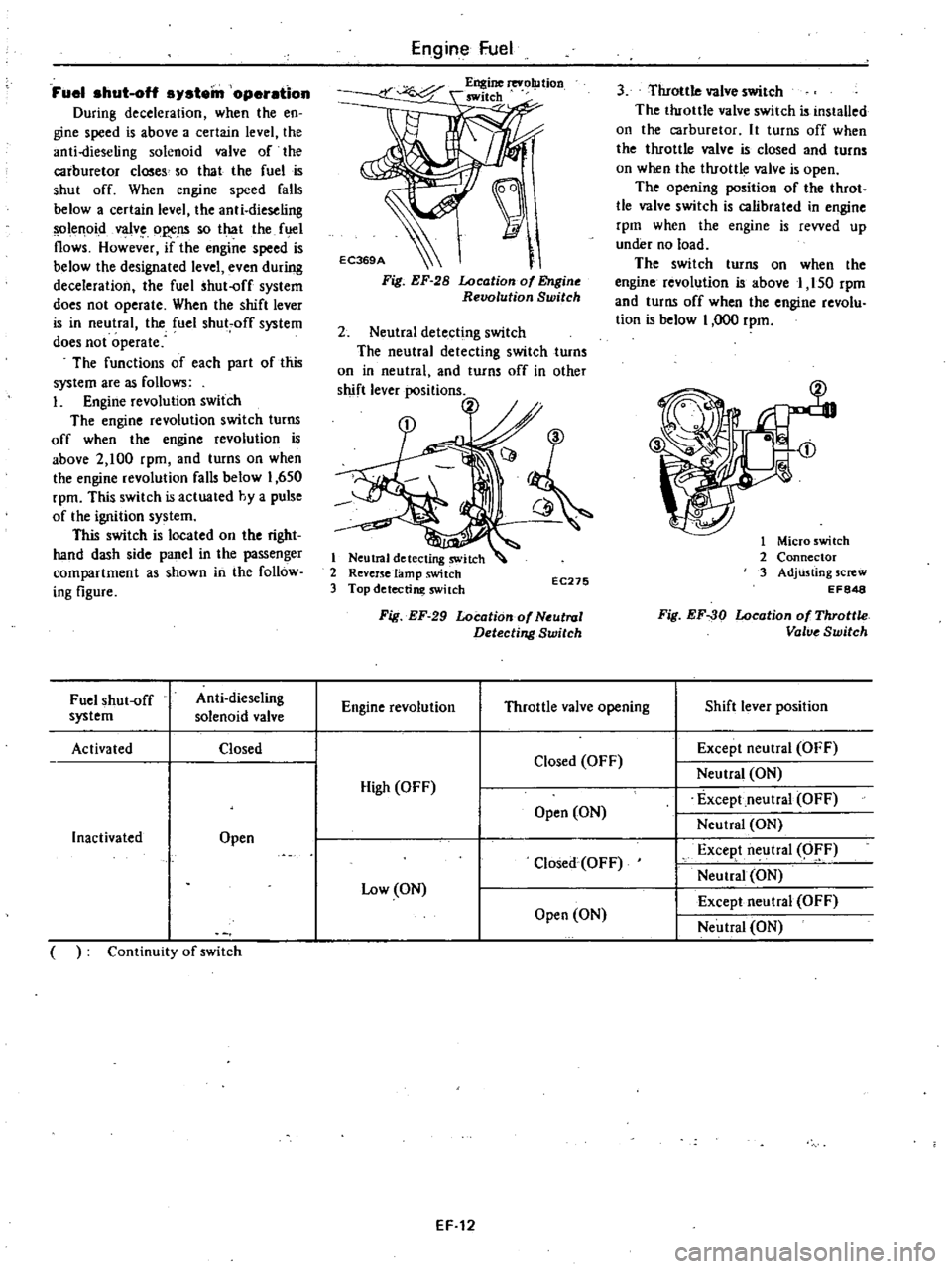
Engine
revolution
switch
The
engine
revolution
switch
turns
off
when
the
engine
revolution
is
above
2
100
rpm
and
turns
on
when
the
engine
revolution
falls
below
1
650
rpm
This
switch
is
actuated
hy
a
pulse
of
the
ignition
system
This
switch
is
located
on
the
right
hand
dash
side
panel
in
the
passenger
compartment
as
shown
in
the
follow
ing
figure
Engine
Fuel
I
Fig
EF
28
Location
of
Engine
Revolution
Switch
2
Neutral
detecting
switch
The
neutral
detecting
switch
turns
on
in
neutral
and
turns
off
in
other
shift
lever
positions
h
1
Neutral
detecting
switch
2
Revenelamp
switch
3
Top
detectim
switch
EC275
3
Throttle
valve
switch
The
throttle
valve
switch
is
installed
on
the
carburetor
It
turns
off
when
the
throttle
valve
is
closed
and
turns
on
when
the
throttle
valve
is
open
The
opening
position
of
the
throt
tle
valve
switch
is
calibrated
in
engine
rpm
when
the
engine
is
revved
up
under
no
load
The
switch
turns
on
when
the
engine
revolution
is
above
1
150
rpm
and
turns
off
when
the
engine
revolu
tion
is
below
1
000
rpm
1
Micro
switch
2
Connector
3
Adjusting
screw
EF848
Fig
EF
30
Location
of
Throttle
Valve
Switch
Fuel
shut
off
Anti
dieseling
Engine
revolution
Throttle
valve
opening
Shift
lever
position
system
solenoid
valve
Activated
Closed
Except
neutral
OFF
Closed
OFF
Neutral
ON
High
OFF
Except
neutral
OFF
Open
ON
Inactivated
Open
Neutral
ON
Closed
OFF
Excep
t
neutral
O
F
Low
ON
Neutral
ON
Except
neutral
OFF
Open
ON
Neutral
ON
Continuity
of
switch
Fig
EF
29
Locotion
of
Neutral
Detecting
Switch
EF
12
Page 98 of 548
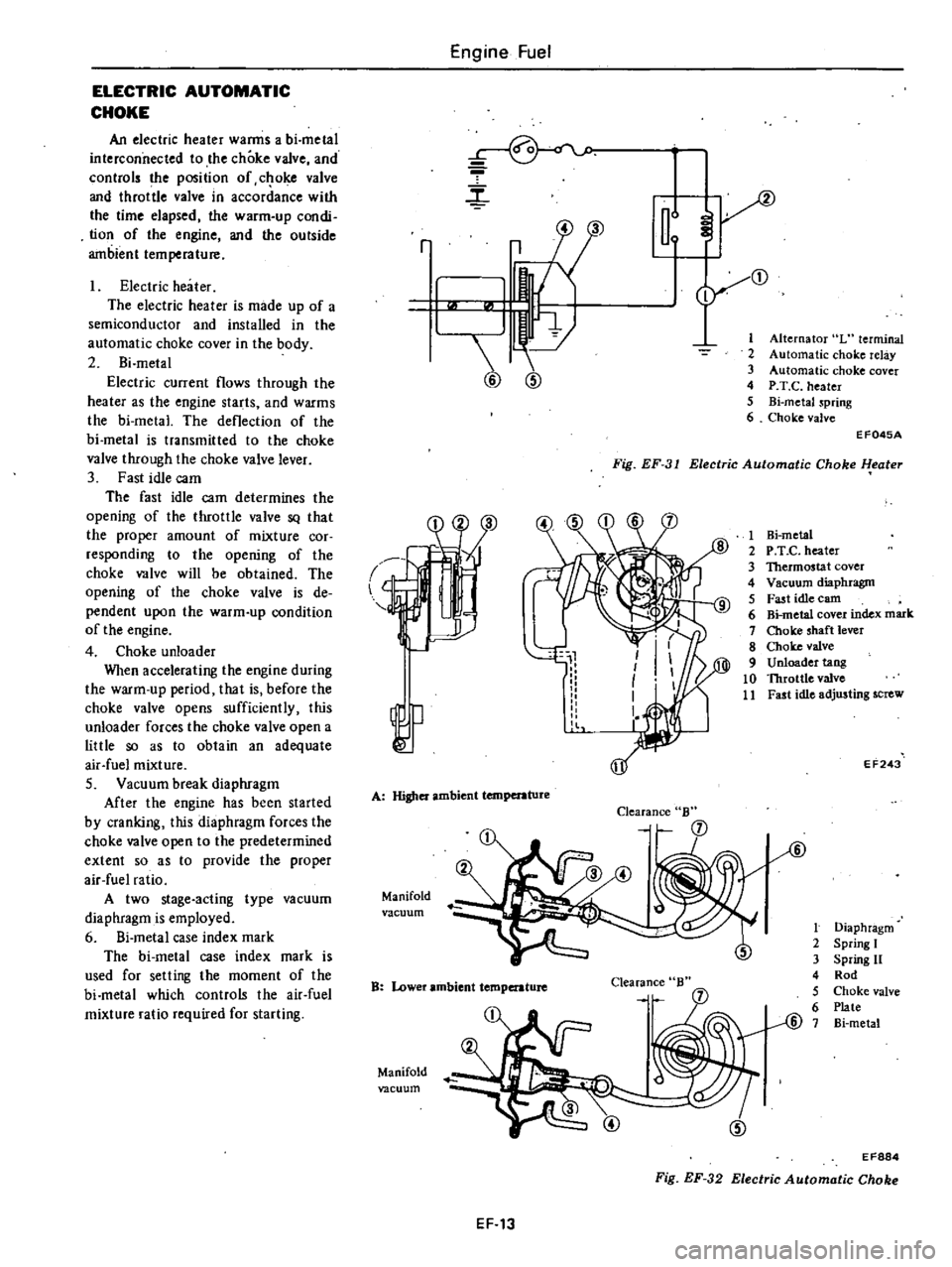
ELECTRIC
AUTOMATIC
CHOKE
An
electric
heater
warms
a
bi
metal
interconnected
to
the
choke
valve
and
controls
the
position
of
c
oke
valve
and
throttle
valve
in
accordance
with
the
time
elapsed
the
warm
up
condi
tion
of
the
engine
and
the
outside
ambient
temperature
Electric
heater
The
electric
heater
is
made
up
of
a
semiconductor
and
installed
in
the
automatic
choke
cover
in
the
body
2
Bi
metal
Electric
current
flows
through
the
heater
as
the
engine
starts
and
warms
the
bi
metal
The
deflection
of
the
bi
metal
is
transmitted
to
the
choke
valve
through
the
choke
valve
lever
3
Fast
idle
cam
The
fast
idle
cam
determines
the
opening
of
the
throttle
valve
SQ
that
the
proper
amount
of
mixture
cor
responding
to
the
opening
of
the
choke
valve
will
be
obtained
The
opening
of
the
choke
valve
is
de
pendent
upon
the
warm
up
condition
of
the
engine
4
Choke
unloader
When
accelerating
the
engine
during
the
warm
up
period
that
is
before
the
choke
valve
opens
sufficiently
this
unloader
forces
the
choke
valve
open
a
little
so
as
to
obtain
an
adequate
air
fuel
mixture
S
Vacuum
break
diaphragm
After
the
engine
has
been
started
by
cranking
this
diaphragm
forces
the
choke
valve
open
to
the
predetermined
extent
so
as
to
provide
the
proper
air
fuel
ratio
A
two
stage
acting
type
vacuum
diaphragm
is
employed
6
Si
metal
case
index
mark
The
bi
metal
case
index
mark
is
used
for
selling
the
moment
of
the
bi
metal
which
controls
the
air
fuel
mixture
ratio
required
for
starting
Engine
Fuel
r
m
2
3
4
5
6
r
3
1
@
@
Alternator
L
terminal
Automatic
choke
relay
Automatic
choke
cover
P
T
C
heater
Bi
metaJ
spring
Choke
valve
Fig
EF
31
Electric
Automatic
Choke
l
eater
EF045A
l
A
Higher
ambient
temperature
Manifold
vacuum
Clearance
B
B
Lower
ambient
temperature
Clearance
Manifold
vacuum
1
Hi
metal
2
P
T
e
heater
3
Thermostat
cover
4
Vacuum
diaphragm
5
Fast
idle
earn
6
Bi
metal
cover
index
mark
7
Choke
shaft
lever
8
Choke
valve
9
Unloader
tang
10
Throttle
valve
11
Fast
idle
adjusting
screw
EF243
t
Diaphragm
2
Spring
I
3
Spring
11
4
Rod
5
Choke
valve
6
Plate
@
7
Bi
metal
EF884
Fig
EF
32
Electric
Automatic
Choke
EF
13
Page 99 of 548
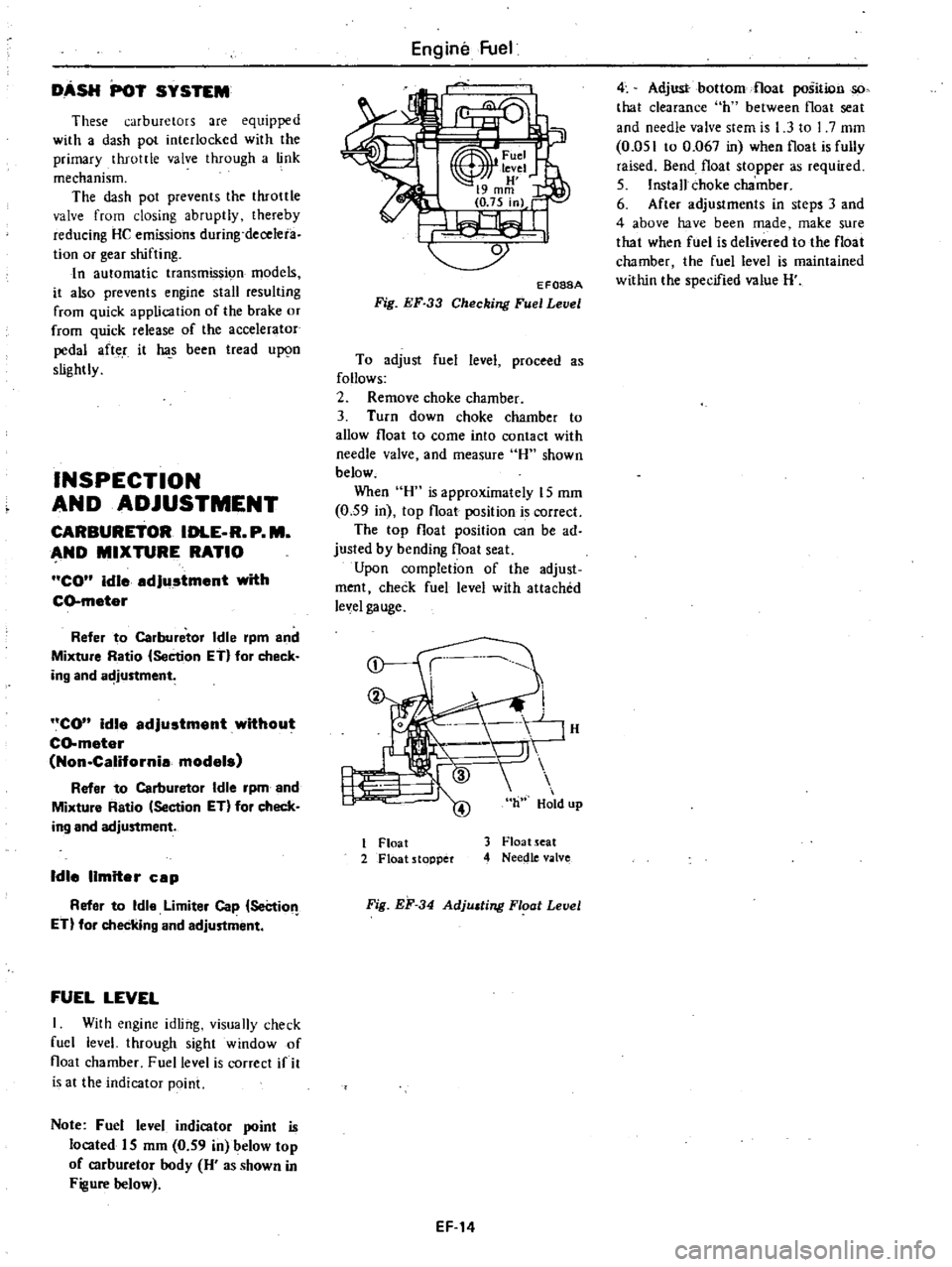
DASH
POT
SYSTEM
These
carburetors
are
equipped
with
a
dash
pot
interlocked
with
the
primary
thrott
Ie
valve
through
a
link
mechanism
The
dash
pot
prevents
the
throttle
valve
from
closing
abruptly
thereby
reducing
He
emissions
during
deceleia
tion
or
gear
shifting
In
automatic
transmissi9fi
models
it
also
prevents
engine
stall
resulting
from
quick
application
of
the
brake
or
from
quick
release
of
the
accelerator
pedal
after
it
s
been
tread
upon
slightly
INSPECTION
AND
ADJUSTMENT
CARBURETOR
IDLE
R
P
M
AND
MIXTURE
RATIO
CO
idle
adjustment
with
CO
meter
Refer
to
Carburetor
Idle
rpm
and
Mixture
Ratio
Section
ET
for
check
ing
and
a
justment
CO
idle
adjustment
without
CO
meter
Non
California
models
Refer
to
Carburetor
Idle
rpm
and
Mixture
Ratio
Section
ETl
fot
check
ing
and
adjustment
Idle
limiter
cap
Refer
to
Idle
Limiter
Cap
SeCtio
ET
for
checking
and
adjustment
FUEL
LEVEL
I
With
engine
idling
visually
check
fuel
level
through
sight
window
of
float
chamber
Fuel
level
is
correct
if
it
is
at
the
indicator
point
Note
Fuel
level
indicator
point
is
located
IS
mm
0
59
in
below
top
of
carburetor
body
H
as
shown
in
Figure
below
Engine
Fuel
EF088A
Fig
EF
33
Checking
Fuel
Level
To
adjust
fuel
level
proceed
as
follows
2
Remove
choke
chamber
3
Turn
down
choke
chamber
to
allow
float
to
come
into
contact
with
needle
valve
and
measure
H
shown
below
When
H
is
approximately
15
mm
0
59
in
top
float
position
is
correct
The
top
float
position
can
be
ad
justed
by
bending
float
seat
Upon
completion
of
the
adjust
ment
check
fuel
level
with
attached
level
gauge
nhH
J
1
Float
2
Float
stopper
3
Float
seat
4
Needle
valve
Fig
EF
34
Adjusting
Floot
Level
EF
14
4
Adjust
bottom
float
position
so
that
clearance
hl
between
float
seat
and
needle
valve
stem
is
1
3
to
I
7
mm
0
051
to
0
067
in
when
float
is
fully
raised
Bend
float
stopper
as
required
5
Install
choke
chamber
6
After
adjustments
in
steps
3
and
4
above
have
been
made
make
sure
that
when
fuel
is
delivered
to
the
float
chamber
the
fuel
level
is
maintained
within
the
specified
value
H
Page 100 of 548
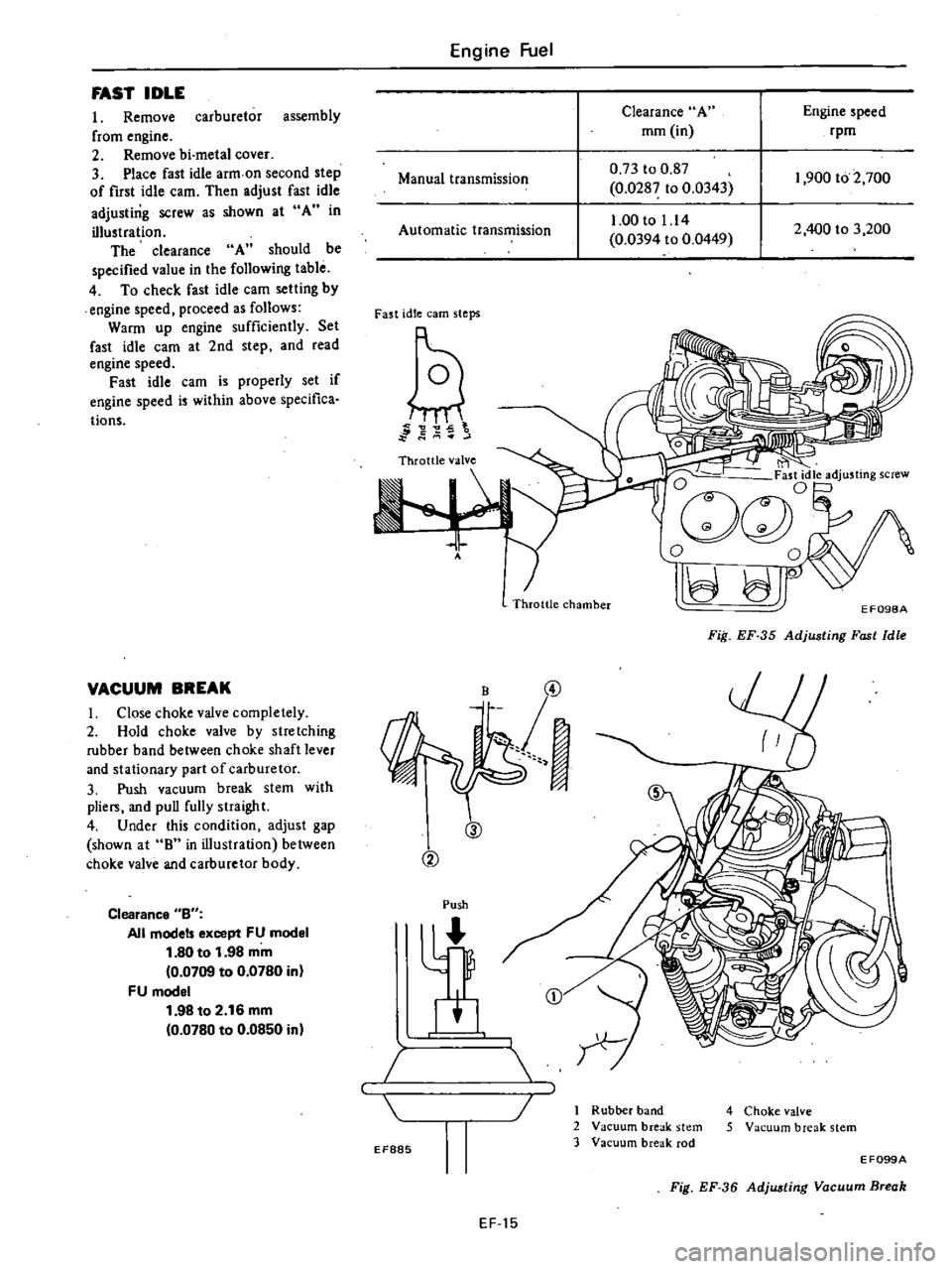
FAST
IDLE
I
Remove
carburetor
assembly
from
engine
2
Remove
bi
metal
cover
3
Place
fast
idle
arm
on
second
step
of
first
idle
cam
Then
adjust
fast
idle
adjusting
screw
as
shown
at
A
in
illustration
The
clearance
A
should
be
specified
value
in
the
following
table
4
To
check
fast
idle
cam
setting
by
engine
speed
proceed
as
follows
Warm
up
engine
sufficiently
Set
fast
idle
cam
at
2nd
step
and
read
engine
speed
Fast
idle
cam
is
properly
set
if
engine
speed
is
within
above
specifica
Hons
VACUUM
BREAK
I
Close
choke
valve
completely
2
Hold
choke
valve
by
stretching
rubber
band
between
choke
shaft
lever
and
stationary
part
of
carburetor
3
Push
vacuum
break
stem
with
plie
and
puD
fully
straight
4
Under
this
condition
adjust
gap
shown
at
8
in
illustration
between
choke
valve
and
carburetor
body
Clearance
Bu
All
model
except
FU
model
1
80
to
1
98
mm
0
0709
to
0
0780
in
FU
model
1
98
to
2
16
mm
0
0780
to
0
0850
in
Engine
Fuel
Clearance
A
mm
in
Engine
speed
rpm
Manual
transmission
0
73
to
0
87
0
0287
to
0
0343
1
00
to
1
14
0
0394
to
0
0449
2
400
to
3
200
1
900
to
2
700
Automatic
transmission
Fast
idle
earn
steps
g
g
2
5
t
to
J
A
ti
Ogc
j
jdle
adjusting
screw
o
0
II
r
Throttle
chamber
EF098A
Fiil
EF
35
Adjusting
Fast
Idle
@
B
@
cv
Push
I
4
Choke
valve
5
Vacuum
break
stem
EF885
1
Rubber
band
2
Vacuum
break
stem
3
Vacuum
break
rod
E
F099A
Fig
EF
36
Adjwtirig
Vacuum
Break
EF
15