ESP LAND ROVER FRELANDER 2 2006 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2006, Model line: FRELANDER 2, Model: LAND ROVER FRELANDER 2 2006Pages: 3229, PDF Size: 78.5 MB
Page 1281 of 3229

Solenoids
ItemPart NumberDescription
1-3-W ay s olenoi d - S1
2-3-W ay s olenoi d - S23-Line press ure cont rol s ol enoi d - SLT
4-Shift cont rol s ol enoi d - SLC2
5-Shift cont rol s ol enoi d - SLC16-Lock-up cont rol s olenoi d - SLU
7-Shift cont rol s ol enoi d - SLC3
8-Shift cont rol s ol enoi d - SLB19-Valve bl ock
Shift Cont rol Solenoids - SLC1, SLC2, SLC3, SLB1
The s hift control sol enoi ds (SLC1, SLC2, SLC3 and SLB1) are ins tal led on t he front valve body. The s olenoids respond t oinputs from t he TCM and control the hydrauli c pres s ure appli ed to the clut ches (C1, C2 and C3) and to the brake B1 t oprovide s moot h s hifti ng. The TCM us es a si ngl e or a combinat ion of t hes e s olenoids to provi de shi ft s from 1s t t o 6t h gear.
If a s ol enoi d fai ls , t he TCM wi ll remove t he current t o t he s hift cont rol s ol enoi ds and the trans mi s si on wil l use limp homemode, to prevent damage t o t he transmis s ion.
Line Pres s ure Cont rol Solenoid - SLT
The li ne pres s ure control s olenoid (SLT) is i nst all ed on t he front val ve body. The sol enoi d i s cont roll ed in a l inear mannerby t he TCM which us es t hrott le openi ng degree s ignals and engine t orque i nformat ion from t he Engi ne Control Module(ECM) t o det ermi ne the sol enoid operati on. The s olenoid controls t he l ine pres s ure appli ed t o t he cl utches and brakes toprovide s moot h s hifti ng.
If the s olenoid fail s, t he TCM will remove the current s uppl ied t o t he s ol enoi d. Maxi mum l ine press ure wil l be appl ied t ot he cl utches and brakes unl ess the fail ure i s due t o the sol enoi d val ve s ti cki ng, whi ch may res ult i n low li ne pres s ure.
Lock-Up Cont rol Solenoid - SLU
The lock-up control sol enoid is i nst all ed on t he front val ve body. The s ol enoi d i s cont roll ed in a l inear manner by t he TCMwhich us es engi ne s peed, t hrott le openi ng degree s ignals and t rans mis s ion s peed s ensor s ignals t o det ermi ne thes olenoi d operat ion. The sol enoi d cont rol s the amount of l ock-up or s l ip requi red for the t orque converter l ock-up cl utch.
If the s olenoid fail s, t he TCM removes the current s uppli ed t o t he sol enoi d which resul ts i n no t orque converter l ock-upbeing appli ed.
3-W ay Solenoi d - S1, S2
The 3-way sol enoid (S1) i s located on t he center valve body and s ol enoi d (S2) i s located on the front valve body. Thes olenoi ds are on/off s olenoids control led by the TCM. A combi nat ion of t he 2 s olenoids i s us ed to operat e ei ther the 1s tgear engine braki ng or enabl e gear s hift s.
If a s ol enoi d fai ls , t he TCM wi ll remove t he current s uppli ed to bot h s olenoids .
Speed Sensors
Page 1293 of 3229

SymbolDescription
44th gear s elected ('CommandShift™ 'mode)
55th gear s elected ('CommandShift™ 'mode)66th gear s elected ('CommandShift™ 'mode)
SPORTSport mode s elected
Message Center Display
The mes s age center i s located bel ow t he speedometer and t he tachometer at t he bot t om of t he ins trument cl ust er. Themes s age center i s a Liqui d Crys tal Di spl ay (LCD) t o rel ay vehi cl e s tat us informat ion t o t he dri ver.For addit ional informat ion, refer t o: Informat ion and Mes s age Cent er (413-08 Informat ion and Mes s age Cent er, Des cript ionand Operat ion).
CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (CAN)
The high s peed CAN broadcast bus net work i s us ed to connect t he powert rai n modules . The CAN bus is connect ed betweent he foll owing el ect ronic uni ts :
High Speed CAN Bus
TCMIns t rument clus terSteering angle s ens orRest rai nts control modul eEngi ne Control Module (ECM)ABS moduleAdapt ive Front l ight ing Syst em (AFS) cont rol moduleDiagnost ic socket .
The CAN bus all ows a fast exchange of dat a between modules . The CAN bus compri ses two wires which are identi fied asCAN hi gh (H) and CAN low (L). The t wo wires are colored yel low/bl ack (H) and yell ow/brown (L) and are twi s ted t oget her tomi ni mi se el ect romagneti c int erference (nois e) produced by the CAN bus mes sages .For addit ional informat ion, refer t o: Communicati ons Net work (418-00 Modul e Communicati ons Net work, Des cript ion andOperat ion).
In the event of CAN bus fai lure, t he fol lowi ng s ympt oms may be obs erved:
Trans mis s ion operat es in default modeTorque converter lock-up clut ch cont rol is dis abl edGear pos it ion indicati on in ins trument cl us t er LCD inoperati ve (t his will al so occur wit h any t rans mis s ion faul t).
DRIVING MODES
A number of different dri ving modes are avai lable. Some can be s elected by the driver and some are aut omati cal ly i nit iatedby t he TCM t o adapt t o di fferent drivi ng condit ions .
NormalSportManual 'CommandShift ™'CoolingHil l Descent Cont rol (HDC)Crui seLimp homeCoastFast off recogni ti onUphill and TrailerDownhillW i de Throt tl eTerrai n Res pons eRevers e lock-out
Normal
Normal mode is automat icall y s elect ed by t he TCM when t he i gni ti on is swi tched on. In this mode all automat ic andadapt ive modes are acti ve. Normal mode uses gear s hi ft and l ock-up maps which provi de the opt imum of fuelcons umpt ion, emis s ions and dri veabil it y, depending on t he dri ving s tyl e.
If the t rans mis s ion is operat ed in sport mode or 'CommandShi ft ™' mode and t he s elector lever is moved back t o t he drive'D' pos it ion, then normal mode operat ion is resumed.
Sport
Sport mode provi des enhanced accelerat ion and respons ivenes s by t he us e of s ports shi ft maps . This mode al lows t het ransmis s ion t o down s hift more readil y and hol d gears for longer at hi gher engine speeds .
Manual 'CommandShift™'
Manual 'CommandShift ' mode al lows t he t rans mis s ion t o operat e as a semi -aut omati c trans mi s si on. The driver can changeup and down t he s ix forward gears wi th the freedom of a manual t rans mis s ion.
Shift maps are provi ded to protect t he engi ne at high s peeds . The TCM wi ll automat icall y change up t o a higher gear rat iot o prevent engine overspeed and change down to a lower gear rati o t o avoi d engine l aboring and s t al li ng.
W hen ki ck-down is reques ted the TCM shi ft s down t o t he lowes t avai lable gear. W hen the vehicl e is st ati onary, t he drivercan s el ect 1s t , 2nd or 3rd t o s tart off.
Page 1294 of 3229

W hen movi ng from a st andst il l, ups hi ft s can be pre-s el ect ed by making '+' s el ect ions wi th the s elect or l ever for thenumber of ups hifts requi red. The TCM t hen performs t he reques ted number of upshi ft s when appropri at e s hift points arereached. For exampl e; when moving off in 1s t gear, if 3 '+' s elect ions are made i n quick s ucces si on, t he TCM willautomat ically ups hift t hrough the gears to 4t h gear as t he vehi cl e accelerates , wit hout any furt her s electi ons bei ng made.
Cooling
Cooling mode is act ivated when t he TCM det ect s exces s ively hi gh trans mi s si on fl uid or engine coolant temperatures . W hent hi s mode i s act ive torque converter l ock-up is acti vat ed earl ier t o mi ni mi ze a further ris e in fl uid and/or engine coolantt emperature and ass i st flui d cool ing.
Hill Descent Control (HDC)
The HDC mode as s is t s t he ABS module i n cont rol li ng the downhil l speed of t he vehi cl e. W hen HDC i s acti ve, t he TCMs elect s t he mos t appropri at e gear for t he descent to maxi mi ze engi ne braking.
Maximum engi ne braking i s applied us i ng a s hift map which i nit iat es later ups hift s and earl y downshi ft s .
Cruise
W hen s peed cont rol i s act ivated, t he TCM receives a speed control acti ve mes s age on the hi gh s peed CAN bus . The TCMact ivat es a s peed cont rol map whi ch minimizes up and down s hifts .
Crui se mode is act ive when s peed cont rol is sel ect ed on and t he transmis s ion i s in drive 'D', s port 'S', HDC or Terrai nRespons e Gras s /gravel /s now program. Unique cruis e maps overri de the current mode t o provide a smoot h driving feel andmode resel ect ion.
Limp Home
If a transmis s ion faul t is det ect ed by t he TCM, the TCM adopt s a l imp home s trategy and a mes s age 'TRANSMISSIONFAULT LIMITED GEARS AVAILABLE' i s dis played in the mes s age cent er. If the fault has an effect on engi ne emis s ions , theMIL in the i nst rument clus t er wi ll als o be il luminat ed.
In li mp home mode, P, R and N functi ons operate normall y (i f the fault al lows t hes e s elect ions) and t he TCM locks t het ransmis s ion i n 3rd gear t o all ow t he dri ver t o t ake the vehicle to a Land Rover deal er or approved repai rer. Torqueconvert er lock-up i s dis abled and reverse-lock-out wil l not funct ion.
If the vehicle is s t opped and s ubsequentl y res tarted in t he li mp home mode condi ti on, t he TCM operat es normall y unti l thefaul t which caus ed t he condi ti on is det ect ed agai n.
Coast
Coast mode provides earli er downs hifts during coast ing dependant on out put shaft decelerat ion rate to improve driveabili tyand refinement by avoi ding negati ve to pos it ive driveli ne torque revers als t rans mi ssion during t he downshi ft s .
Fast Off Recognition
Fast off recogni ti on is act ivated when t he TCM det ect s t hat t he dri ver has releas ed the accel erat or pedal qui ckl y. This isdetected by the TCM monit oring for a high level of negat ive pedal angl e from ECM s ignals on t he high speed CAN bus . Ift hi s condi ti on is det ect ed, t he TCM hol ds the current gear rati o to allow the driver t o compl ete the manoeuvre wi thout t heneed for a downs hift. The mode can remain acti ve for a predet ermined lengt h of ti me or i f the driving s t yl e remainspass i ve.
Fast off recogni ti on mode as si s ts vehicle st abili ty and is us ed i n conjunct ion a lateral accel erat ion i nput duri ng corneri ng tomaint ain t he current gear unti l the corner is negot iated.
Uphill and Trailer
Uphill and t rai ler mode can be acti ve when the trans mi s si on is operat ing in normal, s port or Terrai n Res pons e modes .W hen t he vehicle i s pull ing a t rai ler or dri vi ng up an i ncl ine, the TCM det ects t he i ncreas ed res i st ance by monit oring enginet orque and s peed s i gnal s received from the ECM on the hi gh s peed CAN bus and als o t rans mis s ion out put s haft s peeds ens or s ignals . Uphi ll and t rai ler mode wi ll provide downs hift s t o prevent a drop in t rans mi ss i on torque out put andmaint ain driving force.
Downhill
Downhill mode can be act ive when t he t ransmis s ion i s operati ng in normal, s port or Terrain Res pons e modes . W hen t hevehi cl e i s descendi ng an i ncl ine t he TCM detect s a reducti on in res is t ance by moni toring engine t orque and s peed si gnal sreceived from the ECM on t he high s peed CAN bus and als o t rans mis s ion out put shaft speed s ensor s ignals . Downhill modeas si st s engine braki ng by s elect ing an appropriat e gear reduci ng the load required on t he brakes .
Wide Throttle
W i de open thrott le mode operates for part thrott le ups hifts and ki ck-down ups hifts . It provides cons i st ent wide opent hrott le ups hift performance under all driving condit ions. The full engine s peed range is used i n all driving modes ; normal ,s port, hi ll modes and Commands hi ft . Compens at ion i s used for delays (hydrauli c and electroni c) in gear change reques t togear change s tart to provi de s mooth changes and correct shi ft point correct ion.
Terrain Response
The Terrai n Res pons e s ys tem has a unique s et of shi ft maps for each of t he Terrai n Res pons e programs . Thes e programsoverri de exis ti ng modes; for exampl e when HDC is acti ve and the 'Sand', 'Mud and Ruts ' or 'Grass /Gravel/Snow' programsare sel ect ed, a specific Terrain Res ponse map is used, not the HDC mode s hift map detai led previ ous ly.
Page 1486 of 3229
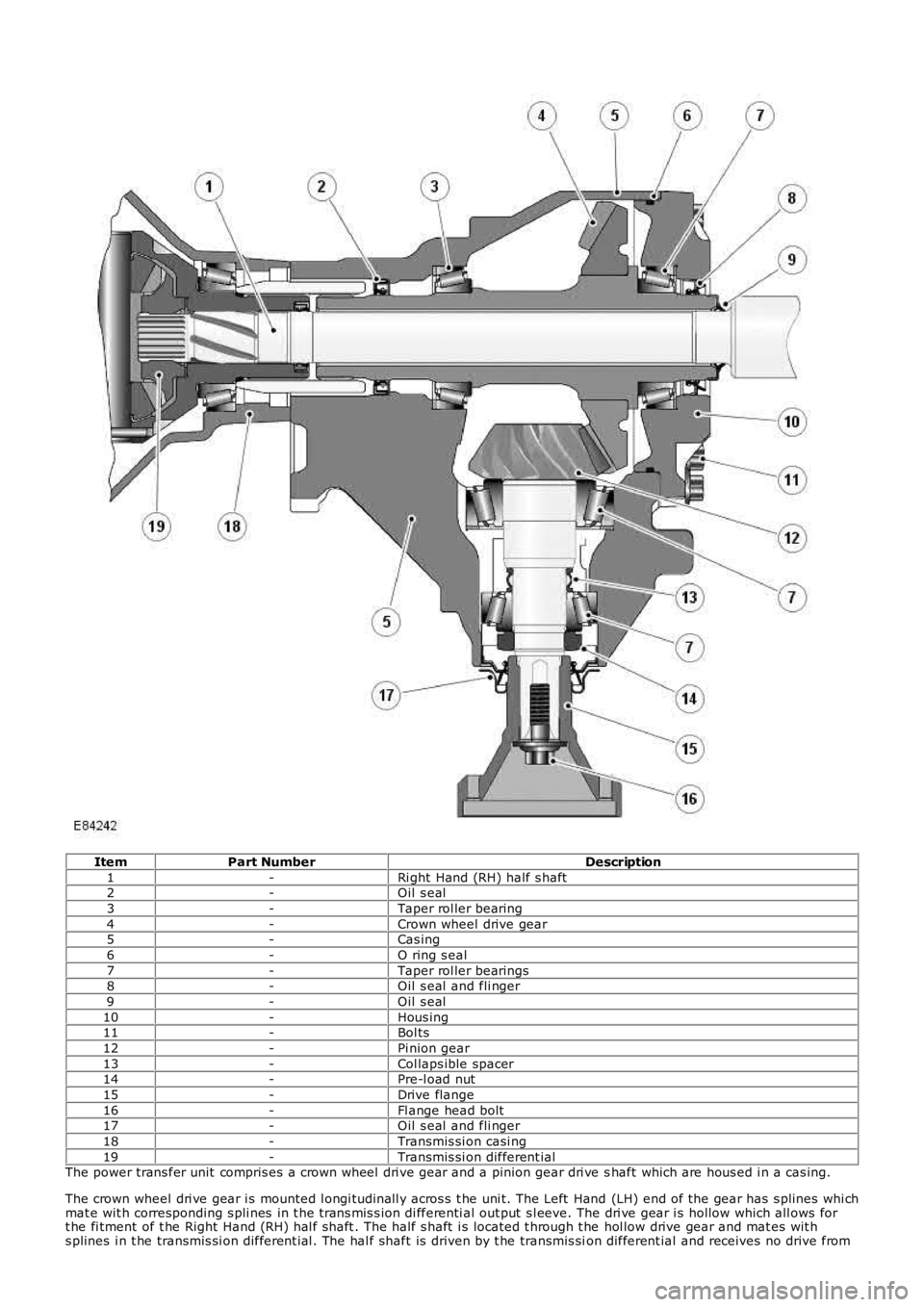
ItemPart NumberDescription
1-Ri ght Hand (RH) half s haft2-Oil s eal
3-Taper rol ler bearing
4-Crown wheel drive gear5-Cas ing
6-O ring s eal
7-Taper rol ler bearings8-Oil s eal and fli nger
9-Oil s eal
10-Hous ing11-Bol ts
12-Pi nion gear
13-Col laps ible spacer14-Pre-l oad nut
15-Drive flange
16-Fl ange head bolt17-Oil s eal and fli nger
18-Transmis si on casi ng
19-Transmis si on different ialThe power trans fer unit compris es a crown wheel dri ve gear and a pinion gear dri ve shaft which are hous ed i n a cas ing.
The crown wheel dri ve gear i s mounted l ongi tudinall y acros s t he uni t. The Left Hand (LH) end of the gear has s plines whi chmat e wit h corresponding s pli nes in t he t rans mis s ion di fferenti al out put s l eeve. The dri ve gear i s hollow which all ows fort he fi tment of t he Right Hand (RH) hal f shaft . The half s haft i s located t hrough t he hol low drive gear and mat es wit hs plines i n t he transmis si on different ial . The hal f shaft is driven by t he transmis sion different ial and receives no drive from
Page 1515 of 3229

5-Gasket
6-Tailpi pe fi nis her (opti onal )
7-Mount ing rubber (6 off)8-Rear muffler
9-Cent re muffler
10-Flange11-Bracket
12-Catalyt ic converter (2 off)
13-Flange14-Catalyt ic converter (2 off)
15-Exhaus t manifol d gas ket s
OVERVIEW
The 3.2L SI6 exhaus t s yst em i s fabricated from s tai nl ess st eel and is s upplied as two separat e as sembl ies ; a front s ect ionincorporat ing t wo catal yt ic convert ers and a rear sect ion i ncorporat ing centre and rear s i lencers.
EXHAUST MANIFOLDS
The exhaus t manifold compri s es two separat e manifold as s embli es . One mani fol d is us ed for cyli nders 1 t o 3 and thes econd mani fold is us ed for cyli nders 4 t o 6. The manifolds are s eal ed to the cyli nder head wi th a gas ket and s ecured wit h14 bolt s .
Each manifol d compri ses t hree fabri cat ed branches whi ch merge i nto an int egral cat alyti c convert er. A threaded bos s isposi ti oned where t he t hree branches merge and provi des for t he fi tment of a pre-catalys t HO2S. The cat alyti c convert eroutl et s have offs et flanges which mat e wi th corres pondi ng fl anges on t he front s ect ion exhaus t s ys tem.
A bracket on each out let flange all ows for t he att achment of an exhaus t mani fold heat s hield.
FRONT SECTION
The front sect ion has t wo flanged pi pes which mat e wi th the offs et fl anges of t he exhaus t manifol ds. The flanges ares eal ed wit h gas ket s and s ecured wit h bolt s . The fl anges are connected vi a curved pipes t o decouplers which provide afl exi ble joint i n the sys tem. The out let from each decoupl er compris es a curved pipe wit h a t hreaded bos s whi ch providesfor t he fit ment of a pos t -catal ys t HO2S.
Each pi pe is connect ed i nt o a smal ler catalyt ic converter whi ch in t urn is connected to a doubl e fl ange which mat es wit ht he rear s ect ion of t he exhaus t s ys t em.
Two mount ing rubbers are l ocat ed at the rear of the flexible coupli ng and are at t ached t o a bracket mounted on the fronts ubframe.
REAR SECTION
The rear s ect ion has a doubl e fl ange which mat es wit h t he doubl e fl ange of the front s ect ion. The doubl e flanges of eachs ect ion are s eal ed wi th a gas ket and s ecured wit h s tuds , washers and nuts . Two s hort pipes from the double fl angeconnect int o the cent re muffl er.
The cent re muffler is a fabricated unit wit h a capaci ty of 7.6 li ters. The muffl er compris es a pair of perforat ed baffle t ubescont ained wi thin the muffler body. The t wo baffle tubes merge into one s ingle t ube which provi des the out let from t hemuffler. A rubber mounti ng is at t ached t o t he rear of the muffler and att aches t o a hanger bracket l ocat ed on theunders ide of t he vehi cl e fl oorpan.
A s i ngl e pipe from t he rear of the centre muffl er is rout ed along t he unders ide of the vehi cl e body to the rear muffler. Thepipe ent ers t he rear muffl er t hrough a connect ion i n t he forward face of the muffl er.
The rear muffl er i s a fabri cat ed uni t wit h a capacit y of 29.3 l it ers . The rear muffler i s pos i ti oned t rans vers ely at t he rear oft he vehi cl e, forward of the rear bumper. The muffler compri ses baffl e plat es and perforated baffle tubes . Each end of t hemuffler body has an outl et which direct exhaus t gas ses to exit at t he rear of t he vehi cl e. The muffler is support ed by as ingle rubber mount ing on t he Left Hand (LH) s ide and by t wo rubber mounti ngs on the Right Hand (RH) s ide.
CATALYTIC CONVERTERS
The cat alyt ic converters are fit t ed in t he front s ect ion of t he exhaus t s ys t em, aft er the HO2S.
The HO2S moni tors the exhaust gas s es leavi ng t he engi ne. The engine management s ys t em us es t hi s informat ion t oprovide accuratel y met ered quant it ies of fuel t o t he combus t ion chambers t o ens ure the mos t efficient us e of fuel and t omi ni mi se the exhaus t emi s si ons .
In the cat alyti c convert ers , t he exhaus t gas es are pas s ed t hrough honeycombed ceramic el ement s coated wi th a s peci als urface t reat ment cal led 'was hcoat '. The was hcoat i ncreas es t he s urface area of the cerami c element s by a fact or ofapproximat el y 7000. O n top of t he was hcoat i s a coat ing cont ai ning plat inum, whi ch is t he act ive cons ti tuent forconvert ing harmful emi ss i ons into inert by-product s. The pl at inum adds oxygen t o the carbon monoxi de and thehydrocarbons i n t he exhaus t gases , to convert t hem i nto carbon di oxi de and water respecti vel y.
Page 1531 of 3229
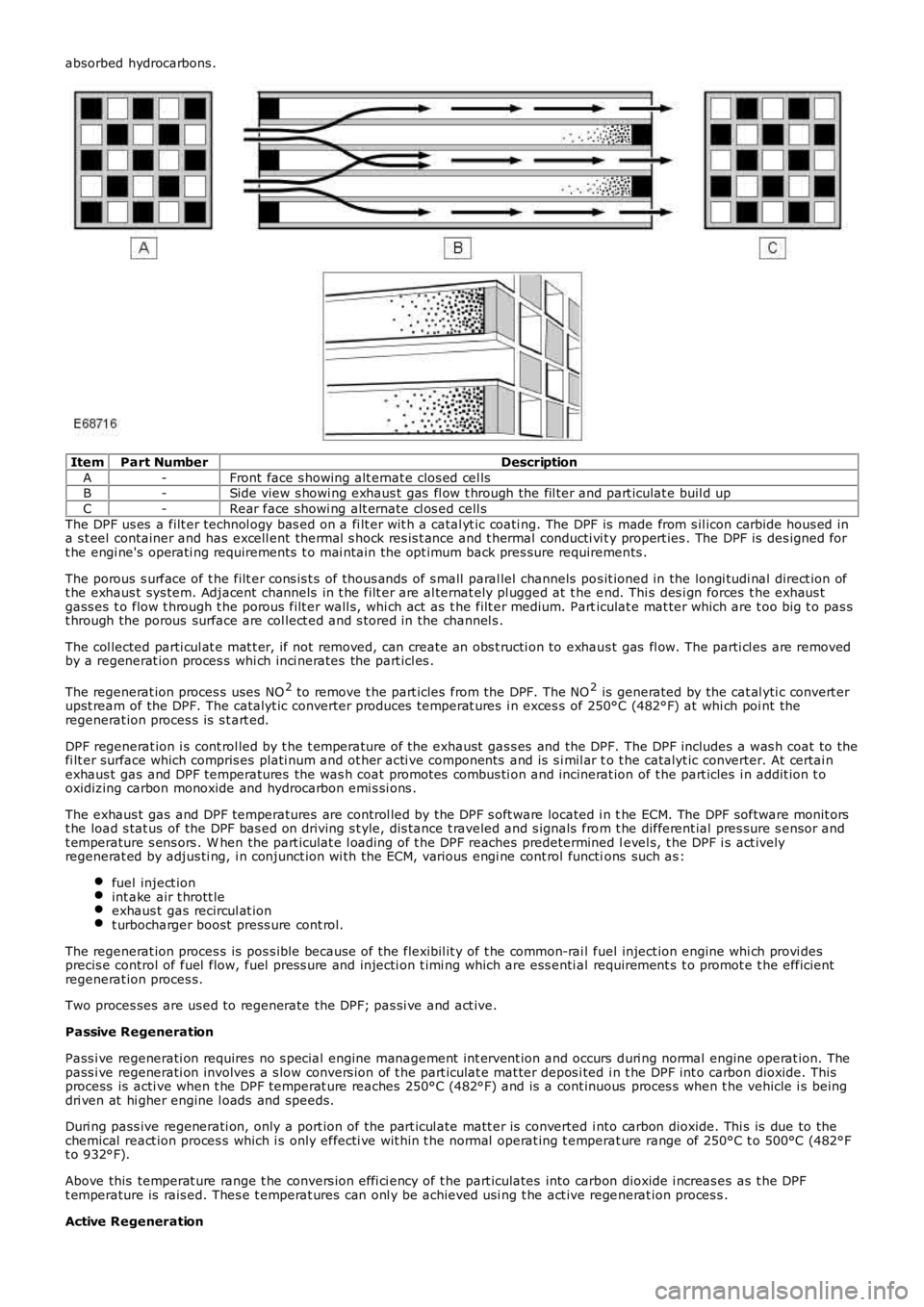
absorbed hydrocarbons .
ItemPart NumberDescription
A-Front face s howing alt ernat e clos ed cel lsB-Side view s howi ng exhaus t gas fl ow t hrough the fil ter and part iculat e buil d up
C-Rear face showi ng alt ernate cl os ed cell s
The DPF us es a filt er technol ogy bas ed on a fi lt er wit h a catal yt ic coati ng. The DPF is made from s il icon carbide hous ed ina s t eel container and has excell ent thermal s hock res is t ance and t hermal conducti vi ty propert ies . The DPF is des igned fort he engi ne's operati ng requirements t o mai ntain the opt imum back pres sure requirements .
The porous s urface of t he filt er cons is t s of thous ands of s mall paral lel channels pos it ioned in the longi tudi nal direct ion oft he exhaus t sys tem. Adjacent channels in t he filt er are al ternat ely pl ugged at t he end. Thi s des i gn forces t he exhaus tgass es t o flow t hrough t he porous filt er wall s, whi ch act as t he filt er medium. Particulat e mat ter which are t oo big t o pas st hrough the porous surface are col lect ed and s t ored in the channel s .
The col lected parti cul at e mat t er, if not removed, can create an obs t ructi on to exhaus t gas fl ow. The parti cl es are removedby a regenerat ion proces s whi ch inci nerates the part icl es .
The regenerat ion proces s uses NO2 to remove t he part icles from the DPF. The NO2 is generated by the cat al yti c convert erupst ream of the DPF. The catalyt ic converter produces temperat ures i n exces s of 250°C (482°F) at whi ch poi nt theregenerat ion proces s is s t art ed.
DPF regenerat ion i s cont rol led by t he t emperature of the exhaust gas s es and the DPF. The DPF includes a was h coat to thefi lt er surface which compris es plati num and ot her acti ve components and is s i mil ar to t he catalyt ic converter. At certai nexhaus t gas and DPF temperatures the was h coat promot es combus ti on and incinerat ion of t he part icles i n addit ion t ooxidizing carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon emi s si ons .
The exhaus t gas and DPF temperatures are control led by the DPF s oft ware located i n the ECM. The DPF software monit orst he load s tat us of the DPF bas ed on driving s t yle, dis tance t raveled and s ignals from t he different ial pres sure s ensor andt emperature s ens ors . W hen the part iculat e l oading of t he DPF reaches predetermined level s, t he DPF i s act ivelyregenerat ed by adjus ti ng, i n conjunct ion wi th the ECM, vari ous engi ne cont rol functions such as :
fuel inject ionint ake air t hrott leexhaus t gas recircul at iont urbocharger boost press ure cont rol.
The regenerat ion proces s is pos s ible because of the flexibil it y of t he common-rai l fuel inject ion engine whi ch provi desprecis e control of fuel flow, fuel pres s ure and injecti on t imi ng which are ess enti al requirement s t o promot e t he efficientregenerat ion proces s.
Two proces ses are us ed to regenerate the DPF; pas si ve and act ive.
Passive Regeneration
Pass i ve regenerati on requires no s pecial engine management int ervent ion and occurs duri ng normal engine operat ion. Thepass i ve regenerati on involves a s low convers ion of t he part iculat e mat ter depos i ted i n t he DPF int o carbon dioxide. Thisprocess is acti ve when t he DPF temperat ure reaches 250°C (482°F) and is a cont inuous proces s when t he vehicle i s beingdri ven at hi gher engine l oads and speeds.
Duri ng pass ive regenerati on, only a port ion of t he part icul ate matt er is converted into carbon dioxide. Thi s is due to thechemical react ion proces s which i s only effecti ve wit hin t he normal operat ing t emperat ure range of 250°C t o 500°C (482°Ft o 932°F).
Above this temperat ure range t he convers ion effi ci ency of t he part iculates into carbon dioxide i ncreas es as t he DPFt emperature is rais ed. Thes e t emperat ures can onl y be achieved usi ng t he act ive regenerat ion proces s .
Active Regeneration
Page 1655 of 3229

Rear Window Heater
The rear window hea ter comprise s a single heat er e leme nt bonded to the inner surf ace of t he glass . The syste m is swi tche don by pre ssing the mome nta ry s witch locate d on the control panel. W he n se lected, the ATC module tra nsmits a he atingreque st on the high spee d CAN bus to the CJB. On recei pt of the me ssa ge, the CJB energiz es t he rear window hea ter relayl ocat ed i n the Auxilia ry Junct ion Box (AJB) by providing a ground pa th for the re lay coil. The energiz ed relay provide s a bat teryf eed to t he heat er e leme nt. Afte r a period of 12 minute s the ATC module re moves the heat ing request . The CJB then powe rsdown the rea r wi ndow he ate r by removing the ground pa th f or t he relay coil .
The ATC module will only reques t re ar window heate r opera tion if the e ngine is running. An engine stat us s ignal is provide d tot he ATC module by t he ECM over the high speed CAN bus.
Exterior Mirror Heaters
O peration of the ext erior mirror heat ers is fully a utomat ic a nd re qui res no input from the driver. The exterior mirror hea tersa re a ctive when the ambient air tempera ture is below 5°C (41°F) and e ngine coolant te mpe rature i s be low 65° C (149° F).Ambi ent air a nd engine coola nt t empera ture val ues are provided by the ECM on the high speed CAN bus. O n re ceipt of the set emperat ure values, the CJB det ermines if e xterior mirror he ating is require d.
The CJB requests exterior mirror hea ting by transmit ting a high spe ed CAN bus mes sage to bot h the drivers and pa sse ngerdoor module s. The door modules provide fee d and ground paths to the respecti ve e xterior mirror he ating el eme nts . W hena mbi ent and engine cool ant tempera ture ris es a bove the va lues sta ted earl ier, the CJB transmi ts a high speed CAN busmess age to the door module s ca nce lling the hea ting reques t.
Seat Heaters
O peration of the sea t he aters is controll ed by the ATC module on re ceipt of a heati ng reque st f rom either of the se at heat ermomenta ry s witches loca ted on the cont rol pane l. The s witches are mounte d in the LH and RH rota ry controllers. A singlepress of a se at heat er switch wi ll implement low level heati ng a nd illumina te a tell-tale LED. A second pre ss of the switch willi mple me nt high l eve l hea ting and ill uminate 2 te ll-t ale LED's. A third press of t he s witch will turn t he s eat hea ter off.
Seat hea ting request s are transmitte d from the ATC module to the seat hea ter control modules on the LIN bus . Two se atheat er control modul es a re f itted, one under each front seat . The se at heat er control modules provide an e lect rical supply tot he s eat hea ter e lement s and a tempera ture sensor loca ted in t he s eat cus hion.
The s eat hea ter cont rol module provides a 5 V reference fee d to the sea t he ate r te mpe rature s ensor. The s eat hea tert emperat ure sensor is an NTC thermistor. By monitoring the ret urne d voltage, t he control module can calculate thet emperat ure of t he s eat. If t he t empera ture rise s above the target tempera ture , the control module wi ll dis abl e operat ion oft he heat er e leme nts .
Page 1739 of 3229

Publi s hed: 11-May-2011
Auxiliary Climate Control - Electric Booster Heater
Des cript ion and Operat ion
COMPONENT LOCATION
ItemPart NumberDescription1-Heater as sembl y
2-Electric boos ter heater
OVERVIEW
Due t o t he s lower warm up t imes as s oci at ed wi th the di es el engi ne, an elect ric booster heat er may be fit ted t o i ncreas eheat er performance. The el ect ri c boos t er heater does t hi s by heati ng the ai r leaving t he heater as sembl y.
The electric boos ter heater compris es cerami c coat ed t hermis t or el ements and a microcontroll er. A reques t for el ect ri cboos t er heat er operat ion origi nat es in the Aut omati c Temperature Control (ATC) module. Thi s reques t is t rans mi tt ed to theCentral Junct ion Box (CJB) over t he medium speed Controll er Area Network (CAN) bus . The CJB int erpret s t hi s reques t andoutputs a Puls e W idth Modul ati on (PW M) s ignal t o t he electric boos ter heater mi crocont roll er. The durat ion of t he puls esprovided by t he CJB is proport ional t o t he amount of heat ing requi red.
The amount of heat ing reques ted by the ATC i s bas ed on:
Ambient air t emperat ureEngi ne Coolant Temperature (ECT)Heati ng request .
Page 1746 of 3229

The cont rol module is powered by a permanent feed from the Bat t ery Junct ion Box (BJB), and communi cat es wi th t he ATCmodule over the medium speed Controller Area Network (CAN) bus .
AUXILIARY COOLANT PUMP
The auxi li ary coolant pump is mount ed on t he heater cas i ng and is us ed t o as si s t coolant flow through t he FFBH and t heheat er core.
The auxi li ary coolant pump runs conti nuous ly whi le the FFBH i s act ive. W hen t he FFBH is inact ive, cool ant flow is reli ant ont he engi ne cool ant pump. Operat ion of t he auxi li ary cool ant pump is controll ed by a power feed di rect from t he cont rolmodule wit hi n t he FFBH.
Stop/Start Vehicles - From 2010 MY
Duri ng a St op/Start cycle when the engine i s s hutdown and consequent ly the engine-driven coolant pump is st ati onary, thedesi red s et cabi n t emperature cannot be mai ntai ned for a prol onged period, especially in col d ambient t emperatures . Tocount eract this an auxi li ary electric coolant -pump, cont rol led by t he ECM (engi ne cont rol module), has been i ntegrat ed int ot he cooli ng s yst em t o mai ntai n the coolant flow t hrough t he cabi n’s heater core. This s upporti ng circulat ion prolongs thes et temperat ure set ti ng in the cabin and accordingly prevent s an earl y engi ne res t art .
On vehicles fit ted wit h a Fuel Fi red Boos ter Heat er (FFBH) t he addit ional auxil iary cool ant pump is not ins t al led. In it splace t he FFBH auxi liary cool ant pump is ut il ized t o circulat e t he cool ant i n an engine s hutdown s i tuati on. The pump isact ivat ed via t he FFBH by t he CJB (central junct ion box).For addit ional informat ion, refer t o: Starti ng Sys t em (303-06C Starti ng Syst em - TD4 2.2L Di es el, Vehicles Bui lt From:01-03-2009, Descripti on and Operat ion).
AMBIENT AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Page 1768 of 3229

and t ransmit s t he engi ne s peed s i gnal t o the ins trument cl us t er on the medi um s peed CAN bus . The s ignal i s received byt he ins trument cl ust er microproces s or and t he output from the microproces sor dri ves the t achomet er.
Engine Temperature Gage
The engi ne t emperature gage is l ocat ed in the center of t he ins trument cl ust er and is driven by medi um s peed CAN busmes s ages from the CJB. The CJB receives an Engine Coolant Temperat ure (ECT) s i gnal from the ECM over t he high s peedCAN bus when t he vehi cle ent ers power mode 6 (ignit ion on). The needl e pointer pos ition t rans lat es to the followi ngapproximat e t emperatures .
Engine Coolant T emperature °C (°F)
Pointer PositionPetrolDiesel
Igni ti on offIgni ti on offPark40 (104)40 (104)Cold (blue s egment)
75 (167)75 (167)Begi nning of normal
119 (246)113 (235)End of normal125 (257)118 (244)Begi nning of hot (red s egment )
130 (266)123 (253)End of hot
If the ECT s i gnal ri s es above 118 °C (244 °F) on dies el vehicles , or 127 °C (260 °F) on petrol vehi cl es , t he ins t rumentclus ter wi ll il lumi nat e t he high ECT warning i ndi cat or. If the ins trument cl us t er fail s t o receive an ECT s i gnal from the CJB,t he engi ne cool ant t emperat ure gage wi ll move t o t he 'end of hot' posi ti on and t he warning indicator wil l be il lumi nat ed.
Fuel Level Gage
The fuel level gage is l ocat ed in the center of the ins trument cl us t er and di s pl ays fuel tank contents when the vehicle is i npower mode 6. W hen t he ignit ion i s s wit ched off, t he point er returns to the park posi ti on.
Two Magneti c Pas s ive Pos it ion Sens ors (MAPPS) are l ocated in t he s addl e t ype fuel tank, one on eit her s i de. Theres is t ance values for bot h s ensors are measured by t he CJB through a series of hardwi red connect ions. The CJB convertsboth val ues t o medi um s peed CAN mes s ages for delivery to the i nst rument clus t er. The ins trument cl ust er uses the 2 CANbus mes sages t o calculate the t otal amount of fuel in bot h halves of the tank. The ins trument cl us t er wil l al so damp t het ot al fuel val ue t o eli minate cons tant point er movement due t o fuel moving in t he t ank.
The fol lowing table shows t he approximat e fuel t ank level and t he respecti ve needle poi nter pos it ion.
Fuel Quantity Liters (US gallons)
Pointer PositionPetrolDiesel0 (0)0 (0)Mechanical zero
1 (0.2)2.5 (0.6)Below empt y
2.8 (0.7)3.8 (1)Indicat ed empty11.9 (3.1)10.3 (2.7)Low fuel level indicator i lluminated
13.9 (3.7)12.3 (3.2)Low fuel level indicator exti ngui shed
16.9 (4.5)16.7 (4.4)Quart er full33.8 (8.9)33.4 (8.8)Half ful l
50.8 (13.4)50 (13.2)Three quart ers full
66.9 (17.7)68 (18)Indicat ed full70.5 (18.6)70.5 (18.6)Over full
If the i nst rument clus ter fails to recei ve t he fuel level si gnal s from t he CJB t he fuel level gage will move to t he empt yposi ti on and t he low fuel level i ndi cat or wil l be il lumi nat ed.
Speedometer
The s peedomet er i s located on the Ri ght Hand (RH) s ide of t he clus ter and i s avai lable i n 3 variants :
Major s cal e mph, mi nor s cale ki lomet ers per hour (kph)Major s cal e kph, minor s cal e mphMajor s cal e kph only.
The s peedomet er i s dri ven by medium speed CAN bus si gnal s transmit ted by t he CJB. The vehicl e s peed s i gnal is providedt o the CJB by the Ant i-lock Brake Sys tem (ABS) module over t he high s peed CAN bus and is an average of al l 4 wheels peed sens or si gnal s.
The s peedomet er al so incorporat es the odomet er.For addit ional informat ion, refer t o: Informat ion and Mes s age Cent er (413-08 Informat ion and Mes s age Cent er, Des cript ionand Operat ion).
WARNING INDICATORS