MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE 1990 Service Manual
ECLIPSE 1990
MITSUBISHI
MITSUBISHI
https://www.carmanualsonline.info/img/19/57103/w960_57103-0.png
MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE 1990 Service Manual
Trending: length, air conditioning, power steering fluid, lumbar support, ignition, brakes, lock
Page 101 of 391
9-16ENGINE- Base Engine
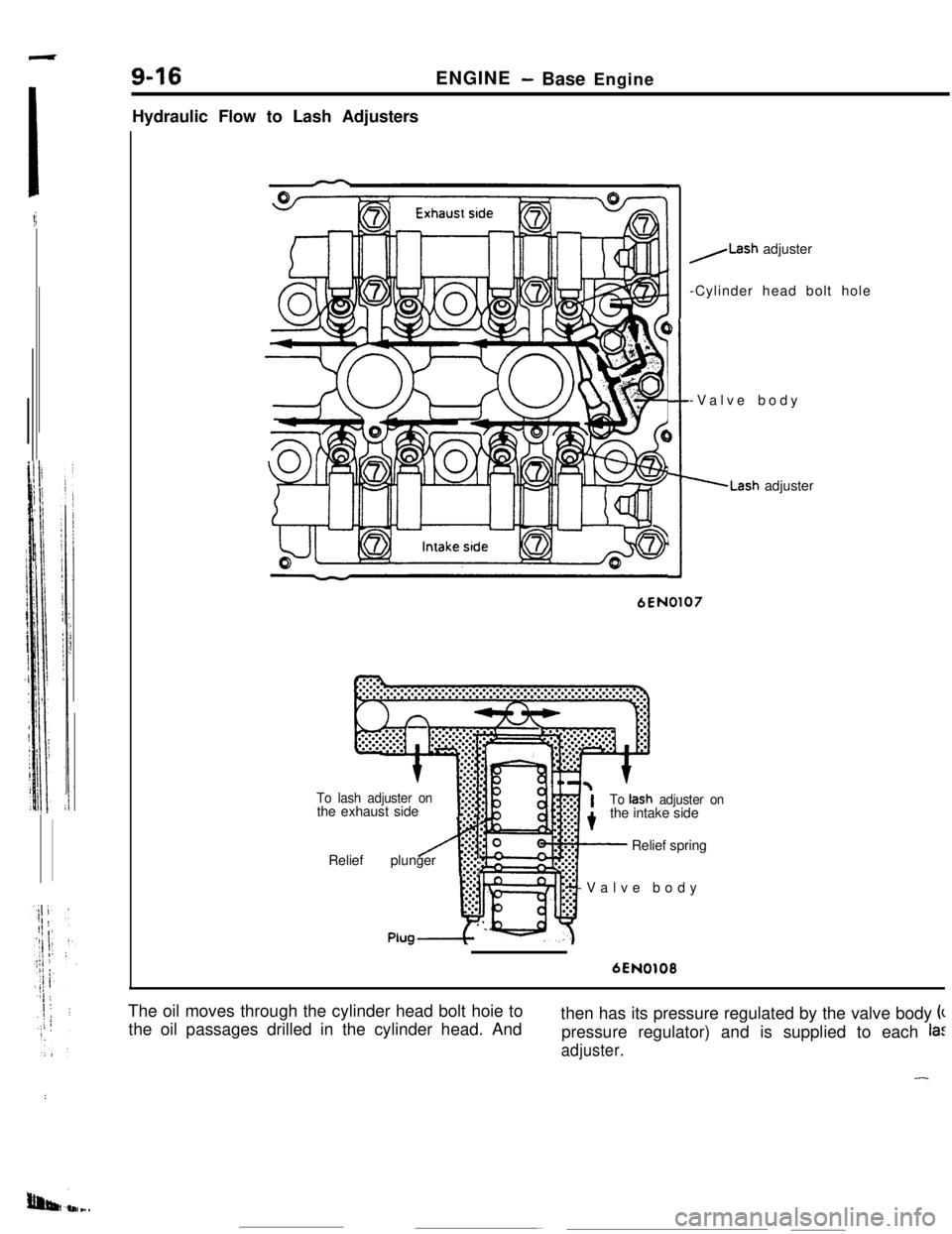
Hydraulic Flow to Lash Adjusters
To lash adjuster onthe exhaust side
P
)
5-Valve body
.Lash adjuster
6EN0107
:.-.
2:.
4
‘.’Relief plunger
I?.,:.:.;
/Lash adjuster
-Cylinder head bolt hole
PlugTo
tash adjuster onthe intake side
Relief spring
-Valve body
6EN0108The oil moves through the cylinder head bolt hoie to
the oil passages drilled in the cylinder head. Andthen has its pressure regulated by the valve body k
pressure regulator) and is supplied to each
la:
adjuster.
-:
Page 102 of 391
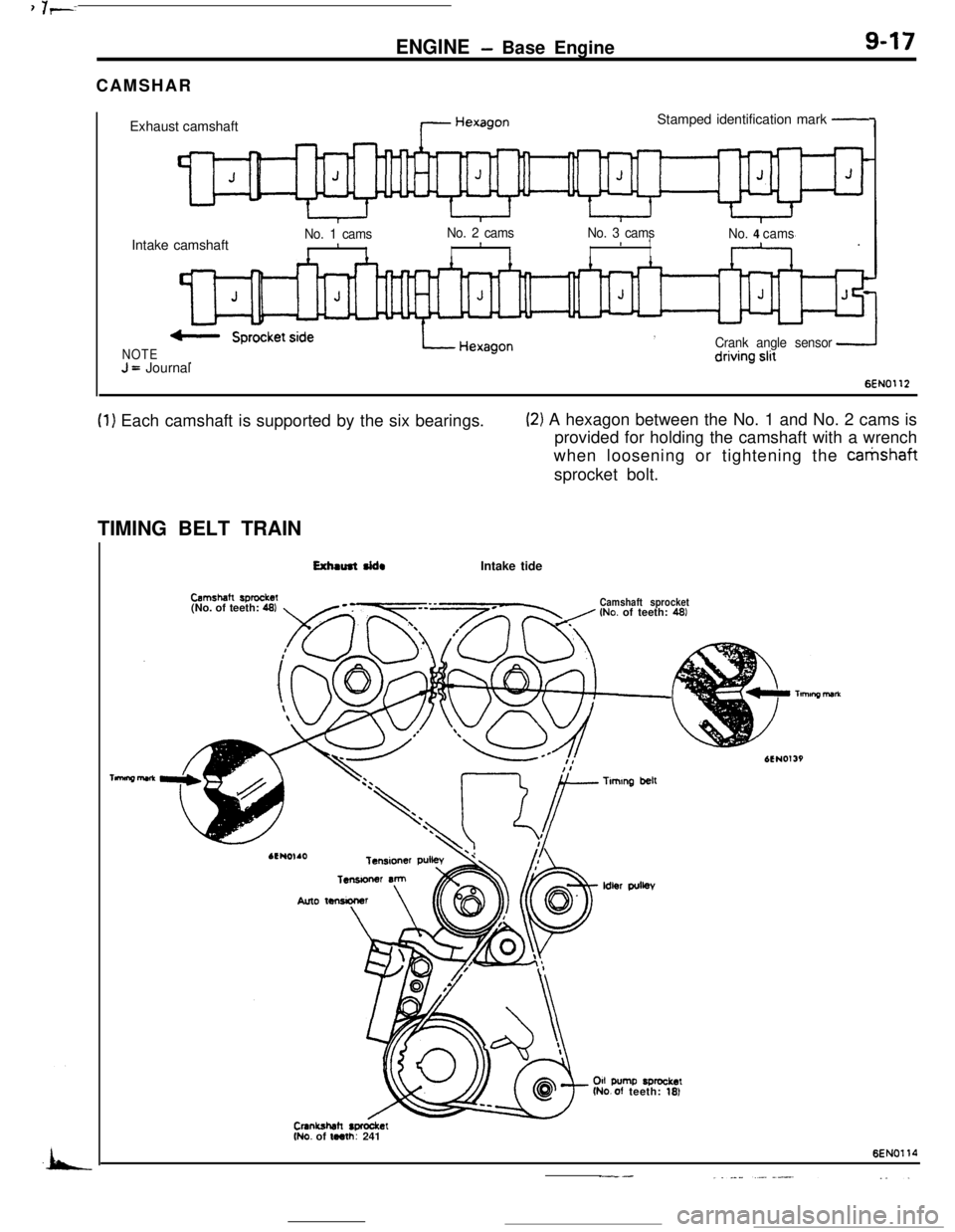
ENGINE- Base Engine9-17CAMSHAR
Exhaust camshaftStamped identification mark
-
-
k--JL---J
No. 1 camsNo. 2 camsNo. 3 cams
No. 4 camsIntake camshaftIt’ II’ II1
NOTEJ = Journal
Crank angle sensor6EN0112
(1) Each camshaft is supported by the six bearings.(2) A hexagon between the No. 1 and No. 2 cams is
provided for holding the camshaft with a wrench
when loosening or tightening the
catishaftsprocket bolt.
TIMING BELT TRAIN
Exhmmt rid.Intake tide
Camshatt sprookec(No. of teeth: 461Camshaft sprocket(No. of teeth: 461
MN0139
6tNOl10
011 Pump stmoket(No. o! teeth: 18)
Crankshatr spmokst(No. of loath: 2416EN0114
Page 103 of 391
9-18ENGINE- Base Engine
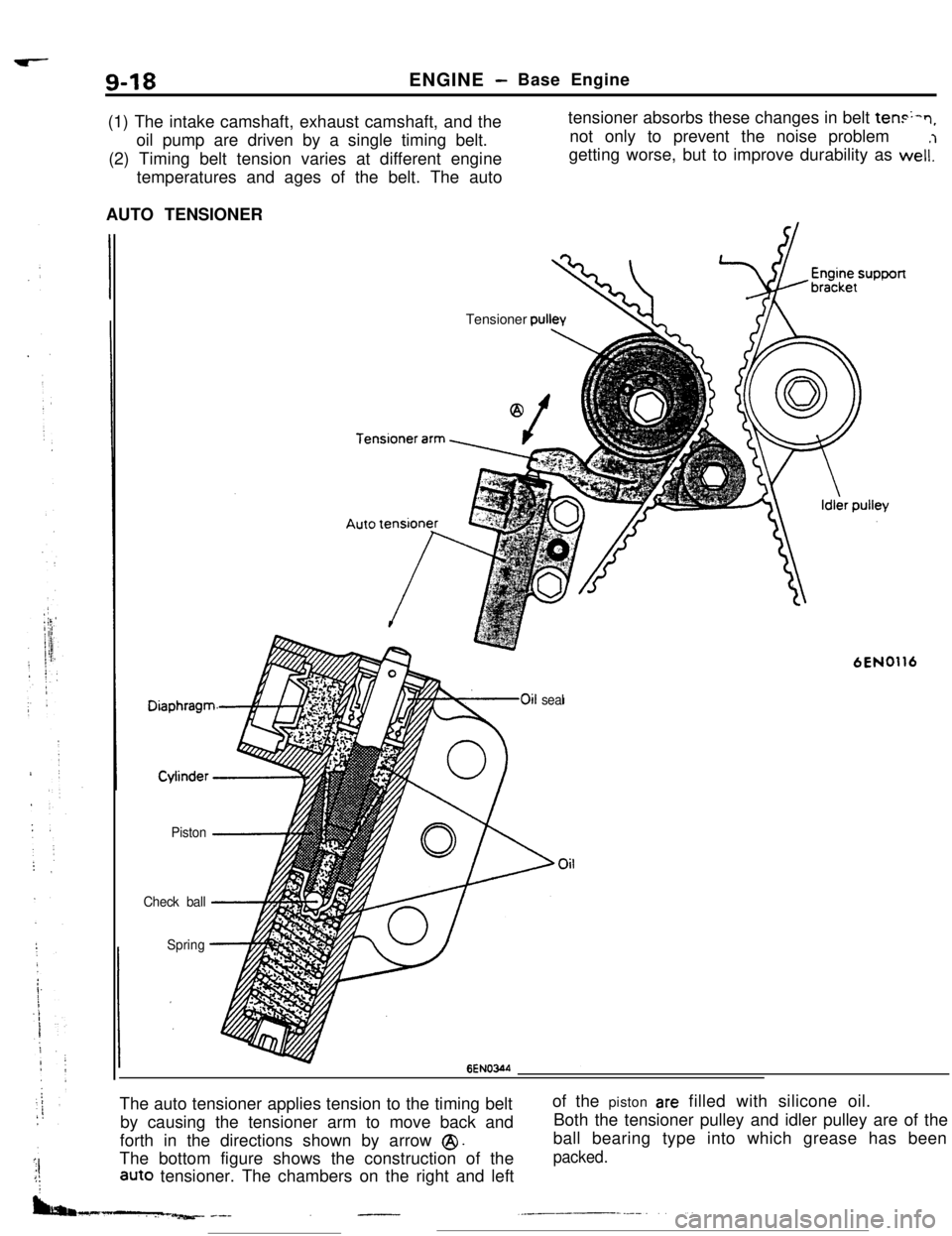
(1) The intake camshaft, exhaust camshaft, and the
oil pump are driven by a single timing belt.
(2) Timing belt tension varies at different engine
temperatures and ages of the belt. The autotensioner absorbs these changes in belt
ten+n,not only to prevent the noise problem
getting worse, but to improve durability as weli’l
AUTO TENSIONER
Piston -1
Check ball-4,
SpringTensioner
cwllev
6EN0116
LOoil seal
6ENOWThe auto tensioner applies tension to the timing belt
by causing the tensioner arm to move back and
forth in the directions shown by arrow
@I.The bottom figure shows the construction of the
aUt0 tensioner. The chambers on the right and leftof the piston
are filled with silicone oil.
Both the tensioner pulley and idler pulley are of the
ball bearing type into which grease has been
packed.
Page 104 of 391
,_-.._-~_._. I _ ‘... ----
ENGINE- Base Engine9-19
Reservoir
chamber/
Reservoir
chamber
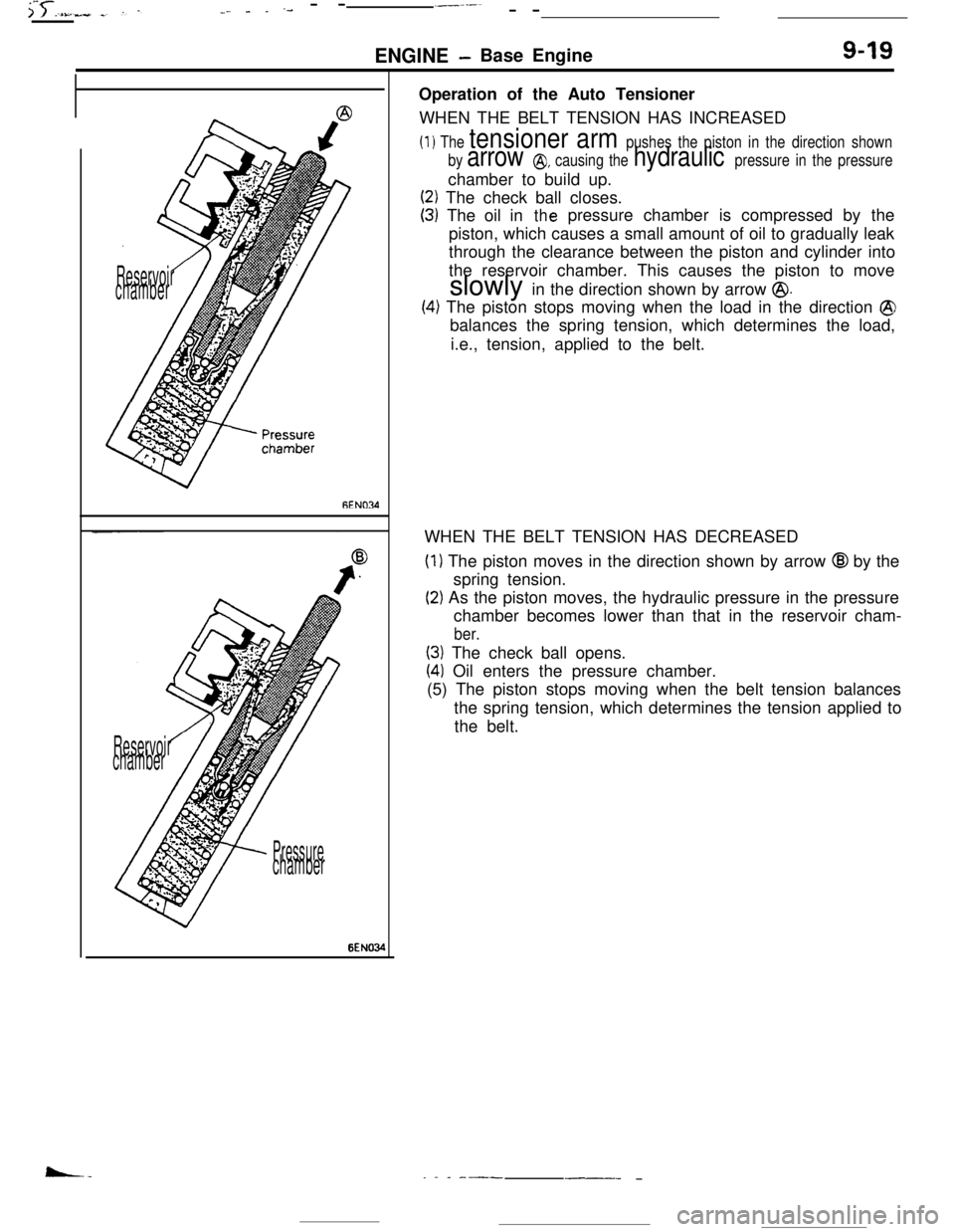
PressurechamberOperation of the Auto Tensioner
WHEN THE BELT TENSION HAS INCREASED
(1) The tensioner arm pushes the piston in the direction shown
by
arrow @, causing the hydraulic pressure in the pressurechamber to build up.
(2) The check ball closes.
(3) The oil inthepressure chamber is compressed by the
piston, which causes a small amount of oil to gradually leak
through the clearance between the piston and cylinder into
the reservoir chamber. This causes the piston to move
slowly in the direction shown by arrow
@.
(4) The piston stops moving when the load in the direction @balances the spring tension, which determines the load,
i.e., tension, applied to the belt.
WHEN THE BELT TENSION HAS DECREASED
(1) The piston moves in the direction shown by arrow @I by the
spring tension.
(2) As the piston moves, the hydraulic pressure in the pressure
chamber becomes lower than that in the reservoir cham-
ber.
(3) The check ball opens.
(41 Oil enters the pressure chamber.
(5) The piston stops moving when the belt tension balances
the spring tension, which determines the tension applied to
the belt.
_ . _ ---___- -
Page 105 of 391
9-20ENGINE- Lubricathn System
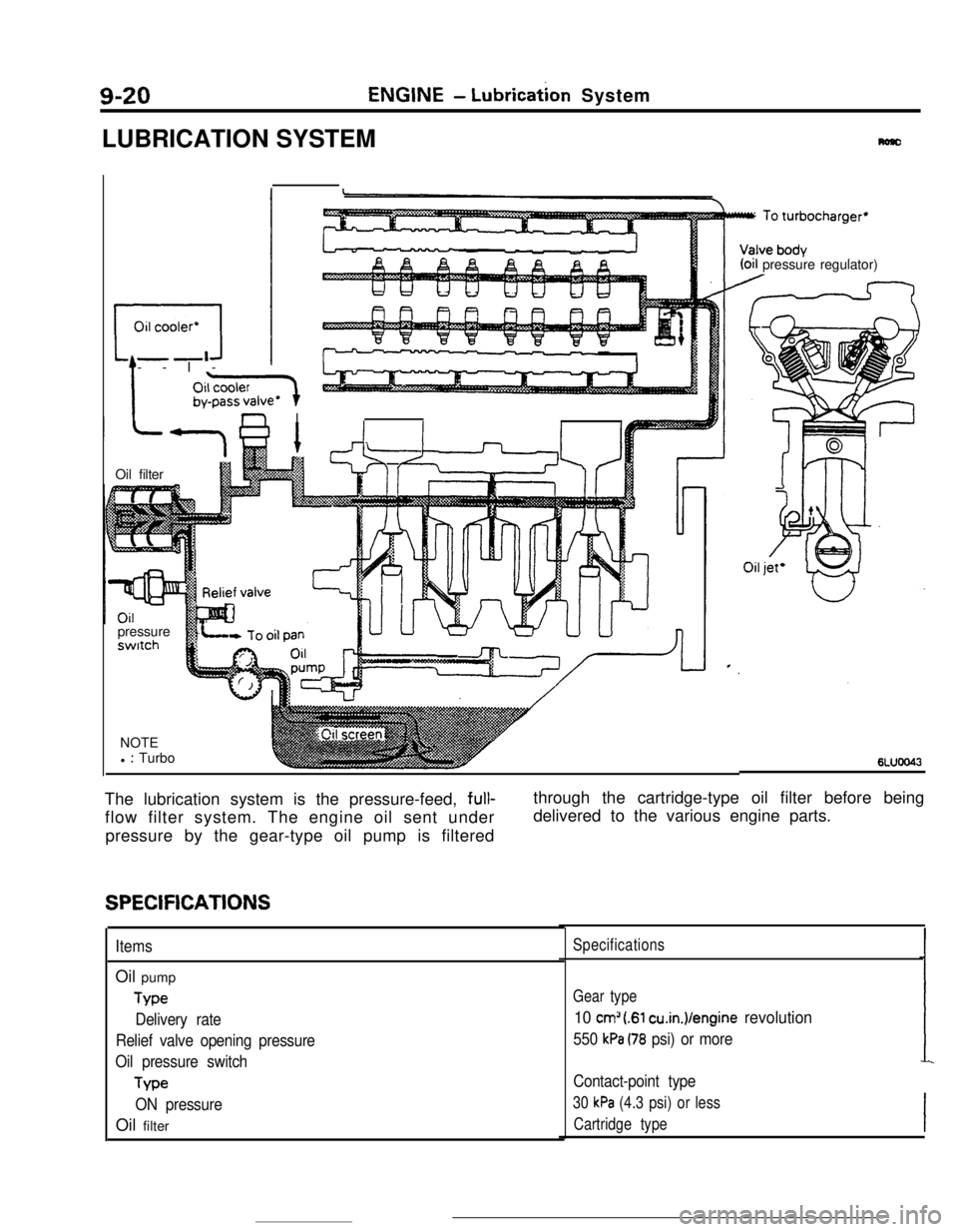
LUBRICATION SYSTEM
nasllOil cooler*
r-4--I-
(oil pressure regulator)
I
n I-1Oil filter
pressureswttch
NOTE
l
: Turbo6LUOO43The lubrication system is the pressure-feed, full-
flow filter system. The engine oil sent under
pressure by the gear-type oil pump is filteredthrough the cartridge-type oil filter before being
delivered to the various engine parts.
SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsOil pump
Type
Delivery rate
Relief valve opening pressure
Oil pressure switch
Type
ON pressureOil filter
Specifications
Gear type
10 cm” (.Sl cu.in.)/engine revolution
550 kPa (78 psi) or more
Contact-point type
30 kPa (4.3 psi) or less
Cartridge type
Page 106 of 391
L1ENGINE
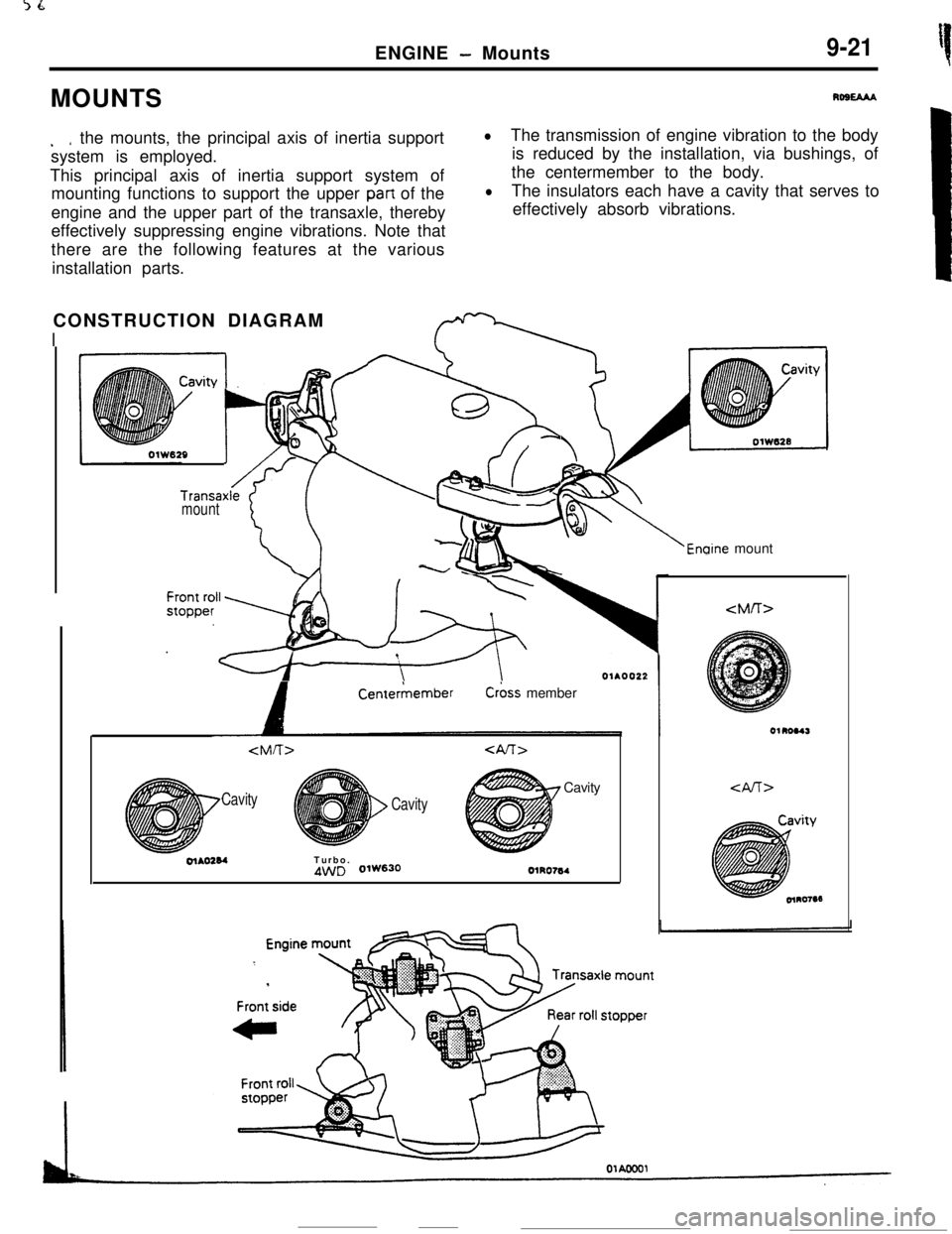
- Mounts9-21MOUNTS
Rost3u
. *the mounts, the principal axis of inertia support
system is employed.
This principal axis of inertia support system of
mounting functions to support the upper
part of the
engine and the upper part of the transaxle, thereby
effectively suppressing engine vibrations. Note that
there are the following features at the various
installation parts.
lThe transmission of engine vibration to the body
is reduced by the installation, via bushings, of
the centermember to the body.
lThe insulators each have a cavity that serves to
effectively absorb vibrations.
CONSTRUCTION DIAGRAM
I
Transaxlemount
‘i::
+g
/v 1b-8
8-,
Enaine mount
A
CenterkemberC&s member
Cavity
CavityCavityolAO284Turbo.
4WD 0lW630OlRO764
Page 107 of 391
9-22ENGINE- Mounts
Principalaxi? of inertia
The
::I: indicates mount positions.01 RO77OlAbsorption action during minute vibrations
ICavity
CavityOlRcl767l
Absorption during large vibrations or “rolling”
Cavity
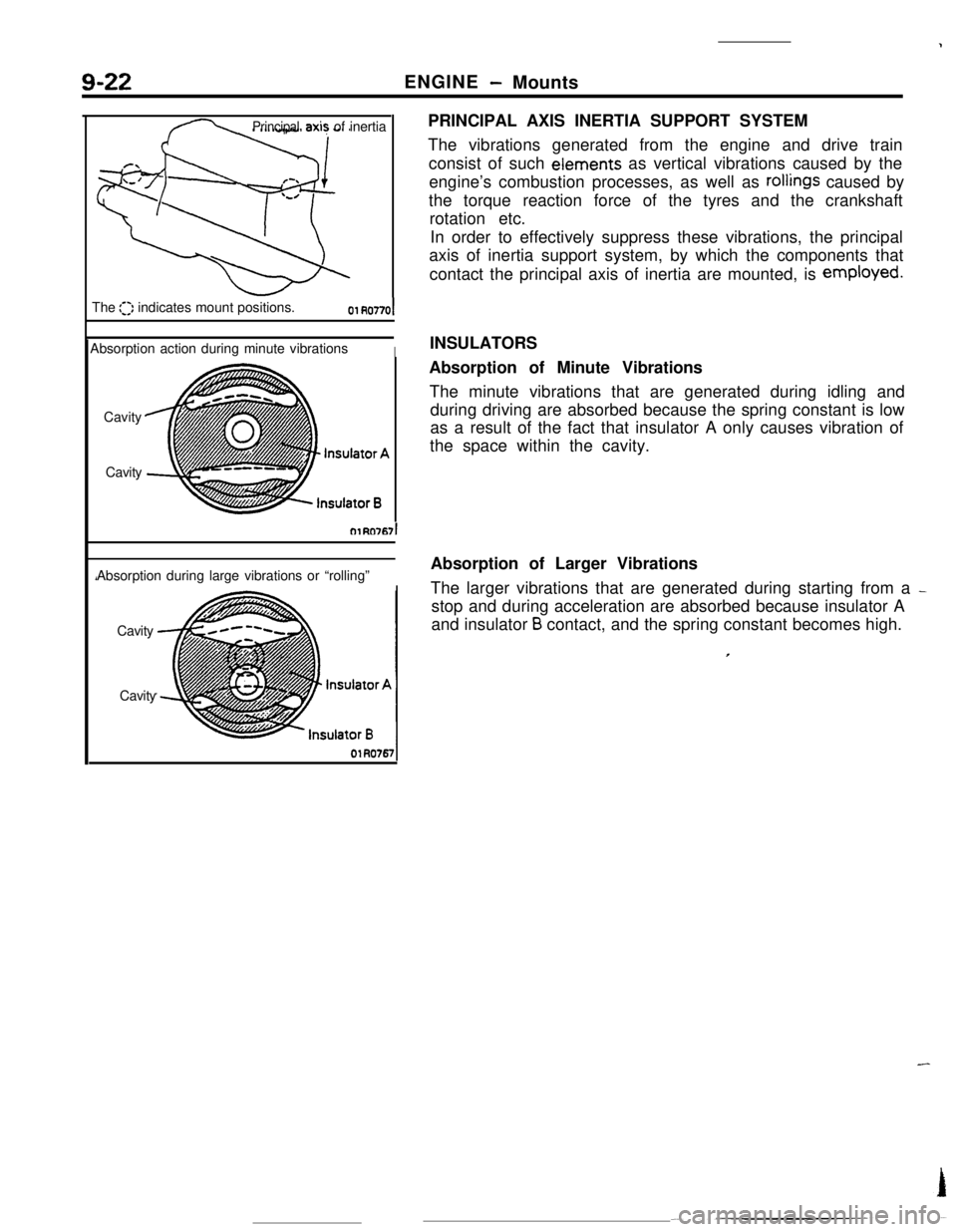
CavityPRINCIPAL AXIS INERTIA SUPPORT SYSTEM
The vibrations generated from the engine and drive train
consist of such eiements as vertical vibrations caused by the
engine’s combustion processes, as well as
rollings caused by
the torque reaction force of the tyres and the crankshaft
rotation etc.
In order to effectively suppress these vibrations, the principal
axis of inertia support system, by which the components that
contact the principal axis of inertia are mounted, is employed.
INSULATORS
Absorption of Minute Vibrations
The minute vibrations that are generated during idling and
during driving are absorbed because the spring constant is low
as a result of the fact that insulator A only causes vibration of
the space within the cavity.
Absorption of Larger Vibrations
The larger vibrations that are generated during starting from a
_stop and during acceleration are absorbed because insulator A
and insulator
B contact, and the spring constant becomes high.
Page 108 of 391
?/.-
II-I
INTAKE AN
3EXHAUST MANIFOLD 2 INTAKE MANIFOLDL........................................ ............................................
..-......................
5
_...--
Page 109 of 391
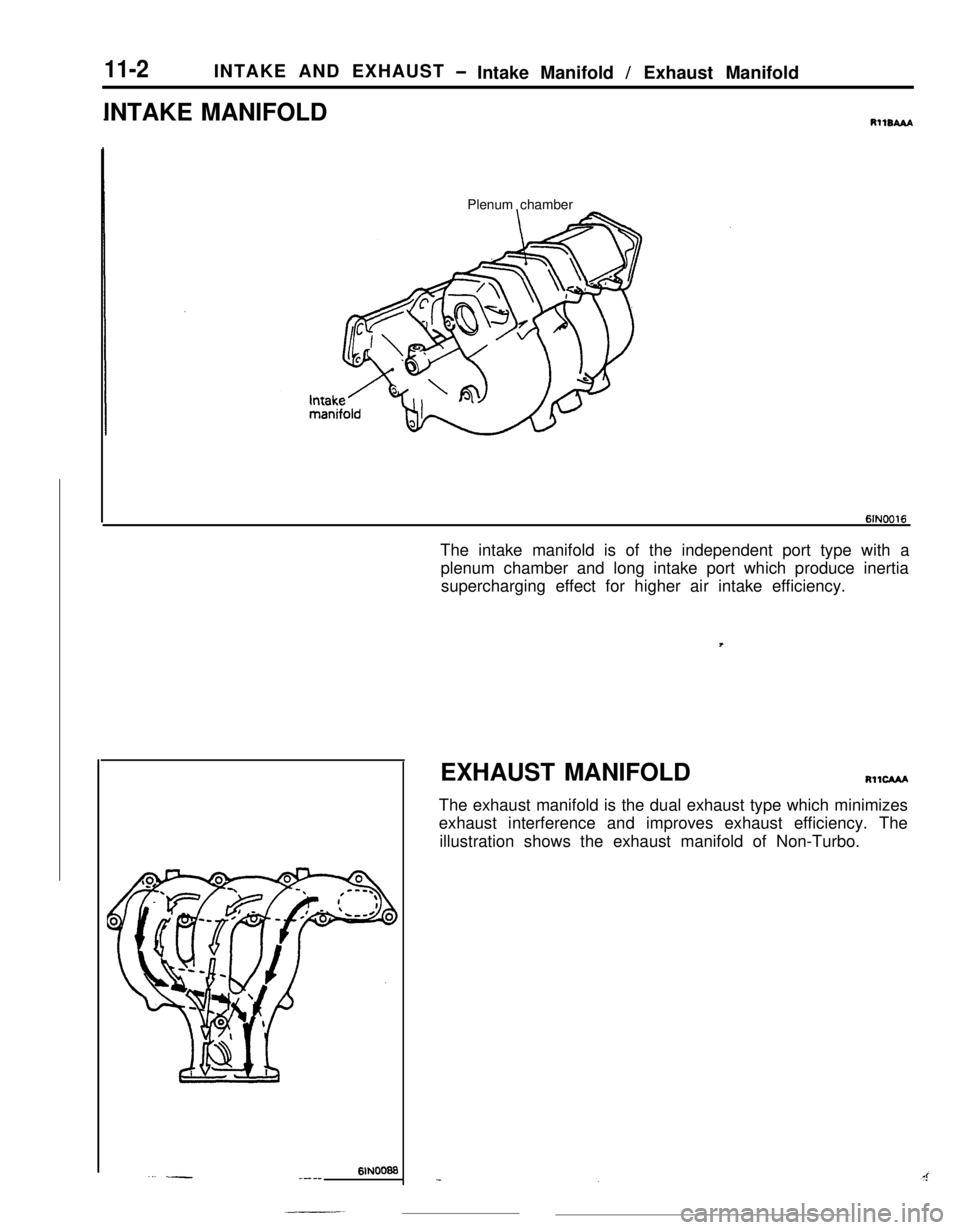
11-2 INTAKE AND EXHAUS T -Intake Manifold / Exhaust Manifold
RllmAA
Plenum chamber
6lNoo16
The intake manifold is of the independent port type with a
61N00@3..’ --_---
EXHAUST MANIFOLDRllcAM
The exhaust manifold is the dual exhaust type which minimizes
Page 110 of 391
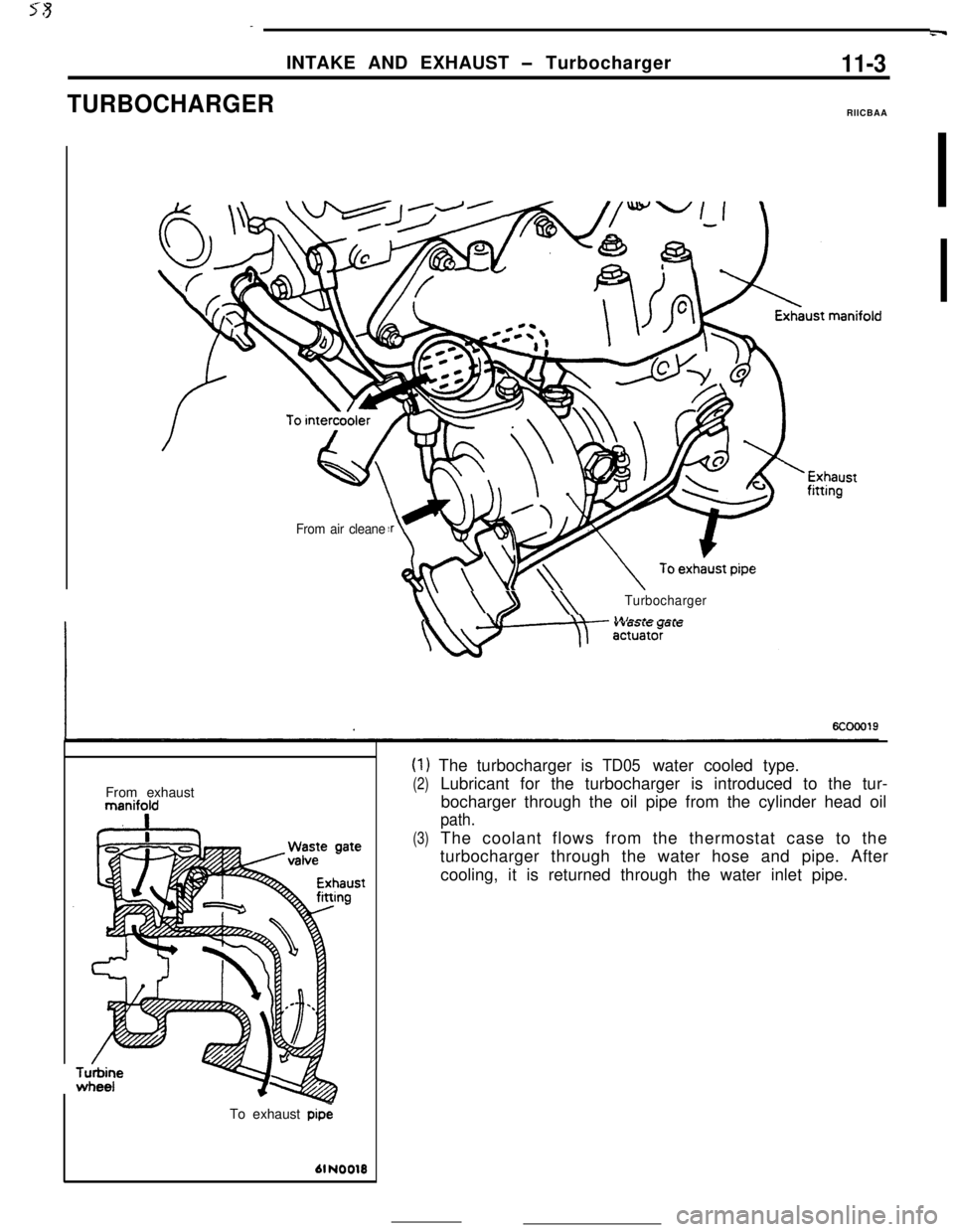
rg_m
INTAKE AND EXHAUST - Turbocharger
13 \Turbocharger
manifold
-J
To exhaust pipe
61 NO010
(1) The turbocharger is TD05 water cooled type.
Trending: oil capacity, fuel filter, spare wheel, low beam, change time, coolant temperature, fuel pressure