DATSUN 210 1979 Service Manual
Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1979, Model line: 210, Model: DATSUN 210 1979Pages: 548, PDF Size: 28.66 MB
Page 171 of 548
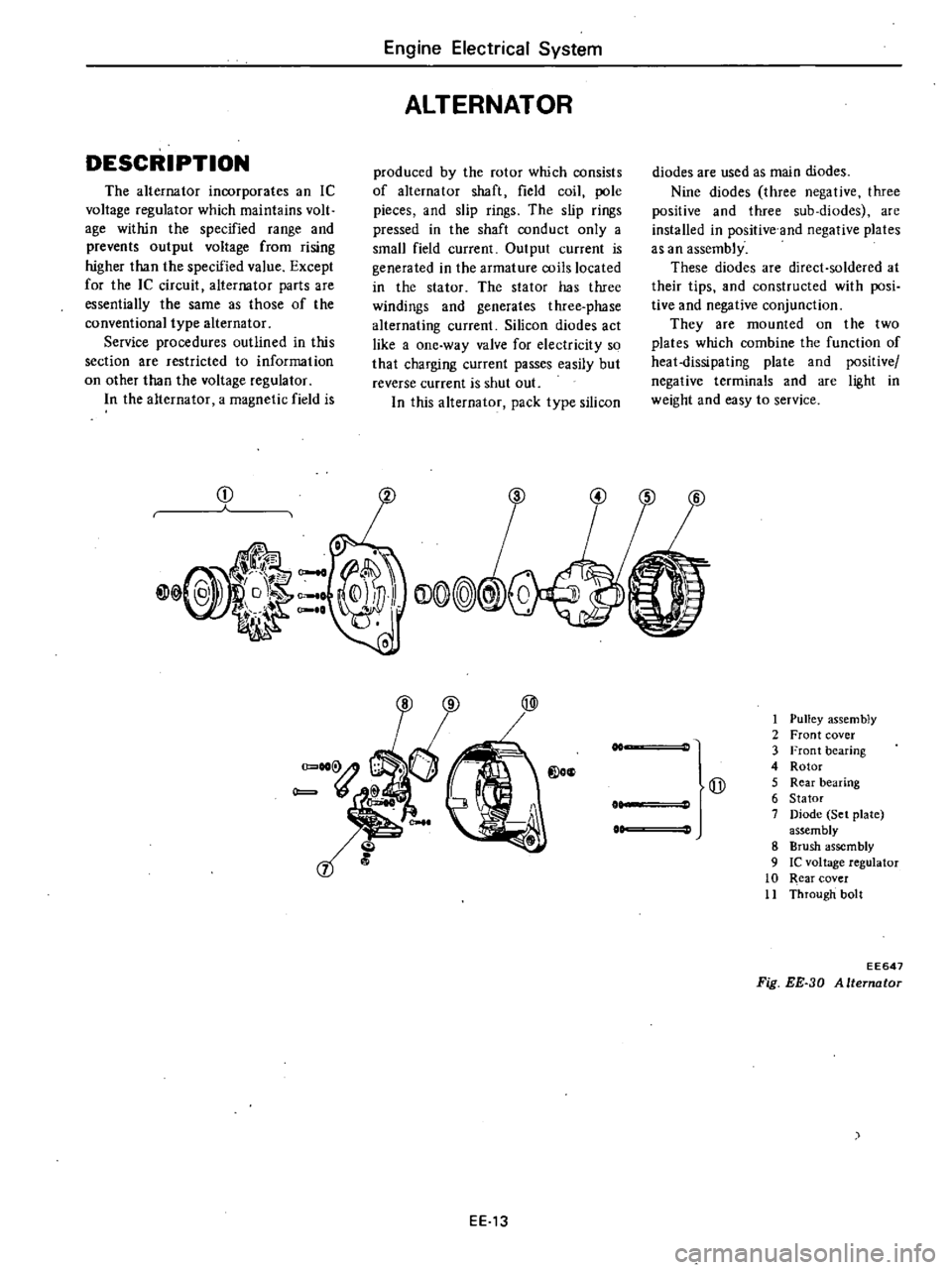
DESCRIPTION
The
alternator
incorporates
an
Ie
voltage
regulator
which
maintains
volt
age
within
the
specified
range
and
prevents
output
voltage
from
rising
higher
than
the
specified
value
Except
for
the
Ie
circuit
alternator
parts
are
essentially
the
same
as
those
of
the
conventional
type
alternator
Service
procedures
outlined
in
this
section
are
restricted
to
information
on
other
than
the
voltage
regulator
In
the
alternator
a
magnetic
field
is
CD
Engine
Electrical
System
ALTERNATOR
produced
by
the
rotor
which
consists
of
alternator
shaft
field
coil
pole
pieces
and
slip
rings
The
slip
rings
pressed
in
the
shaft
conduct
only
a
small
field
current
Output
current
is
generated
in
the
armature
coils
located
in
the
stator
The
stator
has
three
windings
and
generates
three
phase
alternating
current
Silicon
diodes
act
like
a
one
way
valve
for
electricity
so
that
charging
current
passes
easily
but
reverse
current
is
shut
out
In
this
alternator
pack
type
silicon
diodes
are
used
as
main
diodes
Nine
diodes
three
negative
three
positive
and
three
sub
diodes
are
installed
in
positive
and
negative
plates
as
an
assembly
These
diodes
are
direct
soldered
at
their
tips
and
constructed
with
posi
tive
and
negative
conjunction
They
are
mounted
on
the
two
plates
which
combine
the
function
of
heat
dissipating
plate
and
positive
negative
terminals
and
are
light
in
weight
and
easy
to
service
EE13
1
Pulley
assem
bly
2
Front
cover
3
Front
bearing
4
Rotor
Qj
5
Rear
bearing
6
Stator
7
Diode
Set
plate
assembly
8
Brush
assembly
9
Ie
voltage
regulator
10
Rear
cover
11
Through
bolt
EE647
Fig
EE
30
Alternator
Page 172 of 548
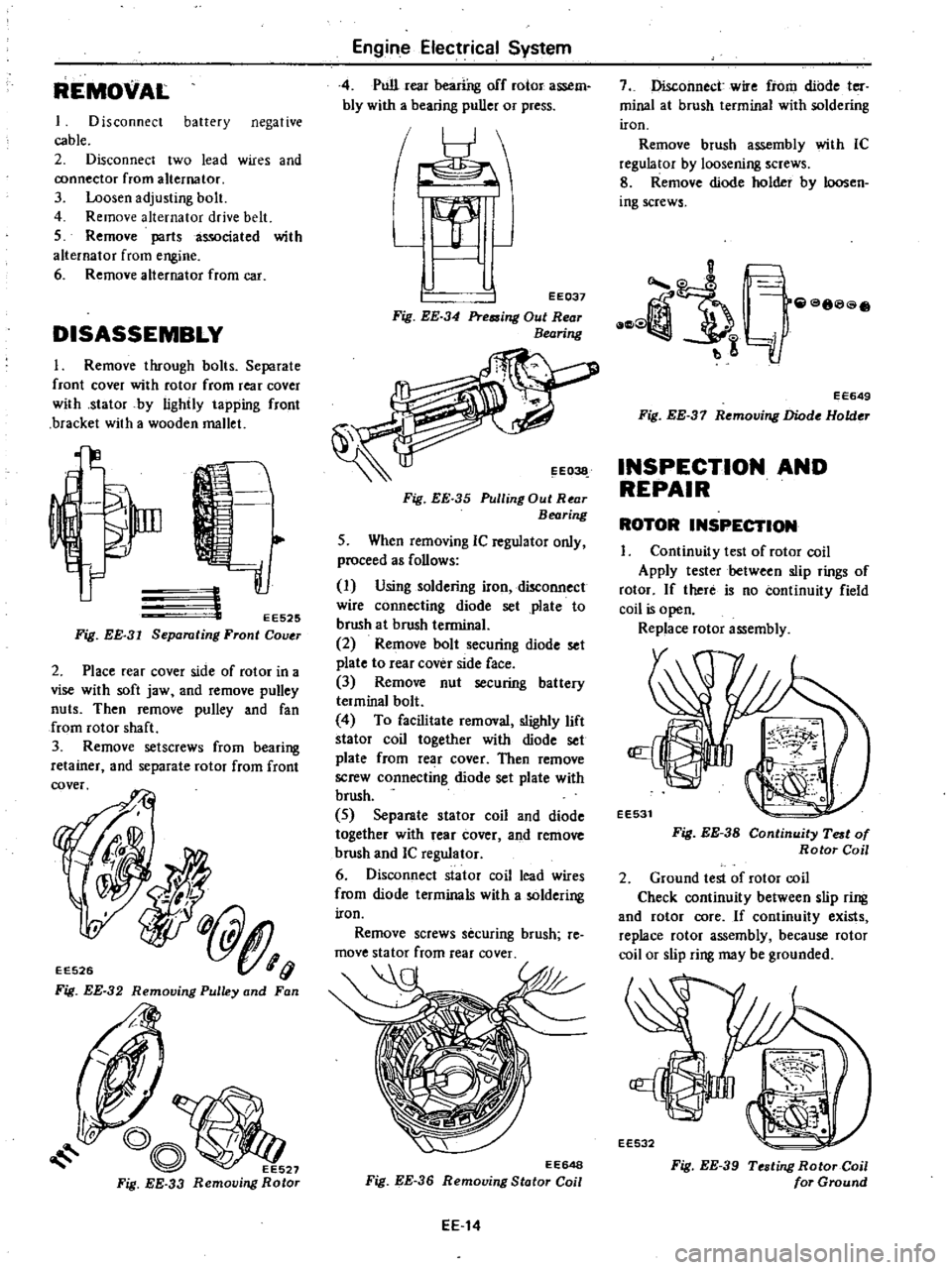
REMOVAL
1
Disconnect
battery
negative
cable
2
Disconnect
two
lead
wires
and
oonnector
from
alternator
3
Loosen
adjusting
bolt
4
Remove
alternator
drive
belt
5
Remove
parts
associated
with
alternator
from
engine
6
Remove
alternator
from
car
DISASSEMBLY
I
Remove
through
bolts
Separate
front
cover
with
rotor
from
rear
cover
with
stator
by
lightly
tapping
front
bracket
with
a
wooden
mallet
rnJ
J
i
EE525
Separating
Front
COI
T
Fig
EE
31
2
Place
rear
cover
side
of
rotor
in
a
vise
with
soft
jaw
and
remove
pulley
nuts
Then
remove
pulley
and
fan
from
rotor
shaft
3
Remove
setscrews
from
bearing
retainer
and
separate
rotor
from
front
EE526
Fig
EE
32
Removing
Pulley
and
Fan
tr
s
0
27
Fig
EE
33
Removing
Rotor
Engine
Electrical
System
4
Pull
rear
bearfug
off
rotor
assem
bly
with
a
bearing
puller
or
press
EE037
Fig
EE
34
Pressing
Out
Rear
Bearing
I
EO
Fig
EE
35
Pulling
Out
Rear
Bearing
5
When
removing
IC
regulator
only
proceed
as
follows
I
Using
soldering
iron
disconnect
wire
connecting
diode
set
plate
to
brush
at
brush
terminal
2
Remove
bolt
securing
diode
set
plate
to
rear
cover
side
face
3
Remove
nut
securing
battery
terminal
bolt
4
To
facilitate
removal
s1ighly
lift
stator
coil
together
with
diode
set
plate
from
re
r
cover
Then
remove
screw
connecting
diode
set
plate
with
brush
5
Separate
stator
coil
and
diode
together
with
rear
cover
and
remove
brush
and
IC
regulator
6
Disconnect
stator
coil
lead
wires
from
diode
terminals
with
a
soldering
iron
Remove
screws
securing
brush
re
move
stator
from
rear
cover
EE648
Fig
EE
36
Removing
Stator
Coil
EE
14
7
Disconnect
wire
from
diode
tor
minal
at
brush
terminal
with
soldering
iron
Remove
brush
assembly
with
IC
regulator
by
loosening
screws
8
Remove
diode
holder
by
loosen
ing
screws
acefii
li
E
E649
Fig
EE
37
Removing
Diode
Holder
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
ROTOR
INSPECTION
I
Continuity
test
of
rotor
coil
Apply
tester
between
slip
rings
of
rotor
If
there
is
no
continuity
field
coil
is
open
Replace
rotor
assembly
Fig
EE
38
Continuity
Test
of
Rotor
Coil
2
Ground
test
of
rotor
coil
Check
continuity
between
slip
ring
and
rotor
core
If
continuity
exists
replace
rotor
assembly
because
rotor
coil
or
slip
ring
may
be
grounded
EE532
Fig
EE
39
Te
ting
Rotor
Coil
for
Ground
Page 173 of 548
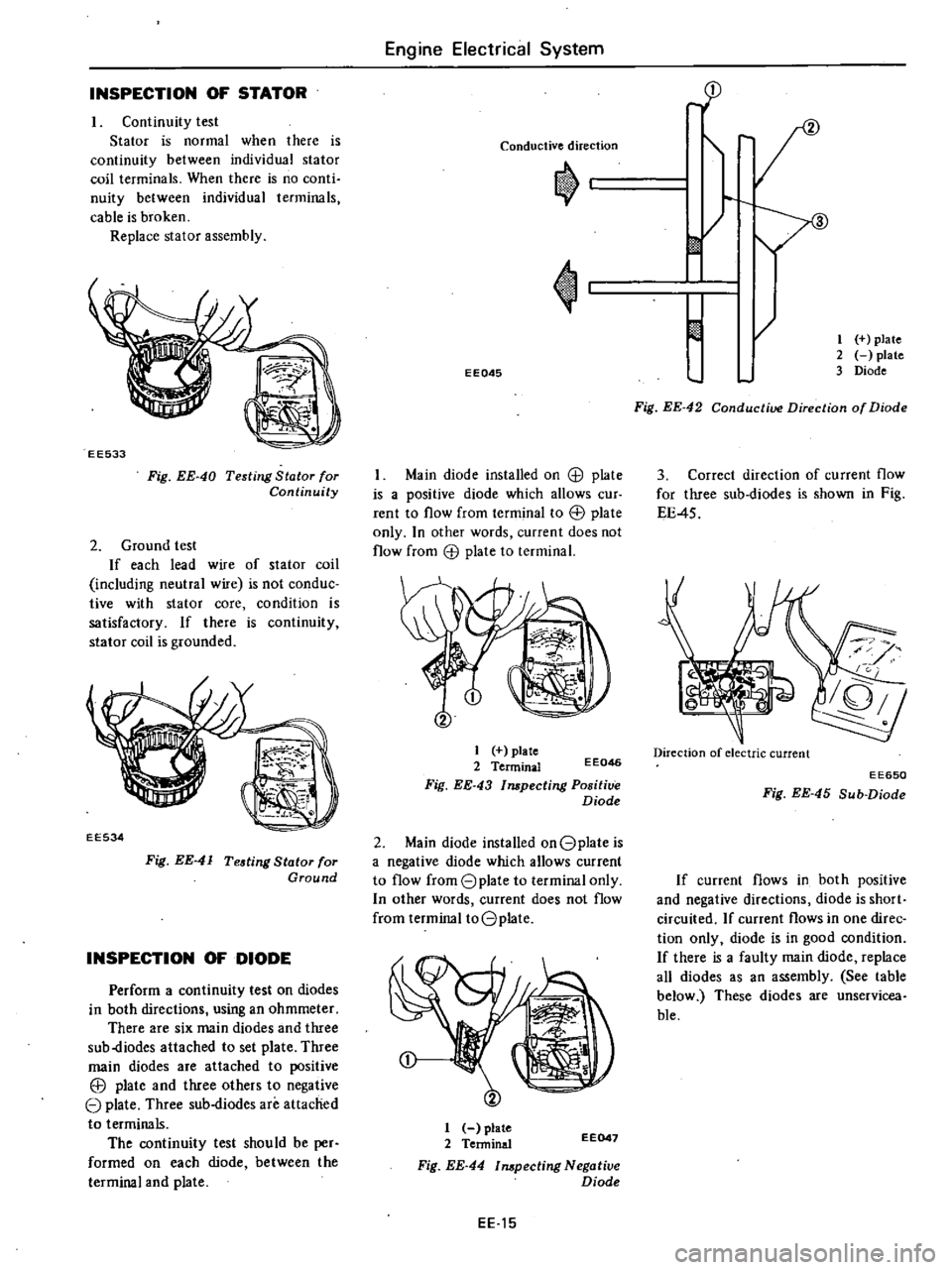
INSPECTION
OF
STATOR
Continuity
test
Stator
is
normal
when
there
is
continuity
between
individual
stator
coil
terminals
When
there
is
no
conti
nuity
between
individual
terminals
cable
is
broken
Replace
stator
assembly
EE533
Fig
EE
40
Testing
Stator
for
Continuity
2
Ground
test
If
each
lead
wire
of
stator
coil
including
neutral
wire
is
not
conduc
tive
with
stator
core
condition
is
satisfactory
If
there
is
continuity
stator
coil
is
grounded
EE534
Fig
EE
41
Testing
Stator
for
Ground
INSPECTION
OF
DIODE
Perform
a
continuity
test
on
diodes
in
both
directions
using
an
ohmmeter
There
are
six
main
diodes
and
tluee
sub
diodes
attached
to
set
plate
Three
main
diodes
are
attached
to
positive
EEl
plate
and
three
others
to
negative
8
plate
Three
sub
diodes
are
attached
to
terminals
The
continuity
test
should
be
per
formed
on
each
diode
between
the
terminal
and
plate
Engine
Electrical
System
Conductive
direction
EE045
Main
diode
installed
on
8
plate
is
a
positive
diode
which
allows
cur
rent
to
flow
from
terminal
to
EEl
plate
only
In
other
words
current
does
not
flow
from
8
plate
to
terminal
1
plate
2
Terminal
Fig
EE
43
Impecting
Positive
Diode
EE046
2
Main
diode
installed
on
Gplate
is
a
negative
diode
which
allows
current
to
flow
from
Gplate
to
terminal
only
In
other
words
current
does
not
flow
from
terminal
toGplate
1
plate
2
Tenninal
Fig
EE
44
Impecting
Negatiue
Diode
EE047
EE
15
rp
m
1
plate
2
ptate
3
Diode
Fig
EE
42
Conductive
Direction
of
Diode
3
Correct
direction
of
current
flow
for
three
sub
diodes
is
shown
in
Fig
EE
4S
Direction
of
electric
current
EE650
Fig
EE
45
Sub
Diode
If
current
flows
in
both
positive
and
negative
directions
diode
is
short
circuited
If
current
flows
in
one
direc
tion
only
diode
is
in
good
condition
If
there
is
a
faulty
main
diode
replace
all
diodes
as
an
assembly
See
table
below
These
diodes
are
unservicea
ble
Page 174 of 548
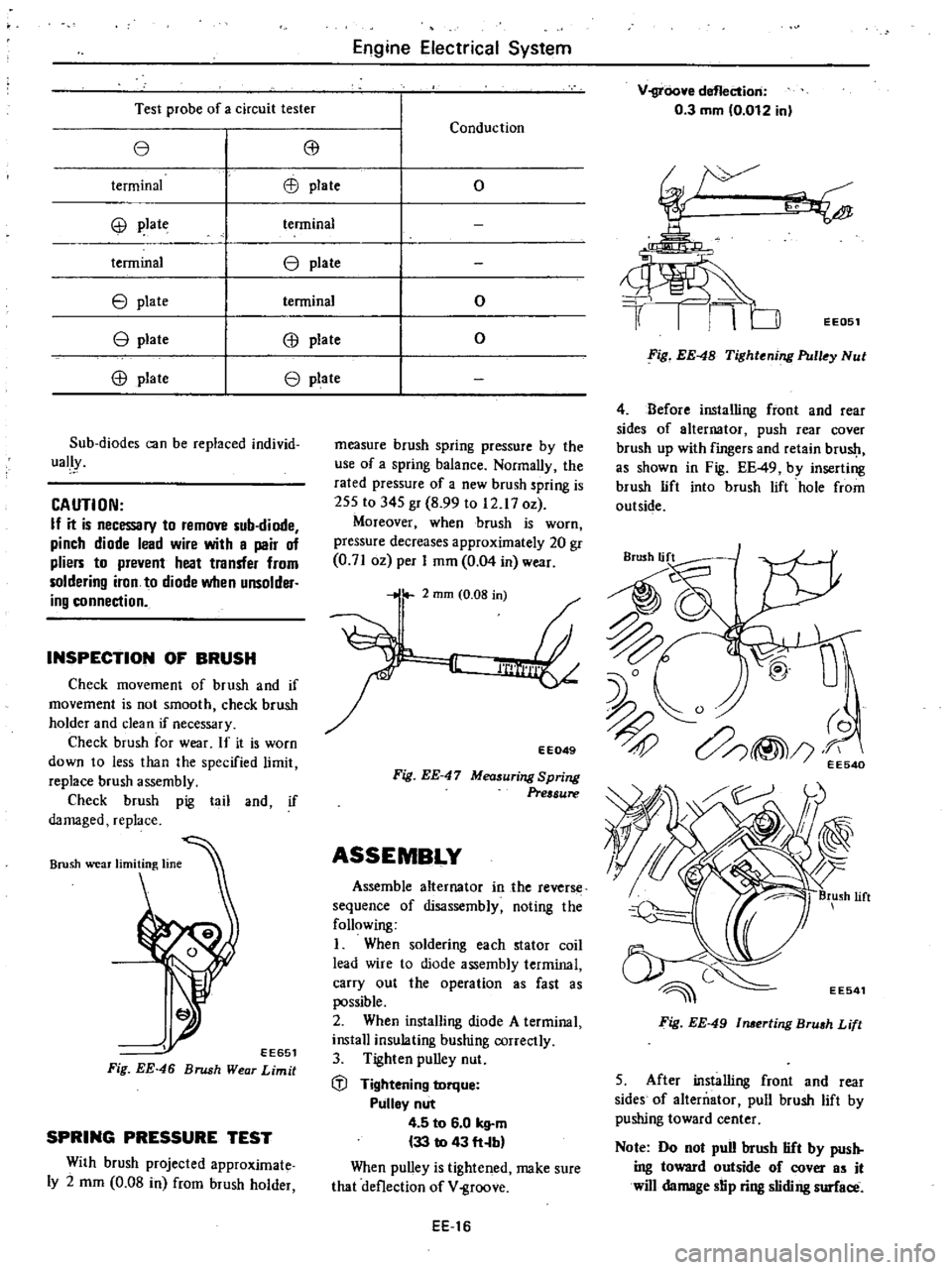
Test
probe
of
a
circuit
tester
e
8J
terminal
EB
plate
@
plate
terminal
terminal
e
plate
e
plate
tenninal
e
plate
8J
plate
EB
plate
e
plate
Sub
diodes
can
be
replaced
individ
ually
CAUTION
If
it
is
necessary
to
remove
sub
diode
pinch
diode
lead
wire
with
a
pair
of
pliers
to
prevent
heat
transfer
from
soldering
iron
to
diode
when
unsolder
ing
connection
INSPECTION
OF
BRUSH
Check
movement
of
brush
and
if
uv
ent
is
not
smooth
check
brush
holder
and
clean
if
necessary
Check
brush
for
wear
If
it
is
worn
down
to
less
than
the
specified
limit
replace
brush
assembly
Check
brush
pig
tail
and
if
damaged
replace
EE651
Fig
EE
46
Brush
Wear
Limit
SPRING
PRESSURE
TEST
With
brush
projected
approximate
Iy
2
mm
0
08
in
from
brush
holder
measure
brush
spring
pressure
by
the
use
of
a
spring
balance
Normally
the
rated
pressure
of
a
new
brush
spring
is
255
to
345
gr
8
99
to
12
17
oz
Moreover
when
brush
is
worn
pressure
decreases
a
pproxirnately
20
gr
O
71
oz
per
I
mm
0
04
in
wear
Bru
h
lift
0
0
lJrJ
EE540
Engine
Electrical
System
Conduction
o
o
o
t
2
mm
0
08
in
L
ee049
Fig
EE
47
Mea
uring
Spring
Pressure
ASSEMBLY
Assemble
alternator
in
the
reverse
sequence
of
disassembly
noting
the
following
I
When
soldering
each
stator
coil
lead
wire
to
diode
assembly
terminal
carry
out
the
operation
as
fast
as
possible
2
When
installing
diode
A
terminal
install
insulating
bushing
conectly
3
Tighten
pulley
nul
dJ
Tightening
torque
Pulley
nut
4
5
to
6
0
kg
m
33
to
43
ft
lbl
When
pulley
is
tightened
make
sure
that
deflection
of
V
groove
EE
16
V
grOove
deflection
0
3
mm
0
012
in
slik
1I
I
I
EE051
Fig
EE
48
Tightening
Pull
y
Nut
4
Before
installing
front
and
rear
sides
of
alternator
push
rear
cover
brush
up
with
fingers
and
retain
brus
J
as
shown
in
Fig
EE
49
by
inserting
brush
tift
into
brush
lift
hole
from
outsi4e
Fig
EE
49
I
rUng
Bru
h
Lift
S
After
installing
front
and
rear
sides
of
alteniator
pull
brush
lift
by
pushing
toward
center
Note
Do
not
puD
brush
lift
by
push
ing
toward
outside
of
cover
as
it
will
damage
slip
ring
sliding
surface
Page 175 of 548
Engine
Electrical
System
6
Tighten
through
bolts
rfl
Tightening
torque
Through
bolts
60
to
70
kg
cm
52
to
61
in
lb
ALTERNATOR
TEST
Before
conducting
an
alternator
test
make
sure
that
the
battery
is
fully
charged
A
30
Volt
voltmeter
and
suitable
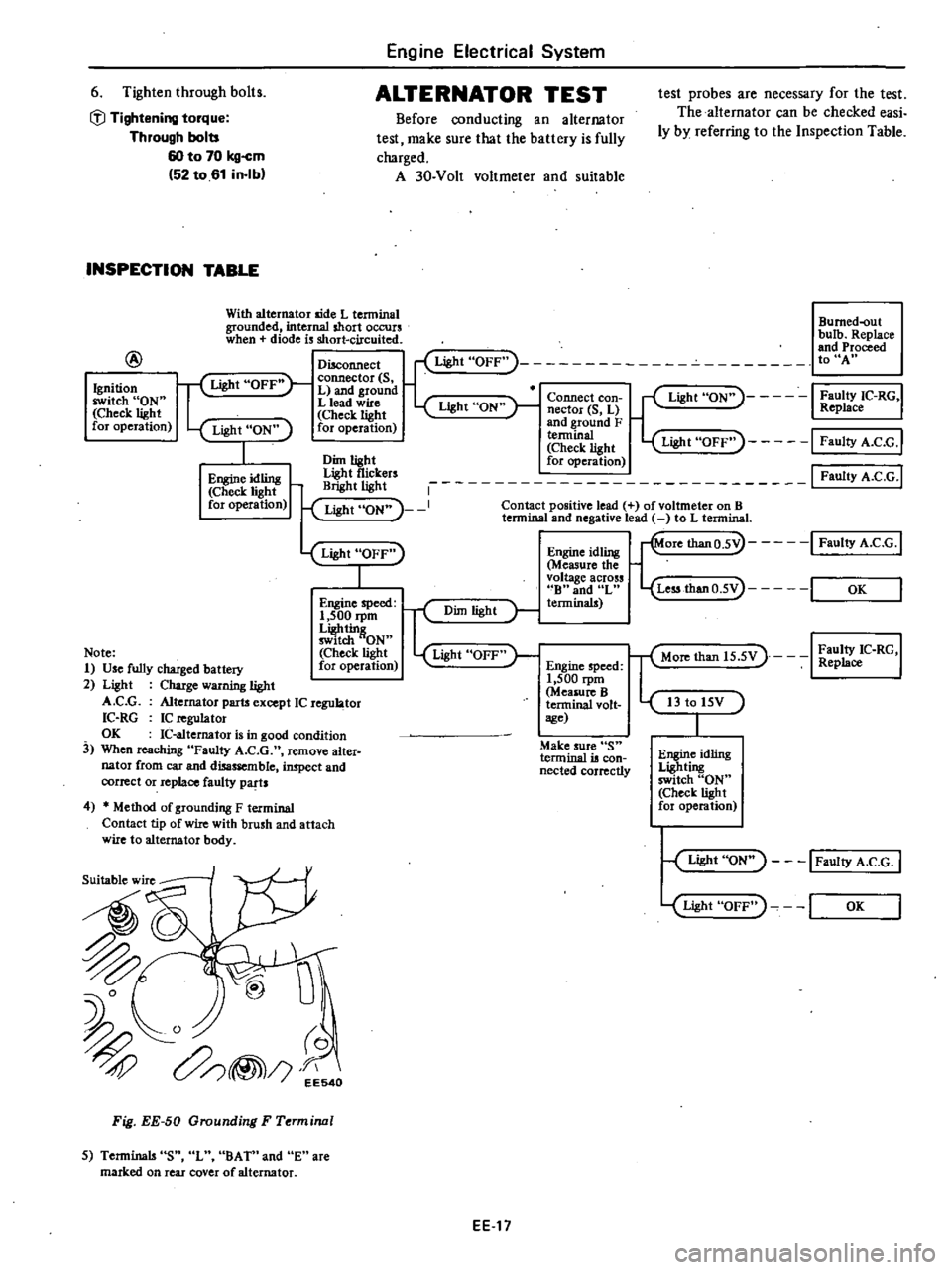
INSPECTION
TABLE
With
alternator
aide
L
tenninal
grounded
internal
short
occurs
when
diode
is
short
circuited
@
test
probes
are
necessary
for
the
test
The
alternator
can
be
checked
easi
ly
by
referring
to
the
Inspection
Table
Bumed
out
bulb
Replace
and
Proceed
toUA
Ignition
switch
ON
Check
light
for
operation
Disconnect
Light
OFF
f
Light
OFF
connector
S
L
and
ground
L
lead
wire
Light
ON
Check
light
for
operation
Light
ON
I
Faulty
IC
RG
Replace
Connect
con
nector
S
L
and
ground
F
a1light
Light
OFF
I
FaultyA
C
G
I
Dim
light
for
operation
tf
i
rs
1
I
Faulty
A
C
G
I
Light
ON
I
Contact
positive
lead
of
voltmeter
on
B
lennina
and
negative
lead
to
L
tenninal
Light
ON
1
Engine
idling
Check
light
for
operation
Light
OFF
I
Engine
idling
Measure
the
voltage
across
B
and
L
terminals
Engine
speed
1
500
rpm
Ligh
tin
switch
ON
Check
light
for
operation
r
Dim
light
Light
OFF
Note
1
Use
fully
charged
battery
2
Light
Charge
warning
light
A
C
G
Alternator
parts
except
IC
regu
tor
IC
RG
IC
n
guJator
OK
IC
altemator
is
in
good
condition
3
When
reaching
Faulty
A
C
G
remove
alter
nator
from
car
and
disassemble
inspect
and
correct
or
replace
faulty
parts
Engine
speed
1
500
rpm
Measure
B
terminal
volt
sge
Make
sure
S
terminal
is
con
nected
correctly
4
Method
of
grounding
F
terminal
Contact
tip
of
wire
with
brush
and
attach
wire
to
alternator
body
Suitable
wire
I
Fig
EE
50
Grounding
F
Terminal
5
Terminals
S
L
BA
Tn
and
E
are
marked
on
rear
cover
of
alternator
EEl7
More
thanO
5V
I
Faulty
A
e
G
1
Less
thanO
5V
I
OK
T
Mon
than
15
5V
I
Z
C
RG
I
I3
to
15V
Engine
idling
Lighting
switch
ON
Check
light
for
operation
Light
ON
I
Faulty
A
C
G
I
Light
OFF
I
OK
Page 176 of 548
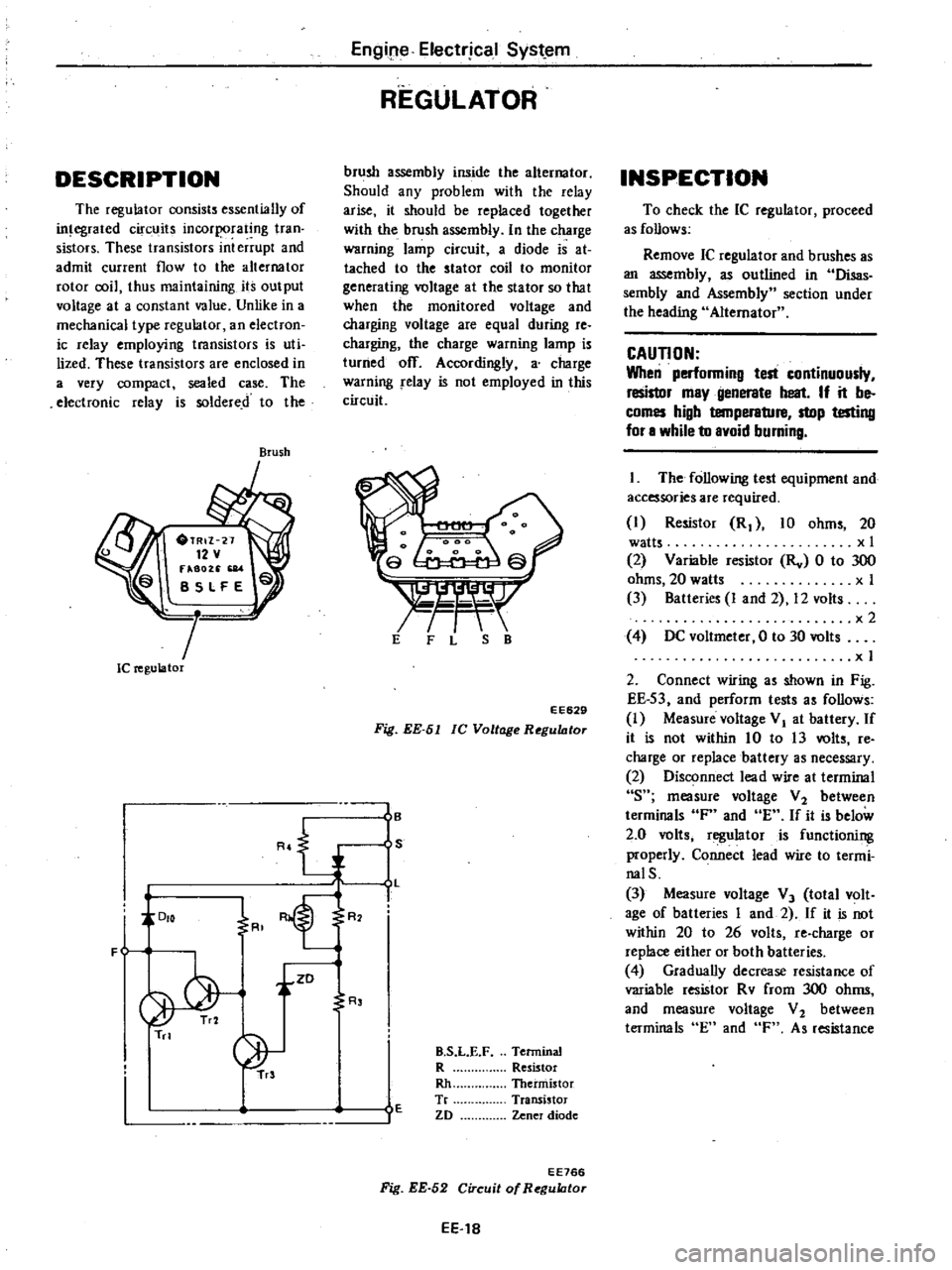
DESCRIPTION
The
regulator
consists
essentially
of
in
egrated
circuits
incorporating
tran
sistors
These
transistors
int
errupt
and
admit
current
flow
to
the
alternator
rotor
coil
thus
maintaining
its
output
voltage
at
a
constant
value
Unlike
in
a
mechanical
type
regulator
an
electron
ic
relay
employing
transistors
is
uti
lized
These
transistors
are
enclosed
in
a
very
compact
sealed
case
The
electronic
relay
is
soldered
to
the
Brush
Ie
regulator
R
J
DIO
F
i
ZD
Tn
Engipe
Electrjcal
Syst
em
REGULATOR
brush
assembly
inside
the
alternator
Should
any
problem
with
the
relay
arise
it
should
be
replaced
together
with
the
brush
assembly
In
the
charge
warning
lamp
circuit
a
diode
is
at
tached
to
the
stator
coil
to
monitor
generating
voltage
at
the
stator
so
that
when
the
monitored
voltage
and
charging
voltage
are
equal
during
re
charging
the
charge
warning
lamp
is
turned
off
Accordingly
a
charge
warning
relay
is
not
employed
in
this
circuit
s
r
t
E
F
L
S
B
EE629
Fig
EE
51
lC
Voltage
RegultJtor
I
B
S
L
I
R
R
E
B
S
L
E
F
Terminal
R
Resistor
Rh
Thermistor
Tr
Transistor
ZD
Zener
diode
EE766
Fig
EE
52
Circuit
of
RegultJtor
EE
18
INSPECTION
To
check
the
IC
regulator
proceed
as
follows
Remove
IC
regulator
and
brushes
as
an
assembly
as
outlined
in
Disas
sembly
and
Assembly
section
under
the
heading
Alternator
CAUTION
When
performing
test
continuously
resistor
may
generate
heat
If
it
be
comes
high
temperature
stop
testing
for
a
while
to
avoid
burning
The
following
test
equipment
and
accessories
are
required
I
Resistor
R
10
ohms
20
watts
x
I
2
Variable
resistor
Rv
0
to
300
ohms
20
watts
x
I
3
Batteries
I
and
2
12
volts
x2
4
DC
voltmeter
0
to
30
volts
x
I
2
Connect
wiring
as
shown
in
Fig
EE
S3
and
perform
tests
as
follows
I
Measure
voltage
VI
at
battery
If
it
is
not
within
10
to
13
volts
re
charge
or
replace
battery
as
necessary
2
Disconnect
lead
wire
at
terminal
s
measure
voltage
V
2
between
terminals
F
and
E
If
it
is
below
2
0
volts
regulator
is
functioning
properly
Connect
lead
wire
to
termi
nalS
3
Measure
voltage
V
3
total
volt
age
of
batteries
I
and
2
If
it
is
not
within
20
to
26
volts
re
charge
or
replace
either
or
both
batteries
4
Gradually
decrease
resistance
of
variable
resistor
Rv
from
300
ohms
and
measure
voltage
V
2
between
terminals
En
and
F
As
resistance
Page 177 of 548
15
5
v
v
o
o
Q
z
o
15
0
14
5
14
0
13
5
13
0
Engine
Electrical
System
l
c
regula
tor
c
j
F
F
T
BATI
1
i
Cf
CO
I
r
J
BAT2
EE631
Fig
EE
53
Testing
Regulator
1
N
N
0
N
0
0
N
0
C
e
0
c
0
S
0
S
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
I
c
o
I
Regulator
case
temperature
DC
OF
EE632
Fig
EE
54
Testing
Reguhltor
5
j
I
C
regulator
E
F
L
S
BATI
1
I
i
R
Cf
Cf
I
l
BAT2
EE633
Fig
EE
55
Testing
Regulator
6
EE
19
varies
voltage
V
2
should
at
a
certain
point
increase
to
as
high
as
voltage
V
I
which
is
measured
in
Step
I
If
there
is
such
a
variation
the
regulator
is
functioning
properly
Hold
variable
resistor
Rv
at
the
same
voltage
as
VI
If
there
is
no
voltage
variation
regula
tor
is
out
of
order
and
must
be
replaced
5
Measure
voltage
V
between
center
tap
of
variable
resistor
R
and
terminal
E
With
Rv
resistance
set
at
a
value
obtained
in
step
4
above
measure
voltage
V
4
to
s
e
if
it
is
within
specified
range
indicated
in
Fig
EE
54
If
it
is
not
regulator
is
not
functioning
properly
Replace
6
Reconnect
wiring
as
shown
in
Fig
EE
55
and
repeat
steps
4
and
5
If
voltage
V
is
0
5
to
2
0
volts
higher
than
that
in
step
5
regulator
is
functioning
properly
If
it
is
not
replace
Page 178 of 548
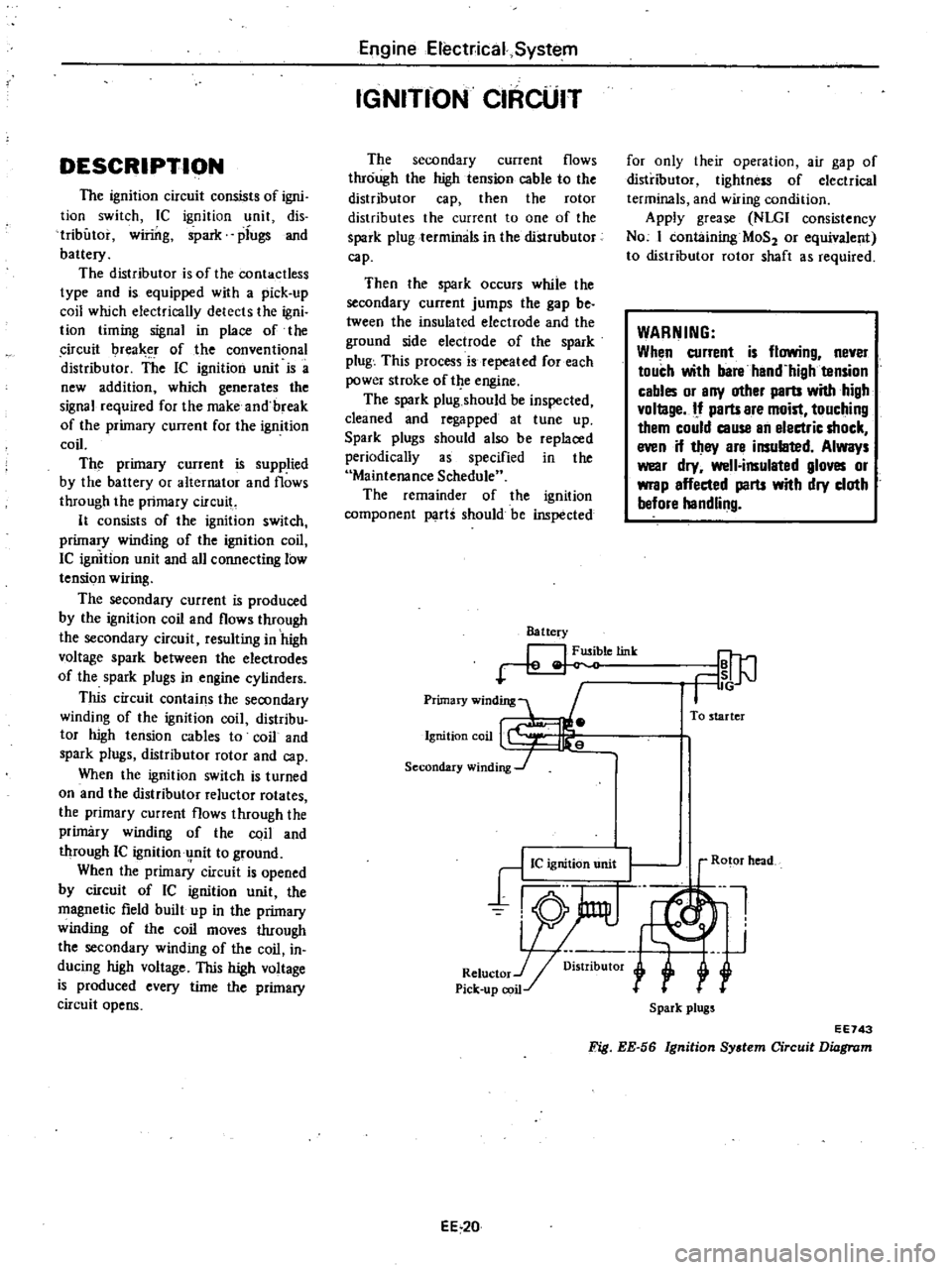
DESCRIPTION
The
ignition
circuit
consists
of
igni
tion
switch
Ie
ignition
unit
dis
tributor
winng
ipark
plugs
and
battery
The
distributor
is
of
the
contactless
type
and
is
equipped
with
a
pick
up
coil
which
electrically
detects
the
igni
tion
timing
signal
in
place
of
the
ircuit
I
rea
r
of
the
conventional
distributor
The
IC
ignition
unit
is
a
new
addition
which
generates
the
signal
required
for
the
make
and
break
of
the
primary
current
for
the
ignition
coil
The
primary
current
is
supplied
by
the
battery
or
alternator
and
flows
through
the
primary
circuit
It
consists
of
the
ignition
switch
primary
winding
of
the
ignition
coil
IC
ignition
unit
and
all
connecting
low
tension
wiring
The
secondary
current
is
produced
by
the
ignition
coil
and
flows
through
the
secondary
circuit
resulting
in
high
voltage
spark
between
the
electrodes
of
the
spark
plugs
in
engine
cylinders
This
circuit
contains
the
secondary
winding
of
the
ignition
coil
distribu
tor
high
tension
cables
to
coil
and
spark
plugs
distributor
rotor
and
cap
When
the
ignition
switch
is
turned
on
and
the
distributor
reluctor
rotates
the
primary
current
flows
through
the
primary
winding
of
the
coil
and
through
IC
ignitionu
nit
to
ground
When
the
primary
circuit
is
opened
by
circuit
of
IC
ignition
unit
the
magnetic
field
built
up
in
the
primary
winding
of
the
coil
moves
through
the
secondary
winding
of
the
coil
in
ducing
high
voltage
This
high
voltage
is
produced
every
time
the
primary
circuit
opens
EngineElect
ical
System
IGNITfON
CIRCUIT
The
secondary
current
flows
through
the
high
tension
cable
to
the
distributor
cap
then
the
rotor
distributes
the
current
to
one
of
the
spark
plug
terminals
in
the
distrubutor
cap
Then
the
spark
occurs
while
the
secondary
current
jumps
the
gap
be
tween
the
insulated
electrode
and
the
ground
side
electrode
of
the
spark
plug
This
process
is
repeated
for
each
power
stroke
of
t
e
engine
The
spark
plug
should
be
inspected
cleaned
and
regapped
at
tune
up
Spark
plugs
should
also
be
replaced
periodically
as
specified
in
the
Maintenance
Schedule
The
remainder
of
the
ignition
component
parti
should
be
inspected
Battery
letink
Primary
winding
1
Ignition
coil
Secondary
winding
J
for
only
their
operation
air
gap
of
distributor
tightness
of
electrical
terminals
and
wiring
condition
Apply
grease
NLGI
consistency
No
I
containing
MaS
or
equivalent
to
distributor
rotor
shaft
as
required
WARNING
When
current
is
flowing
never
touch
with
bare
hand
high
tension
cables
or
any
other
parts
with
high
vollage
If
parts
are
moist
touching
them
could
cause
an
electric
shock
even
if
they
are
insulated
Always
wear
dry
well
insulated
gloves
or
wrap
affected
parts
with
dry
cloth
before
handling
To
starter
EE
20
Ro
or
head
Ul
J
r
Spark
plugs
EE743
Fig
EE
56
Ignition
System
Circuit
Diagram
Page 179 of 548
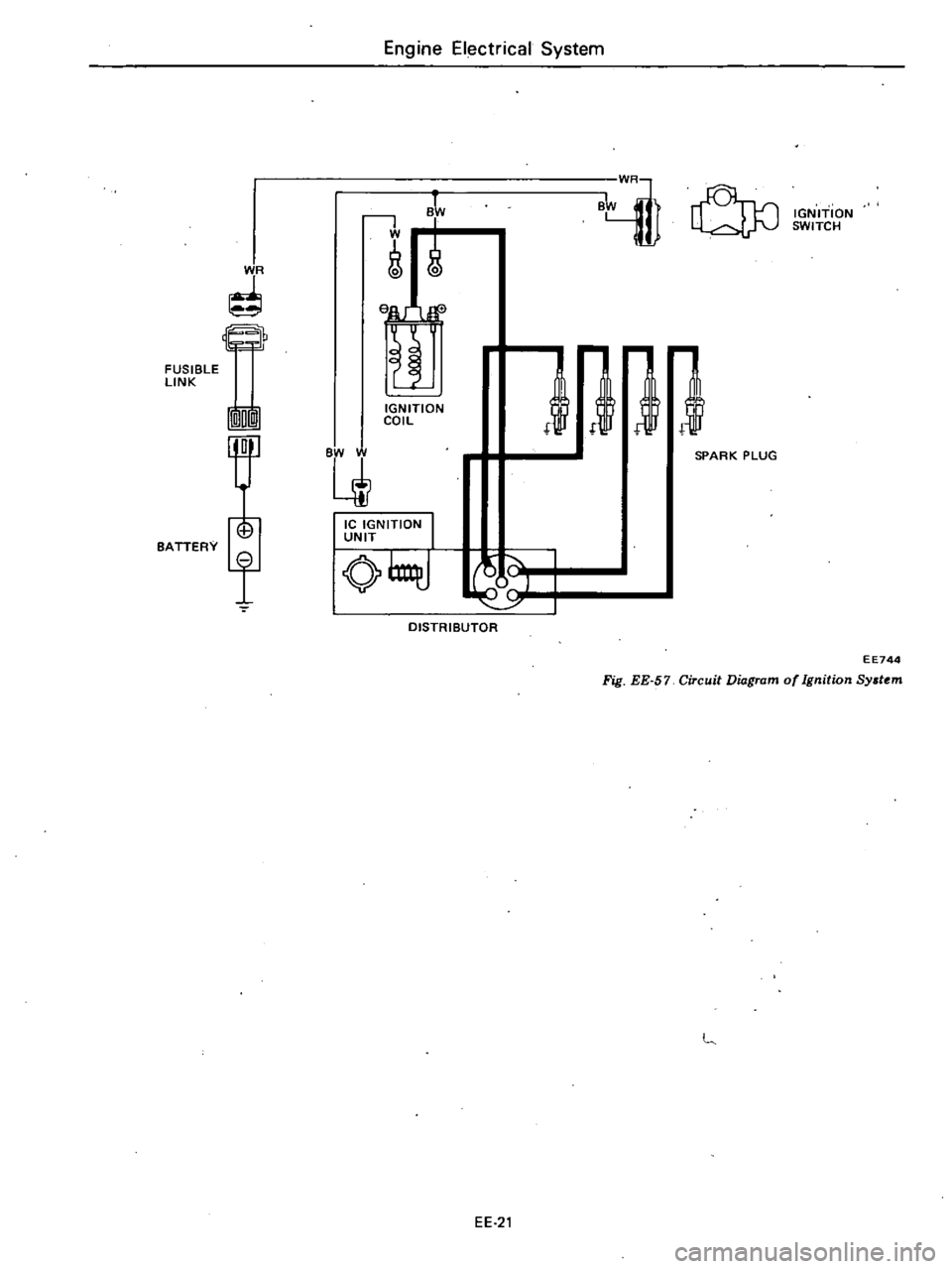
FUSIBLE
LINK
BATTERY
VIR
9
rID
B
V
II
H
Engine
Electrical
System
1
II
1l
IGNITION
COIL
IIC
IGNITION
I
UNIT
O
J
DISTRIBUTOR
EE
21
B4J
QJ
jl
SPARK
PLUG
IGNITiON
SWITCH
EE744
Fig
EE
57
Circuit
DiGgram
of
Ignition
Sy
tem
L
Page 180 of 548
Engine
E
ectrical
System
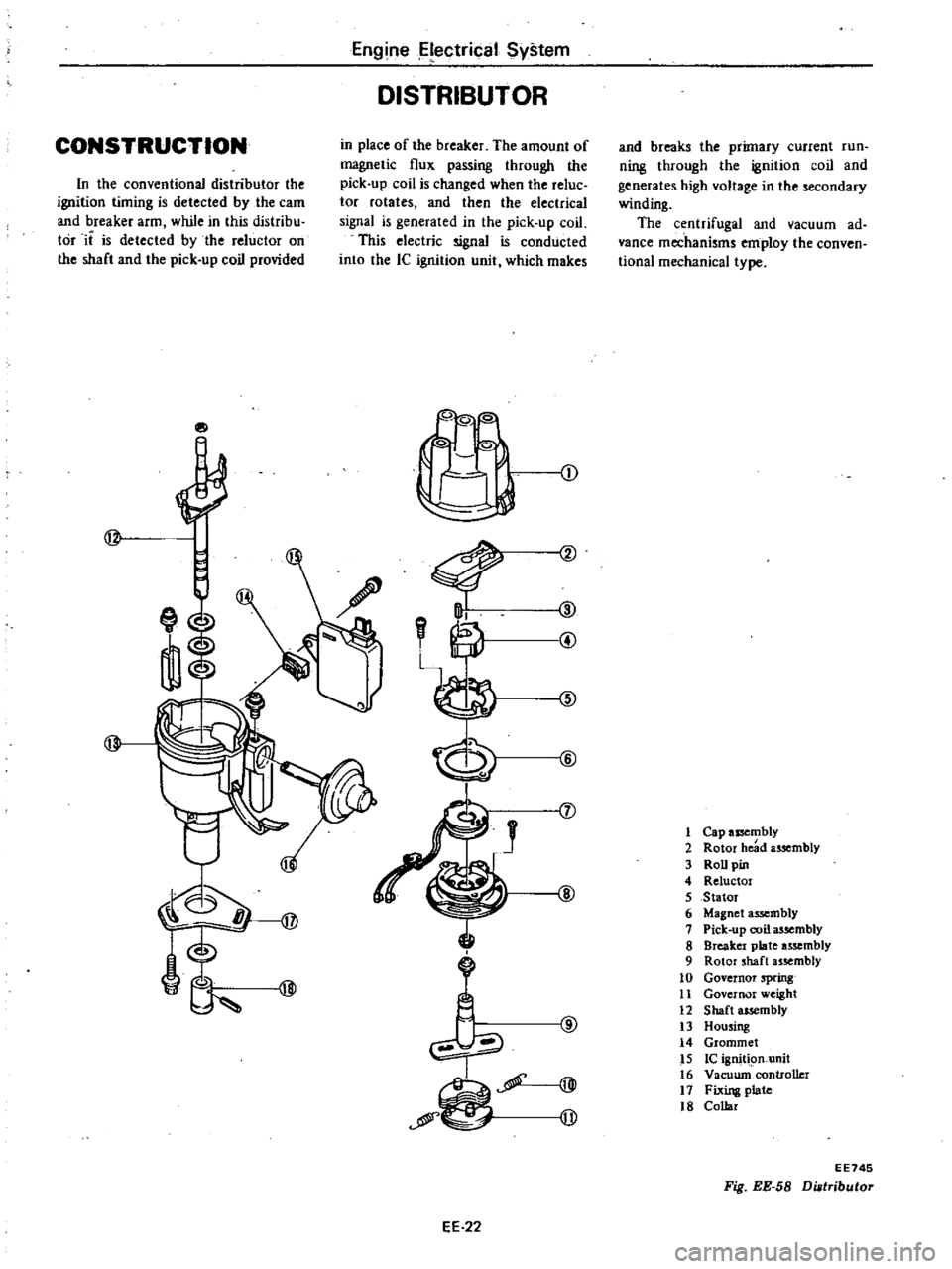
DISTRIBUTOR
CONSTRUCTION
in
place
of
the
breaker
The
amount
of
magnetic
flux
passing
through
the
pick
up
coil
is
changed
when
the
reluc
tor
rotates
and
then
the
electrical
signal
is
generated
in
the
pick
up
coil
This
electric
ignal
is
conducted
into
the
Ie
ignition
unit
which
makes
In
the
conventional
distributor
the
ignition
timing
is
detected
by
the
earn
and
breaker
arm
while
in
this
distribu
tor
it
is
detected
by
the
reluctor
on
the
shaft
and
the
pick
up
coil
provided
and
breaks
the
primary
current
run
ning
through
the
ignition
coil
and
generates
high
voltage
in
the
secondary
winding
The
centrifugal
and
vacuum
ad
vance
mechanisms
employ
the
conven
tional
mechanical
type
I
l
Q
J
1
C
@
@
ID
ID
J
I
Cap
assembly
2
Rotor
head
assembly
3
RoD
pin
4
ReluctoI
@
5
Stator
6
Magnet
assembly
7
Pick
up
coil
assembly
8
Breaker
plate
assembly
9
Rotor
shaft
assembly
10
Governor
spring
11
Governor
weight
12
Shaft
assembly
13
Housing
14
Grommet
15
Ie
igniq
n
unit
@f
rw
16
VacuwncontroUcr
17
Fixing
plate
t8
Collar
EE745
Fig
EE
58
Diatributor
EE
22